理解java容器底层原理--手动实现LinkedList
Node
java 中的 LIinkedList 的数据结构是链表,而链表中每一个元素是节点。
我们先定义一下节点:
package com.xzlf.collection;
public class Node {
Node previous; // 上一个节点
Node next; // 下一个节点
Object element; // 元素数据
public Node(Object element) {
super();
this.element = element;
}
public Node(Node previous, Node next, Object element) {
super();
this.previous = previous;
this.next = next;
this.element = element;
}
}
版本一:基础版本
先创建一个类,完成链表的创建、添加元素、然后重写toString() 方法:
package com.xzlf.collection;
/**
* 自定义一个链表
* @author xzlf
*
*/
public class MyLinkedList {
private Node first;
private Node last;
private int size;
public void add(Object obj) {
Node node = new Node(obj);
if(first == null) {
first = node;
last = node;
}else {
node.previous = last;
node.next = null;
last.next = node;
last = node;
}
size++;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("[");
Node tmp = first;
while(tmp != null) {
sb.append(tmp.element + ",");
tmp = tmp.next;
}
sb.setCharAt(sb.length() - 1, ']');
return sb.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList list = new MyLinkedList();
list.add("a");
list.add("b");
list.add("c");
list.add("a");
list.add("b");
list.add("c");
list.add("a");
list.add("b");
list.add("c");
System.out.println(list);
}
}
测试:
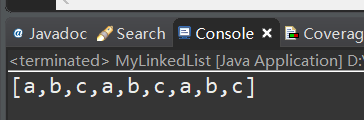
版本二:增加get() 方法
package com.xzlf.collection;
/**
* 自定义一个链表
* 增加get方法
* @author xzlf
*
*/
public class MyLinkedList2 {
private Node first;
private Node last;
private int size;
public void add(Object obj) {
Node node = new Node(obj);
if(first == null) {
first = node;
last = node;
}else {
node.previous = last;
node.next = null;
last.next = node;
last = node;
}
size++;
}
public Object get(int index) {
Node tmp = null;
// 判断索引是否合法
if(index < 0 || index > size - 1) {
throw new RuntimeException("索引不合法:" + index);
}
/*索引位置为前半部分,从头部开始找*/
if (index <= size >> 1) {
tmp = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
tmp = tmp.next;
}
}else {
/*索引位置为或半部分,从未部开始找*/
tmp = last;
for (int i = size -1; i > index; i--) {
tmp = tmp.previous;
}
}
return tmp.element;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("[");
Node tmp = first;
while(tmp != null) {
sb.append(tmp.element + ",");
tmp = tmp.next;
}
sb.setCharAt(sb.length() - 1, ']');
return sb.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList2 list = new MyLinkedList2();
list.add("a");
list.add("b");
list.add("c");
list.add("d");
list.add("e");
list.add("f");
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println(list.get(1));
System.out.println(list.get(4));
}
}
测试:
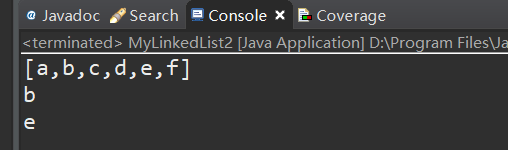
版本三:增加remove() 方法
package com.xzlf.collection;
/**
* 自定义一个链表
* 增加remove
* @author xzlf
*
*/
public class MyLinkedList3 {
private Node first;
private Node last;
private int size;
public void add(Object obj) {
Node node = new Node(obj);
if(first == null) {
first = node;
last = node;
}else {
node.previous = last;
node.next = null;
last.next = node;
last = node;
}
size++;
}
public Object get(int index) {
Node tmp = null;
// 判断索引是否合法
if(index < 0 || index > size - 1) {
throw new RuntimeException("索引不合法:" + index);
}
tmp = getNode(index);
return tmp == null ? null : tmp.element;
}
public void remove(int index) {
Node tmp = getNode(index);
Node up = tmp.previous;
Node down = tmp.next;
if (tmp != null) {
if (up != null) {
up.next = down;
}
if (down != null) {
down.previous = up;
}
// 被删元素是第一个时
if(index == 0) {
first = down;
}
// 被删元素是最后一个时
if(index == size - 1) {
last = up;
}
size--;
}
}
public Node getNode(int index) {
Node tmp = null;
/*索引位置为前半部分,从头部开始找*/
if (index <= size >> 1) {
tmp = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
tmp = tmp.next;
}
}else {
/*索引位置为或半部分,从未部开始找*/
tmp = last;
for (int i = size -1; i > index; i--) {
tmp = tmp.previous;
}
}
return tmp;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("[");
Node tmp = first;
while(tmp != null) {
sb.append(tmp.element + ",");
tmp = tmp.next;
}
sb.setCharAt(sb.length() - 1, ']');
return sb.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList3 list = new MyLinkedList3();
list.add("a");
list.add("b");
list.add("c");
list.add("d");
list.add("e");
list.add("f");
System.out.println(list);
list.remove(2);
System.out.println(list);
list.remove(0);// 删除第一个元素
System.out.println(list);
list.remove(3);// 删除最后一个元素
System.out.println(list);
}
}
测试:
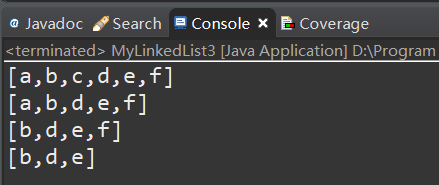
版本四:插入节点
package com.xzlf.collection;
/**
* 自定义一个链表
* 插入节点
* @author xzlf
*
*/
public class MyLinkedList4 {
private Node first;
private Node last;
private int size;
public void add(Object obj) {
Node node = new Node(obj);
if(first == null) {
first = node;
last = node;
}else {
node.previous = last;
node.next = null;
last.next = node;
last = node;
}
size++;
}
public void add(int index, Object obj) {
Node tmp = getNode(index);
Node newNode = new Node(obj);
if(tmp != null) {
Node up = tmp.previous;
up.next = newNode;
newNode.previous = up;
newNode.next = tmp;
tmp.previous = newNode;
}
}
public Object get(int index) {
Node tmp = null;
// 判断索引是否合法
if(index < 0 || index > size - 1) {
throw new RuntimeException("索引不合法:" + index);
}
tmp = getNode(index);
return tmp == null ? null : tmp.element;
}
public void remove(int index) {
Node tmp = getNode(index);
Node up = tmp.previous;
Node down = tmp.next;
if (tmp != null) {
if (up != null) {
up.next = down;
}
if (down != null) {
down.previous = up;
}
// 被删元素是第一个时
if(index == 0) {
first = down;
}
// 被删元素是最后一个时
if(index == size - 1) {
last = up;
}
size--;
}
}
public Node getNode(int index) {
Node tmp = null;
/*索引位置为前半部分,从头部开始找*/
if (index <= size >> 1) {
tmp = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
tmp = tmp.next;
}
}else {
/*索引位置为或半部分,从未部开始找*/
tmp = last;
for (int i = size -1; i > index; i--) {
tmp = tmp.previous;
}
}
return tmp;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("[");
Node tmp = first;
while(tmp != null) {
sb.append(tmp.element + ",");
tmp = tmp.next;
}
sb.setCharAt(sb.length() - 1, ']');
return sb.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList4 list = new MyLinkedList4();
list.add("a");
list.add("b");
list.add("c");
list.add("d");
list.add("e");
list.add("f");
System.out.println(list);
list.add(1, "hello");
System.out.println(list);
}
}
测试:
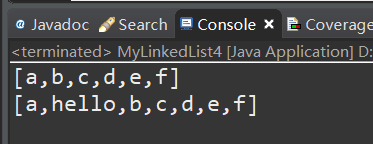
版本五:增加泛型,小的封装
package com.xzlf.collection;
/**
* 自定义一个链表
* 增加泛型,小的封装
* @author xzlf
*
*/
public class MyLinkedList5<E> {
private Node first;
private Node last;
private int size;
public void add(E element) {
Node node = new Node(element);
if(first == null) {
first = node;
last = node;
}else {
node.previous = last;
node.next = null;
last.next = node;
last = node;
}
size++;
}
public void add(int index, E element) {
checkRange(index);
Node tmp = getNode(index);
Node newNode = new Node(element);
if(tmp != null) {
Node up = tmp.previous;
up.next = newNode;
newNode.previous = up;
newNode.next = tmp;
tmp.previous = newNode;
size++;
}
}
private void checkRange(int index) {
if(index < 0 || index > size - 1) {
throw new RuntimeException("索引不合法:" + index);
}
}
public E get(int index) {
Node tmp = null;
// 判断索引是否合法
checkRange(index);
tmp = getNode(index);
return tmp == null ? null : (E) tmp.element;
}
public void remove(int index) {
checkRange(index);
Node tmp = getNode(index);
Node up = tmp.previous;
Node down = tmp.next;
if (tmp != null) {
if (up != null) {
up.next = down;
}
if (down != null) {
down.previous = up;
}
// 被删元素是第一个时
if(index == 0) {
first = down;
}
// 被删元素是最后一个时
if(index == size - 1) {
last = up;
}
size--;
}
}
private Node getNode(int index) {
checkRange(index);
Node tmp = null;
/*索引位置为前半部分,从头部开始找*/
if (index <= size >> 1) {
tmp = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
tmp = tmp.next;
}
}else {
/*索引位置为或半部分,从未部开始找*/
tmp = last;
for (int i = size -1; i > index; i--) {
tmp = tmp.previous;
}
}
return tmp;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("[");
Node tmp = first;
while(tmp != null) {
sb.append(tmp.element + ",");
tmp = tmp.next;
}
sb.setCharAt(sb.length() - 1, ']');
return sb.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
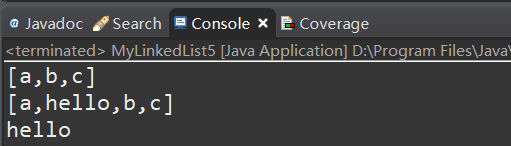
MyLinkedList5<String> list = new MyLinkedList5<>();
list.add("a");
list.add("b");
list.add("c");
System.out.println(list);
list.add(1, "hello");
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println(list.get(1));
}
}
测试:
现在我们在编辑上使用add() 方法后已经提示要插入String类型的数据了:
以上代码测试运行结果:
以上代码可能还有部分细节上的bug,不过作为理解LinkedList数据结构的练习应该够用了。
重视基础,才能走的更远。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号