决策树模型系列——10、XGBoost使用案例
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_california_housing, load_digits
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, mean_squared_error, accuracy_score
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import xgboost as xgb
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from hyperopt import hp, fmin, tpe, Trials
1、XGBoost原生接口
官方文档:Python API Reference — xgboost 2.0.3 documentation
二分类
X, y = load_digits(n_class=2, return_X_y=True)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2)
# 训练集和测试集数据
dtrain = xgb.DMatrix(X_train, y_train)
dtest = xgb.DMatrix(X_test, y_test)
# 模型参数设置
params = {
"max_depth": 2,
"objective": "binary:logistic",
"eval_metric": ["error"],
}
num_booster_round = 50
# 模型训练
dst = xgb.train(
params, dtrain,
num_booster_round,
evals=[(dtrain, 'train'), (dtest, 'test')], # 验证数据集
early_stopping_rounds = 5
)
# 预测结果
preds = bst.predict(dtest)
# 预测准确度
print('--'*25)
print(f"预测准确度:{accuracy_score(y_test, preds):.3f}")
# 混淆矩阵
print('--'*25)
print("混淆矩阵:")
print(confusion_matrix(y_test, preds))
[0] train-error:0.00347 test-error:0.00000
[1] train-error:0.00347 test-error:0.00000
[2] train-error:0.00000 test-error:0.01389
[3] train-error:0.00000 test-error:0.01389
[4] train-error:0.00000 test-error:0.00000
--------------------------------------------------
预测准确度:1.000
--------------------------------------------------
混淆矩阵:
[[36 0]
[ 0 36]]
多分类
X, y = load_digits(n_class=10, return_X_y=True)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2)
# 训练数据和测试数据
dtrain = xgb.DMatrix(X_train, y_train)
dtest = xgb.DMatrix(X_test, y_test)
# 模型参数设置
params = {
"booster": "gbtree",
"verbosity": 1,
"eta": 0.8,
"gamma":0,
"max_depth": 2,
"subsample": 1,
"colsample_bytree": 1,
"colsample_bylevel": 1,
"colsample_bynode": 1,
"lambda": 1,
"alpha": 0,
"tree_method": "hist",
"max_bin": 256,
"objective": "multi:softmax",
"eval_metric": ["merror"],
"num_class": 10 #多分类时需要设置num_class = 标签类别个数
}
num_booster_round = 200
# 模型训练
print("训练过程...")
bst = xgb.train(
params,
dtrain,
num_booster_round,
evals=[(dtrain, 'train'),(dtest, 'test')], # early_stopping_rounds的验证集
early_stopping_rounds = 10
)
# 预测结果(测试集)
preds = bst.predict(dtest, iteration_range=(0, bst.best_iteration + 1))
# 预测准确度
print('--'*25)
print(f"预测准确度:{accuracy_score(y_test, preds):.3f}")
# 混淆矩阵
print('--'*25)
print("混淆矩阵:")
print(confusion_matrix(y_test, preds))
训练过程...
[0] train-merror:0.19068 test-merror:0.26111
[1] train-merror:0.14475 test-merror:0.19167
[2] train-merror:0.09673 test-merror:0.16389
[3] train-merror:0.07168 test-merror:0.13333
[4] train-merror:0.04593 test-merror:0.11667
[5] train-merror:0.03271 test-merror:0.10000
[6] train-merror:0.01740 test-merror:0.08611
[7] train-merror:0.01322 test-merror:0.07500
[8] train-merror:0.01044 test-merror:0.07222
[9] train-merror:0.00696 test-merror:0.06944
[10] train-merror:0.00348 test-merror:0.05833
[11] train-merror:0.00278 test-merror:0.05833
[12] train-merror:0.00139 test-merror:0.05556
[13] train-merror:0.00070 test-merror:0.06111
[14] train-merror:0.00070 test-merror:0.05833
[15] train-merror:0.00070 test-merror:0.05833
[16] train-merror:0.00000 test-merror:0.06111
[17] train-merror:0.00070 test-merror:0.06111
[18] train-merror:0.00000 test-merror:0.05833
[19] train-merror:0.00000 test-merror:0.06111
[20] train-merror:0.00000 test-merror:0.05833
[21] train-merror:0.00000 test-merror:0.05833
[22] train-merror:0.00000 test-merror:0.05833
--------------------------------------------------
预测准确度:0.944
--------------------------------------------------
混淆矩阵:
[[37 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]
[ 0 33 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 2]
[ 1 1 34 2 0 0 0 0 0 1]
[ 0 0 0 30 0 0 0 1 0 0]
[ 0 1 0 0 36 0 0 0 0 0]
[ 0 0 0 0 0 35 0 0 1 2]
[ 0 0 0 0 0 0 45 0 0 0]
[ 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 33 0 1]
[ 0 2 0 1 0 0 0 1 31 0]
[ 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 26]]
回归
# 导入数据集,并拆分为训练集和测试集
X, y = fetch_california_housing(return_X_y=True)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, shuffle=True)
# 构造训练集和测试集
dtrain = xgb.DMatrix(X_train, y_train)
dtest = xgb.DMatrix(X_test, y_test)
# 参数设置(使用hyperopt搜索)
space = {
"eta": hp.uniform("eta", 0.01, 0.1),
"gamma": hp.choice("gamma", [0, 1, 2, 3]),
"max_depth": hp.choice("max_depth", [1, 6, 12]),
}
num_boost_round = 1000
# 目标函数
def objective(params):
bst = xgb.train(
params,dtrain,
num_boost_round=num_boost_round,
evals=[(dtrain, 'train'), (dtest, 'test')], # 验证数据集
early_stopping_rounds = 5
)
preds = bst.predict(dtest)
mse = mean_squared_error(y_test, preds)
return mse
# 运行Hyperopt
trials = Trials()
best = fmin(fn=objective,
space=space,
algo=tpe.suggest,
max_evals=50,
trials=trials
)
print(f"Best-Hyper: {best}")
100%|███████████████████████████████████████████████| 50/50 [22:22<00:00, 26.84s/trial, best loss: 0.22942034509119466]
Best-Hyper: {'eta': 0.08393671868894494, 'gamma': 0, 'max_depth': 1}
cv_result = xgb.cv(best, dtrain, num_boost_round=1000)
# bst = xgb.train(
# best,dtrain,
# num_boost_round=num_boost_round,
# evals=[(dtrain, 'train'), (dtest, 'test')], # 验证数据集
# early_stopping_rounds = 5
# )
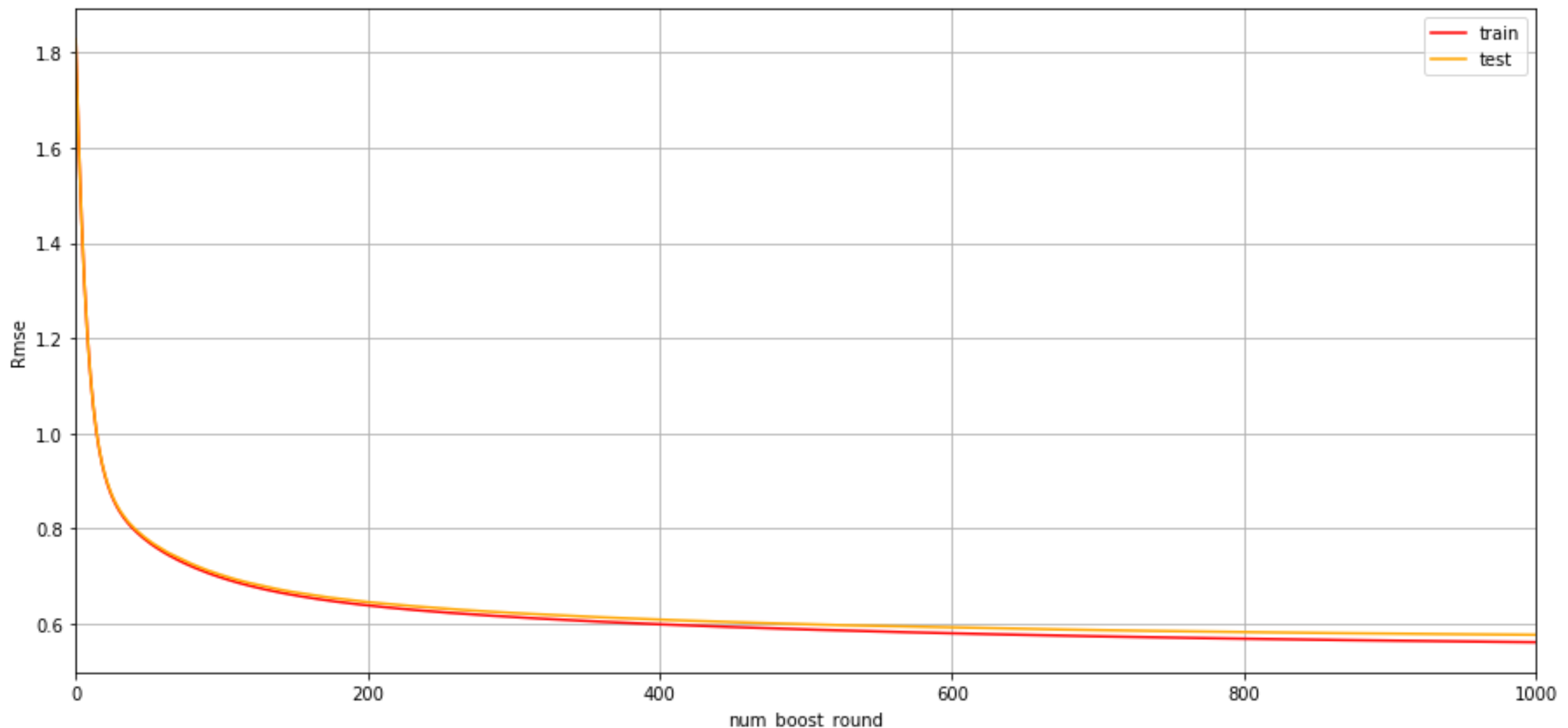
# 绘制误差曲线
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 7))
plt.grid()
plt.plot(range(0, len(cv_result['train-rmse-mean'])),
cv_result['train-rmse-mean'], c='red', label='train')
plt.plot(range(0, len(cv_result['test-rmse-mean'])),
cv_result['test-rmse-mean'], c='orange', label='test')
plt.xlabel('num_boost_round')
plt.ylabel('Rmse')
plt.xlim((0, num_boost_round))
plt.legend()
plt.show()
2、sklearn API
官方文档:Using the Scikit-Learn Estimator Interface — xgboost 2.1.0-dev documentation
二分类
X, y = load_digits(n_class=2, return_X_y=True)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2)
# 参数设置
bst_sk = xgb.XGBClassifier(
n_estimators = 50,
max_depth = 2,
objective = 'binary:logistic',
eval_metric = "error",
early_stopping_rounds = 5
)
# 模型训练
bst_sk.fit(X_train, y_train, eval_set=[(X_test, y_test)])
# 预测结果
preds_sk = bst_sk.predict(X_test)
# 预测准确度
print('--'*25)
print(f"预测准确度:{accuracy_score(y_test, preds_sk):.3f}")
# 混淆矩阵
print('--'*25)
print("混淆矩阵:")
print(confusion_matrix(y_test, preds_sk))
[0] validation_0-error:0.00000
[1] validation_0-error:0.00000
[2] validation_0-error:0.01389
[3] validation_0-error:0.01389
[4] validation_0-error:0.00000
[5] validation_0-error:0.01389
--------------------------------------------------
预测准确度:1.000
--------------------------------------------------
混淆矩阵:
[[36 0]
[ 0 36]]
多分类
X, y = load_digits(n_class=10, return_X_y=True)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2)
# 训练模型
bst_sk = xgb.XGBClassifier(
n_estimators = 100,
max_depth = 2,
learning_rate = 0.8,
verbosity = 0,
objective = "multi:softmax",
booster = 'gbtree',
tree_method = 'hist',
max_bins = 256,
gamma = 0,
subsample = 1,
colsample_bytree = 1,
colsample_bylevel = 1,
colsample_bynode = 1,
reg_alpha = 0,
reg_lambda = 1,
eval_metric = "merror",
early_stopping_rounds = 10
)
bst_sk.fit(X_train, y_train, eval_set=[(X_test, y_test)])
# 预测结果
preds_sk = bst_sk.predict(X_test, iteration_range=(0, bst_sk.best_iteration + 1))
# 预测准确度
print('--'*25)
print(f"预测准确度:{accuracy_score(y_test, preds_sk):.3f}")
# 混淆矩阵
print('--'*25)
print("混淆矩阵:")
print(confusion_matrix(y_test, preds_sk))
[0] validation_0-merror:0.26111
[1] validation_0-merror:0.19167
[2] validation_0-merror:0.16389
[3] validation_0-merror:0.13333
[4] validation_0-merror:0.11667
[5] validation_0-merror:0.10000
[6] validation_0-merror:0.08611
[7] validation_0-merror:0.07500
[8] validation_0-merror:0.07222
[9] validation_0-merror:0.06944
[10] validation_0-merror:0.05833
[11] validation_0-merror:0.05833
[12] validation_0-merror:0.05556
[13] validation_0-merror:0.06111
[14] validation_0-merror:0.05833
[15] validation_0-merror:0.05833
[16] validation_0-merror:0.06111
[17] validation_0-merror:0.06111
[18] validation_0-merror:0.05833
[19] validation_0-merror:0.06111
[20] validation_0-merror:0.05833
[21] validation_0-merror:0.05833
[22] validation_0-merror:0.05833
--------------------------------------------------
预测准确度:0.944
--------------------------------------------------
混淆矩阵:
[[37 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]
[ 0 33 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 2]
[ 1 1 34 2 0 0 0 0 0 1]
[ 0 0 0 30 0 0 0 1 0 0]
[ 0 1 0 0 36 0 0 0 0 0]
[ 0 0 0 0 0 35 0 0 1 2]
[ 0 0 0 0 0 0 45 0 0 0]
[ 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 33 0 1]
[ 0 2 0 1 0 0 0 1 31 0]
[ 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 26]]
回归
# 导入数据集,并拆分为训练集和测试集
X, y = fetch_california_housing(return_X_y=True)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, shuffle=True)
# 训练模型
model = xgb.XGBRegressor(
n_estimators = 1000,
learing_rate = 0.1,
gamma = 0,
max_depth = 1,
booster = 'gbtree',
objective = 'reg:squarederror',
eval_metric = ['rmse'],
early_stopping_rounds = 10,
verbosity = 1
)
model.fit(X_train, y_train, eval_set=[(X_train, y_train), (X_test, y_test)])
# 训练和测试结果
train_rmse = model.evals_result_['validation_0']['rmse']
test_rmse = model.evals_result_['validation_1']['rmse']
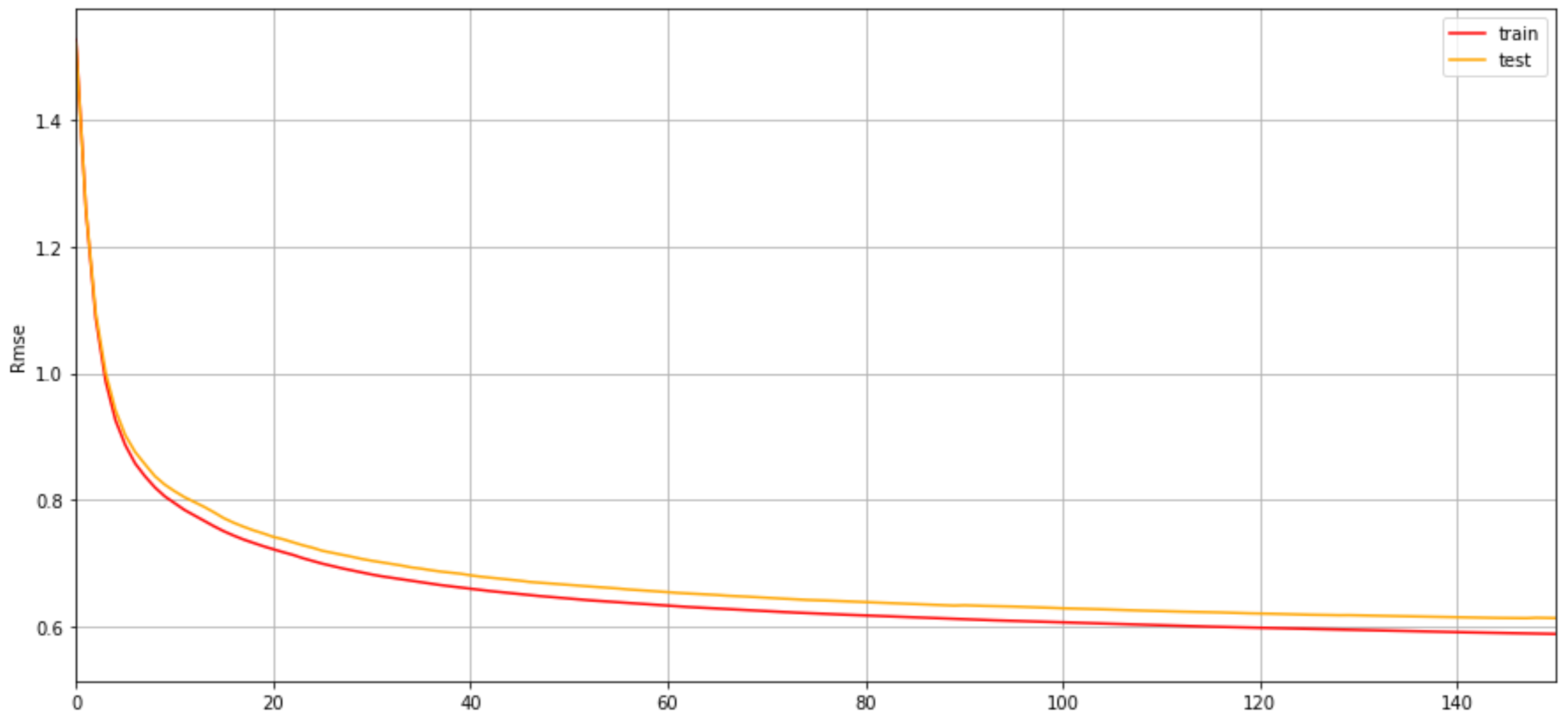
# 绘制误差曲线
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 7))
plt.grid()
plt.plot(range(0, len(train_rmse)),
train_rmse, c='red', label='train')
plt.plot(range(0, len(test_rmse)),
test_rmse, c='orange', label='test')
plt.xlabel('Steps')
plt.ylabel('Rmse')
plt.xlim((0, 150))
plt.legend()
plt.show()








 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号