java数组类型(一维数组和二维数组)
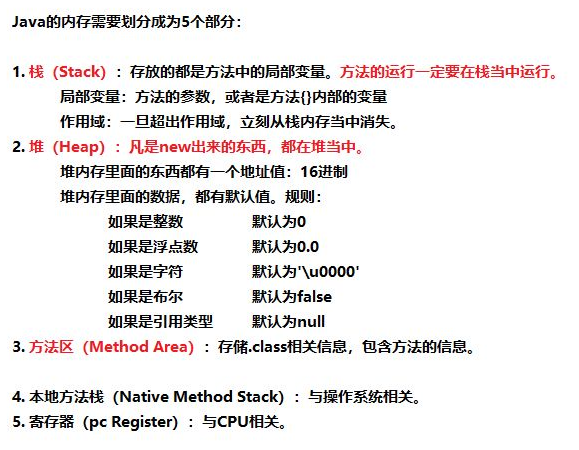
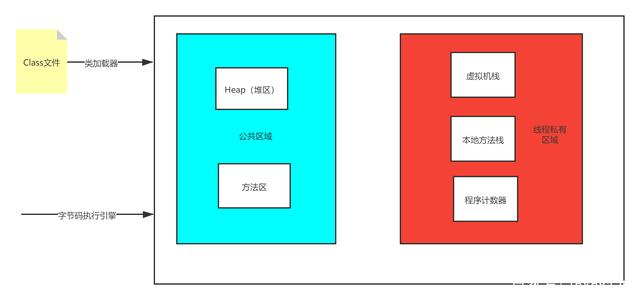
一,java虚拟机内存的划分
内存在计算机中是一个比较重要的原件,他为数据从硬盘传输到cup起到了承上启下的作用。我们编写的程序是放在硬盘中,要运行程序就要放在内存条中,程序运行结束后就会去空内存。
为了提高运行效率,java虚拟机运行程序时,对内存空间进行了分配和管理。
二,一维数组定义及其操作
当我们要储存大量数据时,例如50个学生的考试成绩。这时我们用java的基本数据类型来储存这些数据时要定义50个,这样不仅麻烦,还造成内存的浪费。因此我们可以使用一种容器来进行储存。将所有成绩全部储存到一个容器中,统一操作。
容器:将多个数据存储到一起,期中的每个数据称为容器的元素。
java数组:在保持存储的数据的数据类型的一致的前提下,数组接收存储数据长度固定的容器且该容器的长度是固定的,不能进行修改。
一维数组的创建方式(动态和静态)
动态初始化(指定长度):在创建数组的时候,直接指定数组当中的数据元素个数。
格式: 数组存储的数据类型 [ ] 数组名字 = new 数组存储的数据类型 [ 长度 ];
代码示例:
package cn.itcate.day4demo; public class Demo01Array { public static void main(String[] args) { // 动态初始化 int[] arrayA = new int[300]; double[] arrayB = new double[10]; String[] arrayC = new String[5]; } }
注意:
左侧数据类型:也就是数组当中保存的数据,全都是统一的什么类型
左侧的中括号:代表我是一个数组
左侧数组名称:给数组取一个名字
右侧的new:代表创建数组的动作
右侧数据类型:必须和左边的数据类型保持一致
右侧中括号的长度:也就是数组当中,到底可以保存多少个数据,是一个int数字
静态初始化(指定内容):在创建数组的时候,不直接指定数据个数多少,而是直接将具体的数据内容进行指定。
格式一: 数据类型 [ ] 数组名 = new 数据类型 [ ] {元素1,元素2,元素3...};
代码示例:
package cn.itcate.day4demo; public class Demo02Array { public static void main(String[] args) { // 整数数组 int[] arrayA = new int[] {1,2,3,4,5}; // 字符串数组 String[] arrayB = new String[] {"Hello", "World", "Python", "Java"}; } }
格式二: 数据类型 [ ] 数组名 = {元素1,元素2,元素3...};
代码示例:
package cn.itcate.day4demo; public class Demo03Array { public static void main(String[] args) { // 整数数组 int[] arrayA = {1,2,3,4,5}; // 字符串数组 String[] arrayB = {"Hello", "World", "Java"}; } }
建议:如果不确定数组当中的具体内容,用动态初始化;否则,已经确定了具体的内容,用静态初始化。
一维数组的内存解析图
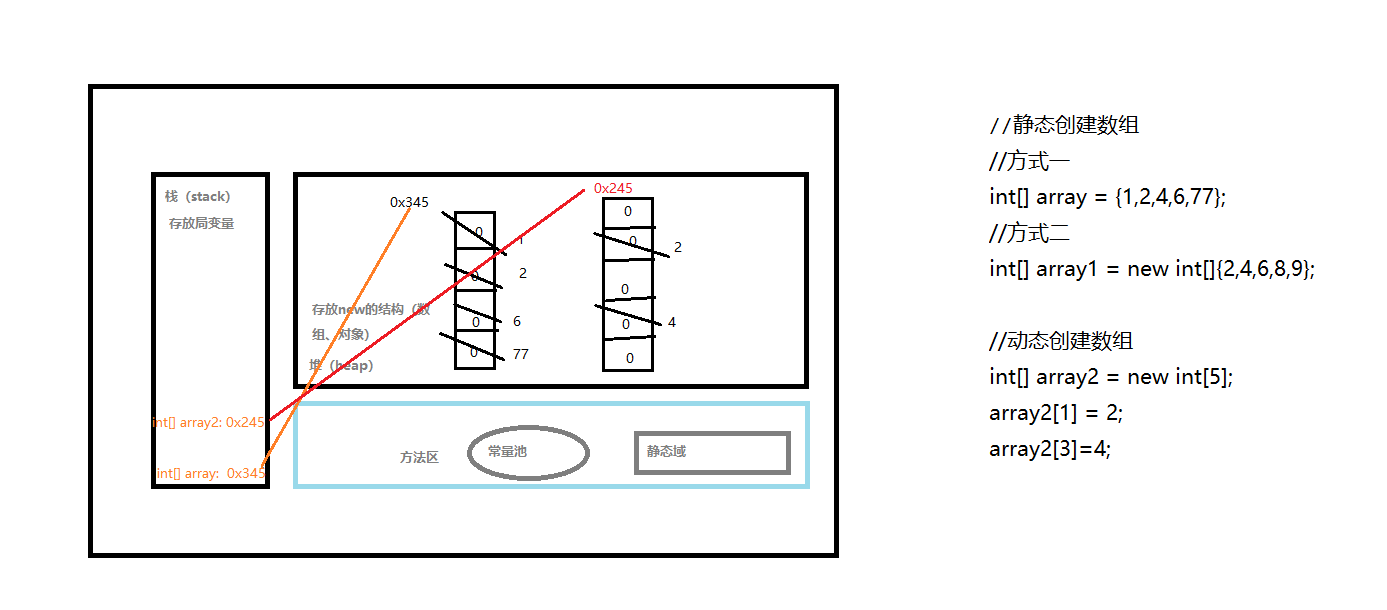
一维数组的访问
数组的索引:存储的到数组的数据都是从0开始自动编号的,这些编号就成为数组的索引。通过索引能访问到数组里面的元素。
格式: 数组名【索引值】
代码如下:
package cn.itcate.day4demo; public class Demo04ArrayUse { public static void main(String[] args) { // 定义一个整数数组 int[] arrayA = new int[] {10, 20, 30, 40, 50}; System.out.println(arrayA); // 数组的索引 System.out.println(arrayA[0]);// 10 System.out.println(arrayA[1]);// 20 System.out.println(arrayA[2]);//30 System.out.println(arrayA[3]);//40 System.out.println(arrayA[4]);//50 // 将一个索引值赋值给一个变量 int num = arrayA[2]; System.out.println(num);// 20 } }
数组的长度属性: 数组名.length -------》 得到最大索引值为:数组名.length-1
代码示例:
package cn.itcate.day4demo; public class Demo05ArrayUse { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = new int[] {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; System.out.println(arr.length);// 5 } }
修改数组中的元素: 数组名[索引] = 数值
代码如下:
package cn.itcate.day4demo; public class Demo06ArrayUse { public static void main(String[] args) { // 定义int类型数组 int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; // 为0索引元素赋值为10 System.out.println(arr[0]); arr[0] = 10; int i = arr[0]; System.out.println(i); System.out.println(arr[0]); } }
三,二维数组定义及其操作
二维数组定义:一维数组里面元素可以是基本数据类型,也可以是引用类型。当一维数组里面的元素是一个一维数组,就形成了二维数组。(一维数组的元素是一个数组)
二维数组的创建方式
动态创建格式: 数组存储的数据类型 [ ][ ] 数组名字 = new 数组存储的数据类型 [ 长度 ][长度 ]或 数组存储的数据类型 [ ][ ] 数组名字 = new 数组存储的数据类型 [ 长度 ][];
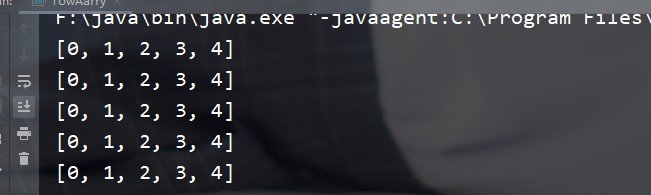
public class TowAarry { public static void main(String[] args){ //动态创建一个二维数组 int[][] array = new int[5][5]; //给二维数组赋值 for(int i=0;i<array.length;i++){ for(int j=0;j<array[i].length;j++){ array[i][j] = j; } } //查看结果 for(int i=0;i<array.length;i++){ System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array[i])); } } }
结果:
静态创建格式: 数组存储的数据类型 [ ][ ] 数组名字 = new 数组存储的数据类型 [ ][ ]{{},{},{}}或 数组存储的数据类型 [ ][ ] 数组名字 = new 数组存储的数据类型 [ ][{},{},{}];
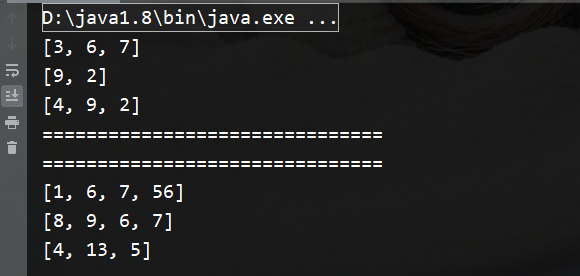
public class ArrayTest { public static void main(String[] args){ //静态创建二维数组 //方式一 int[][] array = {{3,6,7},{9,2},{4,9,2}}; for(int i=0;i < array.length;i++){ System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array[i])); } System.out.println("==============================="); System.out.println("==============================="); //方式二 int[][] array1 = new int[][]{{1,6,7,56},{8,9,6,7},{4,13,5}}; for(int i=0;i<array1.length;i++){ System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array1[i])); } } }
结果:
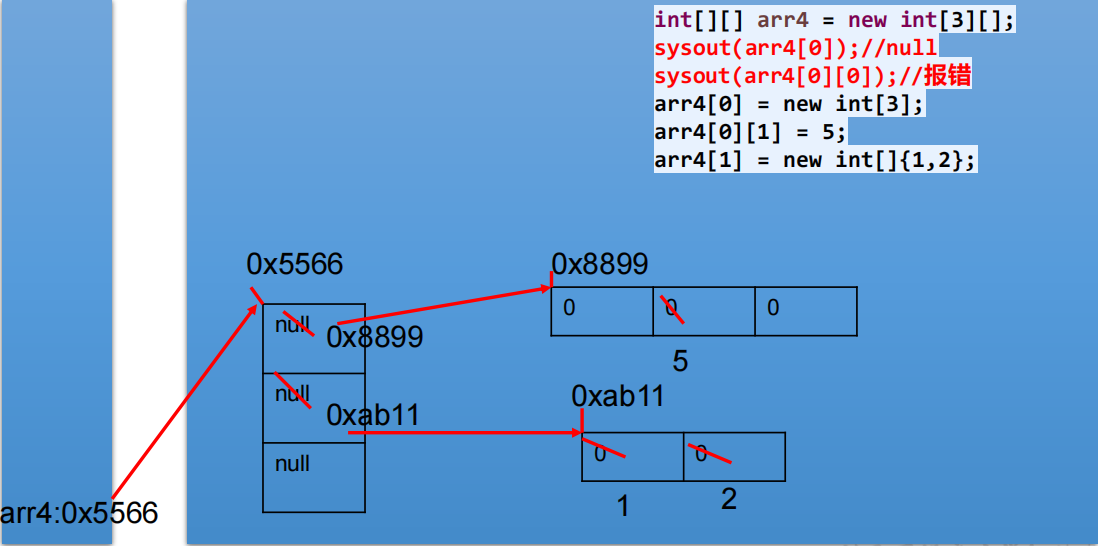
二维数组的内存解析图
二维数组的索引
格式: 数组名【索引值】【索引值】
代码如下:
public class ArrayTest { public static void main(String[] args){ //静态创建二维数组 //方式一 int[][] array = {{3,6,7},{9,2},{4,9,2}}; for(int i=0;i < array.length;i++){ System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array[i])); } //二维数组访问 //获取二行第一列的元素 System.out.println(array[1][0]); //9 //获取三行第三列的元素 System.out.println(array[2][2]); //2 } }
二维数组的长度属性
代码示例:
import java.util.Arrays; public class ArrayTest { public static void main(String[] args){ //静态创建二维数组 //方式一 int[][] array = {{3,6,7},{9,2},{4,9,2}}; for(int i=0;i < array.length;i++){ System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array[i])); } //二维数长度 System.out.println(array.length); //3 System.out.println(array[1].length); //2 } }
修改二维数组中的元素: 数组名[索引][索引] = 数值
代码如下:
public class ArrayTest { public static void main(String[] args){ //静态创建二维数组 //方式一 int[][] array = {{3,6,7},{9,2},{4,9,2}}; for(int i=0;i < array.length;i++){ System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array[i])); } //二维数组赋值 //将第二行第一列赋值为18 array[1][0] = 18; for(int i=0;i < array.length;i++){ System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array[i])); } //[3, 6, 7] //[18, 2] //[4, 9, 2] } }
四,数组常见异常
数组越界异常
public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = {1,2,3}; System.out.println(arr[3]); }
创建数组,赋值3个元素,数组的索引就是0,1,2,没有3索引,因此我们不能访问数组中不存在的索引,程序运
行后,将会抛出 ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException 数组越界异常。在开发中,数组的越界异常是不能出现的,一
旦出现了,就必须要修改我们编写的代码。
数组空指针异常
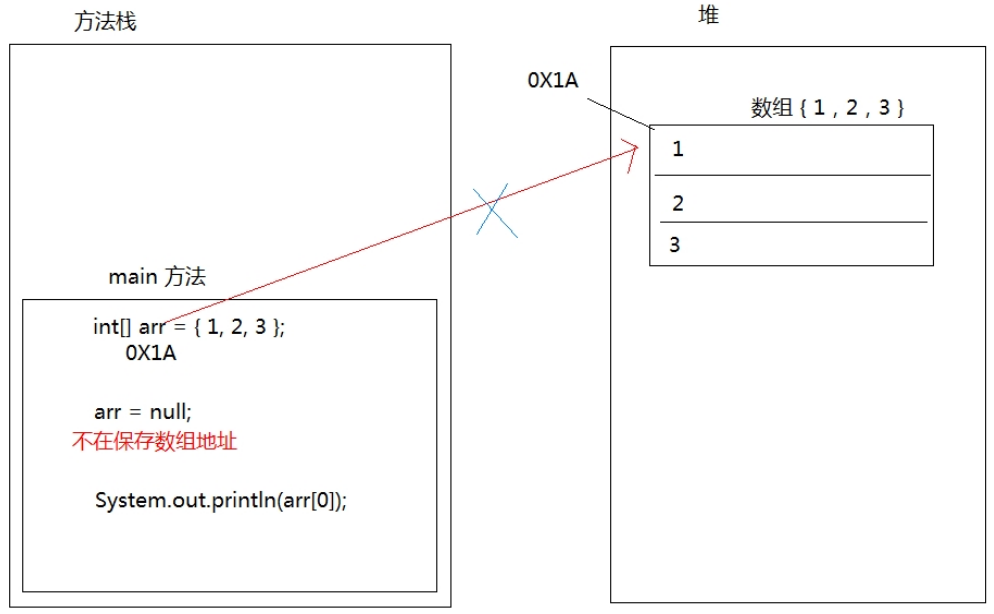
public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = {1,2,3}; arr = null; System.out.println(arr[0]); }
arr = null 这行代码,意味着变量arr将不会在保存数组的内存地址,也就不允许再操作数组了,因此运行的时候
会抛出 NullPointerException 空指针异常。在开发中,数组的越界异常是不能出现的,一旦出现了,就必须要修
改我们编写的代码。
在内存中的表现:
四,数组常见算法

1 public class ArrayTest1 { 2 public static void main(String[] args){ 3 /* 4 * 创建一个长度为6的int型数组,要求取值为1-30,同时元素值各不相同 5 * */ 6 7 //方法一 8 //定义一个长度为的数组 9 int[] array = new int[6]; 10 for(int i=0;i<array.length;i++){ 11 //取值为1-30 [1,31) 12 array[i] = (int)(Math.random()*30+1); 13 //元素值各不相同 14 //定义是否相同flag,ture为相同,false为不相同 15 boolean flag = false; 16 while (true){ 17 for(int j=0;j<i;j++){ 18 if(array[i]==array[j]){ 19 flag = true; 20 break; 21 } 22 } 23 //如果相等重新赋值 24 if(flag){ 25 array[i] = (int)(Math.random()*30+1); 26 flag=false; 27 continue; 28 } 29 break; 30 } 31 } 32 //方法二 33 //定义一个长度为的数组 34 int[] array1 = new int[6]; 35 for(int i=0;i<array1.length;i++){ 36 //取值为1-30 [1,31) 37 array1[i] = (int)(Math.random()*30+1); 38 //循环比较,如果后面元素和前面元素相同,重新赋值进行比较 39 for(int j=0;j<i;j++){ 40 if(array1[i]==array1[j]){ 41 i--; 42 break; 43 } 44 } 45 } 46 for(int i=0;i<array1.length;i++){ 47 System.out.println(array1[i]); 48 } 49 } 50 }
二、使用二维数组打印一个 10 行杨辉三角。

1 public class YangHui { 2 public static void main(String[] args){ 3 //定义一个10行二维数组 4 int[][] yh = new int[10][]; 5 6 //给二维数组赋值 7 for(int i=0;i<yh.length;i++){ 8 //第一行有 1 个元素, 第 n 行有 n 个元素 9 yh[i] = new int[i+1]; 10 //每一行的第一个元素和最后一个元素都是 1 11 yh[i][0]=yh[i][i]=1; 12 //从第三行开始, 对于非第一个元素和最后一个元素的元素 13 if(i>1){ 14 for(int j=1;j<yh[i].length-1;j++){ 15 yh[i][j] = yh[i-1][j-1]+yh[i-1][j]; 16 } 17 } 18 } 19 20 for(int i=0;i<yh.length;i++){ 21 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(yh[i])); 22 } 23 } 24 }

1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 //定义一个一维数组 3 int[] array = {45,67,23,-9,-23,67,23,119}; 4 //最大值 5 int max = array[0]; 6 for(int i=1;i<array.length;i++){ 7 if(array[i]>max){ 8 max = array[i]; 9 } 10 } 11 System.out.println("最大值"+max); 12 13 //最小值 14 int min = array[0]; 15 for(int i=1;i<array.length;i++){ 16 if(array[i] < min){ 17 min=array[i]; 18 } 19 } 20 System.out.println("最小值"+min); 21 22 //求和 23 int count = 0; 24 for (int i = 0; i < array.length ; i++) { 25 count = count + array[i]; 26 } 27 System.out.println("和"+count); 28 29 //请求平均值 30 int avg = count / array.length; 31 System.out.println("平均值"+avg); 32 }

1 public class AarrayCopy { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 //定义一个一维数组 4 int[] array = {45,67,23,-9,-23,67,23,119}; 5 //进行赋值操作 6 int[]array1 = array; 7 // 两个数组进行比较 8 System.out.println(array.equals(array1)); 9 10 // 进行复制操作 11 int[] array2 = new int[array.length]; 12 for (int i=1;i<array2.length;i++){ 13 array2[i] = array[i]; 14 } 15 // 两个数组进行比较 16 System.out.println(array.equals(array2)); 17 } 18 }
2、数组反转

1 public class InversionArray { 2 public static void main(String[] args){ 3 //新建一个数组 4 String[] string = {"aa","bb","cc","dd","ee","ff"}; 5 //反转 6 for (int i = 0; i < string.length/2; i++) { 7 String temp = string[i]; 8 string[i] = string[string.length-1-i]; 9 string[string.length-1-i] = temp; 10 } 11 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(string)); 12 } 13 }

1 public class AarrayFind { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 //创建一个数组 4 int[] array = {34,78,12,3,5,-5,-9,45,-87,9,234,-3,0}; 5 //输入一个数 6 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); 7 System.out.println("输入要查找的数"); 8 int target = sc.nextInt(); 9 //线性查找 10 int linfind = linfind(array, target); 11 System.out.println(linfind); 12 13 //二分查找算法 14 //前提条件数组已经排序好 15 //创建一个排序好数组 16 Arrays.sort(array); 17 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array)); 18 int binarysearch = binarysearch(array, target); 19 System.out.println(binarysearch); 20 } 21 22 //线性查找 23 private static int linfind(int[] array, int target) { 24 for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) { 25 if(target == array[i]){ 26 System.out.println("找到了,当前数的索引为"+i); 27 return i; 28 } 29 } 30 return -1; 31 } 32 33 //二分查找 34 private static int binarysearch(int[] array, int target){ 35 int left = 0; 36 int right = array.length -left; 37 while (left <= right){ 38 int mid = (left + right) / 2; 39 if(array[mid] == target){ 40 return mid; 41 }else if(array[mid] > target){ 42 //向左边查找 43 right = mid -1; 44 } else { 45 //向右边查找 46 left = mid +1; 47 } 48 } 49 return -1; 50 } 51 }
十大内部排序算法
选择排序(直接选择排序、堆排序)
交换排序(冒泡排序、快速排序)
插入排序(直接插入排序、折半插入排序、Shell排序)
归并排序
桶式排序
基数排序
java冒泡排序实现
1、比较相邻的两个元素。如果第一个比第二个大则交换他们的位置(升序排列,降序则反过来)。
2、从列表的开始一直到结尾,依次对每一对相邻元素都进行比较。这样,值最大的元素就通过交换“冒泡”到了列表的结尾,完成第一轮“冒泡”。
3、重复上一步,继续从列表开头依次对相邻元素进行比较。已经“冒泡”出来的元素不用比较(一直比较到结尾也可以,已经“冒泡”到后面的元素即使比较也不需要交换,不比较可以减少步骤)。
4、继续从列表开始进行比较,每轮比较会有一个元素“冒泡”成功。每轮需要比较的元素个数会递减,一直到只剩一个元素没有“冒泡”时(没有任何一对元素需要比较),则列表排序完成

1 public class BubbleSort { 2 public static int[] bubblesort(int[] arr){ 3 for (int i = 0; i < arr.length-1 ; i++) { 4 for (int j = 0; j <arr.length-1-i ; j++) { 5 if(arr[j] > arr[j + 1]){ 6 int temp = arr[j]; 7 arr[j] = arr[j + 1]; 8 arr[j + 1] = temp; 9 } 10 } 11 } 12 return arr; 13 } 14 public static void main(String[] args) { 15 int[] array = {34,78,12,3,5,-5,-9,45,-87,9,234,-3,0}; 16 // 冒泡排序 17 int[] bubblesort = bubblesort(array); 18 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bubblesort)); 19 } 20 }
java快速排序实现
1、定义一个中值(一般是数组第一个元素),通过中值将数组分为两个部分
2、将小于等于中值的元素集中在数组左半部分,将大于等于中值的元素集中在数组右半部分
3、即数组的左半部分的值,均小于或等于中值,数组的右半部分的值,均大于或等于中值
4、此时,又可以将数组的左半部分作为一个新的数组,右半部分也作为一个新的数组,重复上述按中值将数组分为两个部分的过程
5、可以看出,此过程为递归过程,通过递归先将左半部分排好序,然后将右半部分排好序,即全数组都排好了序

1 public class QuickSort { 2 public static void quickSort(int[] arr,int low,int high){ 3 int i,j,temp,t; 4 if(low>high){ 5 return; 6 } 7 i=low; 8 j=high; 9 //temp就是基准位 10 temp = arr[low]; 11 12 while (i<j) { 13 //先看右边,依次往左递减 14 while (temp<=arr[j]&&i<j) { 15 j--; 16 } 17 //再看左边,依次往右递增 18 while (temp>=arr[i]&&i<j) { 19 i++; 20 } 21 //如果满足条件则交换 22 if (i<j) { 23 t = arr[j]; 24 arr[j] = arr[i]; 25 arr[i] = t; 26 } 27 } 28 //最后将基准为与i和j相等位置的数字交换 29 arr[low] = arr[i]; 30 arr[i] = temp; 31 //递归调用左半数组 32 quickSort(arr, low, j-1); 33 //递归调用右半数组 34 quickSort(arr, j+1, high); 35 } 36 public static void main(String[] args){ 37 int[] arr = {10,7,2,4,7,62,3,4,2,1,8,9,19}; 38 quickSort(arr, 0, arr.length-1); 39 for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { 40 System.out.println(arr[i]); 41 } 42 } 43 }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号