1 3.1 cpp:
2
3 #include <iostream>
4 #include <fstream>
5 #include <array>
6 #define N 5
7 int main() {
8 using namespace std;
9 array<int, N> x{ 97, 98, 99, 100, 101 };
10 ofstream out;
11 out.open("data1.dat", ios::binary);
12 if (!out.is_open()) {
13 cout << "fail to open data1.dat\n";
14 return 1;
15 }
16 //把从地址&x开始连续sizeof(x)个字节的数据块以字节数据块方式写入文件data1.txt
17 out.write(reinterpret_cast<char*>(&x), sizeof(x));
18 out.close();
19 }
20
21 3.2 cpp:
22
23 #include <iostream>
24 #include <fstream>
25 #include <array>
26 #define N 5
27 int main() {
28 using namespace std;
29 array<int, N> x;
30 ifstream in;
31 in.open("data1.dat", ios::binary);
32 if (!in.is_open()) {
33 cout << "fail to open data1.dat\n";
34 return 1;
35 }
36 // 从文件流对象in关联的文件data1.dat中读取sizeof(x)字节数据写入&x开始的地址单元
37 in.read(reinterpret_cast<char*>(&x), sizeof(x));
38 in.close();
39 for (auto i = 0; i < N; ++i)
40 cout << x[i] << ", ";
41 cout << "\b\b \n";
42 }
![]()
![]()
int类型的数据占用四个字节,而char型的数据只占用一个字节,array<char, N> x中的x只占用5个字节,而array<int, N> x占用20个字节。
所以在用array<char, N> x中x的地址来读取文件流中的数据,第一个数据97会占用四个字节,97对应的char型数据为a,98为b,只能读取两个数据,而且内存越界了。
1 vector.hpp:
2
3 #include<iostream>
4 using namespace std;
5
6 template<typename T>
7 class Vector {
8 private:
9 int size; //储存数据项个数
10 T* p;
11 public:
12 Vector(int n):size{n}{ p = new T[size]; }
13 Vector(int n, T value): size{ n }
14 {
15 p = new T[size];
16 for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
17 p[i] = value;
18 }
19 Vector(const Vector<T>& obj):size{obj.size}
20 {
21 p = new T[size];
22 for (auto i = 0; i < size; i++)
23 p[i] = obj.p[i];
24 }
25 ~Vector() { delete []p; }
26 int get_size() { return size; }
27 T &at(int index);
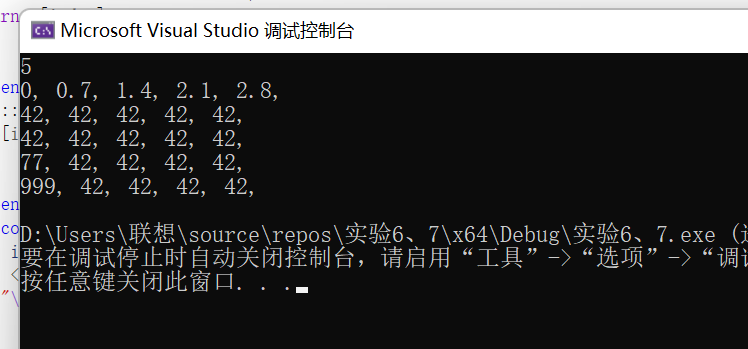
28 T &operator[](int i);
29 template<typename T1>
30 friend void output(const Vector<T1>&p1);
31 };
32
33 template<typename T>
34 T& Vector<T>::at(int index) {
35 if (index >= 0 && index < size)
36 return p[index];
37 }
38
39 template<typename T>
40 T& Vector<T>::operator[](int i) {
41 return p[i];
42 }
43
44 template<typename T1>
45 void output(const Vector<T1>& p1) {
46 for (int i = 0; i < p1.size; i++)
47 cout << p1.p[i] << ", ";
48 cout << "\b\b\n";
49 }
50
51 task4:
52 #include <iostream>
53 #include "vector.hpp"
54
55 void test() {
56 using namespace std;
57
58 int n;
59 cin >> n;
60
61 Vector<double> x1(n);
62 for (auto i = 0; i < n; ++i)
63 x1.at(i) = i * 0.7;
64
65 output(x1);
66
67 Vector<int> x2(n, 42);
68 Vector<int> x3(x2);
69
70 output(x2);
71 output(x3);
72
73 x2.at(0) = 77;
74 output(x2);
75
76 x3[0] = 999;
77 output(x3);
78 }
79
80 int main() {
81 test();
82 }
![]()
1 更改task4:
2 #include <iostream>
3 #include "vector.hpp"
4
5 void test() {
6 using namespace std;
7
8 int n;
9 cin >> n;
10
11 Vector<double> x1(n);
12 for (auto i = 0; i < n; ++i)
13 x1.at(i) = i * 0.5;
14
15 output(x1);
16
17 Vector<int> x2(n, 25);
18 Vector<int> x3(x2);
19
20 output(x2);
21 output(x3);
22
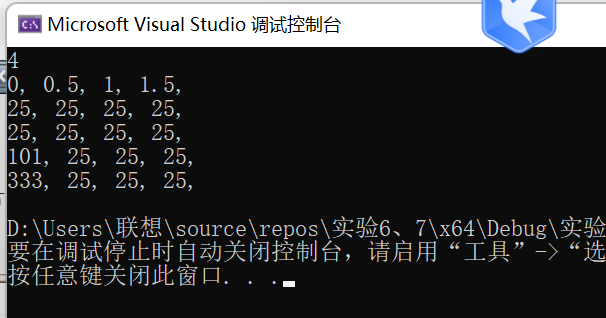
23 x2.at(0) = 101;
24 output(x2);
25
26 x3[0] = 333;
27 output(x3);
28 }
29
30 int main() {
31 test();
32 }
![]()
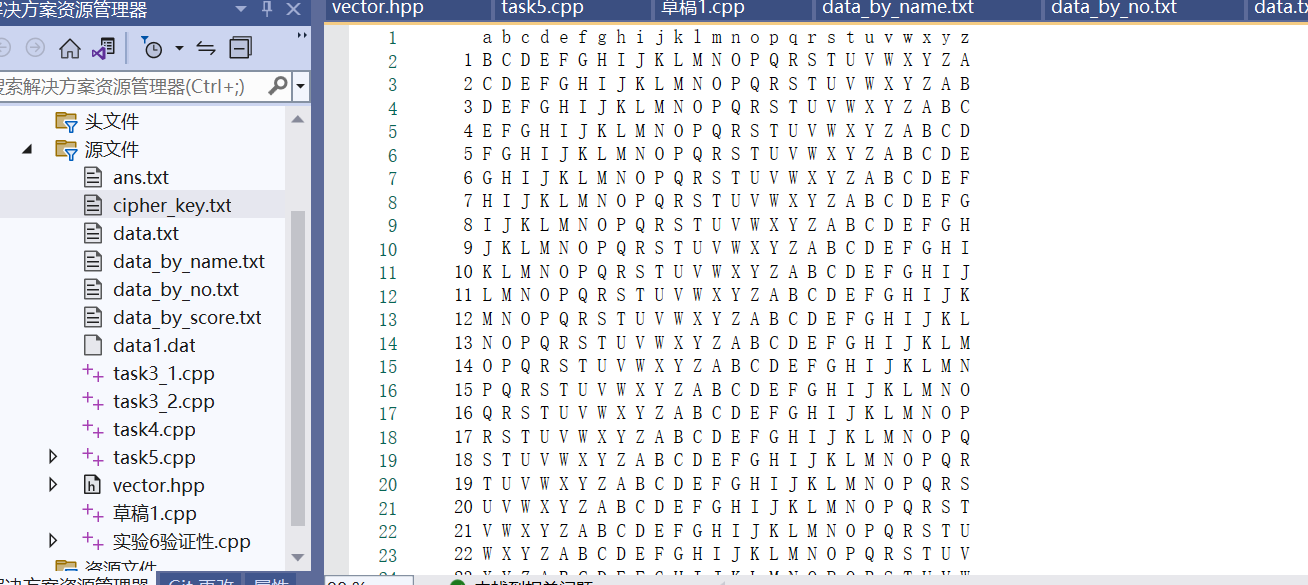
1 task5:
2
3 #include<fstream>
4 #include<iostream>
5 #include<iomanip>
6 using std::ofstream;
7 using std::ios_base;
8 using std::setw;
9 using namespace std;
10 void output(std::ostream& out)
11 {
12 char a[26];
13 char change1;
14 cout << " ";
15 out << " ";
16 for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++)
17 a[i] = char(i+65);
18 for (int i = 97; i <= 122; i++)
19 {
20 cout << setw(2) << char(i);
21 out << setw(2) << char(i);
22 }
23 cout << endl;
24 out << endl;
25 for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++)
26 {
27 cout << setw(2)<<i + 1;
28 out << setw(2) << i + 1;
29 for (int k = 0; k < 25; k++)
30 {
31 change1 = a[k];
32 a[k] = a[k + 1];
33 a[k + 1] = change1;
34 }
35 for (int j = 0; j < 26; j++)
36 {
37 cout <<setw(2)<< a[j];
38 out << setw(2)<<a[j];
39 }
40 cout << endl;
41 out << endl;
42 }
43 }
44
45
46 int main()
47 {
48 ofstream out;
49 out.open("cipher_key.txt", ios::out);
50 if (!out.is_open()) {
51 std::cout << "fail to open file cipher_key.txt" << std::endl;
52 return 1;
53 }
54 output(out);
55 out.close();
56 }
![]()
![]()






 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号