使用简单工厂模式+反射 实现满足开闭原则的工厂
背景:我们在使用简单工厂模式的时候,当新增一种对象时,除了新增这个对象的类,我们往往还需要在工厂类中多加一个if判断,这样违背了开闭原则,是否能将这个if判断的逻辑去掉?
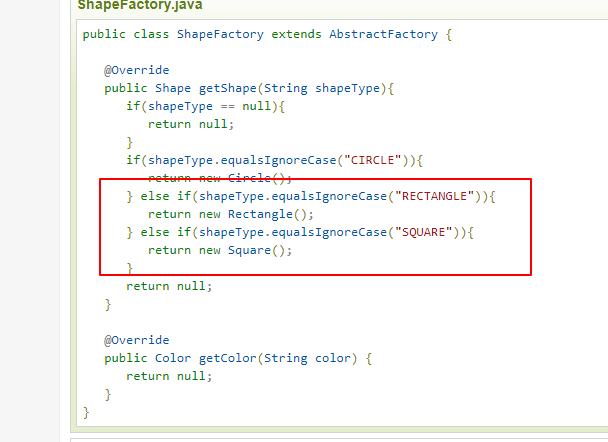
思路:我们可以将所有的目标类放在一个特定的路径,在类初始化时,动态加载这个路径下的满足条件的类
步骤:
1 自定义条件注解
/**
* 标记枚举
*/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface TypeMask {
// 标记枚举类型
String value();
}
2 将对象放在指定路径下:
@TypeMask("A")
public class ProductA implements Product {
@Override
public void tell() {
System.out.println("I am productA");
}
}
@TypeMask("B")
public class ProductB implements Product {
@Override
public void tell() {
System.out.println("I am ProductB");
}
}
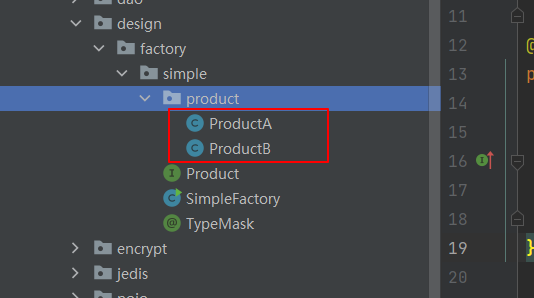
3 通过反射加载product目录下 标了TypeMask的类
package com.xzx.statistics.design.factory.simple;
import com.google.common.collect.Maps;
import lombok.SneakyThrows;
import java.io.File;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 简单工厂
*
* @author XuZhangxing
*/
public class SimpleFactory {
private static final Map<String, Class<?>> map = Maps.newHashMap();
@SneakyThrows
private static void loadToMap() {
// 获取本类的路径
URL resource = SimpleFactory.class.getResource("");
assert resource != null;
String path = resource.getPath();
String newPath = path + File.separator + "product";
File file = new File(newPath);
File[] files = file.listFiles();
// 找到product 的路径
String productPath = SimpleFactory.class.getPackage().getName() + ".product.";
assert files != null;
for (File f : files) {
// 文件夹跳过
if (f.isDirectory()) {
continue;
}
// 不是类文件跳过
if (!f.getName().endsWith(".class")) {
continue;
}
Class<?> forClass = Class.forName(productPath + f.getName().replace(".class", ""));
// 拿到类上的注解
TypeMask[] typeMasks = forClass.getAnnotationsByType(TypeMask.class);
// 没标注解的不取
if (typeMasks.length < 1) {
continue;
}
// 没有实现Product 接口的不取
if (Product.class.isAssignableFrom(forClass)) {
map.put(typeMasks[0].value(), forClass);
}
}
}
// 状态类到map中
static {
loadToMap();
}
@SneakyThrows
public static Product getByCode(String code) {
Class<?> clazz = map.get(code);
if (clazz == null) {
return null;
}
if (Product.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz)) {
return (Product) clazz.newInstance();
}
return null;
}
}
4 客户端调用:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Product productA = getByCode("A");
productA.tell();
Product productB = getByCode("B");
productB.tell();
}
输出结果
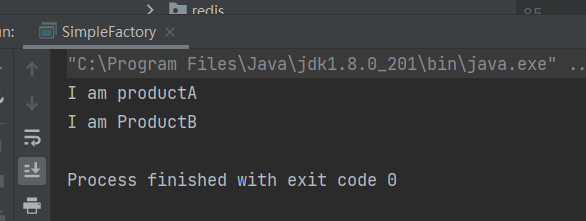
5 总结:
当需要添加新的类时,将类放在product目录下并标注TypeMask注解,而SimpleFactory 类不需要有任何变化
同理可以应用到抽象工厂模式中


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号