实验一
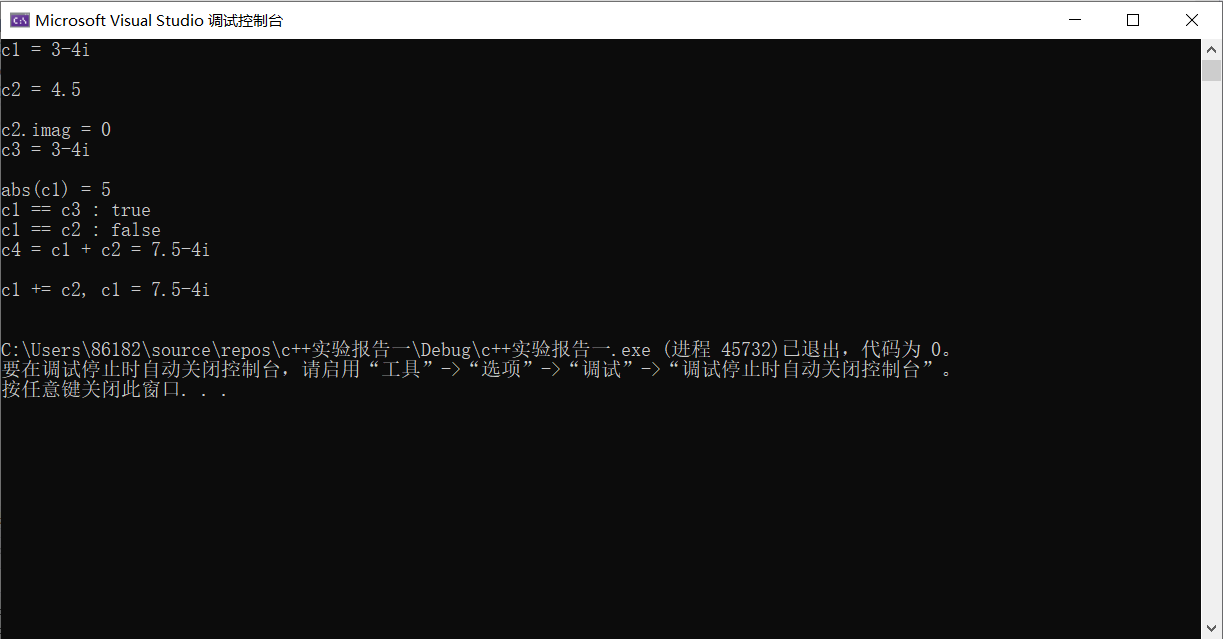
#ifndef COMPLEX_H #define COMPLEX_H #include<iostream> #include<cmath> class Complex { private: float real; float imag; public: Complex(float a = 0, float b = 0) :real(a), imag(b) {}; Complex(const Complex& p) :real(p.real), imag(p.imag) {}; float get_real() const{ return real; }; float get_imag() const{ return imag; }; void show()const; void add(const Complex c); friend Complex add(const Complex c1, const Complex c2); friend bool is_equal(const Complex c1, const Complex c2); friend float abs(const Complex c); }; void Complex::show() const{ std::cout << real; if (imag < 0) std::cout << imag << 'i' << std::endl; else if (imag > 0) std::cout << '+' << imag << 'i' << std::endl; else std::cout << std::endl; } void Complex::add(const Complex c) { real += c.real; imag += c.imag; } Complex add(const Complex c1, const Complex c2) { Complex c; c.real = c1.real + c2.real; c.imag = c1.imag + c2.imag; return c; } bool is_equal(const Complex c1, const Complex c2) { if (c1.real == c2.real && c1.imag == c2.imag) return true; else return false; } float abs(const Complex c) { float out; out = c.real * c.real + c.imag * c.imag; out = sqrt(out); return out; } #endif
#include "Complex.h" #include <iostream> int main() { using namespace std; Complex c1(3, -4); const Complex c2(4.5); Complex c3(c1); cout << "c1 = "; c1.show(); cout << endl; cout << "c2 = "; c2.show(); cout << endl; cout << "c2.imag = " << c2.get_imag() << endl; cout << "c3 = "; c3.show(); cout << endl; cout << "abs(c1) = "; cout << abs(c1) << endl; cout << boolalpha; cout << "c1 == c3 : " << is_equal(c1, c3) << endl; cout << "c1 == c2 : " << is_equal(c1, c2) << endl; Complex c4; c4 = add(c1, c2); cout << "c4 = c1 + c2 = "; c4.show(); cout << endl; c1.add(c2); cout << "c1 += c2, " << "c1 = "; c1.show(); cout << endl; }

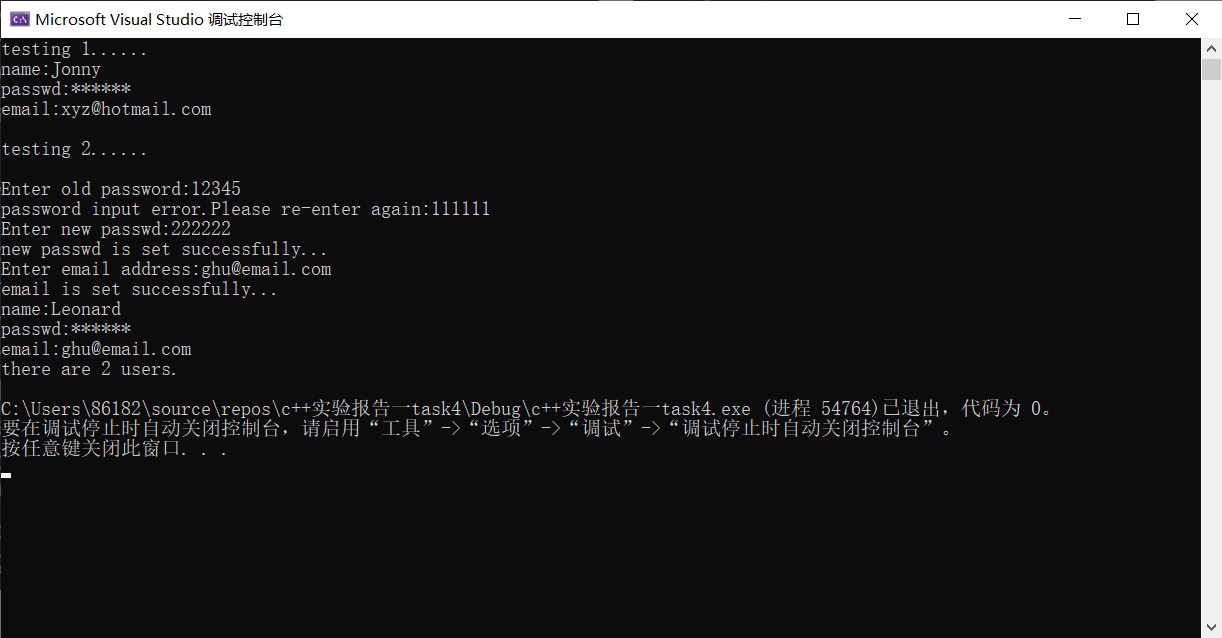
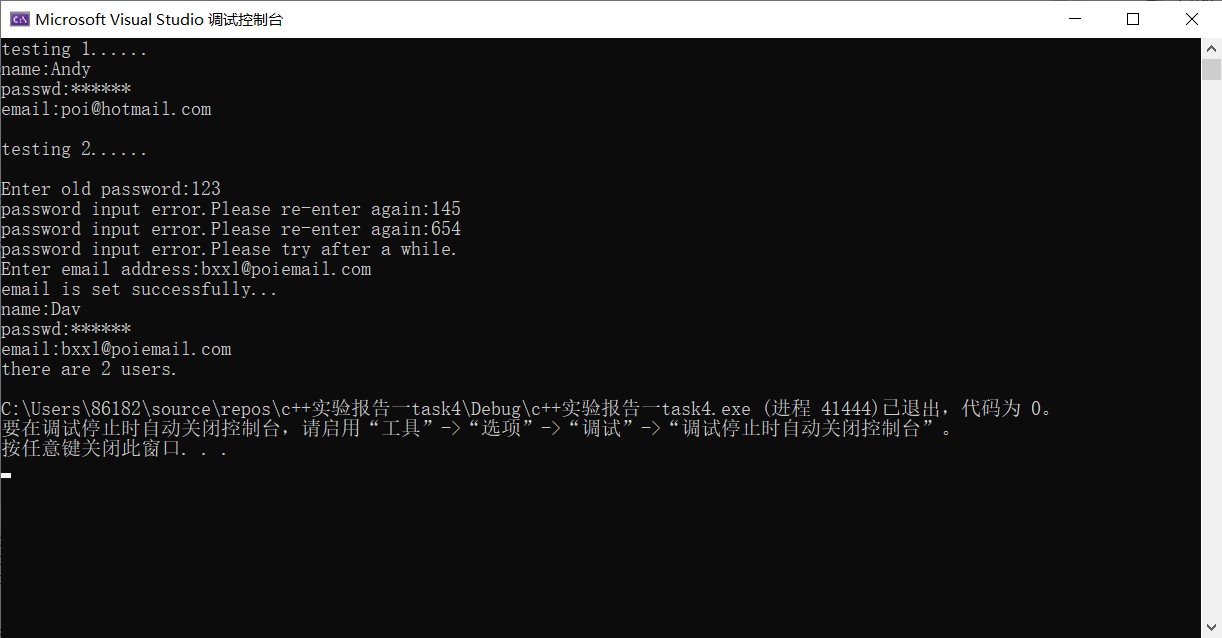
#ifndef USER_H #define USER_H #include<iostream> #include<string> using namespace std; class User { private: string name; string passwd; string email; static int n; public: User(string a, string b = "111111", string c = "\0") :name(a), passwd(b), email(c) { n++; }; void set_email(); void change_passwd(); void print_info(); static void print_n() { cout << "there are " << n << " users." << endl; }; }; int User::n = 0; void User::set_email() { cout << "Enter email address:"; cin >> email; cout << "email is set successfully..." << endl; } void User::change_passwd() { cout << "Enter old password:"; string old; cin >> old; int i; for (i = 0; i < 2; i++) { if (old == passwd){ cout << "Enter new passwd:"; cin >> passwd; cout << "new passwd is set successfully..."<<endl; break; } else{ cout << "password input error.Please re-enter again:"; cin >> old; } } if (i == 2) cout << "password input error.Please try after a while." << endl; } void User::print_info() { cout << "name:" << name << endl; cout << "passwd:******" << endl; cout << "email:" << email << endl; } #endif
#include "User.h" #include <iostream> int main() { using namespace std; cout << "testing 1......" << endl; User user1("Jonny", "92197", "xyz@hotmail.com"); user1.print_info(); cout << endl << "testing 2......" << endl << endl; User user2("Leonard"); user2.change_passwd(); user2.set_email(); user2.print_info(); User::print_n(); }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号