LeetCode链表专题(一)
链表简介:
定义:链表是一种物理存储单元上非连续、非顺序的存储结构;
组成:数据 + 指针(这个指针为指向下一个或者上一个链表节点),注意:各个节点的位置不是排好的,他们可能相隔甚远,但是有指针牵引着,不会失联;
优点:擅长插入和删除某个节点;
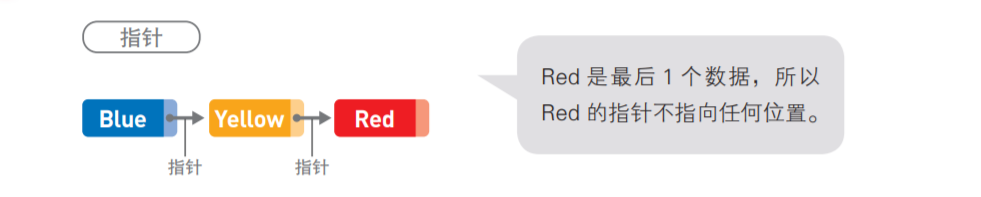
注:图片来自于《我的第一本算法书》,很适合纯小白作入门书籍;
单链表简单实现--java

1 import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; 2 3 /** 4 * @ClassName SingleLinkedList 5 * @Description 单链表的简单实现 6 * @Author peanut 7 * @DATE 2020/5/13 13:45 8 * @Version 1.0 9 */ 10 public class SingleLinkedList { 11 /** 12 * 链表节点个数,头节点 13 */ 14 private int size; 15 private Node head; 16 17 public SingleLinkedList() { 18 size = 0; 19 head = null; 20 } 21 22 /** 23 * 创建节点类 24 */ 25 private class Node { 26 private Object data; 27 private Node next; 28 29 public Node(Object data) { 30 this.data = data; 31 } 32 } 33 34 /** 35 * 在链表头添加元素 36 */ 37 public Object addHead(Object obj) { 38 Node newHead = new Node(obj); 39 if (size == 0) { 40 head = newHead; 41 } else { 42 newHead.next = head; 43 head = newHead; 44 } 45 size++; 46 return obj; 47 } 48 49 /** 50 * 在链表头删除元素 51 */ 52 public Object deleteHead() { 53 Object obj = head.data; 54 head = head.next; 55 size--; 56 return obj; 57 } 58 59 /** 60 * 查找指定元素,找到了返回节点Node,找不到返回null 61 */ 62 public Node find(Object obj) { 63 Node current = head; 64 int tempSize = size; 65 while (tempSize > 0) { 66 if (obj.equals(current.data)) { 67 return current; 68 } else { 69 current = current.next; 70 } 71 tempSize--; 72 } 73 return null; 74 } 75 76 77 /** 78 * 删除指定的元素,删除成功返回true 79 */ 80 public boolean delete (Object value) { 81 if (size == 0) { 82 return false; 83 } 84 Node current = head; 85 Node previous = head; 86 while (current.data != value) { 87 if (current.next == null) { 88 return false; 89 } else { 90 previous = current; 91 current = current.next; 92 } 93 } 94 //如果删除的节点是第一个节点 95 if (current == head) { 96 head = current.next; 97 size--; 98 } else { 99 previous.next = current.next; 100 size--; 101 } 102 return true; 103 } 104 105 public boolean isEmpty() { 106 return (size == 0); 107 } 108 109 public void display() { 110 if (size > 0) { 111 Node node = head; 112 int tempSize = size; 113 if (tempSize == 1) { 114 System.out.println("["+node.data+"]"); 115 return; 116 } 117 while (tempSize > 0) { 118 if (node.equals(head)) { 119 System.out.print("["+node.data+"->"); 120 } else if (node.next == null) { 121 System.out.print(node.data+"]"); 122 } else { 123 System.out.print(node.data+"->"); 124 } 125 node = node.next; 126 tempSize--; 127 } 128 129 System.out.println(); 130 } else { 131 System.out.println("[]"); 132 } 133 } 134 135 @Test 136 public void testSingleLinkedList() { 137 SingleLinkedList singleLinkedList = new SingleLinkedList(); 138 singleLinkedList.addHead("A"); 139 140 141 singleLinkedList.display(); 142 singleLinkedList.delete("A"); 143 singleLinkedList.display(); 144 145 singleLinkedList.addHead("B"); 146 System.out.println(singleLinkedList.find("B")); 147 } 148 }
双端链表简单实现--java,注意区分双端链表和双向链表

1 import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; 2 3 /** 4 * @ClassName SingleLinkedList 5 * @Description 单链表的简单实现 6 * @Author peanut 7 * @DATE 2020/5/13 13:45 8 * @Version 1.0 9 */ 10 public class DoublePointLinkedList { 11 /** 12 * 链表节点个数,头节点 13 */ 14 private int size; 15 private Node head; 16 private Node tail; 17 18 public DoublePointLinkedList() { 19 size = 0; 20 head = null; 21 tail = null; 22 } 23 24 /** 25 * 创建节点类 26 */ 27 private class Node { 28 private Object data; 29 private Node next; 30 31 public Node(Object data) { 32 this.data = data; 33 } 34 } 35 36 /** 37 * 在链表头添加元素 38 */ 39 public void addHead(Object data) { 40 Node node = new Node(data); 41 if (size == 0) { 42 head = node; 43 tail = node; 44 size++; 45 } else { 46 node.next = head; 47 head = node; 48 size++; 49 } 50 } 51 52 /** 53 * 在链表尾添加元素 54 */ 55 public void addTail(Object data) { 56 Node node = new Node(data); 57 if (size == 0) { 58 head = node; 59 tail = node; 60 size++; 61 } else { 62 tail.next = node; 63 tail = node; 64 size++; 65 } 66 } 67 68 69 /** 70 * 在链表头删除元素 71 */ 72 public boolean deleteHead() { 73 if (size == 0) { 74 return false; 75 } 76 if (head.next == null) { 77 head = null; 78 tail = null; 79 } else { 80 head = head.next; 81 } 82 size--; 83 return true; 84 } 85 86 public boolean isEmpty() { 87 return (size == 0); 88 } 89 90 public int getSize() { 91 return size; 92 } 93 94 /** 95 * 查找指定元素,找到了返回节点Node,找不到返回null 96 */ 97 public Node find(Object obj) { 98 Node current = head; 99 int tempSize = size; 100 while (tempSize > 0) { 101 if (obj.equals(current.data)) { 102 return current; 103 } else { 104 current = current.next; 105 } 106 tempSize--; 107 } 108 return null; 109 } 110 111 112 /** 113 * 删除指定的元素,删除成功返回true 114 */ 115 public boolean delete (Object value) { 116 if (size == 0) { 117 return false; 118 } 119 Node current = head; 120 Node previous = head; 121 while (current.data != value) { 122 if (current.next == null) { 123 return false; 124 } else { 125 previous = current; 126 current = current.next; 127 } 128 } 129 //如果删除的节点是第一个节点 130 if (current == head) { 131 head = current.next; 132 size--; 133 } else { 134 previous.next = current.next; 135 size--; 136 } 137 return true; 138 } 139 140 141 public void display() { 142 if (size > 0) { 143 Node node = head; 144 int tempSize = size; 145 if (tempSize == 1) { 146 System.out.println("["+node.data+"]"); 147 return; 148 } 149 while (tempSize > 0) { 150 if (node.equals(head)) { 151 System.out.print("["+node.data+"->"); 152 } else if (node.next == null) { 153 System.out.print(node.data+"]"); 154 } else { 155 System.out.print(node.data+"->"); 156 } 157 node = node.next; 158 tempSize--; 159 } 160 161 System.out.println(); 162 } else { 163 System.out.println("[]"); 164 } 165 } 166 167 @Test 168 public void testDoublePointLinkedList() { 169 DoublePointLinkedList doublePointLinkedList = new DoublePointLinkedList(); 170 doublePointLinkedList.addHead("A"); 171 172 173 } 174 }
有序链表简单实现--java

1 /** 2 * @ClassName OrderLinkedList 3 * @Description TODO 4 * @Author peanut 5 * @DATE 2020/5/13 15:00 6 * @Version 1.0 7 */ 8 public class OrderLinkedList { 9 private Node head; 10 11 private class Node { 12 private int data; 13 private Node next; 14 15 public Node(int data) { 16 this.data = data; 17 } 18 } 19 20 public OrderLinkedList() { 21 head = null; 22 } 23 24 public void insert(int value) { 25 Node node = new Node(value); 26 Node pre = null; 27 Node current = head; 28 while (current != null && value > current.data) { 29 pre = current; 30 current = current.next; 31 } 32 if (pre == null) { 33 head = node; 34 head.next = current; 35 } else { 36 pre.next = node; 37 node.next = current; 38 } 39 } 40 41 public void deleteHead() { 42 head = head.next; 43 } 44 45 public void display() { 46 Node current = head; 47 while (current != null) { 48 System.out.print(current.data + " "); 49 current = current.next; 50 } 51 System.out.println(""); 52 } 53 }
双向链表简单实现--java

1 /** 2 * @ClassName TwoWayLinkedList 3 * @Description TODO 4 * @Author peanut 5 * @DATE 2020/5/13 15:22 6 * @Version 1.0 7 */ 8 public class TwoWayLinkedList { 9 /** 10 * 链表节点个数,头节点 11 */ 12 private int size; 13 private Node head; 14 private Node tail; 15 16 private class Node { 17 private Object data; 18 private Node next; 19 private Node prev; 20 21 public Node(Object data) { 22 this.data = data; 23 } 24 } 25 26 public TwoWayLinkedList() { 27 size = 0; 28 head = null; 29 tail = null; 30 } 31 32 public void addHead(Object value) { 33 Node newNode = new Node(value); 34 if (size == 0) { 35 head = newNode; 36 tail = newNode; 37 size++; 38 } else { 39 head.prev = newNode; 40 newNode.next = head; 41 head = newNode; 42 size++; 43 } 44 } 45 46 public Node deleteHead() { 47 Node temp = head; 48 if (size != 0) { 49 head = head.next; 50 head.prev = null; 51 size--; 52 } 53 return temp; 54 } 55 56 public Node deleteTail() { 57 Node temp = tail; 58 if (size != 0) { 59 tail = tail.prev; 60 tail.next = null; 61 size--; 62 } 63 return temp; 64 } 65 public int getSize() { 66 return size; 67 } 68 69 public boolean isEmpty() { 70 return (size == 0); 71 } 72 73 public void display() { 74 if (size > 0) { 75 Node node = head; 76 int tempSize = size; 77 if (tempSize == 1) { 78 System.out.println("[" + node.data + "]"); 79 return; 80 } 81 while (tempSize > 0) { 82 if (node.equals(head)) { 83 System.out.print("[" + node.data + "->"); 84 } else if (node.next == null){ 85 System.out.print(node.data+"->"); 86 } else { 87 System.out.println( node.data + "]"); 88 } 89 node = node.next; 90 tempSize--; 91 } 92 System.out.println(); 93 } else { 94 System.out.println("[]"); 95 } 96 } 97 }
================================================================================================
2. Add Two Numbers 难度:Medium

1 /** 2 * Definition for singly-linked list. 3 * public class ListNode { 4 * int val; 5 * ListNode next; 6 * ListNode() {} 7 * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } 8 * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } 9 * } 10 */ 11 12 /** 13 * 1.首先用两个链表存储2个数, 243,564 14 * 2.首先循环第一个链表,先取出最低位,保留至val,然后进入第二个链表,取出最低为,与 15 * val 相加,结果保留至val; 16 * 3. 然后验证val是否大于10,若大于10,则进位,进位结果保留至ex,留着下一次循环加在 val上,此次结果保留至节点node 17 * 4. 往复循环,直至两个链表的数都循环完了 18 * 5. 不要忘记最后的进位也要加上; 19 */ 20 class Solution { 21 public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) { 22 int ex = 0; 23 ListNode head = null, tail = null; 24 while (l1 != null || l2 != null) { // 保证两个链表不同时为空 25 // 如果上一次结果大于10,则将进位数加载这一次,循环如此 26 int val = ex; 27 if (l1 != null) { 28 val += l1.val; 29 l1 = l1.next; 30 } 31 32 if (l2 != null) { 33 val += l2.val; 34 l2 = l2.next; 35 } 36 ex = val / 10; 37 ListNode node = new ListNode(val % 10); 38 if (head == null) { // 此时为空链表,给头节点和为节点赋值 39 head = node; 40 tail = node; 41 } else { 42 tail.next = node; 43 // 链表后移 44 tail = tail.next; 45 } 46 } 47 if (ex > 0) { 48 tail.next = new ListNode(ex); 49 } 50 return head; 51 } 52 }
====================================================================================
19. Remove Nth Node From End of List 难度:Medium

1 /** 2 * Definition for singly-linked list. 3 * public class ListNode { 4 * int val; 5 * ListNode next; 6 * ListNode() {} 7 * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } 8 * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } 9 * } 10 */ 11 12 /** 13 * 定义连个指针,一个快指针,一个慢指针,快指针先走n步,然后和慢指针一起走到链表尾部, 14 * 此时慢指针.next 是正在要删除节点位置,将慢指针.next 指向 慢指针.next.next 15 * 然后返回head 16 * 此题依旧是单链表的应用 17 */ 18 class Solution { 19 public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) { 20 ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0); 21 dummy.next = head; 22 ListNode fast = dummy; 23 ListNode low = dummy; 24 25 for (int i = 1; i <= n + 1; i++) { 26 fast = fast.next; 27 } 28 29 30 while (fast != null) { 31 fast = fast.next; 32 low = low.next; 33 } 34 low.next = low.next.next; 35 return dummy.next; 36 } 37 }
======================================================================================
21. Merge Two Sorted Lists 难度:Easy

1 /** 2 * Definition for singly-linked list. 3 * public class ListNode { 4 * int val; 5 * ListNode next; 6 * ListNode() {} 7 * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } 8 * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } 9 * } 10 */ 11 /** 12 * 先检验 l1, l2 是否有空链表,若有,然后直接返回不空的 13 * 创建一个新链表 14 * 比较两个链表节点值大小,将小的先接入之前创建的链表, 15 * 当其中某个链表被循环到头了,则直接将较长链表的剩余部分直接接入之前创建的链表 16 */ 17 18 class Solution { 19 public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) { 20 if (l1 == null || l2 == null) { 21 return (l1 != null ? l1 : l2); 22 } 23 24 ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0); 25 ListNode cur = dummy; 26 while (l1 != null && l2 != null) { 27 if (l1.val < l2.val) { 28 cur.next = l1; 29 l1 = l1.next; 30 } else { 31 cur.next = l2; 32 l2 = l2.next; 33 } 34 cur = cur.next; 35 } 36 cur.next = l1 != null ? l1 : l2; 37 return dummy.next; 38 } 39 }
=========================================================================================
23. Merge k Sorted Lists 难度:Hard
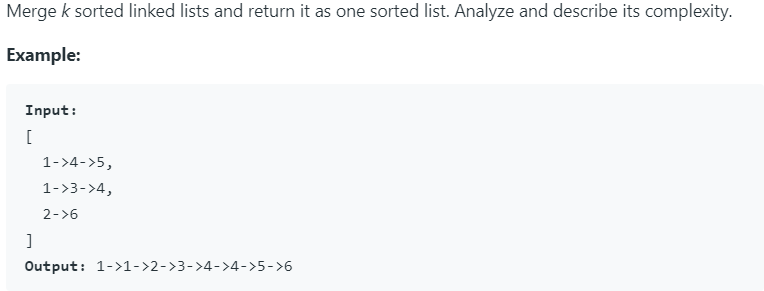

1 /** 2 * Definition for singly-linked list. 3 * public class ListNode { 4 * int val; 5 * ListNode next; 6 * ListNode() {} 7 * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } 8 * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } 9 * } 10 */ 11 class Solution { 12 public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) { 13 if (lists == null || lists.length == 0) { 14 return null; 15 } 16 /** 17 * 因为是ListNode,所以需要自定义比较函数,我们需要将小的值放在前面,下面为lambda表达式 18 * (a,b) -> a.val-b.val表示如果a.val > b.val时,正好会反过来; 19 * public ListNode compare(ListNode a, ListNode b) { 20 * return a.val - b.val; // 重载优先级使其变为小根堆 21 * } 22 * 这是容易看懂的方式 23 * public PriorityQueue(int initialCapacity,Comparator<? super E> comparator) {这是源码的函数声明} 24 */ 25 PriorityQueue<ListNode> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<ListNode>(lists.length ,(a,b) -> a.val-b.val); 26 27 for (ListNode node : lists) { // 将每个链表头节点放到priorityQueue 28 if (node != null) { 29 priorityQueue.offer(node); 30 } 31 } 32 ListNode head = new ListNode(0); 33 ListNode tail = head; 34 35 36 /** 37 * 记得上面将几个链表的头节点放到 pq中,比较完一轮,poll出一个最小的 38 * 然后将poll的节点的下一个节点放到pq中(如果存在的话);就这样一点点比较完所有链表的所有节点 39 */ 40 while (!priorityQueue.isEmpty()) { 41 tail.next = priorityQueue.poll(); 42 tail = tail.next; 43 if (tail.next != null) { 44 priorityQueue.offer(tail.next); 45 } 46 } 47 return head.next; 48 } 49 }
=========================================================================================
24. Swap Nodes in Pairs 难度:Medium
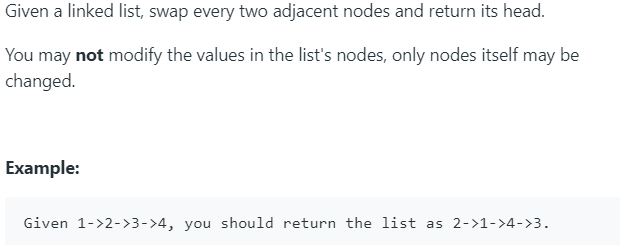

1 /** 2 * Definition for singly-linked list. 3 * public class ListNode { 4 * int val; 5 * ListNode next; 6 * ListNode() {} 7 * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } 8 * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } 9 * } 10 */ 11 12 class Solution { 13 public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) { 14 // // 在链表上创建临时节点,用于移动,应为原头节节点位置不能动 15 // ListNode dummy = head; 16 // while (itr != null) { 17 // // 交换相邻节点的值 18 // int temp = dummy.val; 19 // dummy.val = dummy.next.val; 20 // dummy.next.val = temp; 21 // dummy = dummy.next.next; 22 // } 23 // return head; 24 // 这种方法虽然可以通过测试,但是违背了题目原则 25 // =========================================================================================================== 26 // 下面这种方法是创建一个新链表,将交换过的节点放到新链表中 27 if( head == null || head.next == null) 28 return head; 29 ListNode firstNode = null; 30 ListNode firstNodeLast = null; 31 while( head != null && head.next != null) { 32 ListNode temp = head; 33 head = head.next; 34 temp.next = head.next; 35 head.next = temp; 36 if( firstNode == null) { 37 firstNode = head; 38 firstNodeLast = firstNode.next; 39 } else { 40 firstNodeLast.next = head; 41 firstNodeLast = firstNodeLast.next.next; 42 } 43 head = head.next.next; 44 } 45 return firstNode; 46 47 } 48 }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号