字节输出流写多个字节的方法以及续写和换行
字节输出流写多个字节的方法
public void write(byte[] b ) :将b.length字节从指定的字节数组写入此输出流。
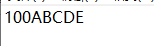
public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //1.创建一个FileOutputStream对象,构造方法中传递写入数据的目的地 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("G:\\44.txt"); //2.调用FileOutputStream对象中的方法write,把数据写入到文件中 fos.write(49); fos.write(48); fos.write(48); /* public void write(byte[] b ) :将b.length字节从指定的字节数组写入此输出流。 一次写多个字节; 如果写的第一个字节是正数,那么显示的时候会查询ASCII表 如果写的第一个字节是负数,那么第一个字节会和第二个字节,两个字节组成一个中文显示,查询系统默认码表(GBK) */ byte[] bytes ={65,66,67,68,69};//ABCDE //byte[] bytes ={-65,-66,-67,68,69};//烤紻E fos.write(bytes); //3.释放资源(流使用会占用一定的内存,使用完毕要把内存清空,提高程序的效率) fos.close(); } }
文件中的内容:
public void write(byte[] b,int off,int len) :从指定的字节数组写入len字节,从偏移量off开始输出到此输出流。
/* public void write(byte[] b,int off,int len) :把字节数组的一部分写入到文件中 int off:数组的开始索引 int length:写几个字节 */ fos.write(bytes,1,2);//BC
写入字符串的方法:可以使用String类中的方法把字符串,转换为字节数组
/* 写入字符串的方法:可以使用String类中的方法把字符串,转换为字节数组 byte[] getBytes() 把字符串转换为字节数组 */ byte[] bytes2 = "您好".getBytes(); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes2)); //[-26, -126, -88, -27, -91, -67] fos.write(bytes2);
文件中的内容:
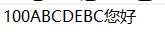
字节输出流的续写和换行
追加写/续写:
使用2个参数的构造方法
FileOutputStream(String name,boolean append)创建一个向具有指定name的文件中写入数据的输出文件流。
FileOutputStream(File file,boolean append)创建一个向指定File对象表示的文件中写入数据的文件输出流。
参数:
String name,File file:写入数据的目的地
boolean append:追加写开关
true:创建对象不会覆盖源文件,继续在文件的末尾追加写数据
false:创建一个新文件,覆盖源文件
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("G:\\44.txt",true); fos.write("你好".getBytes()); fos.close(); }
文件中内容:

写换行:
写换行符号:
windows:\r\n
linux:/n
mac:/r
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("G:\\44.txt",true); for (int i = 0; i <10 ; i++) { fos.write("您好".getBytes()); fos.write("\r\n".getBytes()); } fos.close(); }
文件中内容:




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号