蚁群算法(1) - Python实现
- 抽象来源:模仿自然界中蚂蚁的觅食行为。
- 核心思想:蚁群觅食过程中,每只蚂蚁在所走过的路径上均会释放出一种信息素,该信息素随时间的推移逐渐挥发。因此,每条路径上的信息素同时存在正负反馈两种机制。正反馈:蚂蚁每次经过该路径均会释放信息素使得该路径上的信息素浓度增加;负反馈:每条路径上的信息素随时间推移会逐渐挥发。由此,我们可以判断,在起点与终点之间,当相同数量的蚂蚁初始同时经过两条不同的路径时,路径上初始信息素的浓度是相同的;不过,当路径越短时,信息素挥发时间也越短,残留信息素浓度也将越高。随后的蚂蚁将根据路径上残留信息素浓度的大小对路径进行选择 --- 浓度越高,选择概率越大。最终导致信息素浓度越高的路径上蚂蚁的选择数目越多,而更多的蚂蚁也将同时导致该路径上残留信息素浓度越高(即高者越高,低者越低)。因此,在理想情况下,整个蚁群将逐渐向信息素浓度最高的路径(即最短路径)进行转移。
- 迭代公式:
- 时刻t,蚂蚁k由节点i向节点j的状态转移概率:
\begin{equation}
p_{ij}^{k}(t) =
\left\{
\begin{split}
&\frac{[\tau_{ij}(t)]^{\alpha }\cdot [\eta_{ij}(t)]^{\beta}}{\sum\limits_{s\in allowed_{k}}[\tau_{is}(t)]^{\alpha }\cdot [\eta_{is}(t)]^{\beta}} & \text{ if } j\in allowed_{k}\\
&0 & \text{ if } j\notin allowed_{k}
\end{split}
\right.
\end{equation}
其中$\alpha$为信息启发式因子,$\beta$为期望启发式因子,$\tau$为路径残留信息素,$\eta$为启发函数 - 残留信息素迭代更新方式(在完成一次迭代后集体进行更新):
\begin{equation}
\tau_{ij}(t+1) = (1-\rho)\cdot \tau_{ij}(t)+\Delta\tau_{ij}(t)
\end{equation}
其中$\rho$为信息素挥发速度 --- 负反馈相关,$\Delta\tau_{ij}$为信息素增量 --- 正反馈相关
信息素增量:
$\Delta\tau_{ij}(t) = \sum^{m}_{k=1}\Delta\tau_{ij}^{k}(t)$
每只蚂蚁对信息素增量的贡献:
$\Delta\tau_{ij}^{k}(t) = \begin{cases}
Q/L_k & \text{ if the k_th ant goes through the nodes labeled with i and j on the current iteration} \\
0 & \text{ else }
\end{cases}$
其中,$L_k$代表第k只蚂蚁在当前迭代过程中完整所走过的总路程 - 启发函数表达式:
\begin{equation}
\eta_{ij}(t) = \frac{1}{d_{ij}}
\end{equation}
其中$d_{ij}$为节点i至节点j之间的距离
- 时刻t,蚂蚁k由节点i向节点j的状态转移概率:
- Python代码实现:
![]() View Code
View Code1 import numpy as np 2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 3 4 5 # 建立“蚂蚁”类 6 class Ant(object): 7 def __init__(self, path): 8 self.path = path # 蚂蚁当前迭代整体路径 9 self.length = self.calc_length(path) # 蚂蚁当前迭代整体路径长度 10 11 def calc_length(self, path_): # path=[A, B, C, D, A]注意路径闭环 12 length_ = 0 13 for i in range(len(path_)-1): 14 delta = (path_[i].x - path_[i+1].x, path_[i].y - path_[i+1].y) 15 length_ += np.linalg.norm(delta) 16 return length_ 17 18 @staticmethod 19 def calc_len(A, B): # 静态方法,计算城市A与城市B之间的距离 20 return np.linalg.norm((A.x - B.x, A.y - B.y)) 21 22 23 # 建立“城市”类 24 class City(object): 25 def __init__(self, x, y): 26 self.x = x 27 self.y = y 28 29 30 # 建立“路径”类 31 class Path(object): 32 def __init__(self, A): # A为起始城市 33 self.path = [A, A] 34 35 def add_path(self, B): # 追加路径信息,方便计算整体路径长度 36 self.path.append(B) 37 self.path[-1], self.path[-2] = self.path[-2], self.path[-1] 38 39 40 # 构建“蚁群算法”的主体 41 class ACO(object): 42 def __init__(self, ant_num=50, maxIter=300, alpha=1, beta=5, rho=0.1, Q=1): 43 self.ants_num = ant_num # 蚂蚁个数 44 self.maxIter = maxIter # 蚁群最大迭代次数 45 self.alpha = alpha # 信息启发式因子 46 self.beta = beta # 期望启发式因子 47 self.rho = rho # 信息素挥发速度 48 self.Q = Q # 信息素强度 49 ########################### 50 self.deal_data('coordinates.dat') # 提取所有城市的坐标信息 51 ########################### 52 self.path_seed = np.zeros(self.ants_num).astype(int) # 记录一次迭代过程中每个蚂蚁的初始城市下标 53 self.ants_info = np.zeros((self.maxIter, self.ants_num)) # 记录每次迭代后所有蚂蚁的路径长度信息 54 self.best_path = np.zeros(self.maxIter) # 记录每次迭代后整个蚁群的“历史”最短路径长度 55 ########################### 56 self.solve() # 完成算法的迭代更新 57 self.display() # 数据可视化展示 58 59 def deal_data(self, filename): 60 with open(filename, 'rt') as f: 61 temp_list = list(line.split() for line in f) # 临时存储提取出来的坐标信息 62 self.cities_num = len(temp_list) # 1. 获取城市个数 63 self.cities = list(City(float(item[0]), float(item[1])) for item in temp_list) # 2. 构建城市列表 64 self.city_dist_mat = np.zeros((self.cities_num, self.cities_num)) # 3. 构建城市距离矩阵 65 for i in range(self.cities_num): 66 A = self.cities[i] 67 for j in range(i, self.cities_num): 68 B = self.cities[j] 69 self.city_dist_mat[i][j] = self.city_dist_mat[j][i] = Ant.calc_len(A, B) 70 self.phero_mat = np.ones((self.cities_num, self.cities_num)) # 4. 初始化信息素矩阵 71 # self.phero_upper_bound = self.phero_mat.max() * 1.2 ###信息素浓度上限 72 self.eta_mat = 1/(self.city_dist_mat + np.diag([np.inf]*self.cities_num)) # 5. 初始化启发函数矩阵 73 74 def solve(self): 75 iterNum = 0 # 当前迭代次数 76 while iterNum < self.maxIter: 77 self.random_seed() # 使整个蚁群产生随机的起始点 78 delta_phero_mat = np.zeros((self.cities_num, self.cities_num)) # 初始化每次迭代后信息素矩阵的增量 79 ########################################################################## 80 for i in range(self.ants_num): 81 city_index1 = self.path_seed[i] # 每只蚂蚁访问的第一个城市下标 82 ant_path = Path(self.cities[city_index1]) # 记录每只蚂蚁访问过的城市 83 tabu = [city_index1] # 记录每只蚂蚁访问过的城市下标,禁忌城市下标列表 84 non_tabu = list(set(range(self.cities_num)) - set(tabu)) 85 for j in range(self.cities_num-1): # 对余下的城市进行访问 86 up_proba = np.zeros(self.cities_num-len(tabu)) # 初始化状态迁移概率的分子 87 for k in range(self.cities_num-len(tabu)): 88 up_proba[k] = np.power(self.phero_mat[city_index1][non_tabu[k]], self.alpha) * \ 89 np.power(self.eta_mat[city_index1][non_tabu[k]], self.beta) 90 proba = up_proba/sum(up_proba) # 每条可能子路径上的状态迁移概率 91 while True: # 提取出下一个城市的下标 92 random_num = np.random.rand() 93 index_need = np.where(proba > random_num)[0] 94 if len(index_need) > 0: 95 city_index2 = non_tabu[index_need[0]] 96 break 97 ant_path.add_path(self.cities[city_index2]) 98 tabu.append(city_index2) 99 non_tabu = list(set(range(self.cities_num)) - set(tabu)) 100 city_index1 = city_index2 101 self.ants_info[iterNum][i] = Ant(ant_path.path).length 102 if iterNum == 0 and i == 0: # 完成对最佳路径城市的记录 103 self.best_cities = ant_path.path 104 else: 105 if self.ants_info[iterNum][i] < Ant(self.best_cities).length: self.best_cities = ant_path.path 106 tabu.append(tabu[0]) # 每次迭代完成后,使禁忌城市下标列表形成完整闭环 107 for l in range(self.cities_num): 108 delta_phero_mat[tabu[l]][tabu[l+1]] += self.Q/self.ants_info[iterNum][i] 109 110 self.best_path[iterNum] = Ant(self.best_cities).length 111 112 self.update_phero_mat(delta_phero_mat) # 更新信息素矩阵 113 iterNum += 1 114 115 def update_phero_mat(self, delta): 116 self.phero_mat = (1 - self.rho) * self.phero_mat + delta 117 # self.phero_mat = np.where(self.phero_mat > self.phero_upper_bound, self.phero_upper_bound, self.phero_mat) # 判断是否超过浓度上限 118 119 def random_seed(self): # 产生随机的起始点下表,尽量保证所有蚂蚁的起始点不同 120 if self.ants_num <= self.cities_num: # 蚂蚁数 <= 城市数 121 self.path_seed[:] = np.random.permutation(range(self.cities_num))[:self.ants_num] 122 else: # 蚂蚁数 > 城市数 123 self.path_seed[:self.cities_num] = np.random.permutation(range(self.cities_num)) 124 temp_index = self.cities_num 125 while temp_index + self.cities_num <= self.ants_num: 126 self.path_seed[temp_index:temp_index + self.cities_num] = np.random.permutation(range(self.cities_num)) 127 temp_index += self.cities_num 128 temp_left = self.ants_num % self.cities_num 129 if temp_left != 0: 130 self.path_seed[temp_index:] = np.random.permutation(range(self.cities_num))[:temp_left] 131 132 def display(self): # 数据可视化展示 133 plt.figure(figsize=(6, 10)) 134 plt.subplot(211) 135 plt.plot(self.ants_info, 'g.') 136 plt.plot(self.best_path, 'r-', label='history_best') 137 plt.xlabel('Iteration') 138 plt.ylabel('length') 139 plt.legend() 140 plt.subplot(212) 141 plt.plot(list(city.x for city in self.best_cities), list(city.y for city in self.best_cities), 'g-') 142 plt.plot(list(city.x for city in self.best_cities), list(city.y for city in self.best_cities), 'r.') 143 plt.xlabel('x') 144 plt.ylabel('y') 145 plt.savefig('ACO.png', dpi=500) 146 plt.show() 147 plt.close() 148 149 150 ACO()
笔者所用数据文件名为coordinates.dat,相应坐标信息如下:
![]() View coordinates.dat
View coordinates.dat565.0 575.0 25.0 185.0 345.0 750.0 945.0 685.0 845.0 655.0 880.0 660.0 25.0 230.0 525.0 1000.0 580.0 1175.0 650.0 1130.0 1605.0 620.0 1220.0 580.0 1465.0 200.0 1530.0 5.0 845.0 680.0 725.0 370.0 145.0 665.0 415.0 635.0 510.0 875.0 560.0 365.0 300.0 465.0 520.0 585.0 480.0 415.0 835.0 625.0 975.0 580.0 1215.0 245.0 1320.0 315.0 1250.0 400.0 660.0 180.0 410.0 250.0 420.0 555.0 575.0 665.0 1150.0 1160.0 700.0 580.0 685.0 595.0 685.0 610.0 770.0 610.0 795.0 645.0 720.0 635.0 760.0 650.0 475.0 960.0 95.0 260.0 875.0 920.0 700.0 500.0 555.0 815.0 830.0 485.0 1170.0 65.0 830.0 610.0 605.0 625.0 595.0 360.0 1340.0 725.0 1740.0 245.0
- 结果展示:
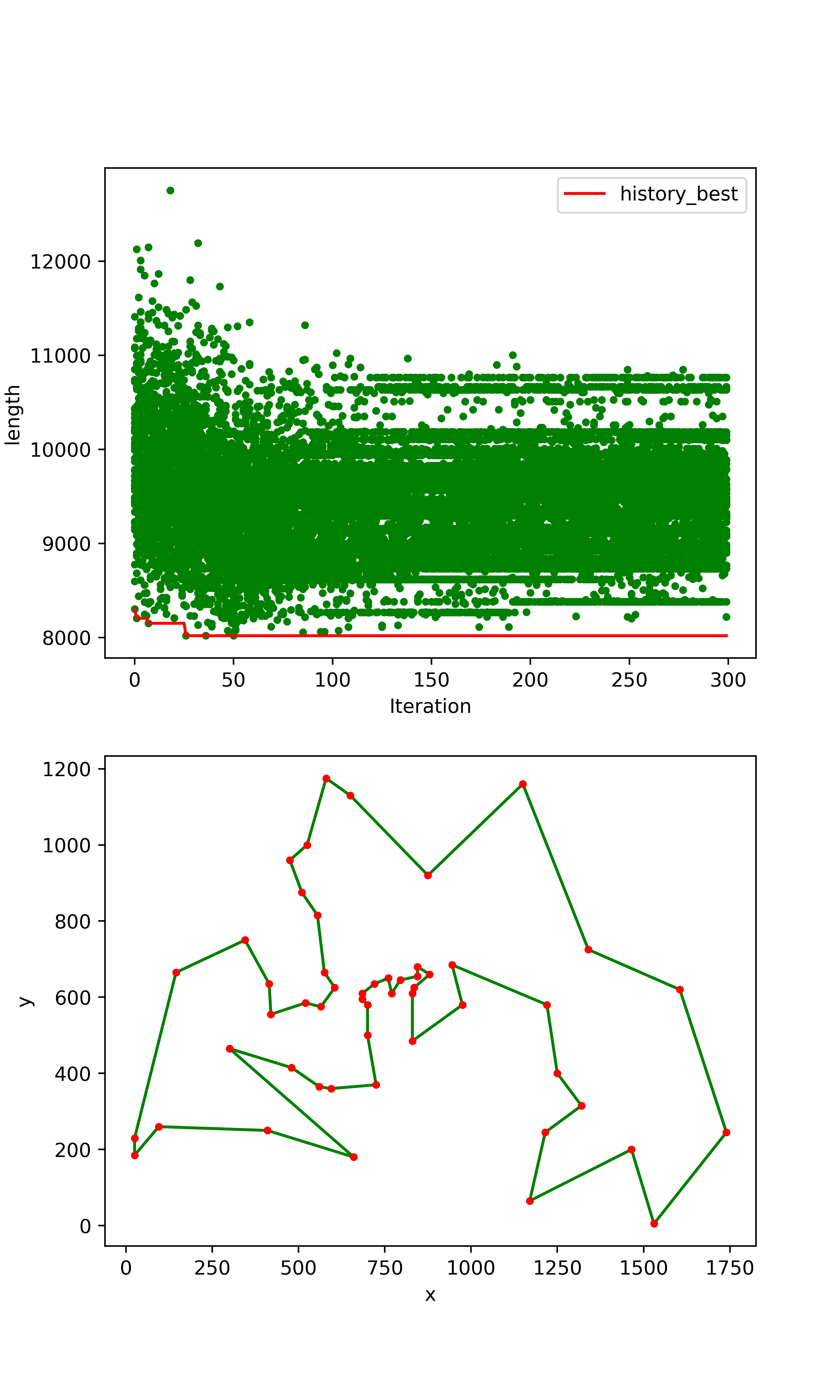
- 参考:https://blog.csdn.net/golden1314521/article/details/45059719






 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号