Dubbo集群容错及负载均衡源码分析(十)
在上面,已经写过服务消费者在启动时被注入一个动态代理类的实现过程,再来回顾一下服务消费者启动过程中做了什么事情:
服务启动过程中,主要会构建一个动态代理类,并且在构建动态代理之前,会从注册中心上获取服务提供者的地址,并且会订阅服务提供者的状态。然后,采用DubboProtocol协议,和服务端建立一个远程通信,并保存到Invoker中进行返回。那接下来,我们再去看服务调用的时候,请求的执行过程。
看到这对消费者启动时初时化的过程就完成了,接下来看客户端调用逻辑
JavassistProxyFactory.getProxy(客户端发起调用阶段)
在创建代理对象时,会执行下面这段代码,一旦代码被调用,就会触发InvokerInvocationHandler。
public <T> T getProxy(Invoker<T> invoker, Class<?>[] interfaces) {
return (T) Proxy.getProxy(interfaces).newInstance(new InvokerInvocationHandler(invoker));
}
当调用方法时,会触发InvokerInvocationHandler.invoker
InvokerInvocationHandler.invoke
进入到InvokerInvocationHandler.invoke方法。其中invoker这个对象, 是在启动注入动态代理类时,初始化的一个调用器对象,我们得先要知道它是谁,才能知道它下一步调用的是哪个对象的方法.它应该是: MockClusterInvoker,因为它是通过MockClusterWrapper来进行包装的。
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
if (method.getDeclaringClass() == Object.class) {
return method.invoke(invoker, args);
}
String methodName = method.getName();
//获得参数类型
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
if (parameterTypes.length == 0) {
if ("toString".equals(methodName)) {
return invoker.toString();
} else if ("$destroy".equals(methodName)) {
invoker.destroy();
return null;
} else if ("hashCode".equals(methodName)) {
return invoker.hashCode();
}
} else if (parameterTypes.length == 1 && "equals".equals(methodName)) {
return invoker.equals(args[0]);
}
//数据传输对象
RpcInvocation rpcInvocation = new RpcInvocation(method, invoker.getInterface().getName(), args);
String serviceKey = invoker.getUrl().getServiceKey();
rpcInvocation.setTargetServiceUniqueName(serviceKey);
if (consumerModel != null) {
rpcInvocation.put(Constants.CONSUMER_MODEL, consumerModel);
rpcInvocation.put(Constants.METHOD_MODEL, consumerModel.getMethodModel(method));
}
return invoker.invoke(rpcInvocation).recreate();
}
}
MockClusterInvoker
Mock,在这里面有两个逻辑
1. 是否客户端强制配置了mock调用,那么在这种场景中主要可以用来解决服务端还没开发好的时候直接使用本地数据进行测试
2. 是否出现了异常,如果出现异常则使用配置好的Mock类来实现服务的降级
@Override
public Result invoke(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
Result result = null;
String value = getUrl().getMethodParameter(invocation.getMethodName(), MOCK_KEY, Boolean.FALSE.toString()).trim();
if (value.length() == 0 || "false".equalsIgnoreCase(value)) {
//no mock
result = this.invoker.invoke(invocation);
} else if (value.startsWith("force")) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("force-mock: " + invocation.getMethodName() + " force-mock enabled , url : " + getUrl());
}
//force:direct mock
result = doMockInvoke(invocation, null);
} else {
//fail-mock
try {
result = this.invoker.invoke(invocation);
//fix:#4585
if(result.getException() != null && result.getException() instanceof RpcException){
RpcException rpcException= (RpcException)result.getException();
if(rpcException.isBiz()){
throw rpcException;
}else {
result = doMockInvoke(invocation, rpcException);
}
}
} catch (RpcException e) {
if (e.isBiz()) {
throw e;
}
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("fail-mock: " + invocation.getMethodName() + " fail-mock enabled , url : " + getUrl(), e);
}
result = doMockInvoke(invocation, e);
}
}
return result;
}
AbstractCluster$InterceptorInvokerNode.invoker
为什么到这个类,看过生成动态代理过程的应该都知道,invoker会通过一个Interceptor进行包装。构建了一个拦截器链。这个拦截器是的组成是: ConsumerContextClusterInterceptor -next-> ZoneAwareClusterInvoker其中before方法是设置上下文信息,接着调用interceptor.interceppt方法进行拦截处理
ClusterInterceptor.intercept
调用ClusterInterceptor的默认方法。
default Result intercept(AbstractClusterInvoker<?> clusterInvoker, Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
return clusterInvoker.invoke(invocation);
}
此时传递过来的clusterInvoker对象,是拦截器链中的第二个节点 ZoneAwareClusterInvoker
AbstractClusterInvoker.invoke
@Override
public Result invoke(final Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
checkWhetherDestroyed();
// 绑定attachment到invocation中
// binding attachments into invocation.
Map<String, Object> contextAttachments = RpcContext.getContext().getObjectAttachments();
if (contextAttachments != null && contextAttachments.size() != 0) {
((RpcInvocation) invocation).addObjectAttachments(contextAttachments);
}
//获取invoker列表,这里的列表应该是直接从directory中获取
List<Invoker<T>> invokers = list(invocation);
//初始化负载均衡算法
LoadBalance loadbalance = initLoadBalance(invokers, invocation);
//调用子类的doInvoke方法
RpcUtils.attachInvocationIdIfAsync(getUrl(), invocation);
return doInvoke(invocation, invokers, loadbalance);
}
ZoneAwareClusterInvoker.doInvoke
ZonAwareCluster,如果一个服务注册在多个注册中心,那么消费者去消费时,会根据区域进行路由,选择一个注册中心进行服务消费。
@Override @SuppressWarnings({"unchecked", "rawtypes"}) public Result doInvoke(Invocation invocation, final List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException { // First, pick the invoker (XXXClusterInvoker) that comes from the local registry, distinguish by a 'preferred' key. //遍历注册中心 for (Invoker<T> invoker : invokers) { // 判断是否需要通过clusterInvoker来触发调用 ClusterInvoker<T> clusterInvoker = (ClusterInvoker<T>) invoker; if (clusterInvoker.isAvailable() && clusterInvoker.getRegistryUrl() .getParameter(REGISTRY_KEY + "." + PREFERRED_KEY, false)) { return clusterInvoker.invoke(invocation); } } // providers in the registry with the same zone // 是否制定了zone进行调用 String zone = invocation.getAttachment(REGISTRY_ZONE); if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(zone)) { for (Invoker<T> invoker : invokers) { ClusterInvoker<T> clusterInvoker = (ClusterInvoker<T>) invoker; if (clusterInvoker.isAvailable() && zone.equals(clusterInvoker.getRegistryUrl().getParameter(REGISTRY_KEY + "." + ZONE_KEY))) { return clusterInvoker.invoke(invocation); } } String force = invocation.getAttachment(REGISTRY_ZONE_FORCE); if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(force) && "true".equalsIgnoreCase(force)) { throw new IllegalStateException("No registry instance in zone or no available providers in the registry, zone: " + zone + ", registries: " + invokers.stream().map(invoker -> ((MockClusterInvoker<T>) invoker).getRegistryUrl().toString()).collect(Collectors.joining(","))); } } // 通过负载均衡算法,从多个注册中心中随机选择一个节点 // load balance among all registries, with registry weight count in. Invoker<T> balancedInvoker = select(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, null); if (balancedInvoker.isAvailable()) {//进入到指定注册中心的服务列表进行调用 return balancedInvoker.invoke(invocation); } //如果没有一个invoker通过负载均衡算法被指定,则选择第一个有效的invoker进行调用。 // If none of the invokers has a preferred signal or is picked by the loadbalancer, pick the first one available. for (Invoker<T> invoker : invokers) { ClusterInvoker<T> clusterInvoker = (ClusterInvoker<T>) invoker; if (clusterInvoker.isAvailable()) { //选择指定的一个区域的invoker进行调用 return clusterInvoker.invoke(invocation); } } //if none available,just pick one return invokers.get(0).invoke(invocation); }
调用链路又会经过一遍 MockClusterInvoker - > AbstractCluster$InterceptorInvokerNode
AbstractCluster$InterceptorInvokerNode.invoker
再次进入到这个方法中,不过此时的调用链路发生了变化。这个拦截器是的组成是: ConsumerContextClusterInterceptor -next-> FailoverClusterInvoker继续进入到AbstractClusterInvoker中的invoke,但是此时AbstractClusterInvoker是通过FailoverClusterInvoker来实现的,所以再次调用doInvoke时,会调用FailoverClusterInvoker中的doInvoke方法
@Override public Result invoke(final Invocation invocation) throws RpcException { checkWhetherDestroyed(); // 绑定attachment到invocation中 // binding attachments into invocation. Map<String, Object> contextAttachments = RpcContext.getContext().getObjectAttachments(); if (contextAttachments != null && contextAttachments.size() != 0) { ((RpcInvocation) invocation).addObjectAttachments(contextAttachments); } //获取invoker列表,这里的列表应该是直接从directory中获取 List<Invoker<T>> invokers = list(invocation); //初始化负载均衡算法 LoadBalance loadbalance = initLoadBalance(invokers, invocation); //调用子类的doInvoke方法 RpcUtils.attachInvocationIdIfAsync(getUrl(), invocation); return doInvoke(invocation, invokers, loadbalance); }
FailoverClusterInvoker.doInvoke
FailoverClusterInvoker,就是集群容错的处理,默认的集群容错策略是重试,所以也不难猜出这里面的实现方式。这段代码逻辑也很好理解,因为之前在说Dubbo的时候说过容错机制,而failover是失败重试,所以这里面应该会实现容错的逻辑
- 获得重试的次数,并且进行循环
- 获得目标服务,并且记录当前已经调用过的目标服务防止下次继续将请求发送过去
- 如果执行成功,则返回结果
- 如果出现异常,判断是否为业务异常,如果是则抛出,否则,进行下一次重试
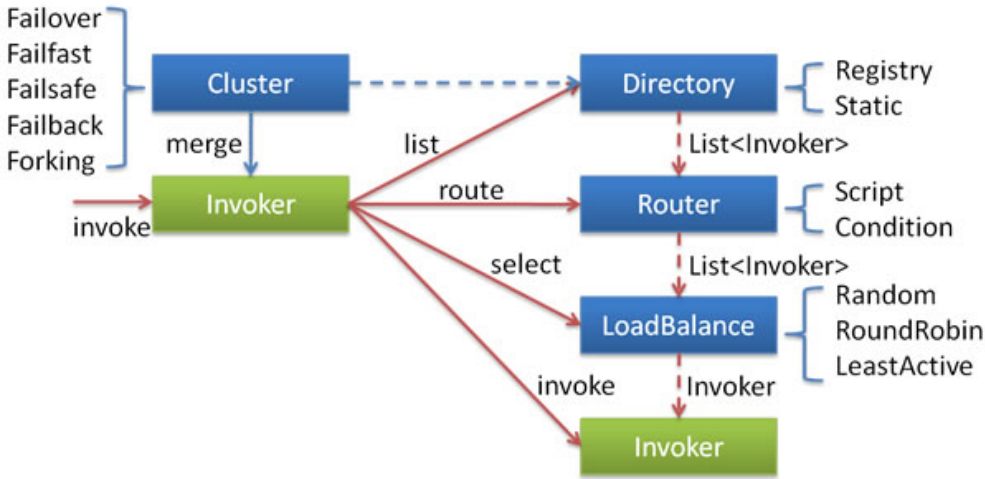
- 这里的 Invoker 是 Provider 的一个可调用 Service 的抽象, Invoker 封装了 Provider 地址及 Service 接口信息
- Directory 代表多个 Invoker ,可以把它看成 List<Invoker> ,但与 List 不同的是,它的值可能是动态变化的,比如注册中心推送变更
- Cluster 将 Directory 中的多个 Invoker 伪装成一个 Invoker ,对上层透明,伪装过程包含了容错逻辑,调用失败后,重试另一个
- Router 负责从多个 Invoker 中按路由规则选出子集,比如读写分离,应用隔离等
- LoadBalance 负责从多个 Invoker 中选出具体的一个用于本次调用,选的过程包含了负载均衡算法,调用失败后,需要重选
@Override @SuppressWarnings({"unchecked", "rawtypes"}) public Result doInvoke(Invocation invocation, final List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException { //获取服务提供者的协议invoker List<Invoker<T>> copyInvokers = invokers; // 校验invoker checkInvokers(copyInvokers, invocation); //获取调用的目标方法名 String methodName = RpcUtils.getMethodName(invocation); //获得重试次数 int len = getUrl().getMethodParameter(methodName, RETRIES_KEY, DEFAULT_RETRIES) + 1; if (len <= 0) { len = 1; } // retry loop. RpcException le = null; // last exception. List<Invoker<T>> invoked = new ArrayList<Invoker<T>>(copyInvokers.size()); // invoked invokers. Set<String> providers = new HashSet<String>(len); //for循环进行重试 for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { //Reselect before retry to avoid a change of candidate `invokers`. //NOTE: if `invokers` changed, then `invoked` also lose accuracy. if (i > 0) { checkWhetherDestroyed(); copyInvokers = list(invocation); // check again checkInvokers(copyInvokers, invocation); } //从多个invoker中通过负载均衡算法,选择一个inovke进行调用。 Invoker<T> invoker = select(loadbalance, invocation, copyInvokers, invoked); //记录已经调用过的目标服务,如果重试时,已经调用过的目标服务 不再发起调用。 invoked.add(invoker); RpcContext.getContext().setInvokers((List) invoked); try { //发起远程调用 Result result = invoker.invoke(invocation); if (le != null && logger.isWarnEnabled()) { logger.warn("Although retry the method " + methodName + " in the service " + getInterface().getName() + " was successful by the provider " + invoker.getUrl().getAddress() + ", but there have been failed providers " + providers + " (" + providers.size() + "/" + copyInvokers.size() + ") from the registry " + directory.getUrl().getAddress() + " on the consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost() + " using the dubbo version " + Version.getVersion() + ". Last error is: " + le.getMessage(), le); } return result; } catch (RpcException e) { if (e.isBiz()) { // biz exception. throw e; } le = e; } catch (Throwable e) { le = new RpcException(e.getMessage(), e); } finally { providers.add(invoker.getUrl().getAddress()); } } throw new RpcException(le.getCode(), "Failed to invoke the method " + methodName + " in the service " + getInterface().getName() + ". Tried " + len + " times of the providers " + providers + " (" + providers.size() + "/" + copyInvokers.size() + ") from the registry " + directory.getUrl().getAddress() + " on the consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost() + " using the dubbo version " + Version.getVersion() + ". Last error is: " + le.getMessage(), le.getCause() != null ? le.getCause() : le); }
负载均衡算法
- loadbalance 表示具体的负载均衡算法实例
- invocation 表示请求的参数
- invokers,表示服务提供者的实例列表,如果有多个,这里就是一个集合
protected Invoker<T> select(LoadBalance loadbalance, Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, List<Invoker<T>> selected) throws RpcException { if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(invokers)) { return null; } String methodName = invocation == null ? StringUtils.EMPTY_STRING : invocation.getMethodName(); boolean sticky = invokers.get(0).getUrl() .getMethodParameter(methodName, CLUSTER_STICKY_KEY, DEFAULT_CLUSTER_STICKY); //ignore overloaded method if (stickyInvoker != null && !invokers.contains(stickyInvoker)) { stickyInvoker = null; } //ignore concurrency problem if (sticky && stickyInvoker != null && (selected == null || !selected.contains(stickyInvoker))) { if (availablecheck && stickyInvoker.isAvailable()) { return stickyInvoker; } } Invoker<T> invoker = doSelect(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, selected); if (sticky) { stickyInvoker = invoker; } return invoker; }
AbstractClusterInvoker.doSelect
进入到AbstractClusterInvoker的doSelect方法中。
- 如果invokers只有一个,则直接返回
- 否则,调用负载均衡算法获得一个目标invoker
private Invoker<T> doSelect(LoadBalance loadbalance, Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, List<Invoker<T>> selected) throws RpcException { if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(invokers)) { return null; } if (invokers.size() == 1) { return invokers.get(0); } Invoker<T> invoker = loadbalance.select(invokers, getUrl(), invocation); //如果selected集合中包含这次选择出来的invoker, 或这invoker是一个失效的服务,则重新选 择一个新的invoker返回。 //If the `invoker` is in the `selected` or invoker is unavailable && availablecheck is true, reselect. if ((selected != null && selected.contains(invoker)) || (!invoker.isAvailable() && getUrl() != null && availablecheck)) { try { Invoker<T> rInvoker = reselect(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, selected, availablecheck); if (rInvoker != null) { invoker = rInvoker; } else { //Check the index of current selected invoker, if it's not the last one, choose the one at index+1. int index = invokers.indexOf(invoker); try { //Avoid collision invoker = invokers.get((index + 1) % invokers.size()); } catch (Exception e) { logger.warn(e.getMessage() + " may because invokers list dynamic change, ignore.", e); } } } catch (Throwable t) { logger.error("cluster reselect fail reason is :" + t.getMessage() + " if can not solve, you can set cluster.availablecheck=false in url", t); } } return invoker; }
RandomLoadBalance.doSelect
执行随机负载均衡算法。
@Override protected <T> Invoker<T> doSelect(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) { // Number of invokers int length = invokers.size(); // Every invoker has the same weight? boolean sameWeight = true; // the weight of every invokers int[] weights = new int[length]; // the first invoker's weight int firstWeight = getWeight(invokers.get(0), invocation); weights[0] = firstWeight; // The sum of weights int totalWeight = firstWeight; // 下面这个循环有两个作用,第一是计算总权重 totalWeight, // 第二是检测每个服务提供者的权重是否相同 for (int i = 1; i < length; i++) { int weight = getWeight(invokers.get(i), invocation); // save for later use weights[i] = weight; // Sum // 累加权重 totalWeight += weight; // 检测当前服务提供者的权重与上一个服务提供者的权重是否相同, // 不相同的话,则将 sameWeight 置为 false。 if (sameWeight && weight != firstWeight) { sameWeight = false; } } // 下面的 if 分支主要用于获取随机数,并计算随机数落在哪个区间上 if (totalWeight > 0 && !sameWeight) { // If (not every invoker has the same weight & at least one invoker's weight>0), select randomly based on totalWeight. // 随机获取一个 [0, totalWeight) 区间内的数字 int offset = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(totalWeight); // Return a invoker based on the random value. // 循环让 offset 数减去服务提供者权重值,当 offset 小于0时,返回相应的 Invoker。 // 举例说明一下,我们有 servers = [A, B, C],weights = [5, 3, 2],offset = 7。 // 第一次循环,offset - 5 = 2 > 0,即 offset > 5, // 表明其不会落在服务器 A 对应的区间上。 // 第二次循环,offset - 3 = -1 < 0,即 5 < offset < 8, // 表明其会落在服务器 B 对应的区间上 for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { // 让随机值 offset 减去权重值 offset -= weights[i]; if (offset < 0) { // 返回相应的 Invoker return invokers.get(i); } } } // 如果所有服务提供者权重值相同,此时直接随机返回一个即可 // If all invokers have the same weight value or totalWeight=0, return evenly. return invokers.get(ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(length)); }
Invoker.invoke
继续回到FailoverClusterInvoker这个类中的代码来,这里会通过负载返回的invoker对象,来调用invoke方法进行远程通信。
Result result = invoker.invoke(invocation);
invoker对象的组成是: RegistryDirectory$InvokerDelegate() -> ProtocolFilterWrapper ->ListenerInvokerWrapper其中,在ProtocolFilterWrapper的调用中,实际会调用一个匿名内部类的invoke方法,这里构建了一个fifilter进行逐项的过滤
AsyncToSyncInvoker.invoke
经过装饰器、过滤器对invoker进行增强和过滤之后,来到了AsyncToSyncInvoker.invoke方法,这里采用的是异步的方式来进行通信
@Override public Result invoke(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException { Result asyncResult = invoker.invoke(invocation); try { //如果配置的是同步通信,则通过get阻塞式获取返回结果 if (InvokeMode.SYNC == ((RpcInvocation) invocation).getInvokeMode()) { /** * NOTICE! * must call {@link java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture#get(long, TimeUnit)} because * {@link java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture#get()} was proved to have serious performance drop. */ asyncResult.get(Integer.MAX_VALUE, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RpcException("Interrupted unexpectedly while waiting for remote result to return! method: " + invocation.getMethodName() + ", provider: " + getUrl() + ", cause: " + e.getMessage(), e); } catch (ExecutionException e) { Throwable t = e.getCause(); if (t instanceof TimeoutException) { throw new RpcException(RpcException.TIMEOUT_EXCEPTION, "Invoke remote method timeout. method: " + invocation.getMethodName() + ", provider: " + getUrl() + ", cause: " + e.getMessage(), e); } else if (t instanceof RemotingException) { throw new RpcException(RpcException.NETWORK_EXCEPTION, "Failed to invoke remote method: " + invocation.getMethodName() + ", provider: " + getUrl() + ", cause: " + e.getMessage(), e); } else { throw new RpcException(RpcException.UNKNOWN_EXCEPTION, "Fail to invoke remote method: " + invocation.getMethodName() + ", provider: " + getUrl() + ", cause: " + e.getMessage(), e); } } catch (Throwable e) { throw new RpcException(e.getMessage(), e); } return asyncResult; }
DubboInvoker.invoke
DubboInvoker继承了AbstractInvoker这个抽象类,而DubboInvoker中没有invoke这个方法,所以这里调用的是AbstractInvoker.invoke方法。
进入到DubboInvoker这个方法中,那么意味着正式进入到服务通信层面了。前面的很多细节分析,无非就是做了三件事
- 多注册中心的拦截以及分发
- 负载均衡以及集群容错
- 请求过滤和包装
@Override public Result invoke(Invocation inv) throws RpcException { // if invoker is destroyed due to address refresh from registry, let's allow the current invoke to proceed if (destroyed.get()) { logger.warn("Invoker for service " + this + " on consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost() + " is destroyed, " + ", dubbo version is " + Version.getVersion() + ", this invoker should not be used any longer"); } RpcInvocation invocation = (RpcInvocation) inv; invocation.setInvoker(this); if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmptyMap(attachment)) { invocation.addObjectAttachmentsIfAbsent(attachment); } Map<String, Object> contextAttachments = RpcContext.getContext().getObjectAttachments(); if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmptyMap(contextAttachments)) { /** * invocation.addAttachmentsIfAbsent(context){@link RpcInvocation#addAttachmentsIfAbsent(Map)}should not be used here, * because the {@link RpcContext#setAttachment(String, String)} is passed in the Filter when the call is triggered * by the built-in retry mechanism of the Dubbo. The attachment to update RpcContext will no longer work, which is * a mistake in most cases (for example, through Filter to RpcContext output traceId and spanId and other information). */ invocation.addObjectAttachments(contextAttachments); } invocation.setInvokeMode(RpcUtils.getInvokeMode(url, invocation)); RpcUtils.attachInvocationIdIfAsync(getUrl(), invocation); AsyncRpcResult asyncResult; try { asyncResult = (AsyncRpcResult) doInvoke(invocation); } catch (InvocationTargetException e) { // biz exception Throwable te = e.getTargetException(); if (te == null) { asyncResult = AsyncRpcResult.newDefaultAsyncResult(null, e, invocation); } else { if (te instanceof RpcException) { ((RpcException) te).setCode(RpcException.BIZ_EXCEPTION); } asyncResult = AsyncRpcResult.newDefaultAsyncResult(null, te, invocation); } } catch (RpcException e) { if (e.isBiz()) { asyncResult = AsyncRpcResult.newDefaultAsyncResult(null, e, invocation); } else { throw e; } } catch (Throwable e) { asyncResult = AsyncRpcResult.newDefaultAsyncResult(null, e, invocation); } RpcContext.getContext().setFuture(new FutureAdapter(asyncResult.getResponseFuture())); return asyncResult; }
DubboInvoker.doInvoke
调用doInvoke方法发起远程请求。
@Override protected Result doInvoke(final Invocation invocation) throws Throwable { RpcInvocation inv = (RpcInvocation) invocation; final String methodName = RpcUtils.getMethodName(invocation); inv.setAttachment(PATH_KEY, getUrl().getPath()); inv.setAttachment(VERSION_KEY, version); //获取一个客户端连接 ExchangeClient currentClient; if (clients.length == 1) { currentClient = clients[0]; } else { //如果有多个连接,则轮询返回 currentClient = clients[index.getAndIncrement() % clients.length]; } try { //是否是单向通信,默认为false boolean isOneway = RpcUtils.isOneway(getUrl(), invocation); int timeout = calculateTimeout(invocation, methodName); if (isOneway) { boolean isSent = getUrl().getMethodParameter(methodName, Constants.SENT_KEY, false); currentClient.send(inv, isSent); return AsyncRpcResult.newDefaultAsyncResult(invocation); } else { //根据配置参数构建线程池 ExecutorService executor = getCallbackExecutor(getUrl(), inv); //使用client发起请求 CompletableFuture<AppResponse> appResponseFuture = currentClient.request(inv, timeout, executor).thenApply(obj -> (AppResponse) obj); // save for 2.6.x compatibility, for example, TraceFilter in Zipkin uses com.alibaba.xxx.FutureAdapter FutureContext.getContext().setCompatibleFuture(appResponseFuture); AsyncRpcResult result = new AsyncRpcResult(appResponseFuture, inv); result.setExecutor(executor); return result; } } catch (TimeoutException e) { throw new RpcException(RpcException.TIMEOUT_EXCEPTION, "Invoke remote method timeout. method: " + invocation.getMethodName() + ", provider: " + getUrl() + ", cause: " + e.getMessage(), e); } catch (RemotingException e) { throw new RpcException(RpcException.NETWORK_EXCEPTION, "Failed to invoke remote method: " + invocation.getMethodName() + ", provider: " + getUrl() + ", cause: " + e.getMessage(), e); } }
ReferenceCountExchangeClient.request
currentClient它实际是一个ReferenceCountExchangeClient(HeaderExchangeClient())所以它的调用链路是ReferenceCountExchangeClient->HeaderExchangeClient->HeaderExchangeChannel->(request方法)最终,把构建好的RpcInvocation,组装到一个Request对象中进行传递
@Override public CompletableFuture<Object> request(Object request, int timeout, ExecutorService executor) throws RemotingException { return client.request(request, timeout, executor); }
- ReferenceCountExchangeClient 用来记录调用次数
- HeaderExchangeClient 用来开启心跳机制、以及启动失败重连任务
HeaderExchangeChannel.request
进入到HeaderExchangeChannel.request 来发起请求,这个类的主要职责就是和服务端进行数据交互
@Override public CompletableFuture<Object> request(Object request, int timeout, ExecutorService executor) throws RemotingException { if (closed) { throw new RemotingException(this.getLocalAddress(), null, "Failed to send request " + request + ", cause: The channel " + this + " is closed!"); } // create request. // 创建请求对象. Request req = new Request(); req.setVersion(Version.getProtocolVersion()); req.setTwoWay(true); req.setData(request); DefaultFuture future = DefaultFuture.newFuture(channel, req, timeout, executor); try { //发送请求 channel.send(req); } catch (RemotingException e) { future.cancel(); throw e; } return future; }
AbstractPeer - >AbstractClient ->NettyChannel.send ,把数据包发送到服务端。
服务端接收数据的处理流程
客户端请求发出去之后,服务端会收到这个请求的消息,然后触发调用。
服务端接收到消息
服务端这边接收消息的处理链路,也比较复杂,回到NettyServer中创建io的过程。
bootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup) .channel(NettyEventLoopFactory.serverSocketChannelClass()) .option(ChannelOption.SO_REUSEADDR, Boolean.TRUE) .childOption(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, Boolean.TRUE) .childOption(ChannelOption.ALLOCATOR, PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT) .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception { // FIXME: should we use getTimeout()? int idleTimeout = UrlUtils.getIdleTimeout(getUrl()); NettyCodecAdapter adapter = new NettyCodecAdapter(getCodec(), getUrl(), NettyServer.this); if (getUrl().getParameter(SSL_ENABLED_KEY, false)) { ch.pipeline().addLast("negotiation", SslHandlerInitializer.sslServerHandler(getUrl(), nettyServerHandler)); } ch.pipeline() // 添加解码器 handler .addLast("decoder", adapter.getDecoder()) // 添加编码器 handler .addLast("encoder", adapter.getEncoder()) .addLast("server-idle-handler", new IdleStateHandler(0, 0, idleTimeout, MILLISECONDS)) // 添加业务handler .addLast("handler", nettyServerHandler); } });
服务端启动的时候,配置的消息处理是handler配置的是nettyServerHandler,就是上面的最后一行
// 业务 handler,这里将Netty 的各种请求分发给NettyServer 的方法。 final NettyServerHandler nettyServerHandler = new NettyServerHandler(getUrl(), this);
所以,服务端收到消息之后,会调用NettyServerHandler中的channelRead方法
handler.channelRead()
服务端收到读的请求是,会进入这个方法。
接着通过handler.received来处理msg,这个handle的链路很长,比较复杂,我们需要逐步剖析
@Override public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception { NettyChannel channel = NettyChannel.getOrAddChannel(ctx.channel(), url, handler); handler.received(channel, msg); }
handler也是一个处理链,在服务器启动时,我们启动Nettyserver的时候,构建的handler。handler.received此时会调用AbsstractPeer.received方法,这个方法用来判断服务端是否关闭了,如果关闭就直接返回,否则,通过handler处理链进行层层调用。为什么调用到这个方法,因为上面的这个handler实际上是NettyServer,而NettyServer继承了AbstractPeer这个抽象类,这个抽象类中定义了received方法
@Override public void sent(Channel ch, Object msg) throws RemotingException { if (closed) { return; } handler.sent(ch, msg); }
接下来这个handler的调用链路为MultiMessageHandler -> HeartbeatHandler -> AllChannelHandler -> DecodeHandler -HeaderExchangeHandler ->最后进入这个方法->DubboProtocol$requestHandler(receive)
MultiMessageHandler: 复合消息处理
HeartbeatHandler:心跳消息处理,接收心跳并发送心跳响应
AllChannelHandler:业务线程转化处理器,把接收到的消息封装成ChannelEventRunnable可执行任务给线程池处理
DecodeHandler:业务解码处理器
HeaderExchangeHandler.received
交互层请求响应处理,有三种处理方式
1. handlerRequest,双向请求
2. handler.received 单向请求
3. handleResponse 响应消息
@Override public void received(Channel channel, Object message) throws RemotingException { final ExchangeChannel exchangeChannel = HeaderExchangeChannel.getOrAddChannel(channel); if (message instanceof Request) { // handle request. Request request = (Request) message; if (request.isEvent()) { handlerEvent(channel, request); } else { if (request.isTwoWay()) { handleRequest(exchangeChannel, request); } else { handler.received(exchangeChannel, request.getData()); } } } else if (message instanceof Response) { handleResponse(channel, (Response) message); } else if (message instanceof String) { if (isClientSide(channel)) { Exception e = new Exception("Dubbo client can not supported string message: " + message + " in channel: " + channel + ", url: " + channel.getUrl()); logger.error(e.getMessage(), e); } else { String echo = handler.telnet(channel, (String) message); if (echo != null && echo.length() > 0) { channel.send(echo); } } } else { handler.received(exchangeChannel, message); } }
handleRequest
接着调用handleRequest方法。这个方法中,构建返回的对象Response,并且最终会通过异步的方式来把msg传递到invoker中进行调用 handler.reply
void handleRequest(final ExchangeChannel channel, Request req) throws RemotingException { Response res = new Response(req.getId(), req.getVersion()); if (req.isBroken()) { Object data = req.getData(); String msg; if (data == null) { msg = null; } else if (data instanceof Throwable) { msg = StringUtils.toString((Throwable) data); } else { msg = data.toString(); } res.setErrorMessage("Fail to decode request due to: " + msg); res.setStatus(Response.BAD_REQUEST); channel.send(res); return; } // find handler by message class. Object msg = req.getData(); try { CompletionStage<Object> future = handler.reply(channel, msg); future.whenComplete((appResult, t) -> { try { if (t == null) { res.setStatus(Response.OK); res.setResult(appResult); } else { res.setStatus(Response.SERVICE_ERROR); res.setErrorMessage(StringUtils.toString(t)); } channel.send(res); } catch (RemotingException e) { logger.warn("Send result to consumer failed, channel is " + channel + ", msg is " + e); } }); } catch (Throwable e) { res.setStatus(Response.SERVICE_ERROR); res.setErrorMessage(StringUtils.toString(e)); channel.send(res); } }
在CompletionStage<Object> future = handler.reply(channel, msg);debugger可以发现此时的handler,应该是DubboProtocol中构建的匿名内部类,理由很简单,debugger可以发现dandler={DubboProtocol$1@7531}中的$号后面跟了一个东西,源码看多的人知道如果$号后面跟了一个东西那很可能是一个内部类;在DubboProtoco-108行。所以调用handler.reply方法,自然就进入到了该匿名内部类中的reply方法中来。进入DubboProtocol中看下他的内部类
DubboProtocol.requestHandler
private ExchangeHandler requestHandler = new ExchangeHandlerAdapter() { @Override public CompletableFuture<Object> reply(ExchangeChannel channel, Object message) throws RemotingException { //如果消息类型不是invocation,则抛出异常表示无法识别 if (!(message instanceof Invocation)) { throw new RemotingException(channel, "Unsupported request: " + (message == null ? null : (message.getClass().getName() + ": " + message)) + ", channel: consumer: " + channel.getRemoteAddress() + " --> provider: " + channel.getLocalAddress()); } //获得请求参数 Invocation inv = (Invocation) message; //根据key从发布的服务列表中查找到指定的服务端invoke,这个就是之前在写服务发布时,涉及 到的invoke对象。 Invoker<?> invoker = getInvoker(channel, inv); // need to consider backward-compatibility if it's a callback if (Boolean.TRUE.toString().equals(inv.getObjectAttachments().get(IS_CALLBACK_SERVICE_INVOKE))) { String methodsStr = invoker.getUrl().getParameters().get("methods"); boolean hasMethod = false; if (methodsStr == null || !methodsStr.contains(",")) { hasMethod = inv.getMethodName().equals(methodsStr); } else { String[] methods = methodsStr.split(","); for (String method : methods) { if (inv.getMethodName().equals(method)) { hasMethod = true; break; } } } if (!hasMethod) { logger.warn(new IllegalStateException("The methodName " + inv.getMethodName() + " not found in callback service interface ,invoke will be ignored." + " please update the api interface. url is:" + invoker.getUrl()) + " ,invocation is :" + inv); return null; } } RpcContext.getContext().setRemoteAddress(channel.getRemoteAddress()); //发起请求调用,此时得到的invoker对象 Result result = invoker.invoke(inv); return result.thenApply(Function.identity()); }
至于为什么调用的是ExchangeHandler requestHandler ,这就要回到创建服务说起了,在DubboProtocol.createServer创建服务时,调用Exchangers.bind时把requestHandler作为参数给传递过去了做为一个参数,这就是过滤器层层包装中最里面的requestHandler
private ProtocolServer createServer(URL url) {
//组装url,在url中添加心跳时间、编解码参数
url = URLBuilder.from(url)
/******* 1. 参数设置 ********/
// 1.1 当服务关闭以后,发送一个只读的事件,默认是开启状态
// send readonly event when server closes, it's enabled by default
.addParameterIfAbsent(CHANNEL_READONLYEVENT_SENT_KEY, Boolean.TRUE.toString())
// enable heartbeat by default
// 1.2 默认启用心跳
.addParameterIfAbsent(HEARTBEAT_KEY, String.valueOf(DEFAULT_HEARTBEAT))
// 1.3 获取传输协议,默认为 Netty
.addParameter(CODEC_KEY, DubboCodec.NAME)
.build();
String str = url.getParameter(SERVER_KEY, DEFAULT_REMOTING_SERVER);
//通过 SPI 检测是否存在 server 参数所代表的 Transporter 拓展,不存在则抛出异常
if (str != null && str.length() > 0 && !ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Transporter.class).hasExtension(str)) {
throw new RpcException("Unsupported server type: " + str + ", url: " + url);
}
/******* 2. 开启服务端口 ********/
//创建ExchangeServer.
ExchangeServer server;
try {
// 2.1 绑定ip端口,开启服务,这里server 默认是NettyServer,
// 需要注意的是这里传入的requestHandler 是最终处理消息的处理器
server = Exchangers.bind(url, requestHandler);
} catch (RemotingException e) {
throw new RpcException("Fail to start server(url: " + url + ") " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
// 2.2 校验客户端的传输协议
str = url.getParameter(CLIENT_KEY);
if (str != null && str.length() > 0) {
Set<String> supportedTypes = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Transporter.class).getSupportedExtensions();
if (!supportedTypes.contains(str)) {
throw new RpcException("Unsupported client type: " + str);
}
}
return new DubboProtocolServer(server);
}
回到DubboProtocol.requestHandler中继续
invoker.invoke()
invoker.invoke,发起本地服务调用,但是此时调用之前,invoke并不是一个直接调用的对象,而是包装过的。
首先第一个就是一条过滤链路,经过过滤链路之后,进入到InvokerWrapper.invoke方法,这个是一个Invoker包装类,包装了URL地址信息和真正的Invoker代理对象
@Override public Result invoke(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException { return invoker.invoke(invocation); }
DelegateProviderMetaDataInvoker
这里是一个委派类,它提供了服务提供者的元数序信息。
@Override public Result invoke(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException { return invoker.invoke(invocation); }
AbstractProxyInvoker
接着进入到AbstractProxyInvoker的invoke方法,在这个方法中,我们可以看到它会调用子类的doInvoke方法,获得返回结果。其中proxy,表示服务端的对象实例,这个实例很显然是在构建动态代理Invoker对象时保存进来的。
@Override public Result invoke(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException { try { // wrapper的invokeMethod方法 Object value = doInvoke(proxy, invocation.getMethodName(), invocation.getParameterTypes(), invocation.getArguments()); CompletableFuture<Object> future = wrapWithFuture(value); CompletableFuture<AppResponse> appResponseFuture = future.handle((obj, t) -> { AppResponse result = new AppResponse(); if (t != null) { if (t instanceof CompletionException) { result.setException(t.getCause()); } else { result.setException(t); } } else { result.setValue(obj); } return result; }); return new AsyncRpcResult(appResponseFuture, invocation); } catch (InvocationTargetException e) { if (RpcContext.getContext().isAsyncStarted() && !RpcContext.getContext().stopAsync()) { logger.error("Provider async started, but got an exception from the original method, cannot write the exception back to consumer because an async result may have returned the new thread.", e); } return AsyncRpcResult.newDefaultAsyncResult(null, e.getTargetException(), invocation); } catch (Throwable e) { throw new RpcException("Failed to invoke remote proxy method " + invocation.getMethodName() + " to " + getUrl() + ", cause: " + e.getMessage(), e); } }
JavassistProxyFactory.doInvoke
@Override public <T> Invoker<T> getInvoker(T proxy, Class<T> type, URL url) { // TODO Wrapper cannot handle this scenario correctly: the classname contains '$' // 为目标类创建 Wrapper final Wrapper wrapper = Wrapper.getWrapper(proxy.getClass().getName().indexOf('$') < 0 ? proxy.getClass() : type); // 创建匿名 Invoker 类对象,并实现 doInvoke 方法。 return new AbstractProxyInvoker<T>(proxy, type, url) { @Override protected Object doInvoke(T proxy, String methodName, Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object[] arguments) throws Throwable { // 调用 Wrapper 的 invokeMethod 方法,invokeMethod 最终会调用目标方法 return wrapper.invokeMethod(proxy, methodName, parameterTypes, arguments); } }; }
至此,服务消费的处理流程就分析完了。
这短短的一生我们最终都会失去,不妨大胆一点,爱一个人,攀一座山,追一个梦




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号