Python学习笔记day11
SqlAlchemy ORM
SQLAlchemy是Python编程语言下的一款ORM框架,该框架建立在数据库API之上,使用关系对象映射进行数据库操作,简言之便是:将对象转换成SQL,然后使用数据API执行SQL并获取执行结果

Dialect用于和数据API进行交流,根据配置文件的不同调用不同的数据库API,从而实现对数据库的操作,如:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
MySQL-Python mysql+mysqldb://<user>:<password>@<host>[:<port>]/<dbname> pymysql mysql+pymysql://<username>:<password>@<host>/<dbname>[?<options>] MySQL-Connector mysql+mysqlconnector://<user>:<password>@<host>[:<port>]/<dbname> cx_Oracle oracle+cx_oracle://user:pass@host:port/dbname[?key=value&key=value...] 更多详见:http://docs.sqlalchemy.org/en/latest/dialects/index.html |
步骤一:
使用 Engine/ConnectionPooling/Dialect 进行数据库操作,Engine使用ConnectionPooling连接数据库,然后再通过Dialect执行SQL语句。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
#!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- from sqlalchemy import create_engine engine.execute( "INSERT INTO ts_test (a, b) VALUES ('2', 'v1')") engine.execute( "INSERT INTO ts_test (a, b) VALUES (%s, %s)", ((555, "v1"),(666, "v1"),))engine.execute( "INSERT INTO ts_test (a, b) VALUES (%(id)s, %(name)s)", id=999, name="v1") result = engine.execute('select * from ts_test')result.fetchall() |
步骤二:
使用 Schema Type/SQL Expression Language/Engine/ConnectionPooling/Dialect 进行数据库操作。Engine使用Schema Type创建一个特定的结构对象,之后通过SQL Expression Language将该对象转换成SQL语句,然后通过 ConnectionPooling 连接数据库,再然后通过 Dialect 执行SQL,并获取结果。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
#!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-from sqlalchemy import create_engine, Table, Column, Integer, String, MetaData, ForeignKeymetadata = MetaData()user = Table('user', metadata, Column('id', Integer, primary_key=True), Column('name', String(20)),)color = Table('color', metadata, Column('id', Integer, primary_key=True), Column('name', String(20)),)metadata.create_all(engine) |
增删改查
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
|
#!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-from sqlalchemy import create_engine, Table, Column, Integer, String, MetaData, ForeignKeymetadata = MetaData()user = Table('user', metadata, Column('id', Integer, primary_key=True), Column('name', String(20)),)color = Table('color', metadata, Column('id', Integer, primary_key=True), Column('name', String(20)),)conn = engine.connect()# 创建SQL语句,INSERT INTO "user" (id, name) VALUES (:id, :name)conn.execute(user.insert(),{'id':7,'name':'seven'})conn.close()# sql = user.insert().values(id=123, name='wu')# conn.execute(sql)# conn.close()# sql = user.delete().where(user.c.id > 1)# sql = user.update().values(fullname=user.c.name)# sql = user.update().where(user.c.name == 'jack').values(name='ed')# sql = select([user, ])# sql = select([user.c.id, ])# sql = select([user.c.name, color.c.name]).where(user.c.id==color.c.id)# sql = select([user.c.name]).order_by(user.c.name)# sql = select([user]).group_by(user.c.name)# result = conn.execute(sql)# print result.fetchall()# conn.close() |
一个简单的完整例子
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
from sqlalchemy import create_enginefrom sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_basefrom sqlalchemy import Column, Integer, Stringfrom sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmakerBase = declarative_base() #生成一个SqlORM 基类class Host(Base): __tablename__ = 'hosts' id = Column(Integer,primary_key=True,autoincrement=True) hostname = Column(String(64),unique=True,nullable=False) ip_addr = Column(String(128),unique=True,nullable=False) port = Column(Integer,default=22)Base.metadata.create_all(engine) #创建所有表结构if __name__ == '__main__': SessionCls = sessionmaker(bind=engine) #创建与数据库的会话session class ,注意,这里返回给session的是个class,不是实例 session = SessionCls() #h1 = Host(hostname='localhost',ip_addr='127.0.0.1') #h2 = Host(hostname='ubuntu',ip_addr='192.168.2.243',port=20000) #h3 = Host(hostname='ubuntu2',ip_addr='192.168.2.244',port=20000) #session.add(h3) #session.add_all( [h1,h2]) #h2.hostname = 'ubuntu_test' #只要没提交,此时修改也没问题 #session.rollback() #session.commit() #提交 res = session.query(Host).filter(Host.hostname.in_(['ubuntu2','localhost'])).all() print(res) |
更多内容详见:
http://www.jianshu.com/p/e6bba189fcbd
http://docs.sqlalchemy.org/en/latest/core/expression_api.html
注:SQLAlchemy无法修改表结构,如果需要可以使用SQLAlchemy开发者开源的另外一个软件Alembic来完成。
步骤三:
使用 ORM/Schema Type/SQL Expression Language/Engine/ConnectionPooling/Dialect 所有组件对数据进行操作。根据类创建对象,对象转换成SQL,执行SQL。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
|
#!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- from sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_basefrom sqlalchemy import Column, Integer, Stringfrom sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmakerfrom sqlalchemy import create_engine Base = declarative_base() class User(Base): __tablename__ = 'users' id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True) name = Column(String(50)) # 寻找Base的所有子类,按照子类的结构在数据库中生成对应的数据表信息# Base.metadata.create_all(engine) Session = sessionmaker(bind=engine)session = Session() # ########## 增 ########### u = User(id=2, name='sb')# session.add(u)# session.add_all([# User(id=3, name='sb'),# User(id=4, name='sb')# ])# session.commit() # ########## 删除 ########### session.query(User).filter(User.id > 2).delete()# session.commit() # ########## 修改 ########### session.query(User).filter(User.id > 2).update({'cluster_id' : 0})# session.commit()# ########## 查 ########### ret = session.query(User).filter_by(name='sb').first() # ret = session.query(User).filter_by(name='sb').all()# print ret # ret = session.query(User).filter(User.name.in_(['sb','bb'])).all()# print ret # ret = session.query(User.name.label('name_label')).all()# print ret,type(ret) # ret = session.query(User).order_by(User.id).all()# print ret # ret = session.query(User).order_by(User.id)[1:3]# print ret# session.commit() |
外键关联
A one to many relationship places a foreign key on the child table referencing the parent.relationship() is then specified on the parent, as referencing a collection of items represented by the child
from sqlalchemy import Table, Column, Integer, ForeignKey
from sqlalchemy.orm import relationship
from sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base
Base = declarative_base()
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
<br>class Parent(Base): __tablename__ = 'parent' id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True) children = relationship("Child")class Child(Base): __tablename__ = 'child' id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True) parent_id = Column(Integer, ForeignKey('parent.id')) |
To establish a bidirectional relationship in one-to-many, where the “reverse” side is a many to one, specify an additional relationship() and connect the two using therelationship.back_populates parameter:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
class Parent(Base): __tablename__ = 'parent' id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True) children = relationship("Child", back_populates="parent")class Child(Base): __tablename__ = 'child' id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True) parent_id = Column(Integer, ForeignKey('parent.id')) parent = relationship("Parent", back_populates="children") |
Child will get a parent attribute with many-to-one semantics.
Alternatively, the backref option may be used on a single relationship() instead of usingback_populates:
|
1
2
3
4
|
class Parent(Base): __tablename__ = 'parent' id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True) children = relationship("Child", backref="parent") |
原生sql join查询
几个Join的区别 http://stackoverflow.com/questions/38549/difference-between-inner-and-outer-joins
- INNER JOIN: Returns all rows when there is at least one match in BOTH tables
- LEFT JOIN: Return all rows from the left table, and the matched rows from the right table
- RIGHT JOIN: Return all rows from the right table, and the matched rows from the left table
select host.id,hostname,ip_addr,port,host_group.name from host right join host_group on host.id = host_group.host_id
in SQLAchemy
session.query(Host).join(Host.host_groups).filter(HostGroup.name=='t1').group_by("Host").all()
group by 查询
select name,count(host.id) as NumberOfHosts from host right join host_group on host.id= host_group.host_id group by name;
in SQLAchemy
from sqlalchemy import func session.query(HostGroup, func.count(HostGroup.name )).group_by(HostGroup.name).all() #another example session.query(func.count(User.name), User.name).group_by(User.name).all() SELECT count(users.name) AS count_1, users.name AS users_name FROM users GROUP BY users.name
堡垒机功能实现需求
业务需求:
- 兼顾业务安全目标与用户体验,堡垒机部署后,不应使用户访问业务系统的访问变的复杂,否则工作将很难推进,因为没人喜欢改变现状,尤其是改变后生活变得更艰难
- 保证堡垒机稳定安全运行, 没有100%的把握,不要上线任何新系统,即使有100%把握,也要做好最坏的打算,想好故障预案
功能需求:
- 所有的用户操作日志要保留在数据库中
- 每个用户登录堡垒机后,只需要选择具体要访问的设置,就连接上了,不需要再输入目标机器的访问密码
- 允许用户对不同的目标设备有不同的访问权限,例:
- 对10.0.2.34 有mysql 用户的权限
- 对192.168.3.22 有root用户的权限
- 对172.33.24.55 没任何权限
- 分组管理,即可以对设置进行分组,允许用户访问某组机器,但对组里的不同机器依然有不同的访问权限
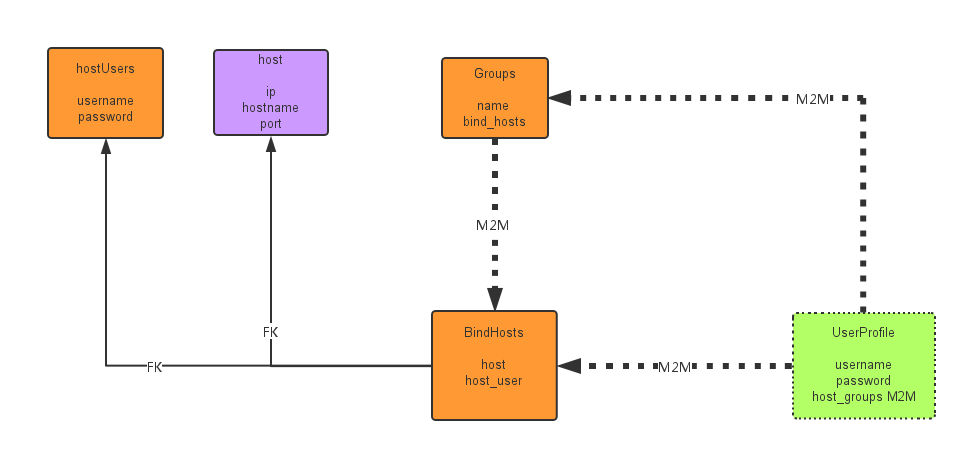
设计表结构:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
|
#_*_coding:utf-8_*___author__ = 'Alex Li'from sqlalchemy import create_engine,Tablefrom sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_basefrom sqlalchemy import Column, Integer, String,ForeignKey,UniqueConstraintfrom sqlalchemy.orm import relationshipfrom sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmakerfrom sqlalchemy import or_,and_from sqlalchemy import funcfrom sqlalchemy_utils import ChoiceType,PasswordTypeBase = declarative_base() #生成一个SqlORM 基类BindHost2Group = Table('bindhost_2_group',Base.metadata, Column('bindhost_id',ForeignKey('bind_host.id'),primary_key=True), Column('group_id',ForeignKey('group.id'),primary_key=True),)BindHost2UserProfile = Table('bindhost_2_userprofile',Base.metadata, Column('bindhost_id',ForeignKey('bind_host.id'),primary_key=True), Column('uerprofile_id',ForeignKey('user_profile.id'),primary_key=True),)Group2UserProfile = Table('group_2_userprofile',Base.metadata, Column('userprofile_id',ForeignKey('user_profile.id'),primary_key=True), Column('group_id',ForeignKey('group.id'),primary_key=True),)class UserProfile(Base): __tablename__ = 'user_profile' id = Column(Integer,primary_key=True,autoincrement=True) username = Column(String(32),unique=True,nullable=False) password = Column(String(128),unique=True,nullable=False) groups = relationship('Group',secondary=Group2UserProfile) bind_hosts = relationship('BindHost',secondary=BindHost2UserProfile) def __repr__(self): return "<UserProfile(id='%s',username='%s')>" % (self.id,self.username)class RemoteUser(Base): __tablename__ = 'remote_user' AuthTypes = [ (u'ssh-passwd',u'SSH/Password'), (u'ssh-key',u'SSH/KEY'), ] id = Column(Integer,primary_key=True,autoincrement=True) auth_type = Column(ChoiceType(AuthTypes)) username = Column(String(64),nullable=False) password = Column(String(255)) __table_args__ = (UniqueConstraint('auth_type', 'username','password', name='_user_passwd_uc'),) def __repr__(self): return "<RemoteUser(id='%s',auth_type='%s',user='%s')>" % (self.id,self.auth_type,self.username)class Host(Base): __tablename__ = 'host' id = Column(Integer,primary_key=True,autoincrement=True) hostname = Column(String(64),unique=True,nullable=False) ip_addr = Column(String(128),unique=True,nullable=False) port = Column(Integer,default=22) bind_hosts = relationship("BindHost") def __repr__(self): return "<Host(id='%s',hostname='%s')>" % (self.id,self.hostname)class Group(Base): __tablename__ = 'group' id = Column(Integer,primary_key=True,autoincrement=True) name = Column(String(64),nullable=False,unique=True) bind_hosts = relationship("BindHost",secondary=BindHost2Group, back_populates='groups' ) user_profiles = relationship("UserProfile",secondary=Group2UserProfile ) def __repr__(self): return "<HostGroup(id='%s',name='%s')>" % (self.id,self.name)class BindHost(Base): '''Bind host with different remote user, eg. 192.168.1.1 mysql passAbc123 eg. 10.5.1.6 mysql pass532Dr! eg. 10.5.1.8 mysql pass532Dr! eg. 192.168.1.1 root ''' __tablename__ = 'bind_host' id = Column(Integer,primary_key=True,autoincrement=True) host_id = Column(Integer,ForeignKey('host.id')) remoteuser_id = Column(Integer,ForeignKey('remote_user.id')) host = relationship("Host") remoteuser = relationship("RemoteUser") groups = relationship("Group",secondary=BindHost2Group,back_populates='bind_hosts') user_profiles = relationship("UserProfile",secondary=BindHost2UserProfile) __table_args__ = (UniqueConstraint('host_id', 'remoteuser_id', name='_bindhost_and_user_uc'),) def __repr__(self): return "<BindHost(id='%s',name='%s',user='%s')>" % (self.id, self.host.hostname, self.remoteuser.username )Base.metadata.create_all(engine) #创建所有表结构if __name__ == '__main__': SessionCls = sessionmaker(bind=engine) #创建与数据库的会话session class ,注意,这里返回给session的是个class,不是实例 session = SessionCls() #h1 = session.query(Host).filter(Host.hostname=='ubuntu4').first() #hg1 = session.query(HostGroup).filter(HostGroup.name=='t2').first() #h2 = Host(hostname='ubuntu4',ip_addr='192.168.1.21') #h3 = Host(hostname='ubuntu5',ip_addr='192.168.1.24',port=20000) #hg= HostGroup(name='TestServers3',host_id=h3.id) #hg2= HostGroup(name='TestServers2',host_id=h2.id) #hg3= HostGroup(name='TestServers3') #hg4= HostGroup(name='TestServers4') #session.add_all([hg3,hg4]) #h2.host_groups = [HostGroup(name="t1"),HostGroup(name="t2")] #h3.host_groups = [HostGroup(name="t2")] #h1.host_groups.append(HostGroup(name="t3") ) #print(h1.host_groups) #print("hg1:",hg1.host.hostname) #join_res = session.query(Host).join(Host.host_groups).filter(HostGroup.name=='t1').group_by("Host").all() #print('join select:',join_res) #group_by_res = session.query(HostGroup, func.count(HostGroup.name )).group_by(HostGroup.name).all() #print("-------------group by res-----") ''' h1=Host(hostname='h1',ip_addr='1.1.1.1') h2=Host(hostname='h2',ip_addr='1.1.1.2') h3=Host(hostname='h3',ip_addr='1.1.1.3') r1=RemoteUser(auth_type=u'ssh-passwd',username='alex',password='abc123') r2=RemoteUser(auth_type=u'ssh-key',username='alex') g1 = Group(name='g1') g2 = Group(name='g2') g3 = Group(name='g3') session.add_all([h1,h2,h3,r1,r2]) session.add_all([g1,g2,g3]) b1 = BindHost(host_id=1,remoteuser_id=1) b2 = BindHost(host_id=1,remoteuser_id=2) b3 = BindHost(host_id=2,remoteuser_id=2) b4 = BindHost(host_id=3,remoteuser_id=2) session.add_all((b1,b2,b3,b4)) all_groups = session.query(Group).filter().all() #first() all_bindhosts = session.query(BindHost).filter().all() #h1 = session.query(BindHost).filter(BindHost.host_id==1).first() #h1.groups.append(all_groups[1]) #print("h1:",h1) #print("----------->",all_groups.name,all_groups.bind_hosts) u1 = session.query(UserProfile).filter(UserProfile.id==1).first() print('--user:',u1.bind_hosts) print('--user:',u1.groups[0].bind_hosts) #u1.groups = [all_groups[1] ] #u1.bind_hosts.append(all_bindhosts[1]) #u1 = UserProfile(username='alex',password='123') #u2 = UserProfile(username='rain',password='abc!23') #session.add_all([u1,u2]) #b1 = BindHost() session.commit() #print(h2.host_groups) ''' |


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号