08 结构体
0、概念:结构体属于用户自定义的数据类型。允许用户存储不同的数据类型。
1、定义及使用方法
1.1定义结构体语句:struct 结构体名 { 结构体成员 };
1.2定义结构体变量语句:
1)struct 结构体名 变量名 (推荐)
2)struct 结构体名 变量名 = {成员1值,成员2值...}
3)定义结构体同时创建变量
//结构体定义
struct student
{
//成员列表
string name;
int age;
int score;
}stu3; //定义结构体同时创建变量创建方式3
int main() {
//结构体变量创建方式1
struct student stu1; //struct 关键字可以省略
stu1.name = "张三"; //结构体变量利用操作符“.”访问其成员
stu1.age = 18;
stu1.score = 100;
cout << "姓名:" << stu1.name << " 年龄:" << stu1.age << " 分数:" << stu1.score << endl;
//结构体变量创建方式2
struct student stu2 = { "李四",19,60 };
cout << "姓名:" << stu2.name << " 年龄:" << stu2.age << " 分数:" << stu2.score << endl;
stu3.name = "王五";
stu3.age = 18;
stu3.score = 80;
cout << "姓名:" << stu3.name << " 年龄:" << stu3.age << " 分数:" << stu3.score << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
2、结构体数组
语法:struct 结构体名 数组名 [ 元素个数 ] = { { },{ },...{ } }
如:struct student arr[3]=
{
{"张三",18,80 },
{"李四",19,60 },
{"王五",20,70 },
};
3、结构体指针
作用:通过指针访问结构体中成员
定义方法:struct 结构体名* 指针名;如: struct student* p
用结构体指针变量访问结构体变量成员有以下两种方式:
对于结构体student 来说
struct student { string name; int age; int score;} student1;
1)(*p).name
2)p->name
两者与 student1.name 是等价的。
//结构体指针示例:
int main()
{ struct student stu = { "张三",18,100, }; struct student * p = &stu; p->score = 80; //指针通过 -> 操作符可以访问成员 cout << "姓名:" << p->name << " 年龄:" << p->age << " 分数:" << p->score << endl; system("pause"); return 0; }
4、结构体嵌套结构体
在结构体中可以定义另一个结构体作为其成员,用来解决实际问题。
示例:老师辅导一个学员,一个老师的结构体中记录一个学生的结构体。
//教师结构体定义 struct teacher { //成员列表 int id; //职工编号 string name; //教师姓名 int age; //教师年龄 struct student stu; //子结构体 学生 }; int main()
{ struct teacher t1; t1.id = 10000; t1.name = "老王"; t1.age = 40; t1.stu.name = "张三"; t1.stu.age = 18; t1.stu.score = 100; cout << "教师 职工编号: " << t1.id << " 姓名: " << t1.name << " 年龄: " << t1.age << endl; cout << "辅导学员 姓名: " << t1.stu.name << " 年龄:" << t1.stu.age << " 考试分数: " << t1.stu.score << endl; system("pause"); return 0; }
5、结构体做函数参数
1)值传递
2)地址传递
示例代码:
void printStudent(student stu ) //值传递 { stu.age = 28; } void printStudent2(student *stu) //地址传递 { stu->age = 28; } int main()
{ student stu = { "张三",18,100};
//值传递 printStudent(stu); cout << "主函数中 姓名:" << stu.name << " 年龄: " << stu.age << " 分数:" << stu.score << endl;//地址传递 printStudent2(&stu); cout << "主函数中 姓名:" << stu.name << " 年龄: " << stu.age << " 分数:" << stu.score << endl; system("pause"); return 0; }
6、结构体中const 使用场景
作用:使用 const 来防止误操作
void printStudent(const student *stu) //加const防止函数体中的误操作 { //stu->age = 100; //操作失败,因为加了const修饰 cout << "姓名:" << stu->name << " 年龄:" << stu->age << " 分数:" << stu->score << endl; } int main()
{ student stu = { "张三",18,100 }; printStudent(&stu); system("pause"); return 0; }
✔练习案例1:
学校正在做毕设项目,每名老师带领5个学生,总共有3名老师,需求如下:
设计学生和老师的结构体,其中在老师的结构体中,有老师姓名和一个存放5名学生的数组作为成员。学生的成员有姓名、考试分数,创建数组存放3名老师,通过函数给每个老师及所带的学生赋值,最终打印出老师数据以及老师所带的学生数据。

1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 5 struct student 6 { 7 char sname; 8 int score; 9 }; 10 11 struct teacher 12 { 13 char tname; 14 student stu[5]; 15 }; 16 17 18 int main() 19 { 20 int k=65; //A的ASCII码值 21 teacher tea[3]; 22 for(int i=0;i<3;i++) 23 { 24 tea[i].tname=(char)(k+i); //三个老师叫A,B,C 25 for(int j=0;j<5;j++) 26 { 27 tea[i].stu[j].sname=(char)(k+5*i+j+32); //15个学生叫a~o,用这种强制类型转换的方式该姓名 28 tea[i].stu[j].score=rand()%40+60; //成绩为60~100的随机数 29 } 30 } 31 32 for(int i=0;i<3;i++) 33 { 34 cout<<tea[i].tname<<" teach's students:"<<endl; 35 for(int j=0;j<5;j++) 36 { 37 cout<<"name: "<<tea[i].stu[j].sname<<" socre: "<<tea[i].stu[j].score<<endl; 38 } 39 cout<<endl; 40 } 41 system("pause"); 42 return 0; 43 }
运行结果:
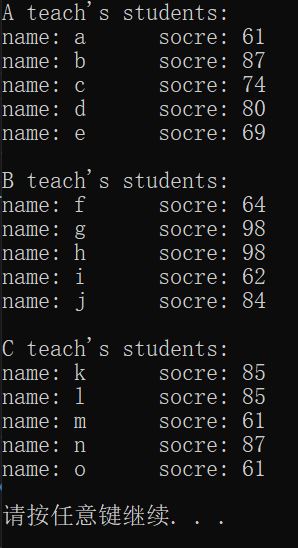
✔练习案例2:
设计一个英雄的结构体,包括成员姓名、武器、武力、智力;创建结构体数组,数组中存放5名英雄。通过冒泡排序的算法,将数组中的英雄按照武力值进行升序排序,最终打印排序后的结果。五名英雄信息如下:
{"关羽","偃月刀","245","180"},
{"张飞","蛇戟","255","60"},
{"赵云",,"黑龙枪""240","200"},
{"徐庶","铁剑","100","240"},
{"诸葛亮","青虹剑","135","255"},

1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 struct hero 5 { 6 string name; 7 string weapon; 8 int force; 9 int intelligrence; 10 }; 11 12 int main() 13 { 14 hero shujiang[5]= 15 { 16 {"关羽","偃月刀",245,180}, 17 {"张飞","蛇戟",255,60}, 18 {"赵云","黑龙枪",240,200}, 19 {"徐庶","铁剑",100,240}, 20 {"诸葛亮","青虹剑",135,255}, 21 }; 22 for(int i=0;i<4;i++) 23 { 24 for(int j=0;j<4;j++) 25 { 26 if(shujiang[j].force>shujiang[j+1].force) 27 { 28 hero temp=shujiang[j+1]; 29 shujiang[j+1]=shujiang[j]; 30 shujiang[j]=temp; 31 32 } 33 } 34 } 35 cout<<"武力值排名(从小到大): "<<endl; 36 for(int i=0;i<5;i++) 37 { 38 cout<<shujiang[i].name<<" "<<endl; 39 } 40 system("pause"); 41 return 0; 42 }
至此入门课程已学完,基础c的内容比较多,例题也很简单,权当复习一遍。转战去leetcode试试水,边找虐边学习吧(⌐■_■)




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号