cuda 编程
线程块:
- 三维向量,
线程索引: index = x + yDx + zDx * Dy
假如 Dx = 10, Dy = 20 , Dz = 30,对于线程(2, 5, 9) 的index = 2 + 5 * 10 + 9 * 10 * 20 = 1852, 总线程数 Dx * Dy * Dz = 10 * 20 * 30 = 6000 = 6k
假如Dx = 6, Dy = 4, Dz = 2 ,如下是对应的线程id编号
第一层:
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
| 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 |
第二层
| 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 | 35 |
| 36 | 37 | 38 | 39 | 40 | 41 |
| 42 | 43 | 44 | 45 | 46 | 47 |
内存模型:
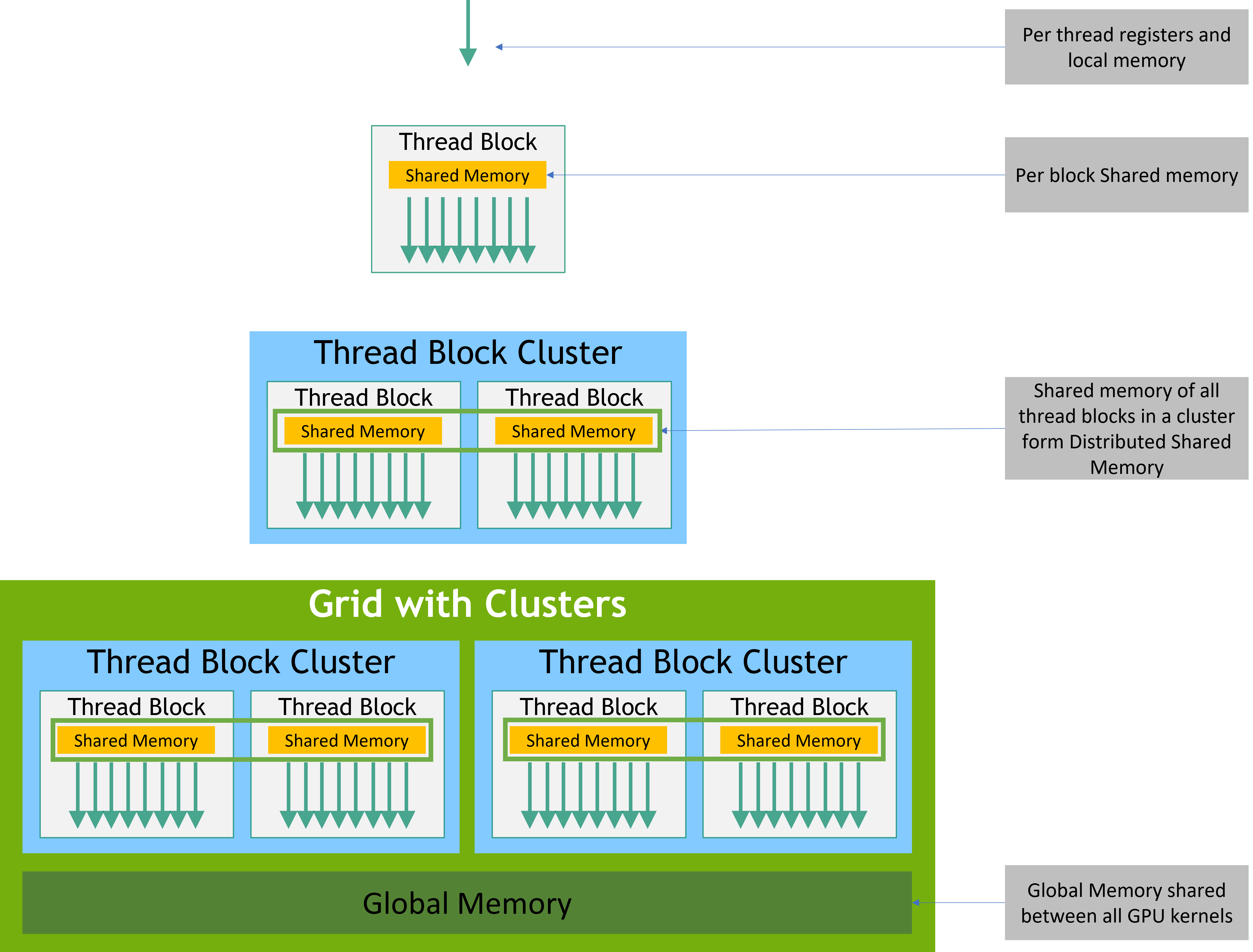
静态与动态内存的区别
| 特性 | 静态共享内存 | 动态共享内存 |
|---|---|---|
| 声明方式 | __shared__ float arr[size]; |
extern __shared__ float[]; |
| 大小确定时机 | 编译时 | 内核启动时 |
| 访问速度 | 略快(地址硬编码) | 略慢(运行时计算偏移) |
| 典型用途 | 固定大小的缓存 | 运行时决定大小的临时存储 |
| 作用域 | 整个集群内的所有线程块 + 非集群内的线程块 | 整个集群内的所有线程块 |
| 大小单位 | 以每个线程块为单位 | 以每个线程块为单位 |
- 统一内存
- 异步SIMT编程
异步屏障(Asynchronous Barrier)
用于实现CUDA线程间的同步机制。
异步内存拷贝(cuda::memcpy_async)
允许在GPU执行计算的同时,异步地从全局内存移动数据。
同步对象:cuda::barrier or a cuda::pipeline,
同步范围: cuda::thread_scope::thread_scope_thread, cuda::thread_scope::thread_scope_block,cuda::thread_scope::thread_scope_device,cuda::thread_scope::thread_scope_system
- 计算能力 SM version
编译
- 即时编译(JIT): ptx 动态加载到设备驱动中, 使用 NVRTC 可以支持运行时编译 cuda c++
- 二进制兼容 , 通过
-code=sm_80编译成针对计算能力8.0的二进制, - ptx兼容, 通过
-arch=compute_50指定C++编译为PTX代码时采用的计算能力,
cuda 运行态
- 每个设备创建一个CUDA上下文
- cudaInitDevice() 和 cudaSetDevice() 会初始化指定设备的上下文
- cudaDeviceReset() 销毁上下文
- CUDA 数组(CUDA arrays for texture fetching) & 线性内存(Linear memory)
- cudaMallocPitch(&devPtr, &pitch, width * sizeof(float), height); // pitch 表示间距
- cudaMallocPitch cudaMalloc3D, cudaMemcpy2D, cudaMemcpy3D // 更好的满足 存储对齐要求
- 支持L2缓存的管理,为持久化访问分配大小
- 页锁主机内存 cudaHostAlloc() and cudaFreeHost() , 可以通过 cudaHostAllocPortable 为所有设备设置可移植性, 通过 cudaHostAllocWriteCombined 支持写合并模式(应用场景:CPU向写入、GPU读取), 写合并内存会释放cpu L1 L2 缓存,同时PCIe总线上传输数据时,写合并内存不会被缓存系统窥探,缺点: cpu读取很慢, 写入很快。
- 内存映射 cudaHostAlloc() 传入 cudaHostAllocMapped ,将一块锁页主机内存映射到设备的地址空间, 主机内存中的地址cudaHostAlloc返回,cudaHostGetDevicePointer获取设备内存地址,好处: 可以在kernel函数中直接访问主机内存,没有设备内存的占用、拷贝和传输,无需使用流。在使用之前 需要通过cudaSetDeviceFlags() 并传入 cudaDeviceMapHost。
- 环境变量 CUDA_LAUNCH_BLOCKING=1 用于禁止内核启动的异步性,用于调试。
- 并行: cpu与gpu并行, kernel的并行, 数据传输与kernel的并行,数据传输与数据传输之间的并行,流与流之间的并行。
要通过流实现内存拷贝间的重叠行为, 页锁是必须的:因为如果使用普通内存,则cudaMemcpyAsync会退化为同步操作, 因为要等待cpu固定页面,而页锁可以使GPU的直接访问内存(DMA)。
cudaStream_t stream[2];
for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i)
cudaStreamCreate(&stream[i]);
float* hostPtr;
cudaMallocHost(&hostPtr, 2 * size);
for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i) {
cudaMemcpyAsync(inputDevPtr + i * size, hostPtr + i * size,
size, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice, stream[i]);
MyKernel <<<100, 512, 0, stream[i]>>>
(outputDevPtr + i * size, inputDevPtr + i * size, size);
cudaMemcpyAsync(hostPtr + i * size, outputDevPtr + i * size,
size, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost, stream[i]);
}
如果GPU设备不支持并行的数据传输 , 其优化方案如下:
for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i)
cudaMemcpyAsync(inputDevPtr + i * size, hostPtr + i * size,
size, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice, stream[i]);
for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i)
MyKernel<<<100, 512, 0, stream[i]>>>
(outputDevPtr + i * size, inputDevPtr + i * size, size);
for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i)
cudaMemcpyAsync(hostPtr + i * size, outputDevPtr + i * size,
size, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost, stream[i]);
这样, 提交到流[1]的主机到设备内存拷贝操作,将与提交到流[0]的内核启动操作产生执行重叠。
- 流之间的显示同步: cudaDeviceSynchronize(), cudaStreamSynchronize(), cudaStreamWaitEvent(),cudaStreamQuery(),
- cudaLaunchHostFunc()在流中任意位置插入CPU函数调用的机制,该函数将在主机上执行, 会等待该函数执行完成后,才继续执行后续的流中的操作, 被加入流中的主机函数不得直接或间接调用任何CUDA API函数,否则可能导致函数等待自身执行完成,从而引发死锁。
void CUDART_CB MyCallback(void *data){
printf("Inside callback %d\n", (size_t)data);
}
...
for (size_t i = 0; i < 2; ++i) {
cudaMemcpyAsync(devPtrIn[i], hostPtr[i], size, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice, stream[i]);
MyKernel<<<100, 512, 0, stream[i]>>>(devPtrOut[i], devPtrIn[i], size);
cudaMemcpyAsync(hostPtr[i], devPtrOut[i], size, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost, stream[i]);
cudaLaunchHostFunc(stream[i], MyCallback, (void*)i);
}
- 创建流时通过cudaStreamCreateWithPriority()指定流的相对优先级。通过cudaDeviceGetStreamPriorityRange()函数可获取设备的优先级范围,
// get the range of stream priorities for this device
int leastPriority, greatestPriority;
cudaDeviceGetStreamPriorityRange(&leastPriority, &greatestPriority);
// create streams with highest and lowest available priorities
cudaStream_t st_high, st_low;
cudaStreamCreateWithPriority(&st_high, cudaStreamNonBlocking, greatestPriority));
cudaStreamCreateWithPriority(&st_low, cudaStreamNonBlocking, leastPriority);
- 编程式依赖启动与同步, (preamble section 部分的并行), 场景:第二个kernel依赖第一个,但是第二个和第一个之间,并不是完全的串行

实现如下: 注意并发和死锁
__global__ void primary_kernel() {
// Initial work that should finish before starting secondary kernel
// Trigger the secondary kernel
cudaTriggerProgrammaticLaunchCompletion();
// Work that can coincide with the secondary kernel
}
__global__ void secondary_kernel()
{
// Independent work
// Will block until all primary kernels the secondary kernel is dependent on have completed and flushed results to global memory
cudaGridDependencySynchronize();
// Dependent work
}
cudaLaunchAttribute attribute[1];
attribute[0].id = cudaLaunchAttributeProgrammaticStreamSerialization;
attribute[0].val.programmaticStreamSerializationAllowed = 1;
configSecondary.attrs = attribute;
configSecondary.numAttrs = 1;
primary_kernel<<<grid_dim, block_dim, 0, stream>>>();
cudaLaunchKernelEx(&configSecondary, secondary_kernel);
也可以使用cuda 图的方式,待研究...
*cuda图: 可以通过api创建, 也可以通过流捕获,cudaStreamBeginCapture() 会将流置于捕获模式。当流处于捕获状态时,提交到该流的工作不会立即排队执行,而是逐步追加到一个正在构建的内部图中
- 跨流的之间的依赖,可以通过在主流中使用cudaEventRecord(), 在分流中使用cudaStreamWaitEvent(), 这样相当于告诉捕获程序,这儿有一个分叉,此时,分流会被自动置于捕获模式,并且将后续的操作捕获在主流的cuda图中,并且要求流2要合并如主流中,
cudaEventRecord(event2, stream2);cudaStreamWaitEvent(stream1, event2); - cudaUserObject_t 用于cuda图捕获的生命周期
- cuda 图更新
- 设备图启动机制:工作流需要在运行时根据数据做出决策,并执行不同的操作。相较于将这些决策过程交由主机处理, 可能导致设备与主机间的往返延迟
- 可从设备端启动的图称为"设备图"
- 无法从设备端启动的图称为"主机图"
- 设备图的创建 cudaGraphInstantiate()传递cudaGraphInstantiateFlagDeviceLaunch
- 设备图要求: 图内所有节点必须位于同一设备, 仅允许包含以下节点类型:内核节点、内存拷贝节点、内存设置节点和子图节点。
- 设备图上传: 使用cudaGraphUpload()函数直接上传,通过cudaGraphInstantiateWithParams()在实例化时请求上传
- 设备图启动:
| 即发即弃启动模式 | cudaStreamGraphFireAndForget |
|---|---|
| 尾部启动模式 | cudaStreamGraphTailLaunch |
| 同级启动模式 | cudaStreamGraphFireAndForgetAsSibling |
即发即弃启动:
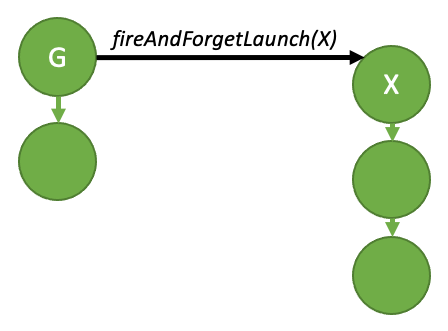
尾部启动:
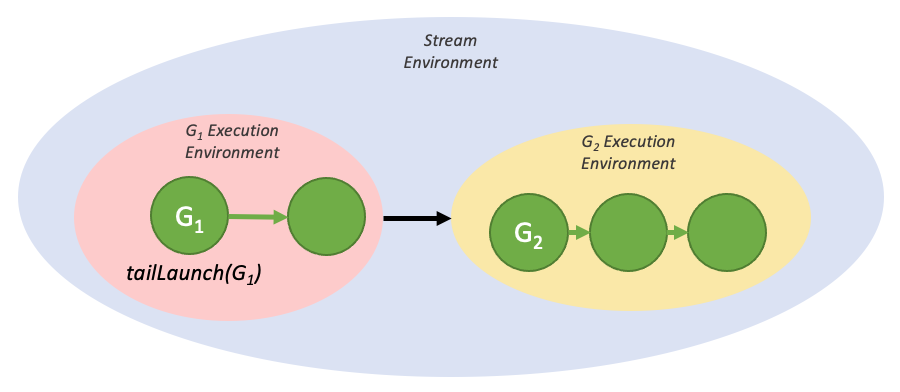
同级启动:
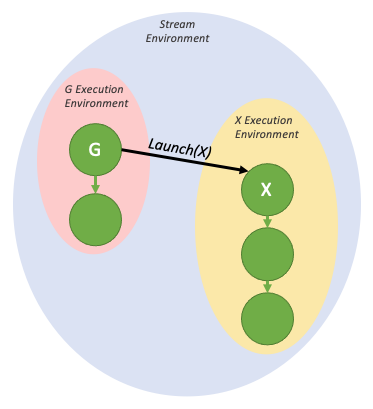
- 图执行环境满足层级结构
- 条件节点: cudaGraphConditionalHandleCreate() 创建条件句柄,cudaGraphAddConditionalNode() 添加条件节点, cudaGraphSetConditional()更新条件值,在创建条件节点时,系统会生成一个空白的子图并返回其句柄,以便用户填充子图内容。该条件体子图可通过以下两种方式构建:使用标准图API直接编辑, 通过cudaStreamBeginCaptureToGraph()函数从流捕获。
事件
- 为了监视设备的执行过程及进度, 在程序任意位置插入记录事件。
- 事件机制构成:cudaEventRecord() + cudaEventQuery()/cudaEventSynchronize()
- 支持cudaEventElapsedTime()计算纳秒级时间间隔
多设备系统
- cudaSetDevice, cudaGetDeviceCount, cudaDeviceProp , cudaGetDeviceProperties
- 在 PCIe/NVLINK 连接的情况下, 可以cudaDeviceEnablePeerAccess(peerDeviceId, 0);激活访问权限, 支持直接指定访问和同一地址空间访问。
- 设备间内存复制:统一地址空间,直接拷贝,非统一地址空间: cudaMemcpyPeer(), cudaMemcpyPeerAsync(), cudaMemcpy3DPeer(),cudaMemcpy3DPeerAsync()等拷贝
对等拷贝:
cudaSetDevice(0); // Set device 0 as current
float* p0;
size_t size = 1024 * sizeof(float);
cudaMalloc(&p0, size); // Allocate memory on device 0
cudaSetDevice(1); // Set device 1 as current
float* p1;
cudaMalloc(&p1, size); // Allocate memory on device 1
cudaSetDevice(0); // Set device 0 as current
MyKernel<<<1000, 128>>>(p0); // Launch kernel on device 0
cudaSetDevice(1); // Set device 1 as current
cudaMemcpyPeer(p1, 1, p0, 0, size); // Copy p0 to p1
MyKernel<<<1000, 128>>>(p1); // Launch kernel on device 1
统一虚拟地址空间
当应用程序以64位进程运行时,主机与所有计算能力2.0及以上的设备将共享统一的虚拟地址空间,
cudaPointerAttributes attributes;
cudaPointerGetAttributes(&attributes, ptr); // 可确定指针位于主机/设备内存
cudaMemcpy(dest, src, size, cudaMemcpyDefault); // 自动识别指针位置
- 错误检查: cudaDeviceSynchronize()后使用 cudaGetLastError()进行错误检查
Texture and Surface Memory //TODO
知识是我们已知的
也是我们未知的
基于已有的知识之上
我们去发现未知的
由此,知识得到扩充
我们获得的知识越多
未知的知识就会更多
因而,知识扩充永无止境




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号