在数据结构实现中重学C语言
typedef
在数据结构学习中,定义结构体常常用typedef struct{...} Stack,...;来定义新结构。
其中typedef的作用是“重新命名”
为基本数据类型重新命名
typedef long double REAL;
此时REAL这个类型就是long double的类型
为自定义结构体重新命名
这就是数据结构中常见的运用
typedef struct //这里没有给struct名字,也是可以的
{
int *base;
int *top;
int stacksize;
}SqStack;
这个自定义的结构就命名成了SqStack
还可以对指针重新命名
typedef struct Lnode
{
int data; //数据域
struct Lnode *next; //指针域
}Lnode,*LinkList;
这里的*LinkList在定义完以后,用LinkList定义的就是指针
值得注意的是,struct Lnode *next;不能用LinkList next;代替,因为在struct后的括号里还没有进行重新命名,此时还“不认识”LinkList是什么,所以必须用struct Lnode标准的形式定义
用.还是->?
在VScode中,只要用.,编译器会自动匹配需要的符号,用错了也没办法正常编译,那么他们的区别是什么?
.(点)运算符和 ->(箭头)运算符用于引用类、结构和共用体的成员: 点运算符应用于实际的对象。箭头运算符与一个指向对象的指针一起使用。
简单来说,访问实体用.,访问指针用->
举个例子
#include<malloc.h>
struct L
{
int a;
};
int main()
{
struct L b; //b是struct L实体
b.a=1;
struct L *c; //c是struct L类型指针
c=(struct L *)malloc(sizeof(struct L));
c->a=1;
return 0;
}
Segmentation fault
在编写数据结构的程序中,无数次遇到了这个错误提示,这个错误叫做“段错误”,编译是没有问题的,但是遇到问题的地方会报错,原因就是没有搞懂指针。
还是上面的例子
#include<malloc.h>
struct L
{
int a;
};
int main()
{
struct L b; //b是struct L实体
b.a=1;
struct L *c; //c是struct L类型指针
c=(struct L *)malloc(sizeof(struct L));
c->a=1;
return 0;
}
运行正常,但是如果我把13行注释掉
#include<malloc.h>
struct L
{
int a;
};
int main()
{
struct L b; //b是struct L实体
b.a=1;
struct L *c; //c是struct L类型指针
//c=(struct L *)malloc(sizeof(struct L));
c->a=1;
return 0;
}
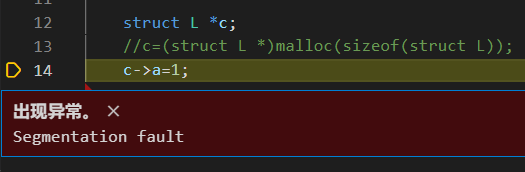
说明这个malloc与指针是罪魁祸首
在12行定义了一个指针c,但是没有给指针赋值,c指向的是NULL,访问c的成员就会报错。正确情况下,我们应该用malloc为c分配空间,让c指向这个空间,我们才能正常访问
可以观察debug中的c
-
c没有用malloc分配内存时
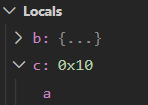
c不指向任何有效空间,无法访问和修改
-
c用了malloc分配内存时
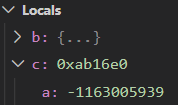
此时我们才能对c所☞的空间进行访问和修改
ERROR:Cannot open file cygwin.S
在写稀疏矩阵三元组算法时,一直到一行代码就报错无法打开“cygwin.S”:,查询是爆栈了
int numb[H.cols];
int cpot[H.cols];
换个例子
int main()
{
int a=10;
int b[a];
}
一样会出现该错误。
神奇的是如果直接使用gcc编译不会出现错误,甚至让vscode直接编译运行程序而不调试也不会出错,该错误只有vscode debug会出现
这是在stackoverflow上检索的答案
debugging - Debugger in C::B. Can't open cygwin.S - Stack Overflow
I received this error when i was trying to debug using gdb in vscode. Vscode don't offer redirected input especially for C. So i was using freopen(). Everything worked fine until it stepped into the declaration part of array.
int arr[n]So I replaced it with a pointer and allocated memory dynamically.
int *arr=(int *) malloc(sizeof(int)*n);and this worked.
I think gdb is unable to handle those arr[variable] declaration. But I may be completely wrong. Hope this helps.
::main must return int
c语言标准已经不准有void main 这种形式出现了。所以int main 或者是main() 才可以正常编译。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号