决策树模型系列——6、集成学习技术框架_Stacking算法
在scikit-learn中提供了两种统一的Stacking methods,分类器StackingClassifier和回归器StackingRegressor,初级学习器estimators和次级学习器final_estimator可以是用户自己定义的,可以是决策树、KNN、SVM、深度学习网络等,最后通过Stacking方法将各初级学习器的输出结果作为次级学习的输入,最后由次级学习器输出预测结果。
Scikit-learn使用案例
import numpy as np
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_openml
from sklearn.utils import shuffle
from sklearn.compose import make_column_selector, make_column_transformer
from sklearn.impute import SimpleImputer
from sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline
from sklearn.preprocessing import OrdinalEncoder, OneHotEncoder, StandardScaler
from sklearn.linear_model import LassoCV, RidgeCV
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor, HistGradientBoostingRegressor, StackingRegressor
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_validate, cross_val_predict
import time
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def load_ames_housing():
"""从OpenML提取Ames Housing数据集
(该数据集有1460个样本,80个特征)"""
df = fetch_openml(name='house_prices', as_frame=True)
X = df.data #特征值
y = df.target #目标值
# 提取其中20个比较感兴趣的特征数据
features = [
"YrSold",
"HeatingQC",
"Street",
"YearRemodAdd",
"Heating",
"MasVnrType",
"BsmtUnfSF",
"Foundation",
"MasVnrArea",
"MSSubClass",
"ExterQual",
"Condition2",
"GarageCars",
"GarageType",
"OverallQual",
"TotalBsmtSF",
"BsmtFinSF1",
"HouseStyle",
"MiscFeature",
"MoSold",
]
X = X.loc[:, features]
X, y = shuffle(X, y, random_state=0) #随机打乱数据
# 提取其中600个数据
X = X.iloc[:600]
y = y.iloc[:600]
return X, np.log(y)
# 使用pipeline预处理数据
# 分类类型选择器
cat_selector = make_column_selector(dtype_include=object)
# 数值类型选择器
num_selector = make_column_selector(dtype_include=np.number)
# 树模型的数据预处理转换器
# 分类型变量用顺序型编码OrdinalEncoder
cat_tree_processor = OrdinalEncoder(
handle_unknown = "use_encoded_value",
unknown_value = -1
)
# 连续型变量设置一个简单处理器SimpleImputer进行处理
num_tree_processor = SimpleImputer(
strategy = 'mean',
add_indicator = True
)
# 变量转换器
tree_preprocessor = make_column_transformer(
(num_tree_processor, num_selector),
(cat_tree_processor, cat_selector)
)
print(tree_preprocessor)

# 线性模型的数据预处理转换器
cat_linear_processor = OneHotEncoder(handle_unknown='ignore')
num_linear_processor = make_pipeline(
StandardScaler(),
SimpleImputer(strategy='mean', add_indicator=True)
)
linear_preprocessor = make_column_transformer(
(num_linear_processor, num_selector),
(cat_linear_processor, cat_selector)
)
print(linear_preprocessor)

# LassoCV模型
lasso_pipeline = make_pipeline(linear_preprocessor, LassoCV())
print(lasso_pipeline)

# RF
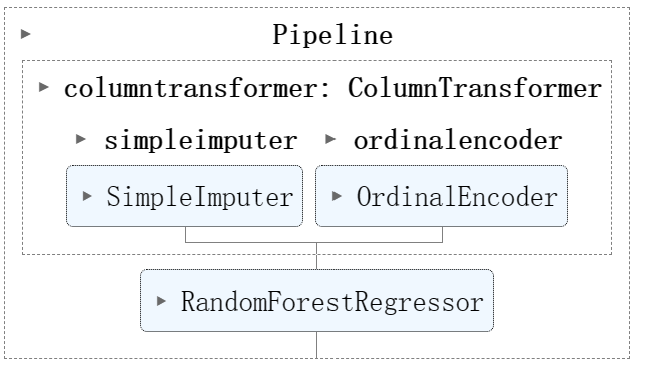
rf_pipeline = make_pipeline(
tree_preprocessor,
RandomForestRegressor(random_state=42)
)
print(rf_pipeline)
#HGBR
gbdt_pipeline = make_pipeline(
tree_preprocessor,
HistGradientBoostingRegressor(random_state=0)
)
print(gbdt_pipeline)

# Stacking
estimators = [
('Random Forest', rf_pipeline),
('Lasso', lasso_pipeline),
('Gradient Boosting', gbdt_pipeline)
]
stacking_regressor = StackingRegressor(
estimators = estimators,
final_estimator = RidgeCV()
)
print(stacking_regressor)

def plot_regression_results(ax, y_true, y_pred, title, scores, elapsed_time):
"""实际值和预测值的散点对比图"""
ax.plot(
[y_true.min(), y_true.max()],
[y_true.min(), y_true.max()],
'--r', linewidth=2
)
ax.scatter(y_true, y_pred, alpha=0.2)
ax.spines['top'].set_visible(False)
ax.spines['right'].set_visible(False)
ax.get_xaxis().tick_bottom()
ax.get_yaxis().tick_left()
ax.spines['left'].set_position(('outward', 10))
ax.spines['bottom'].set_position(('outward', 10))
ax.set_xlim([y_true.min(), y_true.max()])
ax.set_ylim([y_true.min(), y_true.max()])
ax.set_xlabel('Measured')
ax.set_ylabel('Predicted')
extra = plt.Rectangle(
(0, 0), 0, 0, fc='w', fill=False,
edgecolor='none', linewidth=0
)
ax.legend([extra], [scores], loc='upper left')
title = title + '\n Evaluation in {:.2f} seconds'.format(elapsed_time)
ax.set_title(title)
fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(12, 6))
axes = np.ravel(axes)
for ax, (name, est) in zip(axes, estimators + [('Stacking Regressor', stacking_regressor)]):
start_time = time.time()
score = cross_validate(
est, X, y, scoring=['r2', 'neg_mean_absolute_error'],
n_jobs=-1, verbose=0
)
elapsed_time = time.time() - start_time
y_pred = cross_val_predict(est, X, y, n_jobs=-1, verbose=0)
plot_regression_results(
ax, y, y_pred, name,
(f"$R^2={np.mean(score['test_r2']):.2f} \pm {np.std(score['test_r2']):.2f}$"
+ "\n" + f"$MAE={-np.mean(score['test_neg_mean_absolute_error']):.2f} \pm {np.std(score['test_neg_mean_absolute_error']):.2f}$"),
elapsed_time,
)
plt.suptitle('Single predictions versus stacked predictors')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.subplots_adjust(top=0.9)
plt.show()

$ $
参考资料





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号