捕捉异常和异常捕捉机制
捕捉异常
int[] arr = new int[10];
arr[10] = 10;
System.out.println("a");
在这段代码中,我们定义了数组的长度为10,那么他的索引最多只能到9,在我们给索引为10的下标进行赋值时,那它就是错误的
运行结果:
这个就是一个异常,那么发生了异常我们就可以使用try-catch来进行捕捉异常
int[] arr = new int[10];
try {
arr[10] = 10;
System.out.println("a");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("b");
}
catch后面跟发生异常要执行的语句,如果try后面代码块中的代码发生了异常,那么就会立即执行catch中的代码。
当catch中的代码执行完成后会继续向下执行,不会再玩会try中执行未执行的语句
异常捕捉机制
格式:
try{
//程序代码块
}catch(Type1 id1){
//处理Type1异常的代码
}catch(Type2 id2){
//处理Type2异常的代码
}catch(Type3 id3){
//处理Type3异常的代码
}
try后面可以跟多个catch处理不同异常的解决方案
public static void f(){ int[] arr = new int[10]; arr[10] = 10; } public static void main(String[] args) { try { f(); } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("b"); } System.out.println("main"); }
在这段代码中,我们在try中调用了函数,他会通过函数中抛出的异常去执行相匹配的catch
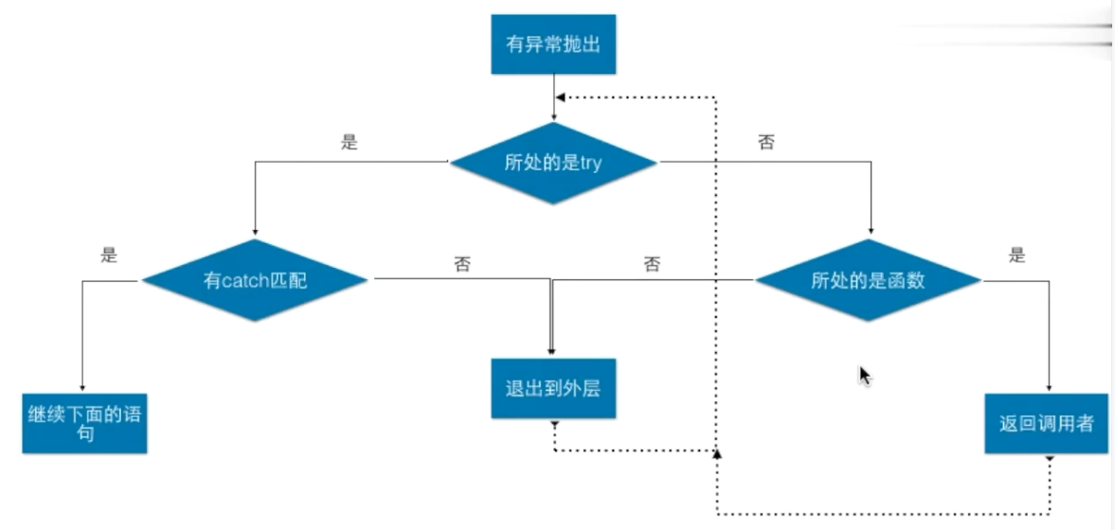
异常捕捉机制:
![]()




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号