非线性逻辑回归
非线性逻辑回归的代码:
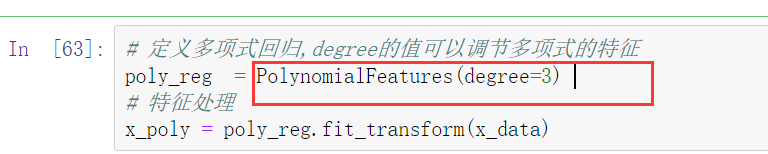
关于 PolynomialFeatures
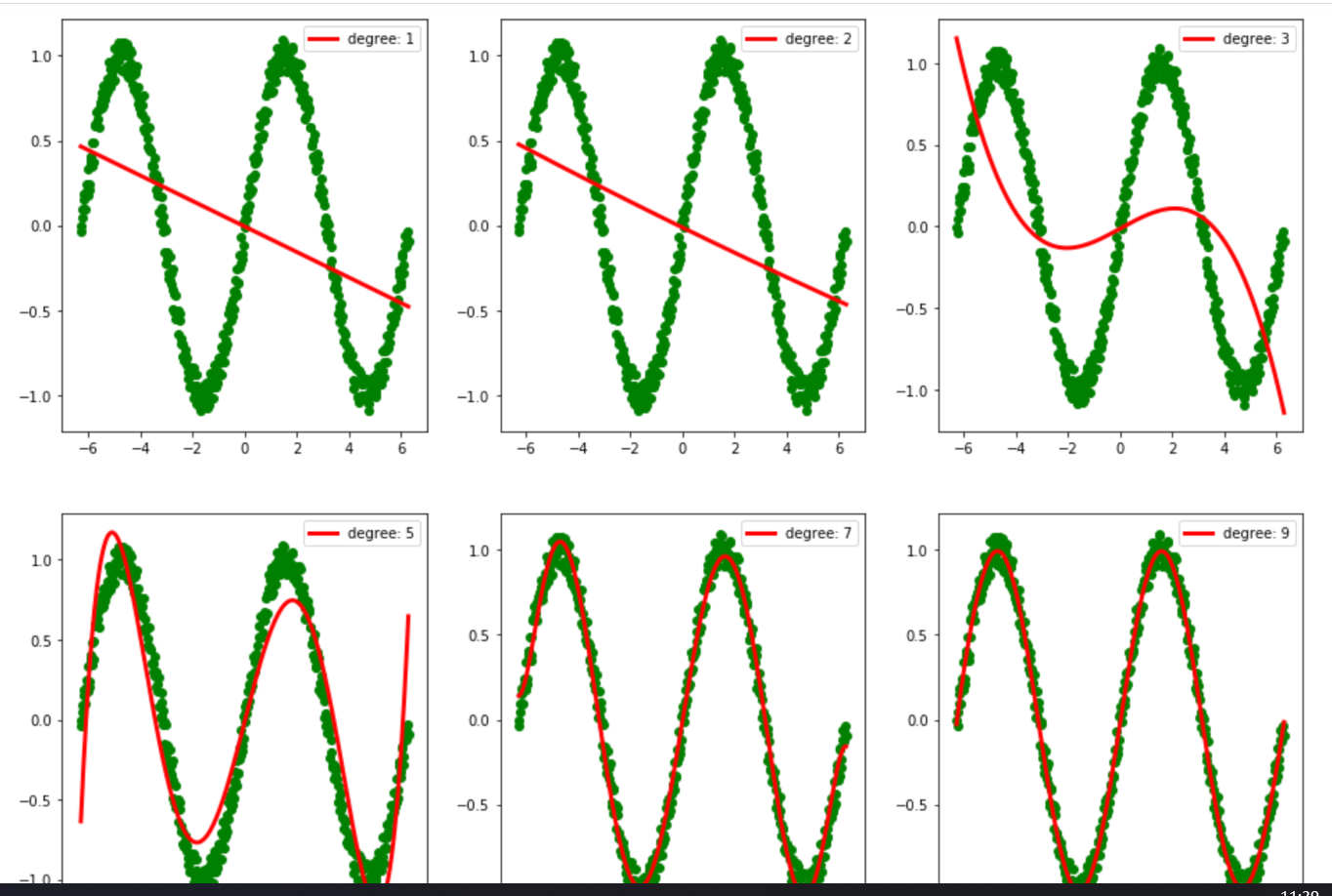
PolynomialFeatures 多项式特征,设置不同的degree,可以变的更拟合,如图
scale = False
数据是否需要标准化
preprocessing.scale(X)直接标准化数据X
np.r—和np.c
# np.r_按row来组合array,
# np.c_按colunm来组合array
#>>> a = np.array([1,2,3])
# >>> b = np.array([5,2,5])
# >>> np.r_[a,b]
# array([1, 2, 3, 5, 2, 5])
# >>> np.c_[a,b]
# array([[1, 5],
# [2, 2],
# [3, 5]])
# >>> np.c_[a,[0,0,0],b]
# array([[1, 0, 5],
# [2, 0, 2],
# [3, 0, 5]])
xx.ravel()
xx.ravel() :表示把一个矩阵行优先展成一个向量.跟flatten一样.
np.meshgrid()函数
X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y) 代表的是将x中每一个数据和y中每一个数据组合生成很多点,然后将这些点的x坐标放入到X中,y坐标放入Y中,并且相应位置是对应的

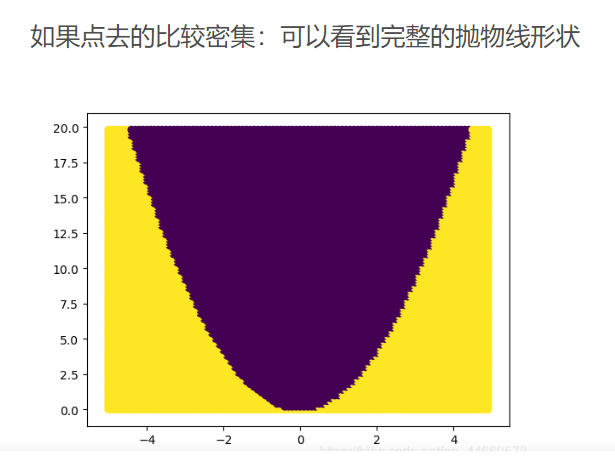
plt.contourf
plt.contourf用来画出不同分类的边界线
return [1 if x >= 0.5 else 0 for x in sigmoid(xMat*ws)]
是先进行for循环,再进行判断后赋值
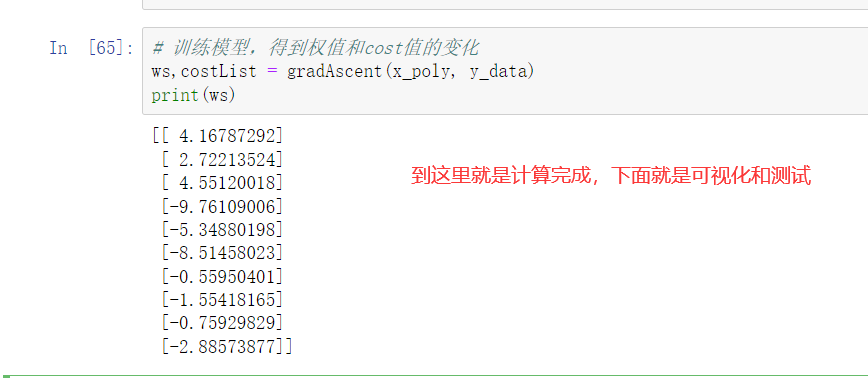
重点:

https://github.com/xinxuann/MachineLearningNote/blob/main/逻辑回归/梯度下降法-非线性逻辑回归.ipynb
https://github.com/xinxuann/MachineLearningNote/blob/main/逻辑回归/sklearn-非线性逻辑回归.ipynb



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号