HashSet存储自定义元素类型以及LinkedHashSet集合
HashSet存储自定义元素类型
set集合保存元素唯一:
存储的元素(String,Integer,Person...)必须重写hashCode方法和equals方法
要求:
同名同年龄的人就是同一个人,只能存储一次
public class Person { private String name; private int age; Getter and Setter 有参无参 toString }
public static void main(String[] args) { HashSet<Person> set = new HashSet<>(); Person p1 = new Person("张三", 18); Person p2 = new Person("张三", 18); Person p3 = new Person("张三", 19); System.out.println(p1.hashCode()); System.out.println(p2.hashCode()); set.add(p1); set.add(p2); set.add(p3); System.out.println(set); }
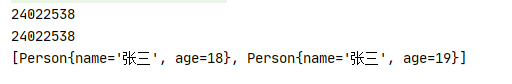
在Person类中没有重写hashCode()和equals()方法,p1和p2的姓名和年龄相同,但是哈希值不同

在Person类中重写hashCode()和equals()方法
public class Person { private String name; private int age; @Override public boolean equals(Object o) { if (this == o) return true; if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false; Person person = (Person) o; return age == person.age && Objects.equals(name, person.name); } @Override public int hashCode() { return Objects.hash(name, age); } Getter and Setter 有参无参 toString }
public static void main(String[] args) { HashSet<Person> set = new HashSet<>(); Person p1 = new Person("张三", 18); Person p2 = new Person("张三", 18); Person p3 = new Person("张三", 19); System.out.println(p1.hashCode()); System.out.println(p2.hashCode()); set.add(p1); set.add(p2); set.add(p3); System.out.println(set); }
重写hashCode()和equals()方法后,姓名相同和年龄相同的哈希值相同,并且也没有添加到set集合中
LinkedHashSet集合
LinkedHashSet集合继承自HashSet集合
LinkedHashse集合特点:
底层是一个哈希表(数组+链表/红黑树)+链表;多了一条链表(记录元素的存储顺序),保证元素有序
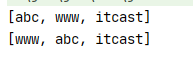
public static void main(String[] args) { HashSet<String> set = new HashSet<>(); set.add("www"); set.add("abc"); set.add("abc"); set.add("itcast"); System.out.println(set);//无序,不允许重复 LinkedHashSet<String> linked = new LinkedHashSet<>(); linked.add("www"); linked.add("abc"); linked.add("abc"); linked.add("itcast"); System.out.println(linked);//有序,不允许重复 }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号