二叉树
概念
-
满二叉树:节点总数2^k -1
-
完全二叉树:除了底层外,其他都满,而且底层必须从左到右连续
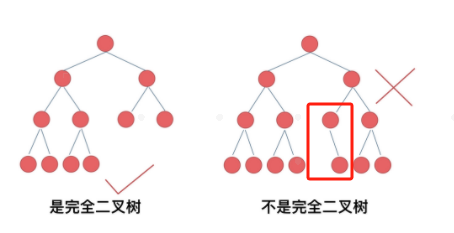
-
二叉搜索树:左子树都小于中间节点,右子树都大于中间节点(子节点也必须满足左小右大)
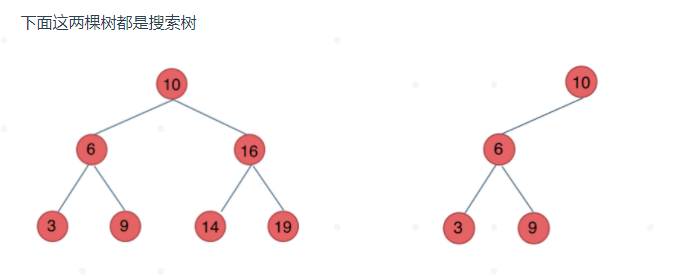
-
平衡二叉搜索树:左子树和右子树的高度差不超过1
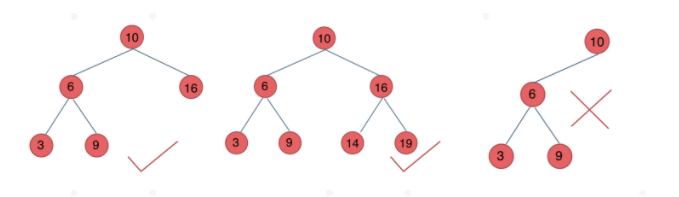
map set multimap multiset底层都是平衡二叉搜索树
存储方式
-
链式存储:用链表
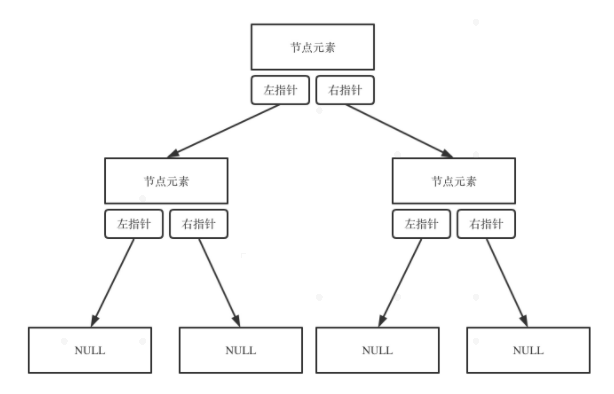
-
顺序存储:用数组(实际上很少应用)找到某节点的子节点 2k + 1 / 2k + 2
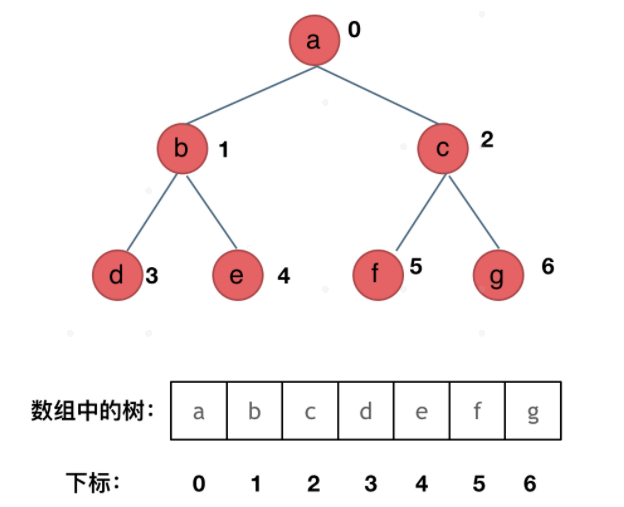
遍历方式
- 深度优先遍历(一般通过递归实现,也可以迭代):攒着一个方向一直搜到最后,然后回退,搜下一个方向
- 前序 中左右
- 中序 左中右
- 后序 左右中
- 广度优先遍历:一层一层的搜索(迭代法,队列)
- 层序
struct TreeNode{
int val;
TreeNode* left;
TreeNode* right;
TreeNode(int x): val(x),left(NULL),right(NULL){}
}
144.二叉树的前序遍历
https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-preorder-traversal/description/
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
void digui(TreeNode* cur, vector<int>& vc){
if(cur == NULL) return;
vc.push_back(cur->val);
digui(cur->left, vc);
digui(cur->right, vc);
}
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
digui(root, res);
return res;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
if(root == NULL) return res;
stack<TreeNode*> sk;
sk.push(root);
//只要栈非空就继续,先把栈顶的节点值push(中),在把右节点压栈 左节点压栈,现在栈顶就是左节点了,下次循环就是操作左节点
while(!sk.empty())
{
TreeNode* cur = sk.top();
sk.pop();
res.push_back(cur->val);
if(cur->right != NULL) sk.push(cur->right);
if(cur->left != NULL) sk.push(cur->left);
}
return res;
}
};
145.二叉树的后序遍历
https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-postorder-traversal/
class Solution {
public:
void digui(TreeNode* cur, vector<int>& vc){
if(NULL == cur) return;
digui(cur->left, vc);
digui(cur->right, vc);
vc.push_back(cur->val);
}
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
digui(root, res);
return res;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
stack<TreeNode*> st;
if(root == NULL) return res;
st.push(root);
while(!st.empty())
{
TreeNode* node = st.top(); // 中
st.pop();
res.push_back(node->val);
if (node->left) st.push(node->left); // 左(空节点不入栈)
if (node->right) st.push(node->right); // 右(空节点不入栈)
}
reverse(res.begin(),res.end());
return res;
}
};
94.二叉树的中序遍历
https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-inorder-traversal/description/
class Solution {
public:
void digui(TreeNode* cur, vector<int> &vc){
if(NULL == cur) return;
digui(cur->left, vc);
vc.push_back(cur->val);
digui(cur->right, vc);
}
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
digui(root, res);
return res;
}
};
每次访问都是从根节点开始的,中序遍历是先左中右,所以访问的不是要处理的!!!
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
//用一个栈和一个指针,依次压入根节点,左节点的中节点,左节点的左节点...(所有遍历过的节点) 遍历到最左边了下一个NULL就出栈
stack<TreeNode*> sk;
TreeNode* cur = root;
vector<int> res;
while(cur != NULL || !sk.empty()) //一定注意这里是或者!!!!!!!
{
if(cur != NULL)
{**
sk.push(cur);
cur = cur->left; //一直找到最左边的节点,然后会在下面被pop出来
}
else
{
cur = sk.top();
sk.pop();
res.push_back(cur->val); //pop出来之后,把他当作中间节点填入结果数组
cur = cur->right; //继续寻找右节点
}
}
return res;
}
};
102.二叉树的层序遍历
https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-level-order-traversal/description/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
//用队列,记录队列长度(每层弹出几个)每次弹出就弹入他的左右节点 弹出的数量到达size 更新size
queue<TreeNode*> q;
vector<vector<int>> res;
if(root != NULL) q.push(root);
while(!q.empty())
{
int size = q.size();
vector<int> vc;
while(size--)
{
TreeNode* cur = q.front();
vc.push_back(cur->val);
q.pop();
if(cur->left) q.push(cur->left);
if(cur->right) q.push(cur->right);
}
res.push_back(vc);
}
return res;
}
};
107.二叉树的层序遍历Ⅱ
https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-level-order-traversal-ii/description/2024-01-10
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> q;
vector<vector<int>> res;
if(root != NULL) q.push(root);
while(!q.empty())
{
int size = q.size();
vector<int> vc;
while(size--)
{
TreeNode* cur = q.front();
vc.push_back(cur->val);
q.pop();
if(cur->left) q.push(cur->left);
if(cur->right) q.push(cur->right);
}
res.push_back(vc);
}
reverse(res.begin(),res.end());
return res;
}
};
199.二叉树的右视图
https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-right-side-view/description/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> rightSideView(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> q;
vector<int> vc;
if(root != NULL) q.push(root);
while(!q.empty())
{
int size = q.size();
while(size--)
{
TreeNode* cur = q.front();
q.pop();
if(size == 0) vc.push_back(cur->val);
if(cur->left) q.push(cur->left);
if(cur->right) q.push(cur->right);
}
}
return vc;
}
};
637.二叉树的层平均值
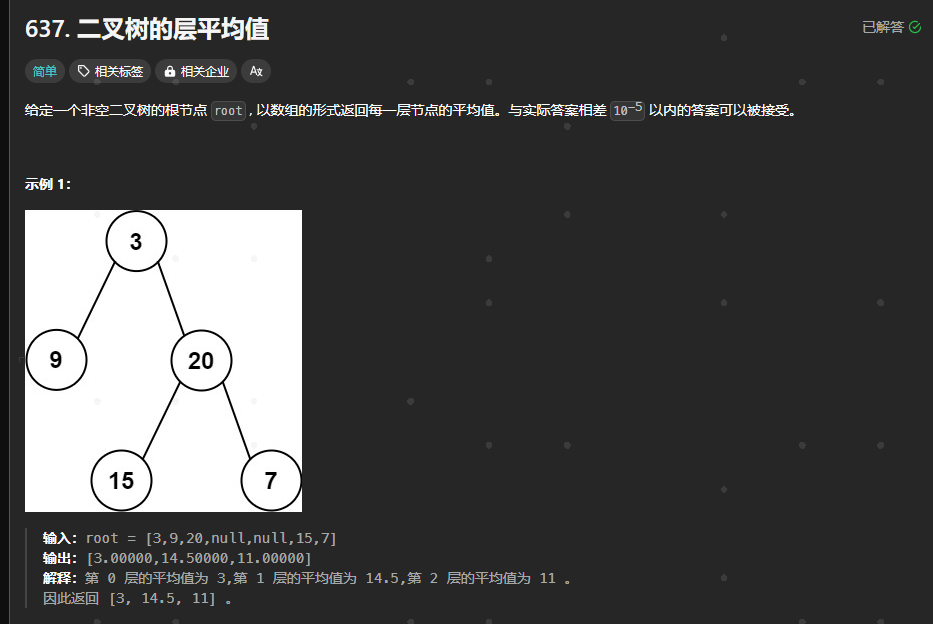
https://leetcode.cn/problems/average-of-levels-in-binary-tree/description/
class Solution {
public:
double calAvg(vector<int> vc){
double sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < vc.size(); i++)
{
sum += vc[i];
}
return (double)sum/vc.size();
}
vector<double> averageOfLevels(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> q;
vector<double> res;
if(root != NULL) q.push(root);
while(!q.empty())
{
int size = q.size();
vector<int> vc;
while(size--)
{
TreeNode* cur = q.front();
vc.push_back(cur->val);
q.pop();
if(cur->left) q.push(cur->left);
if(cur->right) q.push(cur->right);
if(size == 0) res.push_back(calAvg(vc));
}
}
return res;
}
};
429.N叉数的层序遍历
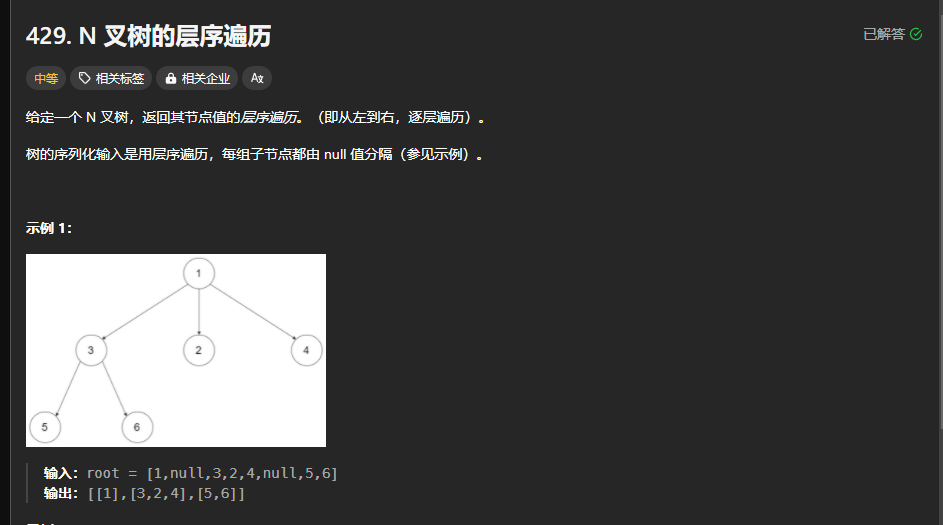
https://leetcode.cn/problems/n-ary-tree-level-order-traversal/description/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(Node* root) {
//用队列记录一次加几个,每弹出一个就加所有孩子节点。再用一个结点指针遍历
queue<Node*> q;
vector<vector<int>> res;
if(root!=NULL) q.push(root);
while(!q.empty())
{
int size = q.size();
vector<int> vc;
while(size--)
{
Node* cur = q.front();
vc.push_back(cur->val);
q.pop();
for(int i = 0; i < cur->children.size(); ++i)
{
if(cur->children[i] != NULL)
q.push(cur->children[i]);
}
}
res.push_back(vc);
}
return res;
}
};
515.在每个树行中找最大值
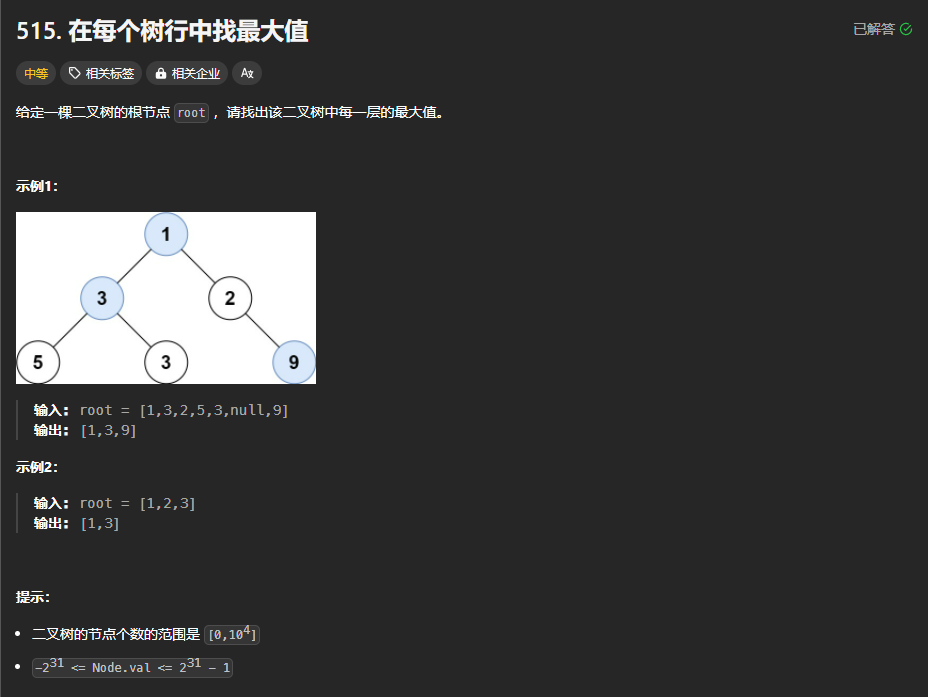
https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-largest-value-in-each-tree-row/description/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> largestValues(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> q;
if(root != NULL) q.push(root);
vector<int> res;
while(!q.empty())
{
int maxVal = INT_MIN;
int size = q.size();
while(size--)
{
TreeNode* cur = q.front();
q.pop();
maxVal = maxVal > cur->val ? maxVal : cur->val;
if(cur->left) q.push(cur->left);
if(cur->right) q.push(cur->right);
}
res.push_back(maxVal);
}
return res;
}
};
116.填充每个节点的下一个右侧指针

https://leetcode.cn/problems/populating-next-right-pointers-in-each-node/description/
class Solution {
public:
Node* connect(Node* root) {
queue<Node*> q;
if(root != NULL) q.push(root);
while(!q.empty())
{
int size = q.size();
while(size--) //这里原来是先判断size是否为0,紧接着就--,然后才执行while内部的语句!!!!!!!!!
{
Node* cur = q.front();
q.pop();
if(size!=0) cur->next = q.front();
if(cur->left) q.push(cur->left);
if(cur->right) q.push(cur->right);
}
}
return root;
}
};
117.填充每个节点的下一个右侧指针Ⅱ

https://leetcode.cn/problems/populating-next-right-pointers-in-each-node-ii/description/
class Solution {
public:
Node* connect(Node* root) {
queue<Node*> q;
if(root != NULL) q.push(root);
while(!q.empty())
{
int size = q.size();
while(size--)
{
Node* cur = q.front();
q.pop();
if(size != 0) cur->next = q.front();
if(cur->left) q.push(cur->left);
if(cur->right) q.push(cur->right);
}
}
return root;
}
};
104.二叉树的最大深度
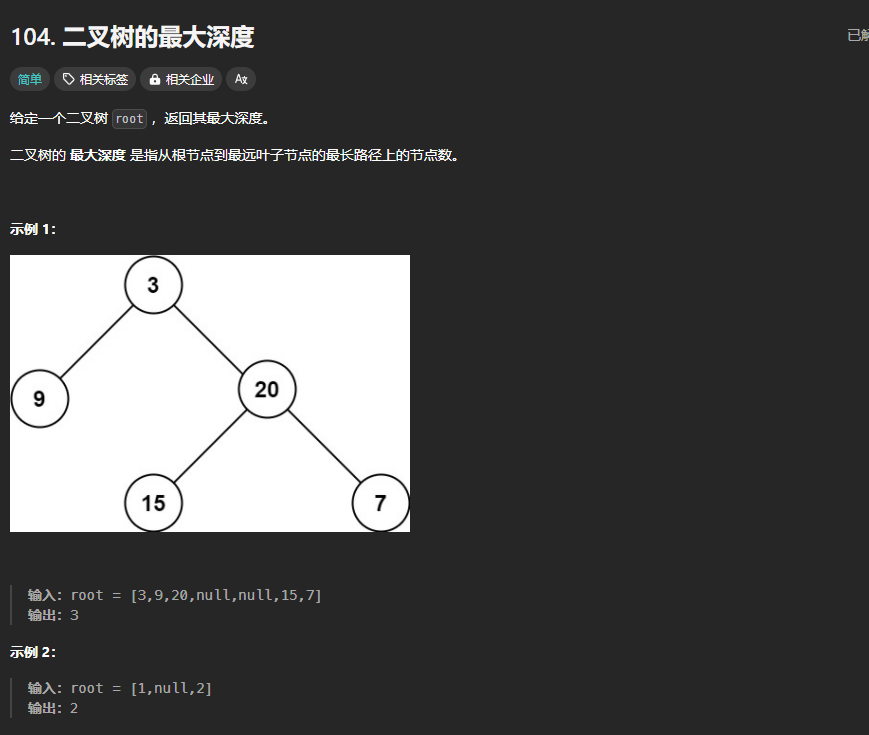
https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/description/
递归
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr) return 0;
return max(maxDepth(root->left), maxDepth(root->right)) + 1;
}
};
广搜
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> q;
if(root != NULL) q.push(root);
int res = 0;
while(!q.empty())
{
int size = q.size();
//res = res > size ? res : size;
res++;
while(size--)
{
TreeNode* cur = q.front();
q.pop();
if(cur->left) q.push(cur->left);
if(cur->right) q.push(cur->right);
}
}
return res;
}
};
559.N叉树的最大深度
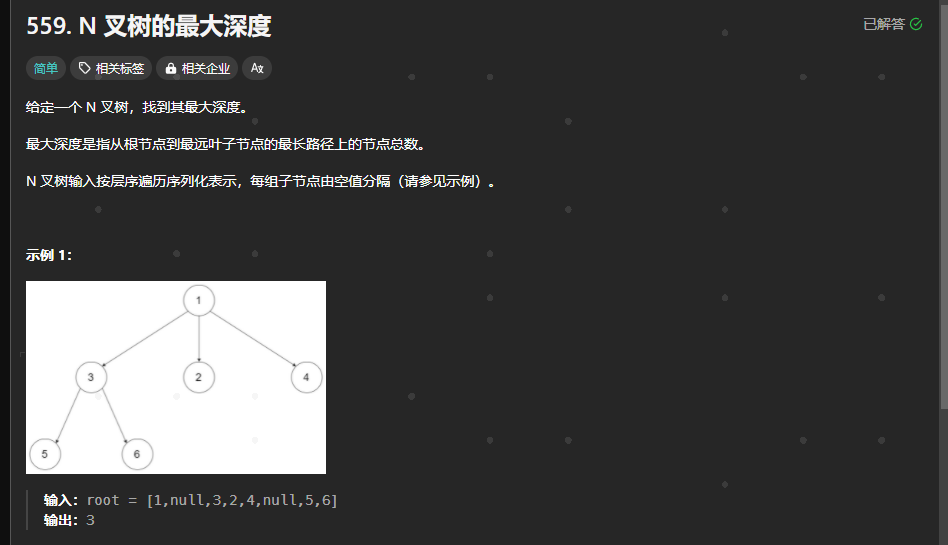
https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-depth-of-n-ary-tree/description/
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(Node* root) {
if(root == NULL) return 0;
if(root->children.size() == 0) return 1;
int res = INT_MIN;
for(int i = 0; i < root->children.size(); i++)
{
//cout<<root->children[i]->val<<endl;
res = max(res,maxDepth(root->children[i]));
}
res++;
return res;
}
};
//层序遍历
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(Node* root) {
queue<Node*> q;
if(root != NULL) q.push(root);
int res = 0;
while(!q.empty())
{
int size = q.size();
res++;
while(size--)
{
Node* cur = q.front();
q.pop();
for(int i = 0; i < cur->children.size(); i++)
{
q.push(cur->children[i]);
}
}
}
return res;
}
};
111.二叉树的最小深度
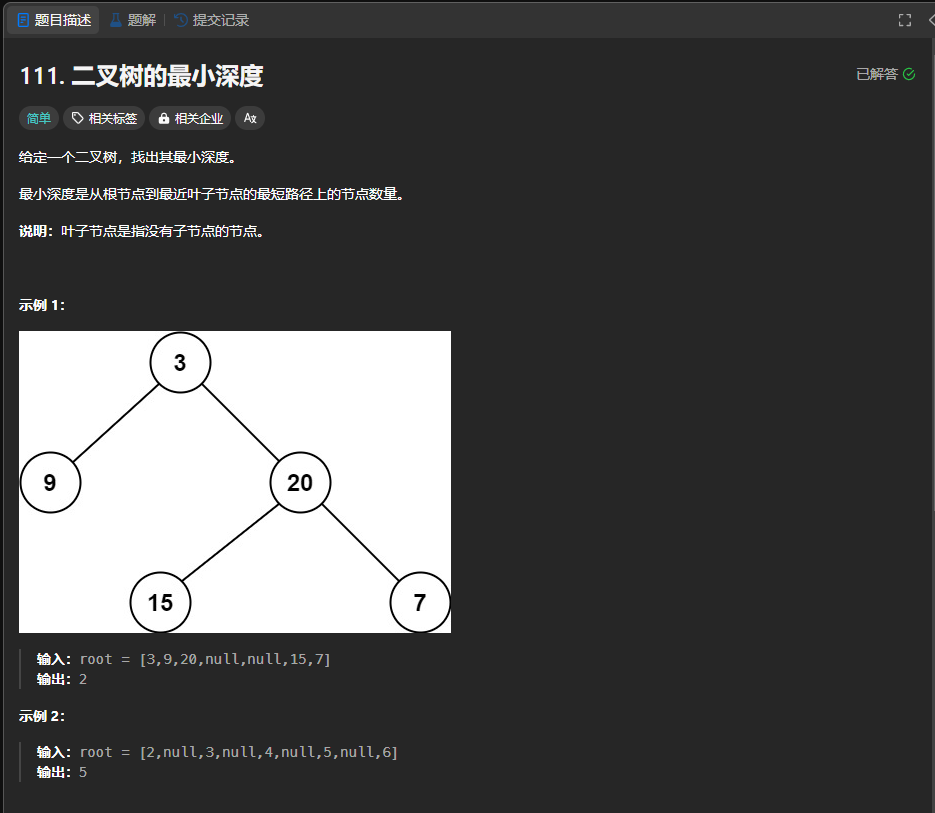
https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-depth-of-binary-tree/description/
class Solution {
public:
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> q;
if(root!=NULL) q.push(root);
int res = 0;
while(!q.empty())
{
res++;
int size = q.size();
while(size--)
{
TreeNode* cur = q.front();
q.pop();
if(cur->left == NULL && cur->right == NULL) return res;
if(cur->left) q.push(cur->left);
if(cur->right) q.push(cur->right);
}
}
return res;
}
};
226.翻转二叉树
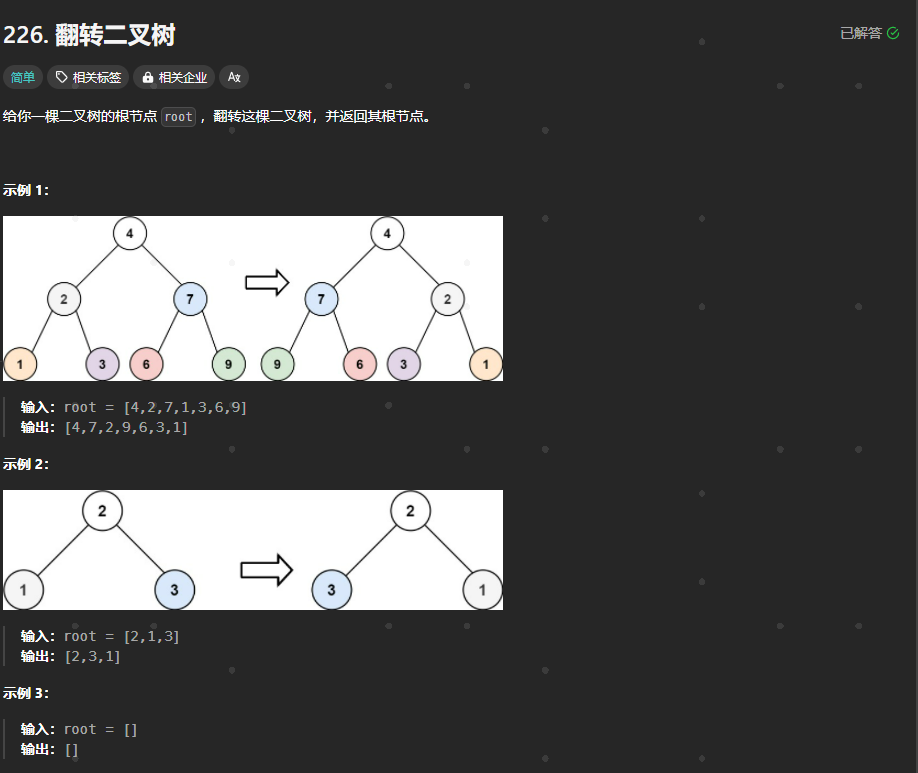
https://leetcode.cn/problems/invert-binary-tree/description/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL) return NULL;
swap(root->left, root->right);
invertTree(root->left);
invertTree(root->right);
return root;
}
};
101.对称二叉树
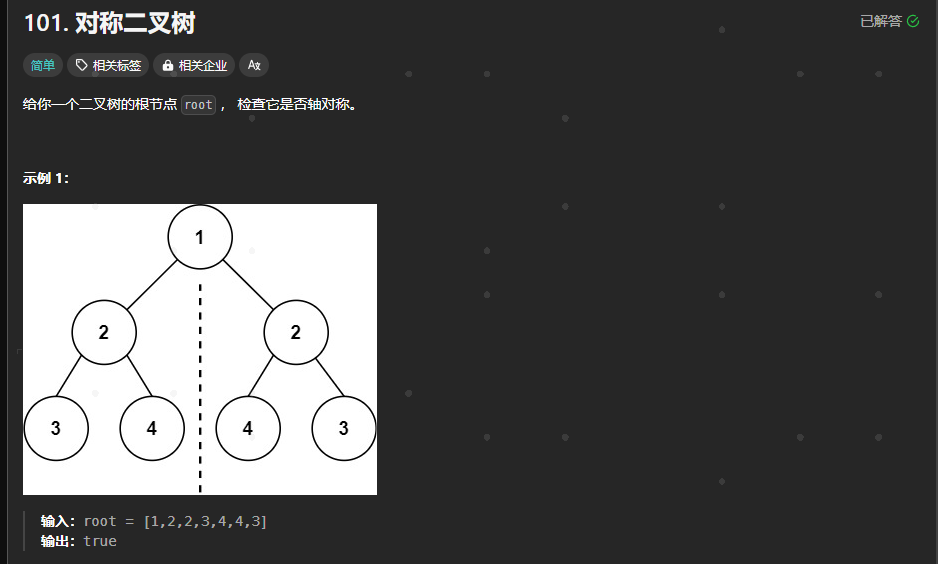
https://leetcode.cn/problems/symmetric-tree/description/
class Solution {
public:
bool cmp(TreeNode* left, TreeNode* right){
//左右一个空 一个不空 肯定不对称的,直接false!!!!左右都是空,肯定对称的,直接true!!!!左右都不空就看数值!!
if(left == nullptr && right != nullptr) return false;
else if(left != nullptr && right == nullptr) return false;
else if(left == nullptr && right == nullptr) return true;
else if(left->val != right->val) return false;
//终止条件结束,现在就剩下了左右都不空,而且两边值相同,要继续向下判断
bool a = cmp(left->left, right->right);
bool b = cmp(left->right, right->left);
//判断到最后,最底下一层对称了
return a&&b;
}
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
//不能用层序遍历!!!!因为层序遍历无法确定对称的两边是一左一右还是都是左/右
if(root == nullptr) return false;
return cmp(root->left, root->right);
}
};
100.相同的树
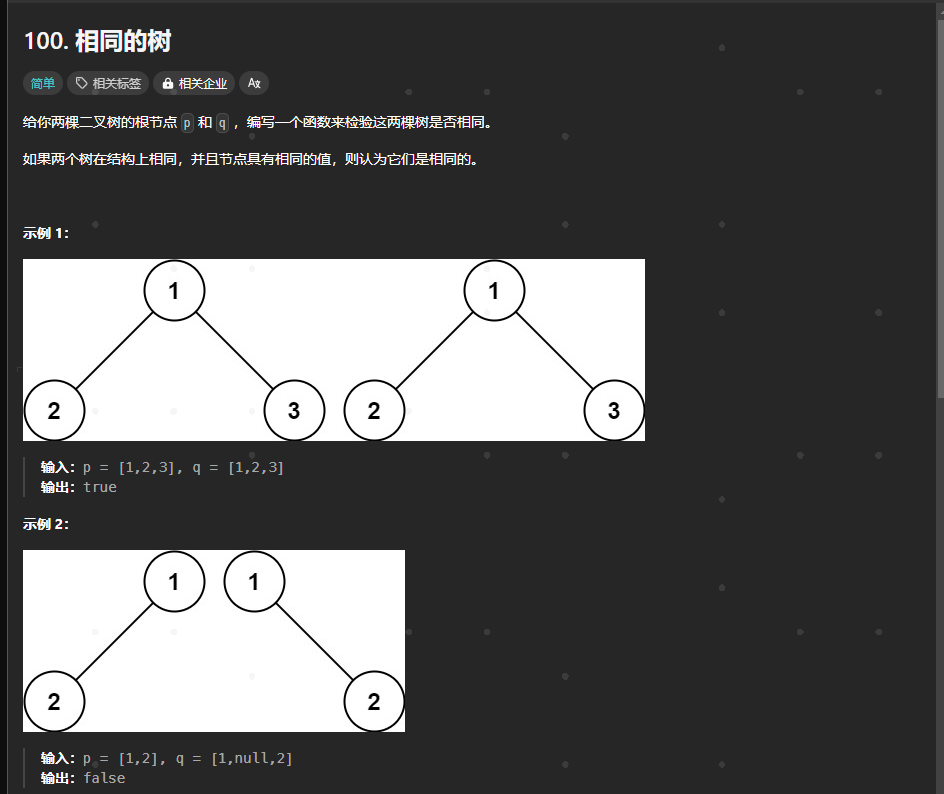
https://leetcode.cn/problems/same-tree/description/
class Solution {
public:
bool isSameTree(TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if(p != nullptr && q == nullptr) return false;
else if(q != nullptr && p == nullptr) return false;
else if(p == nullptr && q == nullptr) return true;
else if(p->val != q->val) return false;
bool l = isSameTree(p->left, q->left);
bool r = isSameTree(p->right, q->right);
return l&&r;
}
};
572.另一棵树的子树
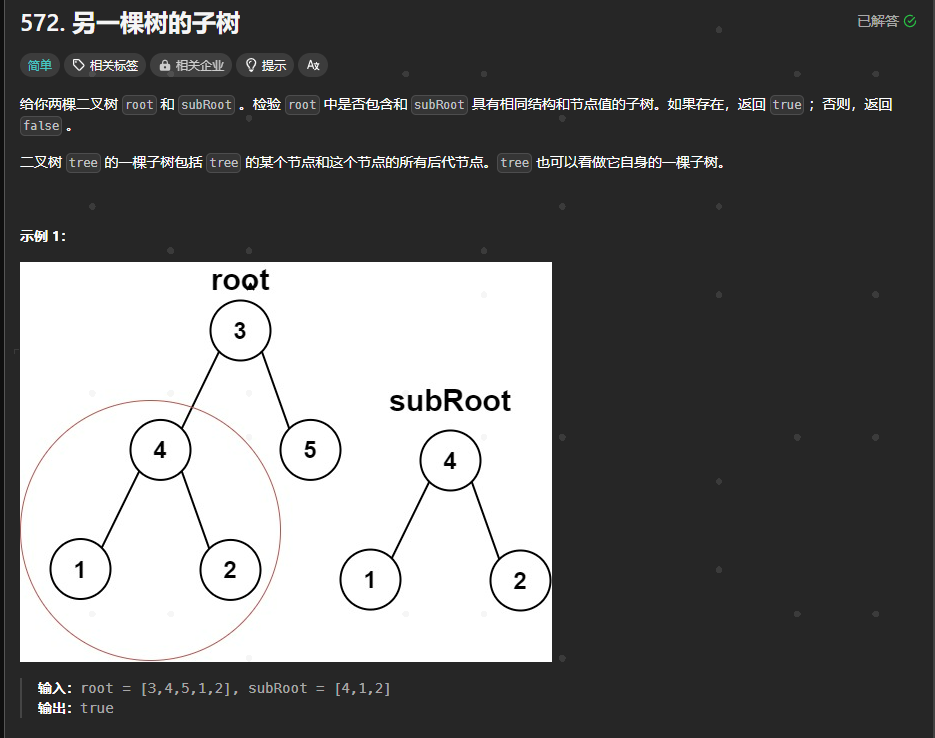
https://leetcode.cn/problems/subtree-of-another-tree/description/
class Solution {
public:
bool isSameTree(TreeNode* a, TreeNode* b){
if(a == nullptr && b != nullptr) return false;
else if(b == nullptr && a != nullptr) return false;
else if(a == nullptr && b == nullptr) return true;
else if(a->val != b->val) return false;
bool c = isSameTree(a->left, b->left);
bool d = isSameTree(a->right, b->right);
return c&&d;
}
bool isSubtree(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* subRoot) {
//下面要用到root的左右孩子,所以保证根节点左右非空!!!
if(root == nullptr && subRoot == nullptr) return true;
if(root == nullptr && subRoot != nullptr) return false;
//要不然是两个相同的树,要不然是左子树下的树,要不然是右子树下的树
return isSameTree(root,subRoot) || isSubtree(root->left,subRoot) || isSubtree(root->right,subRoot);
}
};
222.完全二叉树的节点个数

https://leetcode.cn/problems/count-complete-tree-nodes/
class Solution {
public:
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {
//完全二叉树,子树一定有个满二叉树(一个节点就至少是一个满二叉树)
if(root == nullptr) return 0;
int depL = 0;
int depR = 0;
TreeNode* curL = root->left;
TreeNode* curR = root->right;
//先找到深度多少,比如左右深度都是3 代表这是一颗满二叉树 直接套公式2 ^ 3 - 1
while(curL!= NULL)
{
depL++;
curL = curL->left;
}
while(curR!= NULL)
{
depR++;
curR = curR->right;
}
if(depL == depR) return (2 << depL) - 1;
else return 1 + countNodes(root->left) + countNodes(root->right);
}
};
110.平衡二叉树
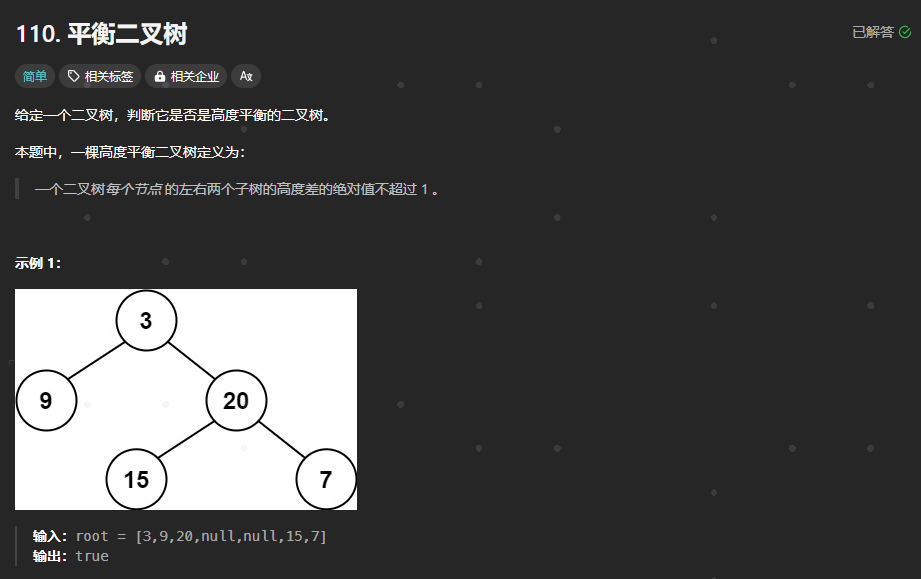
https://leetcode.cn/problems/balanced-binary-tree/description/
class Solution {
public:
int getHeight(TreeNode* root){
if(root == NULL) return 0;
int a = getHeight(root->left);
if(a == -1) return -1; //递归找a的过程中有一次出现了差值大于一
int b = getHeight(root->right);
if(b == -1) return -1;
int height = 1 + max(a,b);
return abs(a-b) > 1 ? -1 : height;
}
bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) {
int res = getHeight(root);
return res == -1 ? false : true;
}
};
257.二叉树的所有路径

https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-paths/description/
class Solution {
public:
string NumToStr(vector<int> path){
string res;
for(int i = 0; i < path.size() - 1; ++i)
{
res += to_string(path[i]);
res += "->";
}
res += to_string(path[path.size() - 1]);
return res;
}
vector<string> calPath(TreeNode* node, vector<int>& path, vector<string>& result){
//前序遍历,到叶子节点停止
path.push_back(node->val); //中 也就是收集每个节点
//找到叶子节点了的话,就收集这条答案,执行到if内部就一定不会执行下面的左右逻辑了!!!
if(node->left == NULL && node->right == NULL)
{
result.push_back(NumToStr(path));
}
if(node->left)
{
//一层一层的把节点加入到path, 然后剥离出来直到根节点
calPath(node->left, path, result);
path.pop_back();
}
if(node->right)
{
//一层一层的把节点加入到path, 然后剥离出来直到根节点
calPath(node->right, path, result);
path.pop_back();
}
return result;
}
vector<string> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> path;
vector<string> res;
return calPath(root, path, res);
}
};
404.左叶子之和

https://leetcode.cn/problems/sum-of-left-leaves/description/
class Solution {
public:
int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode* root) {
//左叶子:A的左子树不为空 A的左子树的左右都为空,那么A的左子树就是左叶子
if(root == NULL) return 0;
//进入递归,遇到空节点终止,先判断当前节点是否是左叶子的上一个,是的话就记录一下这个值,
int l,r = 0;
l = sumOfLeftLeaves(root->left);
if(root->left != NULL && root->left->left == NULL && root->left->right == NULL)
l = root->left->val;
r = sumOfLeftLeaves(root->right);
return l + r;
}
};
513.找树最左下角的值
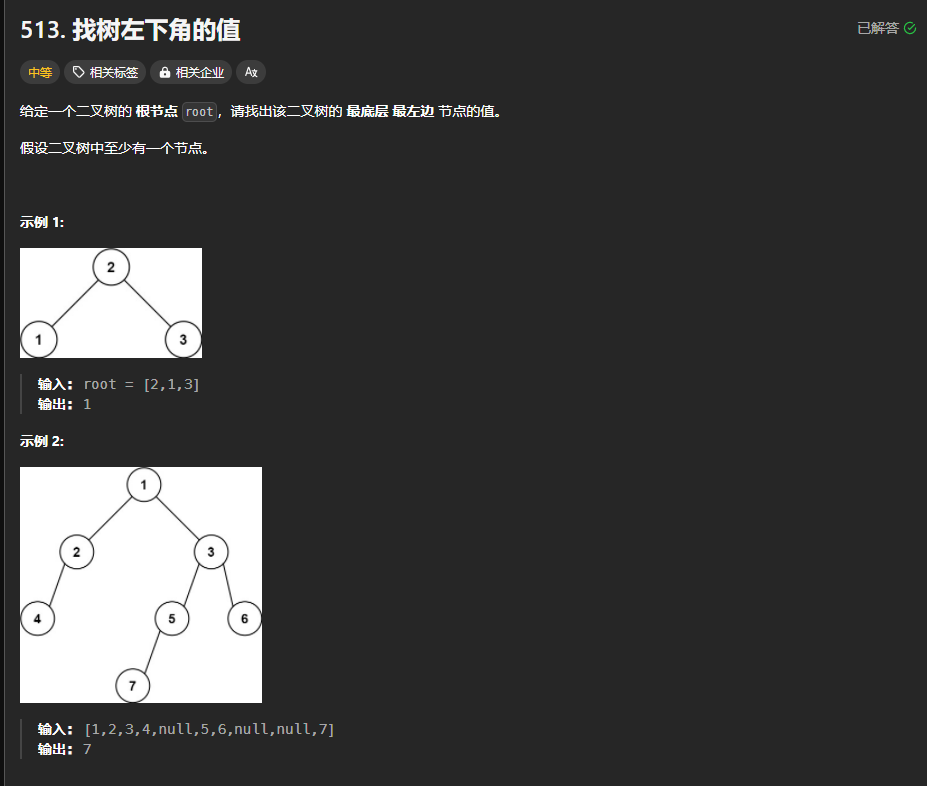
https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-bottom-left-tree-value/description/
class Solution {
public:
int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
int res;
while(!q.empty())
{
int size = q.size();
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
TreeNode* cur = q.front();
if(i == 0) res = cur->val;
q.pop();
if(cur->left) q.push(cur->left);
if(cur->right) q.push(cur->right);
}
}
return res;
}
};
112.路径总和
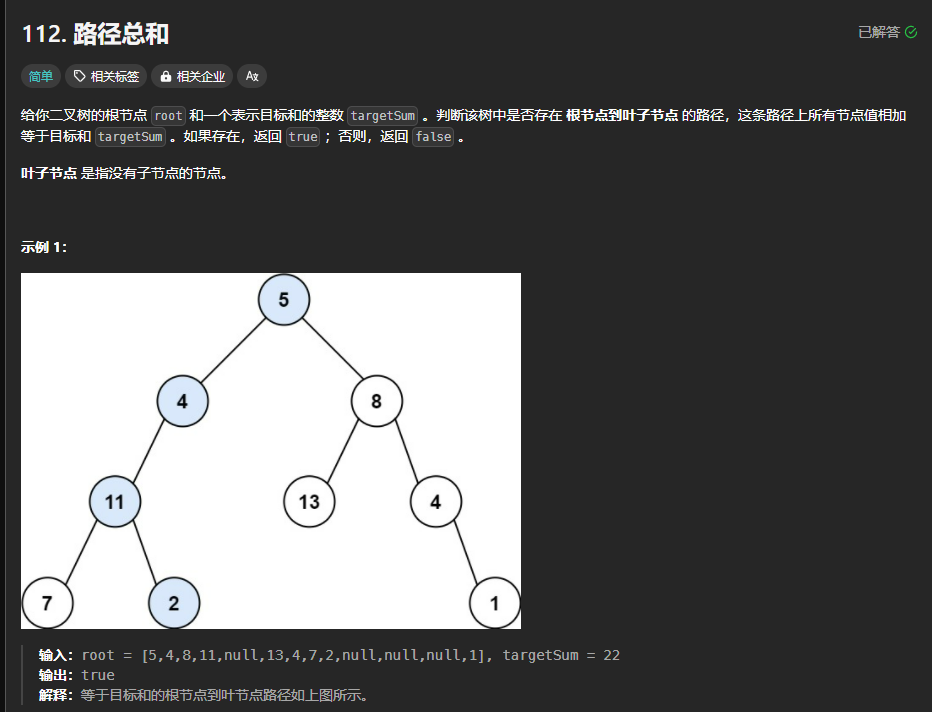
https://leetcode.cn/problems/path-sum/description/
class Solution {
public:
bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
if(root == NULL) return false;
//当遍历到叶子节点且和为0就停止了
if(root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)
{
if(targetSum == root->val) return true;
return false;
}
if(root->left)
{
targetSum -= root->val;
if(hasPathSum(root->left, targetSum)) return true;
targetSum += root->val;
}
//5 22 -> 5 17 -> 4 17 -> 4 13 -> 11 13 -> 11 2 -> 7 2 ->
if(root->right)
{
targetSum -= root->val;
if(hasPathSum(root->right, targetSum)) return true;
targetSum += root->val;
}
return false;
}
};
113.路径总和Ⅱ
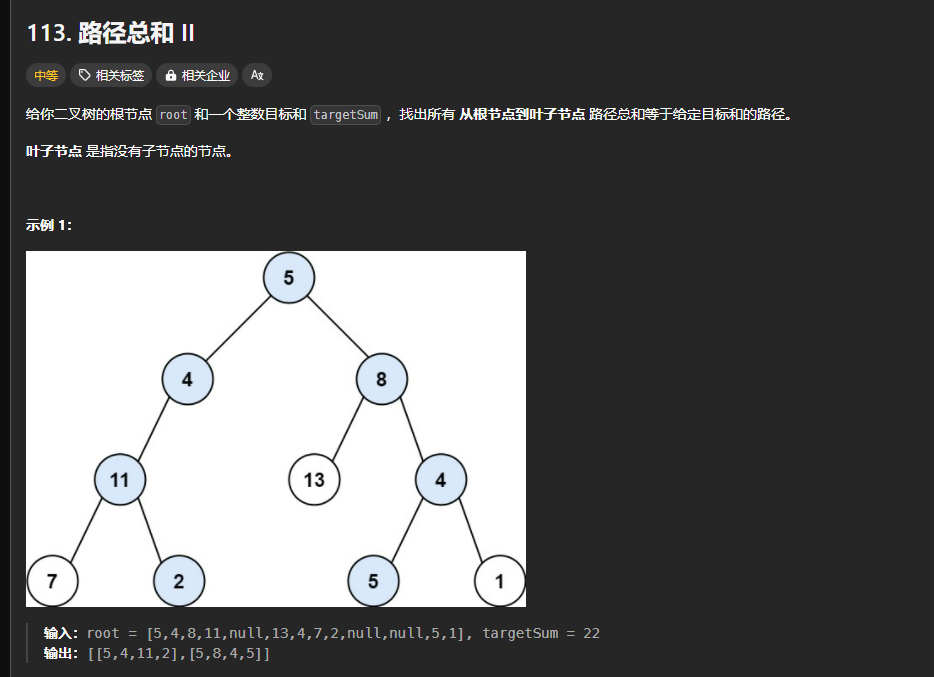
https://leetcode.cn/problems/path-sum-ii/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> res;
vector<int> cur;
void calPath(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
if(root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)
{
if(targetSum == 0) res.push_back(cur);
return;
}
if(root->left)
{
cur.push_back(root->left->val);
targetSum -= root->left->val;
calPath(root->left, targetSum);
targetSum += root->left->val;
cur.pop_back();
}
if(root->right)
{
cur.push_back(root->right->val);
targetSum -= root->right->val;
calPath(root->right, targetSum);
targetSum += root->right->val;
cur.pop_back();
}
}
vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
if(root == NULL) return res;
cur.push_back(root->val);
calPath(root, targetSum - root->val);
return res;
}
};
106.用中序和后序构建二叉树
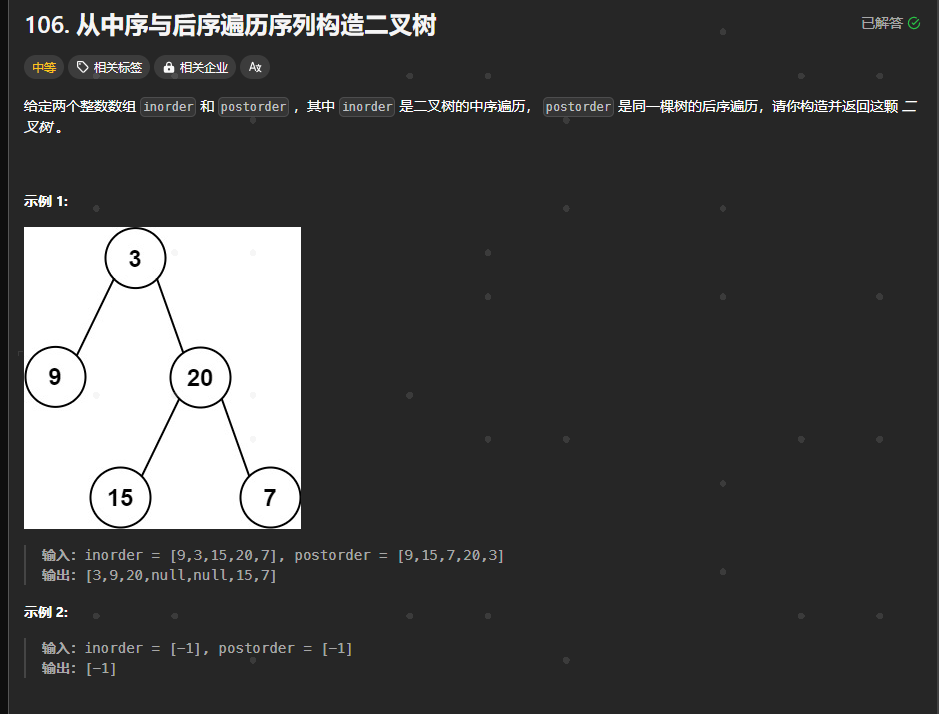
https://leetcode.cn/problems/construct-binary-tree-from-inorder-and-postorder-traversal/description/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {
if(inorder.size() == 0 || postorder.size() == 0) return NULL;
//中序 左中右 后序 左右中,取后序的最后一个,分割中序为左中 右中,分割后序,左中的长度就是后序的左子树
int mid = postorder[postorder.size() - 1];
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(mid);
if (postorder.size() == 1) return root;
int i;
for(i = 0; i < inorder.size(); i++)
{
if(mid == inorder[i]) break;
}
postorder.resize(postorder.size()-1);
vector<int> leftmid(inorder.begin(), inorder.begin() + i);
vector<int> rightmid(inorder.begin() + i + 1, inorder.end());
vector<int> leftend(postorder.begin(), postorder.begin() + leftmid.size());
vector<int> rightend(postorder.begin() + leftmid.size(), postorder.end());
root->left = buildTree(leftmid, leftend);
root->right = buildTree(rightmid, rightend);
return root;
}
};
654.最大二叉树

https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-binary-tree/description/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* calMaxTree(vector<int>& nums, int left, int right){
if(left >= right) return NULL;
int maxIndex = left;
for(int i = left + 1; i < right; i++)
{
if(nums[i] > nums[maxIndex]) maxIndex = i;
}
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(nums[maxIndex]);
//[left, maxIndex) [maxIndex, right)
root->left = calMaxTree(nums, left, maxIndex);
root->right = calMaxTree(nums, maxIndex + 1, right);
return root;
}
TreeNode* constructMaximumBinaryTree(vector<int>& nums) {
return calMaxTree(nums, 0, nums.size());
}
};
617.合并二叉树
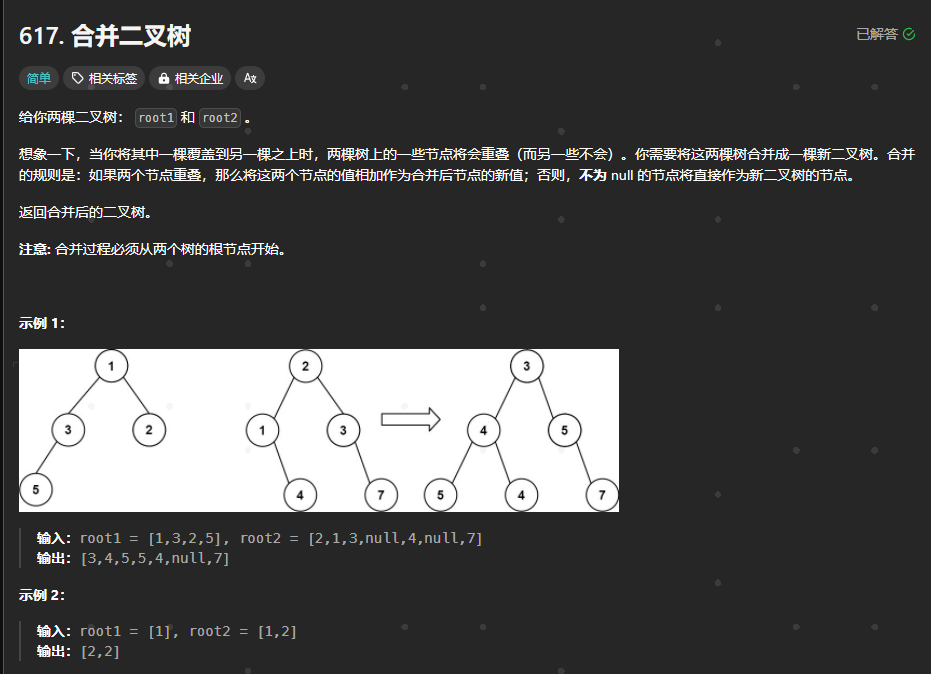
https://leetcode.cn/problems/merge-two-binary-trees/description/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* mergeTrees(TreeNode* root1, TreeNode* root2) {
if(root1==NULL) return root2;
if(root2==NULL) return root1;
root1->val += root2->val;
root1->left = mergeTrees(root1->left, root2->left);
root1->right = mergeTrees(root1->right, root2->right);
return root1;
}
};
700. 二叉搜索树的搜索
https://leetcode.cn/problems/search-in-a-binary-search-tree/description/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* searchBST(TreeNode* root, int val) {
//二叉搜索树 左小右大
while(root != NULL)
{
if(root->val > val) root = root->left;
else if(root->val < val) root = root->right;
else return root;
}
return NULL;
}
};
98.验证二叉搜索树
https://leetcode.cn/problems/validate-binary-search-tree/description/
class Solution {
public:
long long MaxvVal = LONG_MIN;
bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root) {
//搜索树的中序遍历肯定是递增序列!!!!
if(root == NULL) return true;
bool l = isValidBST(root->left);
if(MaxvVal < root->val) MaxvVal = root->val;
else return false;
bool r = isValidBST(root->right);
return l&&r;
}
};
530.二叉搜索树的最小绝对值差
https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-absolute-difference-in-bst/description/
class Solution {
public:
int res = INT_MAX;
TreeNode* pre = NULL;
void calDiff(TreeNode* cur){
if(cur == NULL) return;
calDiff(cur->left);
if(pre != NULL)
res = min(res, cur->val - pre->val);
pre = cur;
calDiff(cur->right);
}
int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode* root) {
calDiff(root);
return res;
}
};


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号