mysql_基本使用(by official doc)/大小写规则/状态和数据查询
文章目录
获取 mysql 外部命令帮助
mysql --help
linux 中,输入 mysql --help|less会更易读一些
Usage: mysql [OPTIONS] [database]
-?, --help Display this help and exit.
-I, --help Synonym for -?
连接到数据库
- 连接到数据库 root 用户
mysql -h hostName -u root -p- 该命令要求输入 root 密码
- 如果 hostName 是本地主机,可以省略该选项和参数
- 如果是远程连接,主要远程主机的安全组和相关管理软件的端口的放行
基本使用逻辑
/* 登陆数据库上的某个用户后,可以执行类似于以下的命令 */
SHOW databases;
USE test_db;
SHOW tables;
SHOW COLUMNS FROM products;
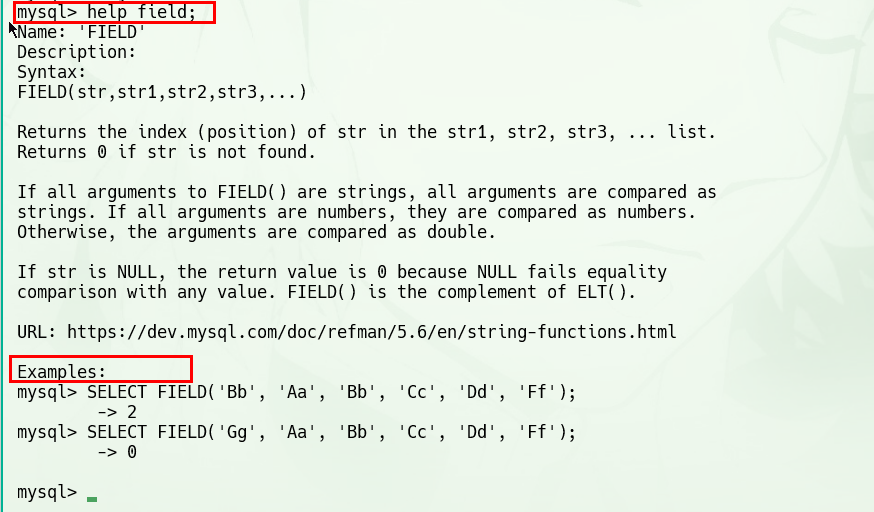
SELECT
prod_name
From
products;
获取 mysql 内部文档帮助
登录到某个用户之后,可以使用内部的帮助文档
help
- 不带
;即可回车生效的指令:- 以下是几条常用的指令
![img]()
例如
- 以下是几条常用的指令
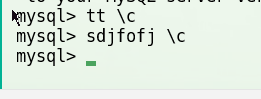
废弃当前输入
\c作废当前行的输入- 遇到没有结尾的字符串,需要补全另一半引号,然后
\c废弃;
mysql> sdjfofjds\c
mysql>
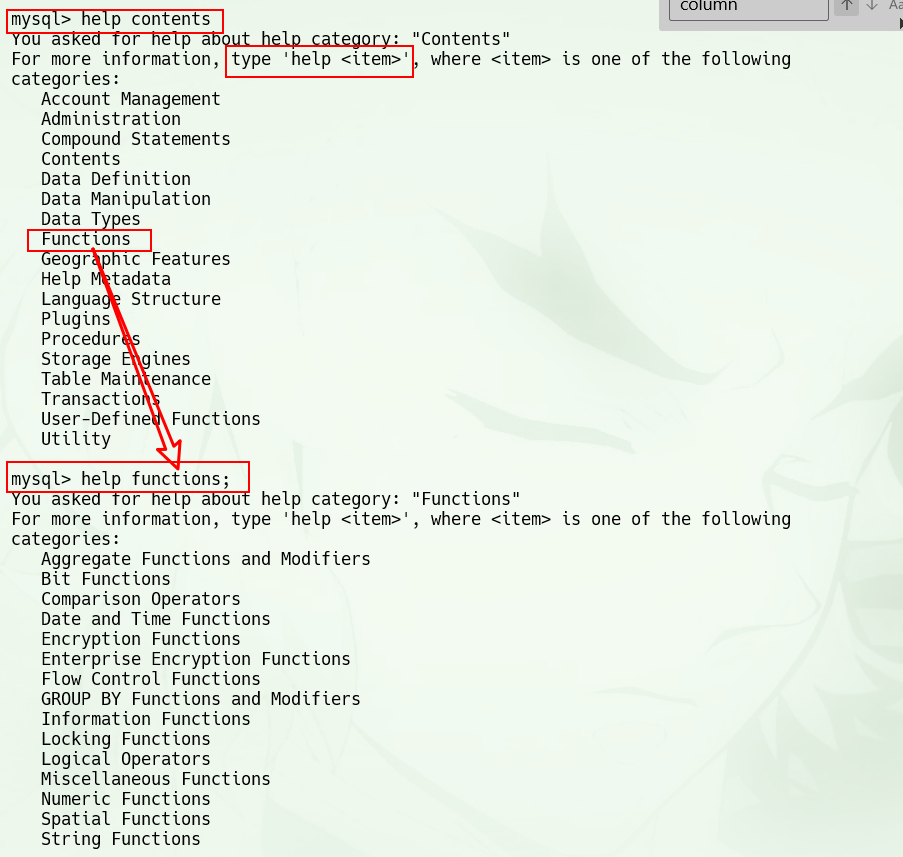
获取服务端帮助help contents
- 下表列出了服务端帮助的所有门类,
contents本身就是一个门类;- 并且,这个门类是用来列出其他门类的
mysql> help contents
You asked for help about help category: "Contents"
For more information, type 'help <item>', where <item> is one of the following
categories:
Account Management
Administration
Compound Statements
Contents
Data Definition
Data Manipulation
Data Types
Functions
Geographic Features
Help Metadata
Language Structure
Plugins
Procedures
Storage Engines
Table Maintenance
Transactions
User-Defined Functions
Utility
mysql>
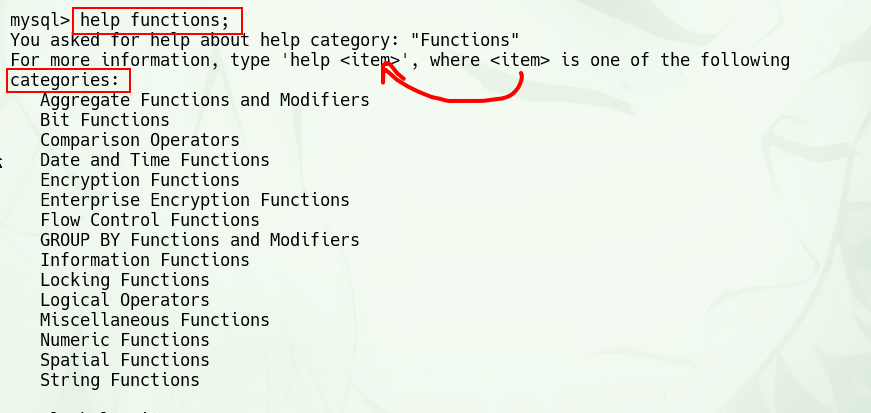
help 可以查找内些内容?
获取所有(大)门类
help contents;
获取门类下的所有话题topics
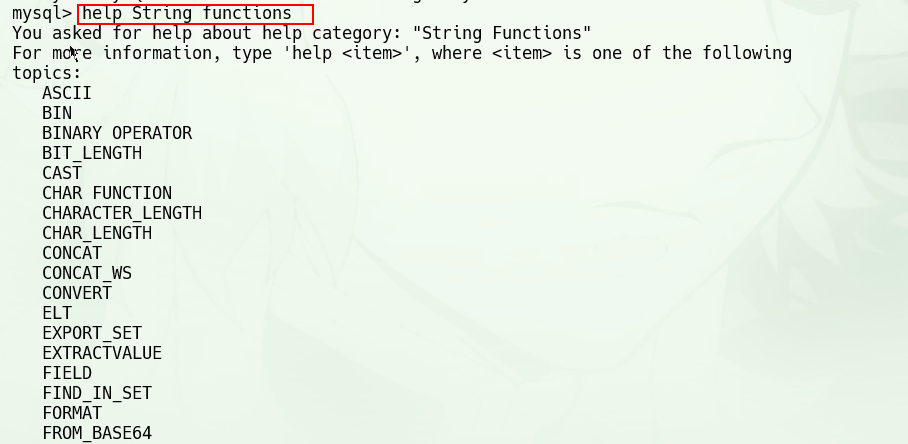
取子门类中的具体话题(topic)帮助
实例
总的查询流程(小结)(针对 mysql 的基本信息和标准规范)
入门阶段
获取所有门类(子门类)
-
mysql> help contents;
列出所有门类(categories)
(对于复杂话题,可能还有子门类) -
mysql> help data types;
获取门类下的话题topic(例如我这里查询 datatime 这一数据类型) -
mysql> help datetime;
查看具体话题的介绍
熟练阶段
可以直接查阅第三层的具体词条
通用帮助
使用搜索引擎搜索文档
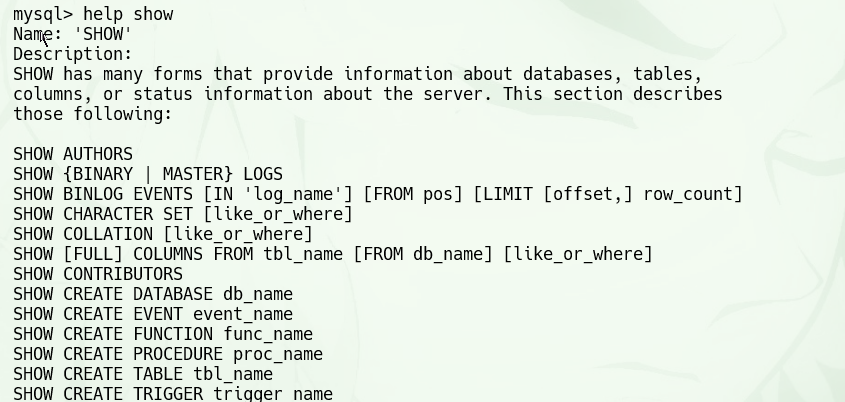
help show
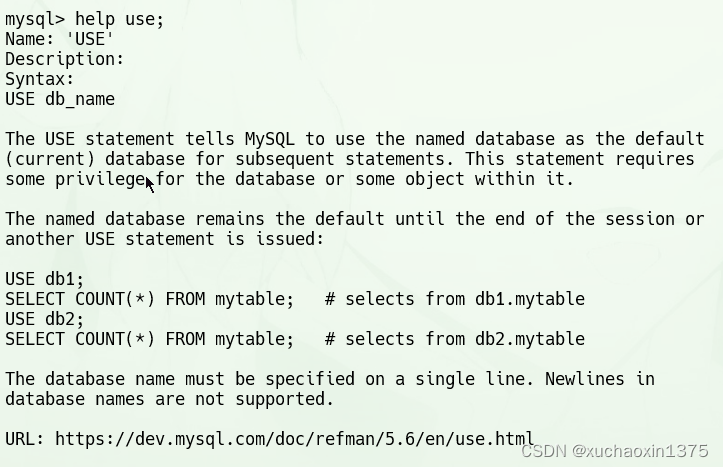
help use
结束 SQL 语句
-
如果你使用的是 mysql 命令行,必须加上分号来结束 SQL 语句。
-
多条 SQL 语句必须以分号(;)分隔。
-
MySQL 如同多数 DBMS 一样,不需要在单条 SQL 语句后加分号。
- 但特定的 DBMS 可能必须在单条 SQL 语句后加上分号。
- 当然,如果愿意可以总是加上分号。
- 事实上,即使不一定需要,但加上分号肯定没有坏处。
SQL 语句和大小写
- 请注意,SQL 语句不区分大小写,因此 SELECT 与 select 是相同的。
- 许多 SQL 开发人员喜欢对所有 SQL 关键字使用大写,而对所有列和表名使用小写,这样做使代码更易于阅读和调试。
表达式
字符串比较
- 字符串比较默认对大小写不敏感
- 可以使用binary等控制大小写敏感
root 用户和 root 可见的常见数据库
- Use the SHOW statement to find out what databases currently exist on the server:
➜ ~ mysql -u root -p
Enter password:
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 57
Server version: 8.0.24 Source distribution
Copyright (c) 2000, 2021, Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| ela |
| information_schema |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| sys |
+--------------------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
- 上方的 root 用户可以查询中查到 5 个数据库
- 其中名为
mysql的数据库记录了:Themysqldatabase describes- user access privileges.
mysql 这个数据库
mysql> use mysql;
Database changed
mysql> show tables
-> ;
+------------------------------------------------------+
| Tables_in_mysql |
+------------------------------------------------------+
| columns_priv |
| component |
| db |
| default_roles |
| engine_cost |
| func |
| general_log |
| global_grants |
| gtid_executed |
| help_category |
| help_keyword |
| help_relation |
| help_topic |
| innodb_index_stats |
| innodb_table_stats |
| password_history |
| plugin |
| procs_priv |
| proxies_priv |
| replication_asynchronous_connection_failover |
| replication_asynchronous_connection_failover_managed |
| role_edges |
| server_cost |
| servers |
| slave_master_info |
| slave_relay_log_info |
| slave_worker_info |
| slow_log |
| tables_priv |
| time_zone |
| time_zone_leap_second |
| time_zone_name |
| time_zone_transition |
| time_zone_transition_type |
| user |
+------------------------------------------------------+
35 rows in set (0.00 sec)
- USE, like QUIT, does not require a semicolon. (You can terminate such statements with a semicolon if you like; it does no harm.) The USE statement is special in another way, too:
- it must be given on a single line.
数据库授权
- 授权分为两方面:
- 数据库用户授权
- 数据库可见主机授权
- 以上两者缺一不可
root 用户将 menagerie 数据库授权给用户 ela 使用:
mysql> grant all on menagerie.* to 'ela'@'localhost';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
- 注意,后面的 mysql 用户名和该用户的登录主机名都各自用引号引起来,是单独的字符串
root用户检查可被登录的已有mysql用户
- 让root用户下选中名为
mysql的特殊数据库 mysql这个数据库的user表,可以查询权限- 从下表可见,root用户被设置为任何主机都有权限访问(在有密码的情况下)
- 而ela用户也是如此
- 同时又localhost和
%(代表任意值),则又%决定
- 同时又localhost和
root权限下可见的mysql数据库的user表
- 部分字段一览表
mysql> describe user;
+--------------------------+-----------------------------------+------+-----+-----------------------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+--------------------------+-----------------------------------+------+-----+-----------------------+-------+
| Host | char(255) | NO | PRI | | |
| User | char(32) | NO | PRI | | |
| Select_priv | enum('N','Y') | NO | | N | |
| Insert_priv | enum('N','Y') | NO | | N | |
| Update_priv | enum('N','Y') | NO | | N | |
| Delete_priv | enum('N','Y') | NO | | N | |
| Create_priv | enum('N','Y') | NO | | N | |
| Drop_priv | enum('N','Y') | NO | | N | |
| Reload_priv | enum('N','Y') | NO | | N | |
| Shutdown_priv | enum('N','Y') | NO | | N | |
| Process_priv | enum('N','Y') | NO | | N | |
| File_priv | enum('N','Y') | NO | | N | |
| Grant_priv | enum('N','Y') | NO | | N | |
| References_priv | enum('N','Y') | NO | | N | |
| Index_priv | enum('N','Y') | NO | | N | |
| Alter_priv | enum('N','Y') | NO | | N | |
| Show_db_priv | enum('N','Y') | NO | | N | |
mysql> select host,user from user ;
+-----------+------------------+
| host | user |
+-----------+------------------+
| % | ela |
| % | root |
| localhost | ela |
| localhost | mysql.infoschema |
| localhost | mysql.session |
| localhost | mysql.sys |
+-----------+------------------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
被授权用户检查自己的可使用数据库
- 在被授权的主机(本例是 localhost)上使用 ela 用户查看
- 前一次查询时授权前,后一次查询是授权后(后者多了可用数据库
menagerie)- məˈnædʒəri
mysql> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| ela |
| information_schema |
+--------------------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| ela |
| information_schema |
| menagerie |
+--------------------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
在被授权主机意外的主机,即使是同一个用户,仍然无法查看/使用相关数据库
mysql> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| ela |
| information_schema |
+--------------------+
2 rows in set (0.06 sec)
数据库的选中和查询
登录后选中数据库
mysql> select database();
+------------+
| database() |
+------------+
| NULL |
+------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> use mysql;
Database changed
mysql> select database();
+------------+
| database() |
+------------+
| mysql |
+------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
登录时立刻选中数据库
➜ ~ mysql -u ela -p menagerie
Enter password:
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
任意时刻查询当前使用的数据库
You can see at any time which database is currently selected using
SELECT DATABASE().
此处的select语句用于调用函数database()并显示返回结果;
select作为数据库查询指令
也作为函数调用指令.
mysql> select database();
+------------+
| database() |
+------------+
| menagerie |
+------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql>
为数据库添加/创建表
CREATE TABLE pet (name VARCHAR(20), owner VARCHAR(20), species VARCHAR(20), sex CHAR(1), birth DATE, death DATE);
mysql> show tables;
Empty set (0.00 sec)
mysql> CREATE TABLE pet (name VARCHAR(20), owner VARCHAR(20), species VARCHAR(20), sex CHAR(1), birth DATE, death DATE);
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.05 sec)
mysql> show tables;
+---------------------+
| Tables_in_menagerie |
+---------------------+
| pet |
+---------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql>
检查表的创建/字段情况
mysql> describe pet;
+---------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+---------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| name | varchar(20) | YES | | NULL | |
| owner | varchar(20) | YES | | NULL | |
| species | varchar(20) | YES | | NULL | |
| sex | char(1) | YES | | NULL | |
| birth | date | YES | | NULL | |
| death | date | YES | | NULL | |
+---------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
为表导入数据
检查是否开启 local infile
mysql> show variables like 'local_infile';
+---------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+---------------+-------+
| local_infile | OFF |
+---------------+-------+
如果没有,则需要 root 用户权限开启该功能
mysql> set global local_infile=on;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
正式导入只当数据库的指定表中
- 被导入数据 pets.txt
- You could create a text file pet.txt containing one record per line, with values separated by tabs, and given in the order in which the columns were listed in the CREATE TABLE statement.
- For missing values (such as unknown sexes or death dates for animals that are still living), you can use NULL values.
- To represent these in your text file, use \N (backslash, capital-N). For example, the record for
- Whistler the bird would look like this (where the whitespace between values is a single tab character):
- Whistler Gwen bird \N 1997-12-09 \N
Fluffy Harold cat f 1993-02-04 \N
Claws Gwen cat m 1994-03-17 \N
Buffy Harold dog f 1989-05-13 \N
Fang Benny dog m 1990-08-27 \N
Bowser Diane dog m 1979-08-31 1995-07-29
Chirpy Gwen bird f 1998-09-11 \N
Whistler Gwen bird \N 1997-12-09 \N
Slim Benny snake m 1996-04-29 \N
mysql> load data local infile './pets.txt' into table pet;
Query OK, 8 rows affected, 10 warnings (0.01 sec)
Records: 8 Deleted: 0 Skipped: 0 Warnings: 10
查询某条记录的所有字段
mysql> SELECT * FROM pet WHERE name = 'Bowser';
+--------+-------+---------+------+------------+------------+
| name | owner | species | sex | birth | death |
+--------+-------+---------+------+------------+------------+
| Bowser | Diane | dog | m | 1989-08-31 | 1995-07-29 |
+--------+-------+---------+------+------------+------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
条件:时间区间
mysql> select * from pet where birth >='1991-01-01';
+----------+--------+---------+------+------------+-------+
| name | owner | species | sex | birth | death |
+----------+--------+---------+------+------------+-------+
| Puffball | Diane | hamster | f | 1999-03-30 | NULL |
| Fluffy | Harold | cat | f | 1993-02-04 | NULL |
| Claws | Gwen | cat | m | 1994-03-17 | NULL |
| Chirpy | Gwen | bird | f | 1998-09-11 | NULL |
| Slim | Benny | snake | m | 1996-04-29 | NULL |
+----------+--------+---------+------+------------+-------+
复合条件
- and
mysql> select * from pet where birth >='1991-01-01'and species='cat' ;
+--------+--------+---------+------+------------+-------+
| name | owner | species | sex | birth | death |
+--------+--------+---------+------+------------+-------+
| Fluffy | Harold | cat | f | 1993-02-04 | NULL |
| Claws | Gwen | cat | m | 1994-03-17 | NULL |
+--------+--------+---------+------+------------+-------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
- or
mysql> select * from pet where birth >='1991-01-01'or species='cat' ;
+----------+--------+---------+------+------------+-------+
| name | owner | species | sex | birth | death |
+----------+--------+---------+------+------------+-------+
| Puffball | Diane | hamster | f | 1999-03-30 | NULL |
| Fluffy | Harold | cat | f | 1993-02-04 | NULL |
| Claws | Gwen | cat | m | 1994-03-17 | NULL |
| Chirpy | Gwen | bird | f | 1998-09-11 | NULL |
| Slim | Benny | snake | m | 1996-04-29 | NULL |
+----------+--------+---------+------+------------+-------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
配合括号区分优先级
mysql> SELECT * FROM pet WHERE (species = 'cat' AND sex = 'm')
-> OR (species = 'dog' AND sex = 'f');
+-------+--------+---------+------+------------+-------+
| name | owner | species | sex | birth | death |
+-------+--------+---------+------+------------+-------+
| Claws | Gwen | cat | m | 1994-03-17 | NULL |
| Buffy | Harold | dog | f | 1989-05-13 | NULL |
+-------+--------+---------+------+------------+-------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
查询指定列
mysql> select name,birth from pet where species='dog';
+--------+------------+
| name | birth |
+--------+------------+
| Buffy | 1989-05-13 |
| Fang | 1990-08-27 |
| Bowser | 1989-08-31 |
+--------+------------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
distinct 去重查询
mysql> select distinct owner from pet where birth>='1980-01-01';
+--------+
| owner |
+--------+
| Diane |
| Harold |
| Gwen |
| Benny |
+--------+
查询排序后的结果(order by)
升序排列(默认)
- 显示强调:关键字:
asc - eg.
select name,birth,owner from pet where birth>='1991-01-01' order by birth asc;
mysql> select name,birth, owner from pet where birth>='1980-01-01' order by birth;
+----------+------------+--------+
| name | birth | owner |
+----------+------------+--------+
| Buffy | 1989-05-13 | Harold |
| Bowser | 1989-08-31 | Diane |
| Fang | 1990-08-27 | Benny |
| Fluffy | 1993-02-04 | Harold |
| Claws | 1994-03-17 | Gwen |
| Slim | 1996-04-29 | Benny |
| Chirpy | 1998-09-11 | Gwen |
| Puffball | 1999-03-30 | Diane |
+----------+------------+--------+
8 rows in set (0.00 sec)
逆向排序
- 关键字
desc
SELECT name, birth FROM pet ORDER BY birth DESC; - The DESC keyword applies only to the column name immediately preceding it (birth); it does not affect the species column sort order.
多列排序
将 species 和 owner 降序排列
select name,species,birth,owner from pet order by birth,species desc,owner desc;
函数的应用
mysql> SELECT name, birth, CURDATE(), TIMESTAMPDIFF(YEAR,birth,CURDATE()) AS age FROM pet order by age;
+----------------------+------------+------------+------+
| name | birth | CURDATE() | age |
+----------------------+------------+------------+------+
| Puffball | 1999-03-30 | 2022-03-26 | 22 |
| Chirpy | 1998-09-11 | 2022-03-26 | 23 |
| Slim | 1996-04-29 | 2022-03-26 | 25 |
| Claws | 1994-03-17 | 2022-03-26 | 28 |
| Fluffy | 1993-02-04 | 2022-03-26 | 29 |
| Fang | 1990-08-27 | 2022-03-26 | 31 |
| Buffy | 1989-05-13 | 2022-03-26 | 32 |
| Bowser | 1989-08-31 | 2022-03-26 | 32 |
+----------------------+------------+------------+------+
17 rows in set (0.00 sec)
在上述查询语句中
name, birth, CURDATE(), TIMESTAMPDIFF(YEAR,birth,CURDATE()) AS age共同指定结果列表中的字段;
函数名可以作为一个字段;别名亦可以作为一个字段.
mysql> SELECT name, birth, death,curdate() as currentTime, TIMESTAMPDIFF(YEAR,birth,death) AS age FROM pet WHERE death IS NOT NULL ORDER BY age;
+----------+------------+------------+-------------+------+
| name | birth | death | currentTime | age |
+----------+------------+------------+-------------+------+
| Bowser | 1989-08-31 | 1995-07-29 | 2022-03-26 | 5 |
+----------+------------+------------+-------------+------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
查询哪些动物将在下一个月过生日
- 在 mysql8 的文档中有个类似问题,
- 我们主要解决 12 月份+1 的问题得到的 13 月份如何转化为 1 月份的问题.
- 解决该问题的方案有多种
- 利用 curDate()获取当前年月日
- 利用 data_add()对时间进行加法计算(该加法不会使得 12 月份超过 13)
- 再利用 Month()函数就可以求得距离当前时间的下一个月是什么月份.
- 另一种方案是使用 Mod()求模的方法来使得月份不会溢出 12 月份
- 采用求模 12 方案,所有的月份将落在 0~11 内其中,仅有 12 月份对 12 求模后值发生变换(变为 1),其余月份(1 到 11)求模 12 不变,我们将求模后的数字+1,得到的就是距离查询时刻下一个月所对应的月份.
具体语句:
#查询出哪些动物将在下一个月过生日
#方案1:
mysql> SELECT name, birth FROM pet
WHERE MONTH(birth) = MONTH(DATE_ADD(CURDATE(),INTERVAL 1 MONTH));
# 方案2
mysql> SELECT name, birth FROM pet
WHERE MONTH(birth) = MOD(MONTH(CURDATE()), 12) + 1;
Null 值
判断和比较 Null
select 语句既可以用于查询数据库,也可以用于简单的计算某些表达式
即,select 可以不做用于具体数据库;
mysql> SELECT 1 IS NULL, 1 IS NOT NULL;
+-----------+---------------+
| 1 IS NULL | 1 IS NOT NULL |
+-----------+---------------+
| 0 | 1 |
+-----------+---------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select 5+3/2;
+--------+
| 5+3/2 |
+--------+
| 6.5000 |
+--------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
逻辑值和 Null
- Because the result of any arithmetic comparison with NULL is also NULL, you cannot obtain any meaningful
results from such comparisons.
- In MySQL, 0 or NULL means false and anything else means true. The default truth value from a boolean
operation is 1. Not Null不会限制空串和0的插入;因为-
mysql> SELECT 0 IS NULL, 0 IS NOT NULL, '' IS NULL, '' IS NOT NULL; +-----------+---------------+------------+----------------+ | 0 IS NULL | 0 IS NOT NULL | '' IS NULL | '' IS NOT NULL | +-----------+---------------+------------+----------------+ | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | +-----------+---------------+------------+----------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
-
插入一条数据
mysql> INSERT INTO pet VALUES ('Puffball','Diane','hamster','f','1999-03-30',NULL);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
更新某一条数据
mysql> update pet set birth='1989-08-31' where name='Bowser';
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0
使用统配符查询
like,not like关键字- SQL pattern matching enables you to use
_to match any single character and%to match an arbitrary number of characters (including zero characters).
- In MySQL, SQL patterns are case-insensitive by default. Some examples are shown here. Do not use
=or<>when you use SQL patterns. Use theLIKEorNOT LIKEcomparison operators instead.
- SQL pattern matching enables you to use
mysql> select * from pet where name like 'b%';
+----------------------+--------+---------+------+------------+------------+
| name | owner | species | sex | birth | death |
+----------------------+--------+---------+------+------------+------------+
| Buffy | Harold | dog | f | 1989-05-13 | NULL |
| Bowser | Diane | dog | m | 1989-08-31 | 1995-07-29 |
+----------------------+--------+---------+------+------------+------------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
统计查询结果
- 统计是有力的工具
- 一般是count()系列函数和Group by 关键字进行配合使用
值得一提的是,如果使用了count()并且还有其他字段名,应当出现相应的group by,否则要么出现不可靠的结果,要么直接报错
简单统计
mysql> SELECT owner, COUNT(*) as sum FROM pet GROUP BY owner;
+--------+-----+
| owner | sum |
+--------+-----+
| NULL | 8 |
| Diane | 2 |
| Harold | 2 |
| Gwen | 3 |
| Benny | 2 |
+--------+-----+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
联合统计(多属性统计)
mysql> SELECT species, sex, COUNT(*) FROM pet GROUP BY species, sex;
+---------+------+----------+
| species | sex | COUNT(*) |
+---------+------+----------+
| NULL | NULL | 8 |
| hamster | f | 1 |
| cat | f | 1 |
| cat | m | 1 |
| dog | f | 1 |
| dog | m | 2 |
| bird | f | 1 |
| bird N | 1 | 1 |
| snake | m | 1 |
+---------+------+----------+
9 rows in set (0.00 sec)
局部联合统计
- 配合where,我们可以进一步精确统计
SELECT species, sex, COUNT(*) FROM pet
WHERE sex IS NOT NULL
GROUP BY species, sex;
+---------+------+----------+
| species | sex | COUNT(*) |
+---------+------+----------+
| hamster | f | 1 |
| cat | f | 1 |
| cat | m | 1 |
| dog | f | 1 |
| dog | m | 2 |
| bird | f | 1 |
| bird N | 1 | 1 |
| snake | m | 1 |
+---------+------+----------+
8 rows in set (0.00 sec)
多表查询
内连接(条件连接)
除了where可以跟条件意外,多表查询时,可以用
ON来连接若干个条件
处理多表查询,from后面通过[inner] join 连接多个表(可以是别名语句)
mysql> SELECT p1.name, p1.sex, p2.name, p2.sex, p1.species
FROM pet AS p1 INNER JOIN pet AS p2
ON
p1.species = p2.species
AND p1.sex = 'f' AND p1.death IS NULL
AND p2.sex = 'm' AND p2.death IS NULL;
+--------+------+-------+------+---------+
| name | sex | name | sex | species |
+--------+------+-------+------+---------+
| Fluffy | f | Claws | m | cat |
| Buffy | f | Fang | m | dog |
+--------+------+-------+------+---------+



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号