Mybatis Insert、update、delete流程
上文mybatis源码简书我们讲到sqlsession中通过executor来执行sql,我们接着往下看
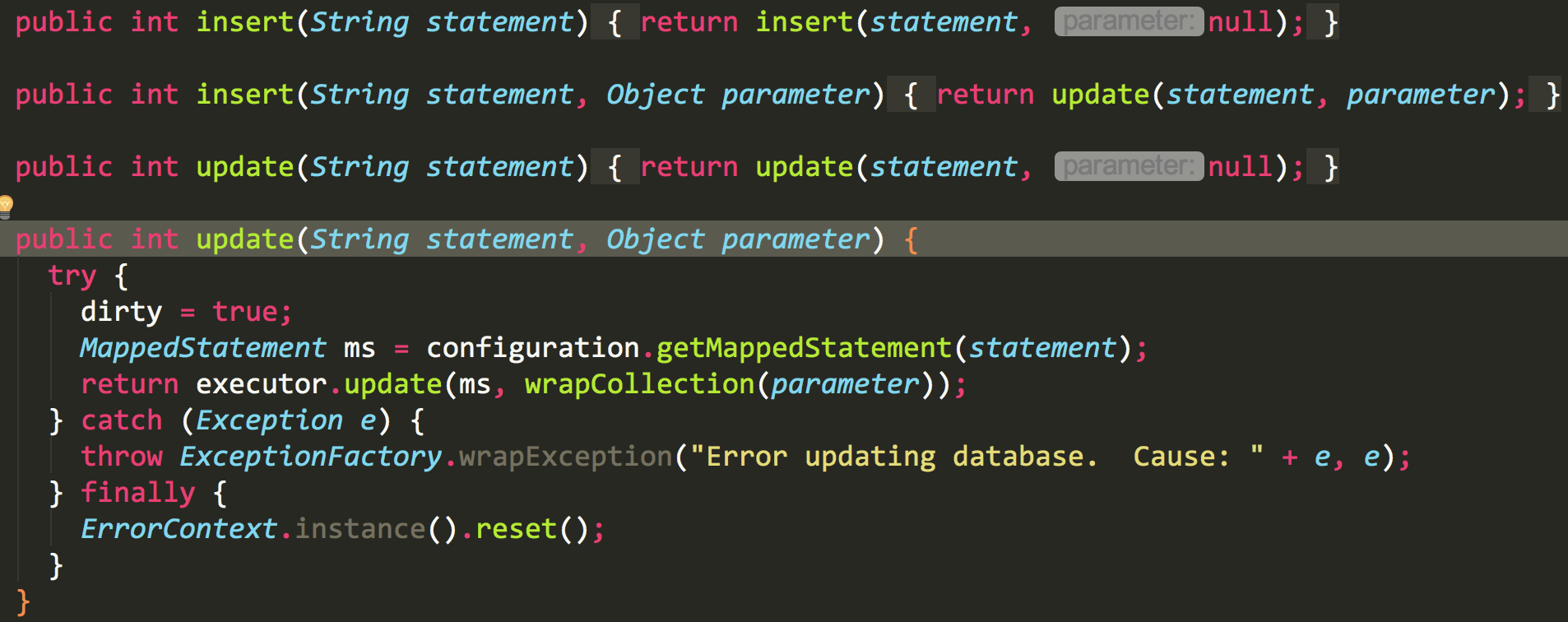
update方法点进去,我们进到baseexecutor

这里我们看到 clearLocalCache 方法,可见每次更新都会清除缓存
我们再看到doUpdate
1 public int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException { 2 Statement stmt = null; 3 try { 4 Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration(); 5 StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this, ms, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT, null, null); 6 stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog()); 7 return handler.update(stmt); 8 } finally { 9 closeStatement(stmt); 10 } 11 }
先看第5行,生成一个 StatementHandler,StatementHandler是mybatis4大对象之一,负责处理Mybatis与JDBC之间Statement的交互。
我们再看下newStatementHandler,

这里又看 RoutingStatementHandler,先不管,再点进去,会发现会有不同类型的StatementHandler
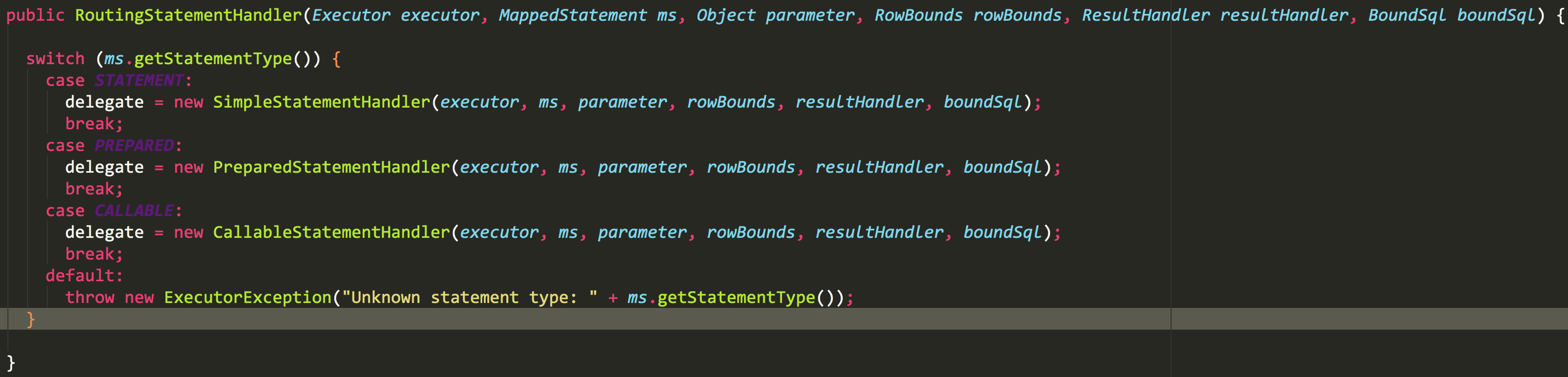
SimpleStatementHandler,这个很简单了,就是对应我们JDBC中常用的Statement接口,用于简单SQL的处理;
PreparedStatementHandler,这个对应JDBC中的PreparedStatement,预编译SQL的接口;
CallableStatementHandler,这个对应JDBC中CallableStatement,用于执行存储过程相关的接口;
RoutingStatementHandler,这个接口是以上三个接口的路由,没有实际操作,只是负责上面三个StatementHandler的创建及调用。
这几个StatementHandler他有共同的构造器,都在BaseStatementHandler
1 protected BaseStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) { 2 this.configuration = mappedStatement.getConfiguration(); 3 this.executor = executor; 4 this.mappedStatement = mappedStatement; 5 this.rowBounds = rowBounds; 6 7 this.typeHandlerRegistry = configuration.getTypeHandlerRegistry(); 8 this.objectFactory = configuration.getObjectFactory(); 9 10 if (boundSql == null) { // issue #435, get the key before calculating the statement 11 generateKeys(parameterObject); 12 boundSql = mappedStatement.getBoundSql(parameterObject); 13 } 14 15 this.boundSql = boundSql; 16 17 this.parameterHandler = configuration.newParameterHandler(mappedStatement, parameterObject, boundSql); 18 this.resultSetHandler = configuration.newResultSetHandler(executor, mappedStatement, rowBounds, parameterHandler, resultHandler, boundSql); 19 }
这里顺便创建了parameterHandler和 resultSetHandler
parameterHandler的作用就是进行参数预编译设置,resultSetHandler封装我们得到的结果。
public int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException { 2 Statement stmt = null; 3 try { 4 Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration(); 5 StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this, ms, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT, null, null); 6 stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog()); 7 return handler.update(stmt); 8 } finally { 9 closeStatement(stmt); 10 } 11 }
再看第六行,我们在生成StatementHandler,开始执行prepareStatement
1 private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException { 2 Statement stmt; 3 Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog); 4 //调用StatementHandler.prepare 5 stmt = handler.prepare(connection); 6 //调用StatementHandler.parameterize 7 handler.parameterize(stmt); 8 return stmt; 9 }
我们看到prepare方法,生成statement,用过jdbc的都知道,Statement对象主要用于将 SQL 语句发送到数据库中,执行对数据库的数据的检索或者更新
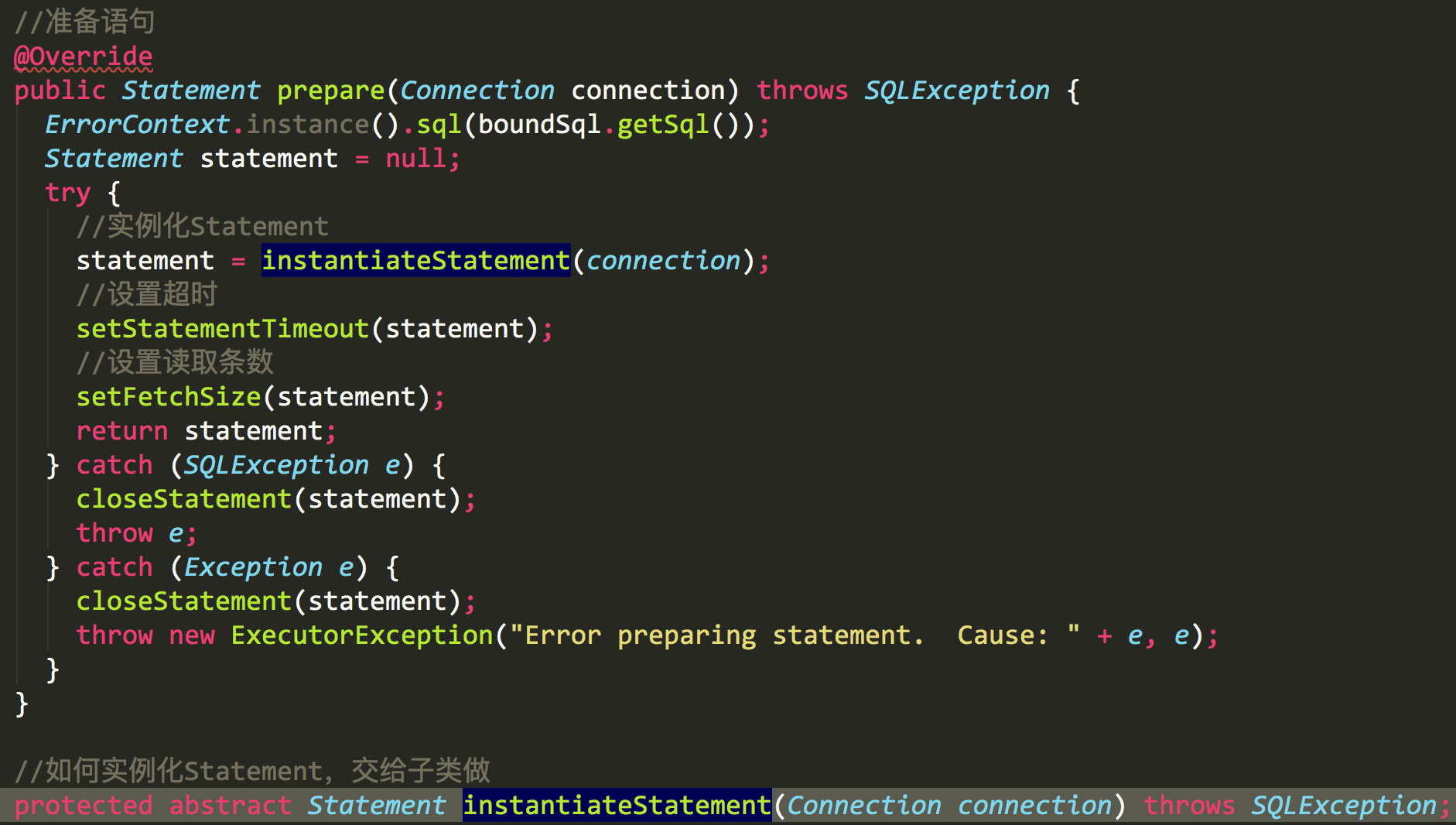
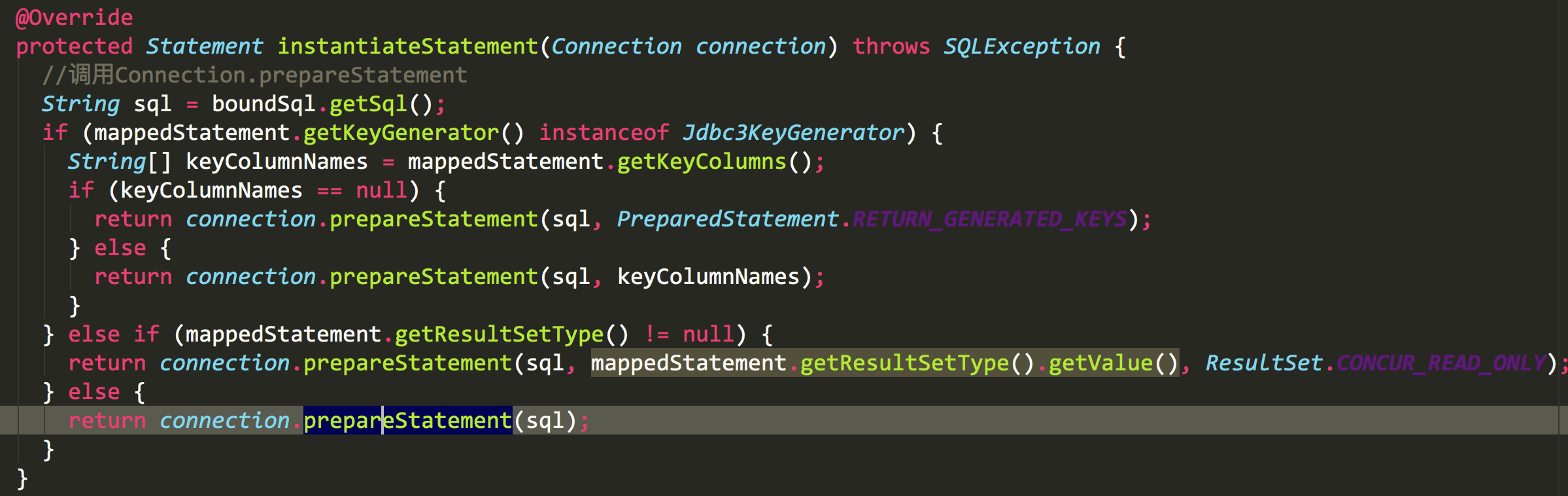
生成好statement后,我们再看下第7行
public int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException { 2 Statement stmt = null; 3 try { 4 Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration(); 5 StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this, ms, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT, null, null); 6 stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog()); 7 return handler.update(stmt); 8 } finally { 9 closeStatement(stmt); 10 } 11 }
这里就是真正的执行sql的地方。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号