C# LINQ
一、概述
关键字:from、where、orderby、descending、select
表达式必须以 from 开头,以select 或者group 结束。在这之间可以使用 where、orderby、join、let和其他 from子句。
下面用几个实例来了解LINQ的拓展方法

1 class Racer : IComparable<Racer>, IFormattable 2 { 3 public string FirstName { get; set; } 4 public string LastName { get; set; } 5 public string Country { get; set; } 6 public int Wins { get; set; } 7 public int Starts { get; set; } 8 public string[] Cars { get; set; } 9 public int[] Years { get; set; } 10 11 public Racer(string firstName = null, string lastName=null,string country=null,int starts=0,int wins=0,IEnumerable<int> years=null,IEnumerable<string> cars=null) 12 { 13 this.FirstName = firstName; 14 this.LastName = lastName; 15 this.Country = country; 16 this.Wins = wins; 17 this.Starts = starts; 18 19 var yearsList = new List<int>(); 20 foreach (var year in years) 21 yearsList.Add(year); 22 this.Years = yearsList.ToArray(); 23 var carList = new List<string>(); 24 foreach (var car in cars) 25 carList.Add(car); 26 this.Cars = carList.ToArray(); 27 } 28 29 public override string ToString() 30 { 31 return String.Format($"{this.FirstName} {this.LastName}"); 32 } 33 34 public int CompareTo( Racer other) 35 { 36 if (other == null) throw new ArgumentNullException("other"); 37 38 return this.LastName.CompareTo(other.LastName); 39 } 40 41 public string ToString(string format) 42 { 43 return ToString(format, null); 44 } 45 46 public string ToString(string format, IFormatProvider formatProvider) 47 { 48 switch (format) 49 { 50 case "N": 51 return ToString(); 52 case "F": 53 return this.FirstName; 54 case "L": 55 return this.LastName; 56 case "C": 57 return this.Country; 58 case "S": 59 return this.Starts.ToString(); 60 case "W": 61 return this.Wins.ToString(); 62 case "A": 63 return String.Format($"{this.FirstName} {this.LastName}, {this.Country}; starts: {this.Starts}, Wins: {this.Wins}"); 64 default: 65 throw new FormatException(String.Format($"Format {format} not supported")); 66 67 68 } 69 } 70 }

1 //车队 2 class Team 3 { 4 public string Name { get; set; } 5 public int[] Years { get; set; } 6 public Team(string name,params int[] years) 7 { 8 this.Name = name; 9 this.Years = years; 10 } 11 }

1 static class Formula1 2 { 3 private static List<Racer> racers; 4 5 //Fomula1类在GetChampions()方法中返回一组赛手。 6 //这个列表包含了1950~2008年之间的所有一级方程式冠军 7 public static IList<Racer> GetChampions() 8 { 9 if (racers == null) 10 { 11 racers = new List<Racer>(40); 12 racers.Add(new Racer("Nino", "Farina", "Italy", 33, 5, new int[] { 1950 }, new string[] { "Alfa Romeo" })); 13 racers.Add(new Racer("Alberto", "Ascari", "Italy", 32, 10, new int[] { 1952, 1953 }, new string[] { "Ferrari" })); 14 racers.Add(new Racer("Juan Manuel", "Fangio", "Argentina", 51, 24, new int[] { 1951, 1954, 1955, 1956, 1957 }, new string[] { "Alfa Romeo", "Maserati", "Mercedes", "Ferrari" })); 15 racers.Add(new Racer("Mike", "Hawthorn", "UK", 45, 3, new int[] { 1958 }, new string[] { "Ferrari" })); 16 racers.Add(new Racer("Phil", "Hill", "USA", 48, 3, new int[] { 1961 }, new string[] { "Ferrari" })); 17 racers.Add(new Racer("John", "Surtees", "UK", 111, 6, new int[] { 1964 }, new string[] { "Ferrari" })); 18 racers.Add(new Racer("Jim", "Clark", "UK", 72, 25, new int[] { 1963, 1965 }, new string[] { "Lotus" })); 19 racers.Add(new Racer("Jack", "Brabham", "Australia", 125, 14, new int[] { 1959, 1960, 1966 }, new string[] { "Cooper", "Brabham" })); 20 racers.Add(new Racer("Denny", "Hulme", "New Zealand", 112, 8, new int[] { 1967 }, new string[] { "Brabham" })); 21 racers.Add(new Racer("Graham", "Hill", "UK", 176, 14, new int[] { 1962, 1968 }, new string[] { "BRM", "Lotus" })); 22 racers.Add(new Racer("Jochen", "Rindt", "Austria", 60, 6, new int[] { 1970 }, new string[] { "Lotus" })); 23 racers.Add(new Racer("Jackie", "Stewart", "UK", 99, 27, new int[] { 1969, 1971, 1973 }, new string[] { "Matra", "Tyrrell" })); 24 racers.Add(new Racer("Emerson", "Fittipaldi", "Brazil", 143, 14, new int[] { 1972, 1974 }, new string[] { "Lotus", "McLaren" })); 25 racers.Add(new Racer("James", "Hunt", "UK", 91, 10, new int[] { 1976 }, new string[] { "McLaren" })); 26 racers.Add(new Racer("Mario", "Andretti", "USA", 128, 12, new int[] { 1978 }, new string[] { "Lotus" })); 27 racers.Add(new Racer("Jody", "Scheckter", "South Africa", 112, 10, new int[] { 1979 }, new string[] { "Ferrari" })); 28 racers.Add(new Racer("Alan", "Jones", "Australia", 115, 12, new int[] { 1980 }, new string[] { "Williams" })); 29 racers.Add(new Racer("Keke", "Rosberg", "Finland", 114, 5, new int[] { 1982 }, new string[] { "Williams" })); 30 racers.Add(new Racer("Niki", "Lauda", "Austria", 173, 25, new int[] { 1975, 1977, 1984 }, new string[] { "Ferrari", "McLaren" })); 31 racers.Add(new Racer("Nelson", "Piquet", "Brazil", 204, 23, new int[] { 1981, 1983, 1987 }, new string[] { "Brabham", "Williams" })); 32 racers.Add(new Racer("Ayrton", "Senna", "Brazil", 161, 41, new int[] { 1988, 1990, 1991 }, new string[] { "McLaren" })); 33 racers.Add(new Racer("Nigel", "Mansell", "UK", 187, 31, new int[] { 1992 }, new string[] { "Williams" })); 34 racers.Add(new Racer("Alain", "Prost", "France", 197, 51, new int[] { 1985, 1986, 1989, 1993 }, new string[] { "McLaren", "Williams" })); 35 racers.Add(new Racer("Damon", "Hill", "UK", 114, 22, new int[] { 1996 }, new string[] { "Williams" })); 36 racers.Add(new Racer("Jacques", "Villeneuve", "Canada", 165, 11, new int[] { 1997 }, new string[] { "Williams" })); 37 racers.Add(new Racer("Mika", "Hakkinen", "Finland", 160, 20, new int[] { 1998, 1999 }, new string[] { "McLaren" })); 38 racers.Add(new Racer("Michael", "Schumacher", "Germany", 250, 91, new int[] { 1994, 1995, 2000, 2001, 2002, 2003, 2004 }, new string[] { "Benetton", "Ferrari" })); 39 racers.Add(new Racer("Fernando", "Alonso", "Spain", 132, 21, new int[] { 2005, 2006 }, new string[] { "Renault" })); 40 racers.Add(new Racer("Kimi", "Räikkönen", "Finland", 148, 17, new int[] { 2007 }, new string[] { "Ferrari" })); 41 racers.Add(new Racer("Lewis", "Hamilton", "UK", 44, 9, new int[] { 2008 }, new string[] { "McLaren" })); 42 } 43 44 return racers; 45 } 46 47 48 private static List<Team> teams; 49 50 //返回车队的冠军列表 51 public static IList<Team> GetContructorChampions() 52 { 53 if (teams == null) 54 { 55 teams = new List<Team>() 56 { 57 new Team("Vanwall", 1958), 58 new Team("Cooper", 1959, 1960), 59 new Team("Ferrari", 1961, 1964, 1975, 1976, 1977, 1979, 1982, 1983, 1999, 2000, 2001, 2002, 2003, 2004, 2007, 2008), 60 new Team("BRM", 1962), 61 new Team("Lotus", 1963, 1965, 1968, 1970, 1972, 1973, 1978), 62 new Team("Brabham", 1966, 1967), 63 new Team("Matra", 1969), 64 new Team("Tyrrell", 1971), 65 new Team("McLaren", 1974, 1984, 1985, 1988, 1989, 1990, 1991, 1998), 66 new Team("Williams", 1980, 1981, 1986, 1987, 1992, 1993, 1994, 1996, 1997), 67 new Team("Benetton", 1995), 68 new Team("Renault", 2005, 2006 ) 69 }; 70 } 71 return teams; 72 } 73 }
一个简单的查询:
//查询所有来自巴西的世界冠军 public static void LinqQueryBrazil() { Console.WriteLine(); var query = from r in Formula1.GetChampions() where r.Country == "Brazil" orderby r.Wins descending select r; foreach (Racer r in query) Console.WriteLine($"{r:A}"); }
扩展方法查询:

1 static class StaticThis 2 { 3 public static IEnumerable<T> Where<T>(this IEnumerable<T> source, Func<T, bool> predicate) 4 { 5 foreach (T item in source) 6 { 7 if (predicate(item)) 8 yield return item; 9 } 10 } 11 }
1 //使用Enumerable类中的拓展方法Where()、OrderbyDescending()和Select(),这些方法都返回 IEnumerable<T>,所以可以使用前面的结果依次调用这些方法 2 static void ExtensionMethons() 3 { 4 Console.WriteLine(); 5 var champions = new List<Racer>(Formula1.GetChampions()); 6 IEnumerable<Racer> brazilChampions = 7 champions.Where(r => r.Country == "Brazil"). 8 OrderByDescending(r => r.Wins). 9 Select(r => r); 10 11 foreach (Racer r in brazilChampions) 12 { 13 Console.WriteLine($"{r:A}"); 14 } 15 }
推迟查询效果测试(yield return)
1 //推迟查询的执行(需要时查询 yield return) 2 //当返回的是一个List或者Array这种就不行了,即用了 ToXXX() 方法的,因为这样返回的就是一个集合 3 static void DelayQuery() 4 { 5 Console.WriteLine(); 6 var names = new List<string> { "Nino", "Alberto", "Juan", "Mike", "Phil" }; 7 var namesWithJ = from n in names 8 where n.StartsWith("J") 9 orderby n 10 select n; 11 Console.WriteLine("First iteration"); 12 foreach (string item in namesWithJ) 13 { 14 Console.WriteLine(item); 15 } 16 Console.WriteLine(); 17 18 names.Add("John"); 19 names.Add("Jim"); 20 names.Add("Jack"); 21 names.Add("Denny"); 22 23 Console.WriteLine("Second iteration"); 24 foreach (string item in namesWithJ) 25 { 26 Console.WriteLine(item); 27 } 28 }
因为每次查询是在遍历的时候才进行,所以可以保持数据更新后查询结果也一起更新。
二、标准的查询操作符
以下是各类操作符:
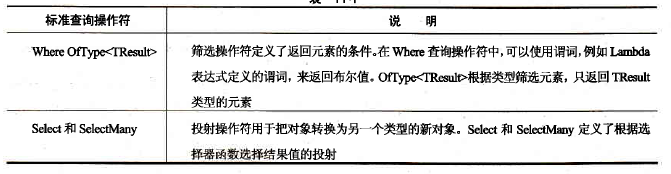
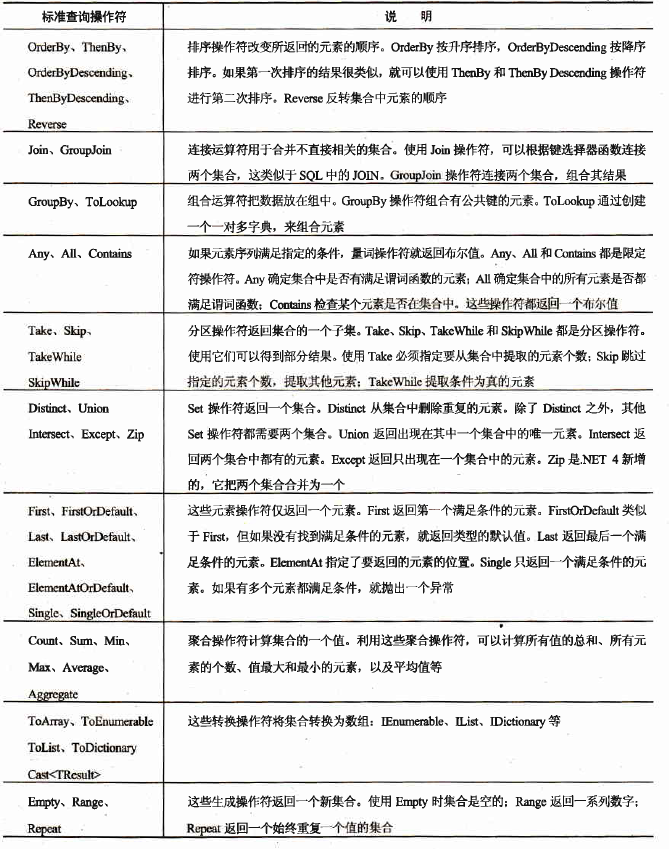
下面让我们用一下例子来实操一下
1、筛选
找出赢得至少15场比赛的巴西和奥地利选手。
//找出至少赢得15场的巴西和奥地利选手 static void ChooseAtLeast15BA() { Console.WriteLine(); var racres = from r in Formula1.GetChampions() where r.Wins > 15 && (r.Country == "Brazil" || r.Country == "Austria") select r; foreach (var item in racres) { Console.WriteLine($"{item:A}"); } }
并不是所有的查询都可以用 LINQ查询完成。也不是所有的扩展方法都映射到LINQ查询子句上。高级查询需要使用扩展方法。为了更好地理解带扩展方法的复杂查询,最好看看简单的查询是如何映射的,使用扩展方法Where() 和select() ,会生成与前面LINQ查询非常类似的结果:
static void ChooseAtLeast15BA2() { Console.WriteLine(); var racres = Formula1.GetChampions().Where(r => r.Wins > 15 && (r.Country == "Brazil" || r.Country == "Austria")). Select(r => r);//谓词条件是r,也就是没有条件只传入一个参数 foreach (var item in racres) { Console.WriteLine($"{item:A}"); } }
2、用索引筛选
不能使用LINQ查询的一个例子是 Where() 方法的重载。在 Where() 方法的重载中,可以传递第二个参数——索引。索引是筛选器返回的每个结果的计数器。可以在表达式中使用这个索引,执行基于索引的计算。下面的代码由Where() 扩展方法调用,它使用索引返回姓氏以A开头、索引为偶数的赛车手:
//索引筛选 static void ChooseByIndex() { var racers = Formula1.GetChampions(). Where((r, index) => r.LastName.StartsWith("A") && index % 2 != 0); foreach (var item in racers) { Console.WriteLine($"{item:A}"); } }
3、类型筛选
用到了 OfType() 扩展方法。
//类型筛选 static void ChooseByType() { Console.WriteLine(); object[] data = { "one", 2, 3, "der", 6, "fa" }; var query = data.OfType<string>(); foreach(var item in query) { Console.WriteLine(item); } }
4、复合的 from 子句
当需要筛选的对象的成员本身是一个系列,就可以用到复合的 from 子句。Racer 中的Cars是一个字符串数组。筛选所有驾驶法拉利的冠军。
//复合from筛选 static void ChoosesWithComposite() { Console.WriteLine(); var ferrariDrivers = from r in Formula1.GetChampions() from c in r.Cars where c == "Ferrari" orderby r.LastName select r.FirstName + " " + r.LastName; foreach (var item in ferrariDrivers) { Console.WriteLine(item); } }
C#编译器把复合的from 子句和 LINQ 查询转换为SelectMany() 扩展方法。SelectMany() 方法可用于迭代序列的序列。其中 SelectMany() 方法的重载版本如下所示:
public static IEnumerable<TResult> SelectMany<TSource, TCollection, TResult>( this IEnumerable<TSource> source, Func<TSource, IEnumerable<TCollection>> collectionSelector, Func<TSource, TCollection, TResult> resultSelector);
第一个是隐式参数,它从 GetChampions() 方法中接受Racer 对象序列。第二个参数是 collectionSelector 委托,其中定义了内部序列。在 Lambda 表达式 r=>r.Cars 中,应返回赛车集合。第三个参数是一个委托,现在为每辆赛车调用该委托,接受 Racer 和 Car 对象。Lambda 表达式创建了一个匿名类型,它有 Racer 和 Car 属性。这个 SelectMany() 方法的结果是摊平了赛车手和赛车的层次结构,为每辆车返回匿名类型的一个新对象集合。
这个新集合传递给 Where() 方法,筛选出驾驶法拉利的赛手。最后,调用 OrderBy() 和Select() 方法:
static void ChooseWithComposite2() { Console.WriteLine(); var ferrariDrivers = Formula1.GetChampions(). SelectMany(r => r.Cars, (r, c) => new { RRacer = r, CCar = c }). Where(r => r.CCar == "Ferrari"). OrderBy(r => r.RRacer.LastName). Select(r => r.RRacer.FirstName + " " + r.RRacer.LastName); foreach (var item in ferrariDrivers) { Console.WriteLine(item); } }
解析一下就是下面的方法:
public static IEnumerable<TResult> SelectMany<Racer, string, TResult>( this IEnumerable<Racer> source, Func<Racer, IEnumerable<string>> collectionSelector, Func<Racer, string, TResult> resultSelector);
5、排序
orderby子句解析为 OrderBy() 方法,orderby descending 子句解析为 OrderByDescending() 方法。
OrderBy() 和 OrderByDescending() 方法返回 IOrderEnumerable<TSource>。这个接口派生自 IEnumerable<TSource> 接口,但包含一个额外的方法 CreateOrderedEnumerable<TSource>()。这个方法用于进一步给序列排序。如果根据关键字选择器来排序,其中有两项相同,就可以使用 ThenBy() 和ThenByDescending() 方法继续继续排序。这两个方法需要 IOrderEnumerable<TSource> 接口才能工作,但也返回这个接口。所以就可以添加任意多个 ThenBy() 和 ThenByDescending() 方法,对集合排序。
排序时用 , (逗号)隔开不同关键字即可,这里赛车手按国家排,再按姓氏,最后按名字:
//排序 static void Sort1() { Console.WriteLine(); var racers = (from r in Formula1.GetChampions() orderby r.Country, r.LastName, r.FirstName select r).Take(15); foreach (var item in racers) { Console.WriteLine($"{item:C} {item:F} {item:L} "); } }
使用OrderBy() 和 ThenBy() 方法一样操作:
static void Sort2() { Console.WriteLine(); var racers = Formula1.GetChampions(). OrderBy(r=>r.Country). ThenBy(r=>r.LastName).ThenBy(r=>r.FirstName). Take(15); foreach (var item in racers) { Console.WriteLine($"{item:C} {item:F} {item:L} "); } }
6、分组
要根据一个关键字对查询结果进行分组,可以使用 group 子句。现在一级方程式冠军应按照国家分组,并列出一个国家的冠军数。子句 group r by r.Country into g 根据 Country 属性组合所有的赛车手,并定义一个新的标识符 g ,它以后用于访问分组的结果信息。group子句的结果根据应用到分组的结果上的扩展方法 Count() 来排序,如果冠军数相同,就根据关键字来排序,该关键字是国家,因为这是分组所使用的关键字。
where子句根据至少有两项的分组来筛选结果,select子句创建一个带 Country 和 Count 属性的匿名类型。
//分组 static void Grouping1() { Console.WriteLine(); var countries = from r in Formula1.GetChampions() group r by r.Country into g orderby g.Count() descending, g.Key where g.Count() >= 2 select new { Country = g.Key, Count = g.Count() }; foreach (var item in countries) { Console.WriteLine($"{item.Country} {item.Count}"); } }
使用扩展方法执行相同的操作,groupby 子句解析为 GroupBy() 方法。在 GroupBy() 方法的声明中,注意它返回实现了 IGrouping 接口的枚举对象。IGrouping 接口定义了 Key 属性,所以在定义了对这个方法的调用后,可以访问分组的关键字:
static void Grouping2() { Console.WriteLine(); var countries = Formula1.GetChampions(). GroupBy(r => r.Country). OrderByDescending(g => g.Count()). ThenBy(g => g.Key). Where(g => g.Count() >= 2). Select(g => new { Country = g.Key, Count = g.Count() }); foreach (var item in countries) { Console.WriteLine($"{item.Country} {item.Count}"); } }
7、对嵌套对象的分组
如果分组的对象包含嵌套的序列,就可以改变 select 子句创建的匿名类型。在下面的例子中,所返回的国家不仅包含国家名.和赛车手数量这两个属性,还包含赛车手名序列。这个序列用一个赋予 Racerss 属性的 from/in 内部子句指定,内部的from 子句使用分组标识符 g 获得该分组中的所有赛车手,用姓氏对它们排序,再根据姓名创建一个新的字符串:
//对嵌套的对象分组 static void Grouping3() { Console.WriteLine(); var countries = from r in Formula1.GetChampions() group r by r.Country into g orderby g.Count() descending, g.Key where g.Count() >= 2 select new { Country = g.Key, Count = g.Count(), Racers = from r1 in g orderby r1.LastName select r1.FirstName + " " + r1.LastName }; foreach (var item in countries) { Console.WriteLine($"{item.Country} {item.Count}"); foreach (var name in item.Racers) { Console.Write($"{name}; "); } Console.WriteLine(); } }
8、连接
join 子句可以根据特定的条件合并两个数据源,但之前要获得两个连接的列表。
在一级方程式比赛中,有赛车手冠军和车队冠军。赛车手从 GetChampions() 方法中返回,车队从 GetConstructorChampions() 方法中返回。现在要获得一个年份列表,列出每年的赛手冠军和车队冠军。
先定义两个查询,用于查询赛车手和车队:

1 static void JoinRacer() 2 { 3 var racers = from r in Formula1.GetChampions() 4 from y in r.Years 5 where y > 2003 6 select new 7 { 8 Year = y, 9 Name = r.FirstName + " " + r.LastName 10 }; 11 var teams = from t in Formula1.GetContructorChampions() 12 from y in t.Years 13 where y > 2003 14 select new 15 { 16 Year = y, 17 Name = t.Name 18 }; 19 //有了这两个查询,再通过子句 join t in teams on r.Year equals t.Year, 20 //根据年份进行连接即可 21 var racerAndTeams = from r in racers 22 join t in teams on r.Year equals t.Year 23 select new 24 { 25 Year = r.Year, 26 Racer = r.Name, 27 Team = t.Name 28 }; 29 Console.WriteLine($"Year Racer Team"); 30 foreach (var item in racerAndTeams) 31 { 32 Console.WriteLine($"{item.Year} {item.Racer} {item.Team}"); 33 } 34 }
也可以都写一起:

1 static void JoinRacer2() 2 { 3 Console.WriteLine(); 4 int year = 2003; 5 var racersAndTeams = from r in 6 from r1 in Formula1.GetChampions() 7 from yr in r1.Years 8 where yr > year 9 select new 10 { 11 Year = yr, 12 Name = r1.FirstName + " " + r1.LastName 13 } 14 join t in 15 from t1 in 16 Formula1.GetContructorChampions() 17 from yt in t1.Years 18 where yt > year 19 select new 20 { 21 Year = yt, 22 Name = t1.Name 23 } 24 on r.Year equals t.Year 25 select new 26 { 27 Year = r.Year, 28 Racer = r.Name, 29 Team = t.Name 30 }; 31 Console.WriteLine($"Year Racer Team"); 32 foreach (var item in racersAndTeams) 33 { 34 Console.WriteLine($"{item.Year} {item.Racer} {item.Team}"); 35 } 36 }
9、集合操作
扩展方法 Distinct() 、Union()、Intersect() 和 Except() 都是集合操作。
创建一个驾驶法拉利的一级方程式冠军序列和驾驶迈凯伦的一级方程式序列,然后确定是否有驾驶法拉利和迈凯伦的冠军。
这里就可以直接全部都用LINQ操作,较为繁杂,就不是多说
我们直接用Intersect() 方法
//集合 static void SetOperations() { Func<string, IEnumerable<Racer>> racersByCar = car => from r in Formula1.GetChampions() from c in r.Cars where c == car orderby r.LastName select r; Console.WriteLine("World champion with Ferrari and McLaren"); foreach (var racer in racersByCar("Ferrari").Intersect(racersByCar("McLaren"))) { Console.WriteLine(racer); } }
集合操作通过调用实体类的 GetHash() 和 Equals() 方法来比较对象。对于自定义比较,还可以传递一个实现了IEqualityComparer<T>接口的对象。在这里的示例中,GetChampions() 方法总是返回相同的对象,因此默认的比较操作是有效的。
10、合并
Zip()方法是 .NET4 新增的,允许一个谓词函数把两个相关的序列合并为一个。
需要用相同的方法筛选(排序)出两个相关的序列。因为在合并中,每一项都对应合并,如果两个序列的项数不同,Zip() 方法就在到达较小集合的末尾停止。项A有属性 a,项B有属性 b、c,合并后项C 就有属性
a、b、c了。

1 static void ZipOperation() 2 { 3 var racerNames = from r in Formula1.GetChampions() 4 where r.Country == "Italy" 5 orderby r.Wins descending 6 select new 7 { 8 Name = r.FirstName + " " + r.LastName 9 }; 10 11 var racerNamesAndStarts = from r in Formula1.GetChampions() 12 where r.Country == "Italy" 13 orderby r.Wins descending 14 select new 15 { 16 LastName = r.LastName, 17 Starts = r.Starts 18 }; 19 20 21 var racers = racerNames.Zip(racerNamesAndStarts, (first, second) => first.Name + ", starts: " + second.Starts); 22 foreach (var r in racers) 23 { 24 Console.WriteLine(r); 25 } 26 27 }
11、分区
扩展方法 Take() 和 Skip() 等的分区操作可用于分页,例如显示 5×5个赛车手:

1 static void Partitioning() 2 { 3 int pageSize = 5; 4 5 int numberPages = (int)Math.Ceiling(Formula1.GetChampions().Count() / 6 (double)pageSize); 7 8 for (int page = 0; page < numberPages; page++) 9 { 10 Console.WriteLine("Page {0}", page); 11 12 var racers = 13 (from r in Formula1.GetChampions() 14 orderby r.LastName 15 select r.FirstName + " " + r.LastName). 16 Skip(page * pageSize).Take(pageSize); 17 18 foreach (var name in racers) 19 { 20 Console.WriteLine(name); 21 } 22 Console.WriteLine(); 23 } 24 25 }
就是在后面使用 Skip()方法和Take()方法
分页在 Windows 或 Web 应用程序上非常有用,可以只给用户显示一部分数据
这个分页的机制是延迟查询的,可以根据需求修改。
12、聚合操作符
聚合操作符(如 Count()、Sum()、Min()、Max()、Average() 和 Aggregate())返回的是一个值。
Count() 方法返回集合中的项数

1 static void Aggregate() 2 { 3 var query = from r in Formula1.GetChampions() 4 where r.Years.Count() > 3 5 orderby r.Years.Count() descending 6 select new 7 { 8 Name = r.FirstName + " " + r.LastName, 9 TimesChampion = r.Years.Count() 10 }; 11 12 foreach (var r in query) 13 { 14 Console.WriteLine("{0} {1}", r.Name, r.TimesChampion); 15 } 16 }
Sum() 方法汇总序列中的所有数字,返回这些数字的和。

1 static void Aggregate2() 2 { 3 var countries = (from c in 4 from r in Formula1.GetChampions() 5 group r by r.Country into c 6 select new 7 { 8 Country = c.Key, 9 Wins = (from r1 in c 10 select r1.Wins).Sum() 11 } 12 orderby c.Wins descending, c.Country 13 select c).Take(5); 14 15 foreach (var country in countries) 16 { 17 Console.WriteLine("{0} {1}", country.Country, country.Wins); 18 } 19 20 }
Min() 最小值,Max() 最大值,Average() 平均值
Aggregate() 方法,可以传递一个 Lambda 表达式,该表式对所有的值进行聚合。
13、转换
前面也提到过,查询是推迟到访问数据项时执行,在迭代中使用查询时,查询会执行。而使用转换操作符会立即执行查询,把查询结果放在数组、列表或字典中。
如果需要在非类型的集合上(如 ArrayList)使用LINQ查询,就可以使用 Cast() 方法。
下个例子中,基于Object类型的ArrayList集合用Racer对象填充。为了定义强类型化的查询,可以使用Cast() 方法。

1 static void Untyped() 2 { 3 var list = new System.Collections.ArrayList(Formula1.GetChampions() as System.Collections.ICollection); 4 5 var query = from r in list.Cast<Racer>() 6 where r.Country == "USA" 7 orderby r.Wins descending 8 select r; 9 foreach (var racer in query) 10 { 11 Console.WriteLine("{0:A}", racer); 12 } 13 14 }
14、生成操作符
生成操作符Range()、Empty()和Repear()不是扩展方法,而不是返回序列的正常静态方法。在 LINQ to Objects 中,这些方法可适用于 Enumerable 类。
var values = Enumerable.Range(1, 20); foreach (var item in values) { Console.Write($"{item} "); }
注:Range()方法不返回填充了所定义值的集合,这个方法与其他方法一样,也推迟执行查询,并返回一个RangeEnumerable,其中只有一条yield return语句,来递增值。
可以把该结果与其他扩展方法合并起来,获得另一个结果,例如,使用Select()扩展方法:
var values = Enumerable.Range(1,20).Select(n=>n*3);
Empty()方法返回一个不返回值的迭代器,它可以用于需要一个集合的参数,其中可以给参数传递空集合。
Repeat()方案返回一个迭代器,该迭代器把同一个值重复特定的次数。
三、并行LINQ
.NET4 在System.Linq 名称空间中包含一个新类 ParalleEnumerable,可以分解查询的工作使其分布在多线程上,尽管 Enumerable 类给 IEnumerable<T> 接口定义了扩展方法,但 ParallelEnumerable 类的duoshu-扩展方法是 ParallelQuery<TSource> 类的扩展。一个重要的例外是 AsParallel() 方法,它扩展了 IEnumerable<TSOource> 接口,返回 ParallelQuery<TSource> 类,所以正常的集合类可以以平行方式查询。
1、并行查询
下面准备一个大型集合,便于说明并行LINQ。对于可以放在CPU的缓存中的小集合,并行LINQ看不出效果。

1 static void CurrentLinq() 2 { 3 //大数组 4 const int arraySize = 1000000000; 5 var data = new int[arraySize]; 6 var r = new Random(); 7 for (int i = 0; i < arraySize; i++) 8 { 9 data[i] = r.Next(40); 10 } 11 //筛选操作 12 var sum = (from x in data.AsParallel() 13 where x < 20 14 select x).Sum(); 15 //因为AsParallel返回类型是 ParallelQuery<TSource>, 16 //所以后面的Where等方法都是ParallelEnumerable.Where()方法 17 //var sum = data.AsParallel().Where(x => x < 20).Select(x => x).Sum(); 18 }
与Enumerable类的实现代码相反,对于ParalleEnumerable类,查询时分区的,以便多个线程可以同时处理该查询。数组可以分成多个部分,其中每个部分由不同的线程处理,以筛选其余项。完成分区的工作后,就需要合并,获得所有部分的总和。
运行就能发现系统的所有的CPU都在忙碌。如果删除AsParallel() 方法,就不可能使用多个CPU。当然,系统没有多个CPU也是看不见并行版本带来的改进。
2、分区器
AsParallel() 方法不仅扩展了IEnumerable<T> 接口,还扩展了 Partitioner 类。通过它,可以影响要创建的分区。
Partitioner 类用 System.Collection.Concurrent 名称空间定义,并且有不同的变体。Creat() 方法接受实现了 IList<T>类的数组或对象。根据这一点,以及类型的参数 loadBanlance 和该方法的一些重载版本,会返回一个不同的 Partitioner 类型。对于数组,.NET4 包含派生自抽象基类 OrderablePartitioner<TSource> 的 DynamicPartitionerForArray<TSource> 类和 StaticPartitionerForArray<TSource> 类。
手动创建一个分区其,而不是使用默认的分区器:
var sum = (from x in Partitioner.Create(data,true).AsParallel() where x < 20 select x).Sum();

3、取消
.NET 4 提供了一种标准方式,来取消长时间运行的任务,这也适用于并行LINQ
在查询后添加 WithCancellation() 方法,并传递一个 CancellationToken令牌作为参数。CancellationToken 令牌从CancellationTokenSource 类中创建。该查询在单线程中运行,在该线程中,捕获一个 OperationCanceledException 类型的异常。如果取消了查询,就出发这个异常。在主线程中,调用 CancellationTokenSource 类的 Cancel() 方法可以取消任务。

1 //取消 2 var cts = new CancellationTokenSource(); 3 new Thread 4 ( 5 () => 6 { 7 try 8 { 9 var sum = (from x in data.AsParallel().WithCancellation(cts.Token) 10 where x < 80 11 select x).Sum(); 12 Console.WriteLine($"query finished, sum: {sum}"); 13 } 14 catch (OperationCanceledException ex) 15 { 16 Console.WriteLine(ex.Message); 17 } 18 } 19 ).Start(); 20 Console.WriteLine("query started"); 21 Console.WriteLine("cancel? "); 22 int input = Console.Read(); 23 if (input == 'Y' || input == 'y') 24 { 25 //cancel 26 cts.Cancel(); 27 }
CancellationToken令牌以后再详细了解
四、表达式树
在LINQ to Objects中,扩展方法需要将一个委托类型作为参数,这样就可以将lambda表达式赋予参数。lambda表达式也可以赋予Expression<T>类型的参数。C#编译器根据类型给lambda表达式定义不同的行为。如果类型是Expression<T>,编辑器就从lambda表达式中创建一个表达式树,并存储在程序集中。这样,就可以在运行期间分析表达式树,并进行优化,以便于查询数据源。
(就不是很能理解,经典每个字都认识,组一起就搞不懂它的逻辑关系了,以后回来补充)
续:
表达式树就是一个二叉树结构,将一堆数据两两组合,最后形成一个完整的SQL语句,一般是一个Lambda,但是只能有一行。
五、LINQ 提供程序
LINQ还有专门用于技术的方法,例如XML、SQL等,这里就不多说,没用上所以印象也不会深。
六、小结
LINQ查询与查询所基于的语言结构,如扩展方法和Lambda 表达式,以及各种查询操作符。
并行LINQ可以轻松地并行化运行时间较长的查询
表达式树很重要,他能在运行期间构建对数据源的查询,因为表达式树存储在程序集中。但理解不是很透彻,以后还会再见到的。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号