【数据结构与算法(java)】稀疏sparse array数组
数据结构与算法(Java)
稀疏数组和队列
稀疏sparse array数组
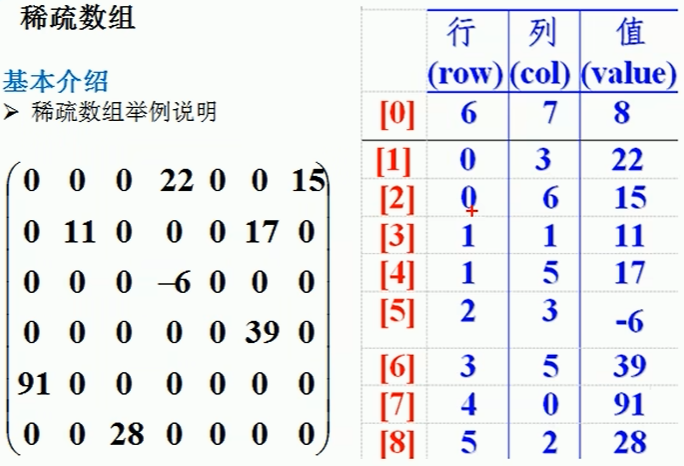
其中,[0]的行即原始数组的行数,[0]的列即原始数组的列数,[0]的值即原始数组中非0数的个数。
其他的,分别记录非0数的行列序号和值。
二维数组转稀疏数组的思路
- 遍历原始的二维数组,得到有效数据的个数sum
- 根据sum就可以创建稀疏数组
sparseArr int[sum+1][3] - 将二维数组的有效数据数据存入到稀疏数组
稀疏数组转原始的二维数组的思路
- 先读取稀疏数组的第一行,根据第一行的数据,创建原始的二维数组,比如上面的
chessArr2=int[11][11] - 在读取稀疏数组后几行的数据,并赋给原始的二维数组即可
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class SparseArray {
// save to file
public static void saveSparseArray(int[][] sparseArray, String filePath) {
try (BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(filePath))) {
for (int[] row : sparseArray) {
writer.write(row[0] + "," + row[1] + "," + row[2]);
writer.newLine();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// read from file
public static int[][] readSparseArray(String filePath) {
int rowCnt=0;
try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filePath))) {
String line;
while ((line = reader.readLine())!=null) {
rowCnt++;
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filePath))) {
String line;
int[][] sparseArr = new int[rowCnt][3];
int index = 0;
while ((line = reader.readLine())!=null) {
String[] parts = line.split(",");
sparseArr[index][0] = Integer.parseInt(parts[0]);
sparseArr[index][1] = Integer.parseInt(parts[1]);
sparseArr[index][2] = Integer.parseInt(parts[2]);
index++;
}
return sparseArr;
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int rowCnt = 11;
int colCnt = 11;
int chessArr1[][] = new int[rowCnt][colCnt];
chessArr1[1][2] = 1;
chessArr1[2][3] = 2;
// output
System.out.println("原始数组");
for (int[] row : chessArr1) {
for (int data : row) {
System.out.printf("%d\t", data);
}
System.out.println();
}
int cnt = 0;
for (int[] row : chessArr1) {
for (int data : row) {
if (data != 0) {
cnt++;
}
}
}
int sparseArr[][] = new int[cnt + 1][3];
sparseArr[0][0] = rowCnt;
sparseArr[0][1] = colCnt;
sparseArr[0][2] = cnt;
int index = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < rowCnt; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < colCnt; j++) {
if (chessArr1[i][j] != 0) {
sparseArr[index][0] = i;
sparseArr[index][1] = j;
sparseArr[index][2] = chessArr1[i][j];
index++;
}
}
}
// output
System.out.println("稀疏数组");
for (int[] row : sparseArr) {
for (int data : row) {
System.out.printf("%d\t", data);
}
System.out.println();
}
// 保存稀疏数组到 map.data 文件
saveSparseArray(sparseArr, "map.data");
// 从 map.data 文件读取稀疏数组并恢复原数组
int[][] readSparseArr = readSparseArray("map.data");
int rowCnt2 = readSparseArr[0][0];
int colCnt2 = readSparseArr[0][1];
int cnt2 = readSparseArr[0][2];
int chessArr2[][] = new int[rowCnt2][colCnt2];
for (int i = 1; i <= cnt2; i++) {
chessArr2[readSparseArr[i][0]][readSparseArr[i][1]] = readSparseArr[i][2];
}
// output
System.out.println("还原数组");
for (int[] row : chessArr2) {
for (int data : row) {
System.out.printf("%d\t", data);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号