一、方案总览
1. 核心目标
解决商超商品搜索的语义匹配不足与人工干预缺失两大痛点,弥补 Elasticsearch(ES)在语义理解上的局限,实现:
- 语义相似排序(如搜 “西蓝花” 时,按 “有机西蓝花→普通西蓝花→有机花菜→普通花菜” 优先级排序);
- 人工自定义关联(如 “大料” 强制关联 “花椒、八角、桂皮”,且优先级高于自动匹配);
- 架构简化(基于 PostgreSQL 原生能力,无需额外部署向量数据库)。
2. 技术栈
| 组件 | 选型说明 |
|---|---|
| 数据库 | PostgreSQL 16.9+(支持分区表)+ pgvector 0.8.1+(向量存储与相似度计算) |
| NLP 向量模型 | Sentence-BERT(中文模型:uer/sbert-base-chinese-nli) |
| 文本过滤 | Elasticsearch 8.x(负责 “粗过滤”,如商品名称模糊匹配,减少向量计算量) |
| 后端服务 | Python 3.9+(FastAPI:接口开发;psycopg2:PG 交互;elasticsearch-py:ES 交互) |
2.1 postgresql
[root@uctg-yjfb-db-7-105 ~]# psql -Upostgres psql (16.9) Type "help" for help. postgres=# select version(); version --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- PostgreSQL 16.9 on x86_64-pc-linux-gnu, compiled by gcc (GCC) 8.5.0 20210514 (Red Hat 8.5.0-26), 64-bit (1 row)
2.2 pgvector
postgres=# CREATE EXTENSION IF NOT EXISTS vector; CREATE EXTENSION postgres=# SELECT extname, extversion postgres-# FROM pg_extension postgres-# WHERE extname = 'vector'; extname | extversion ---------+------------ vector | 0.8.1 (1 row) postgres=#
二、方案架构设计
1. 整体流程
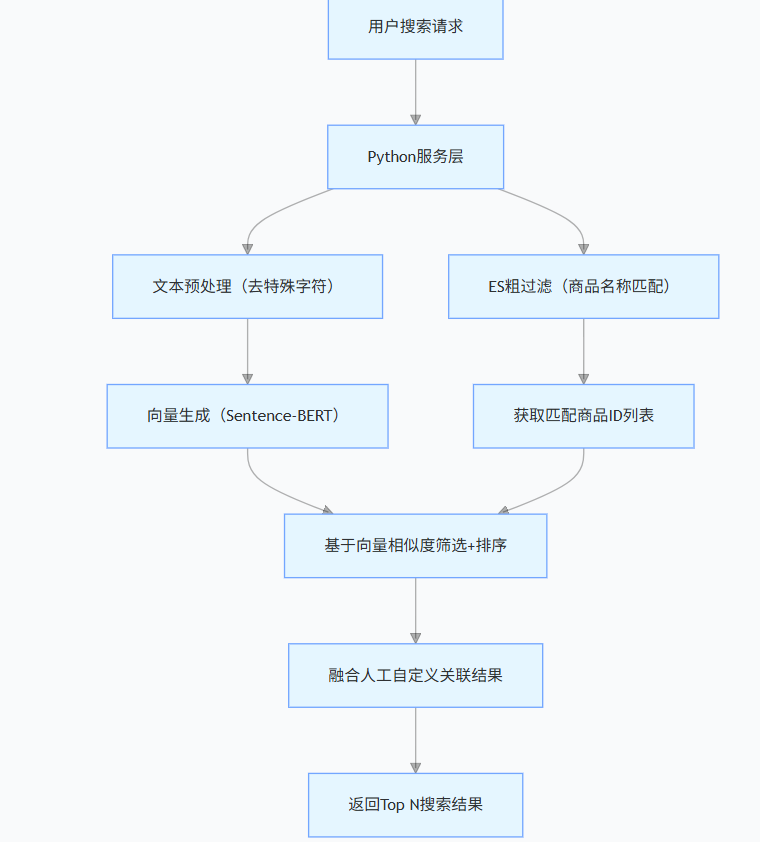
2. 组件分工
| 组件 | 核心职责 |
|---|---|
| ES | 1. 商品名称模糊匹配(如 “西蓝” 匹配 “西蓝花”);2. 过滤无效商品(如下架商品);3. 输出匹配商品 ID 列表,减少 PG 计算量 |
| PostgreSQL | 1. 存储商品基础数据(名称、价格、库存);2. 存储商品语义向量(pgvector 字段);3. 存储人工自定义关联规则;4. 执行向量相似度计算与排序 |
| Python 服务 | 1. 协调 ES 过滤与 PG 向量查询;2. 生成语义向量;3. 融合 “自动相似度结果” 与 “人工关联结果”;4. 提供 RESTful 搜索接口 |
三、数据层设计(PostgreSQL+pgvector)
1. 分表策略
按商品分类做列表分区(符合商超业务逻辑,如蔬菜类、调料类单独分区),优势:
- 减少单表数据量,提升查询性能;
- 便于按分类管理数据(如蔬菜类促销活动仅操作蔬菜分区表)。
2. 表结构创建 SQL
(1)主表与分区表(商超商品表)
-- 1. 主表:商超商品表(启用分区)
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS product (
product_id BIGSERIAL PRIMARY KEY, -- 商品唯一ID
product_name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, -- 商品名称(如“有机西蓝花”)
product_desc TEXT, -- 商品描述(如“无农药残留”)
category_id INT NOT NULL, -- 分区键:1=蔬菜类,2=调料类
price DECIMAL(10,2) NOT NULL, -- 售价
stock INT NOT NULL DEFAULT 0, -- 库存
product_vec VECTOR(768) NOT NULL -- 768维语义向量(pgvector核心字段)
) PARTITION BY LIST (category_id); -- 按分类列表分区
-- 2. 分区表:蔬菜类(category_id=1)
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS product_vegetable
PARTITION OF product FOR VALUES IN (1);
-- 3. 分区表:调料类(category_id=2)
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS product_seasoning
PARTITION OF product FOR VALUES IN (2);
-- 4. 索引设计(提升查询效率)
CREATE INDEX IF NOT EXISTS idx_product_veg_vec ON product_vegetable USING hnsw (product_vec vector_cosine_ops); -- 蔬菜类向量索引(HNSW算法,适合高并发)
CREATE INDEX IF NOT EXISTS idx_product_sea_vec ON product_seasoning USING hnsw (product_vec vector_cosine_ops); -- 调料类向量索引
CREATE INDEX IF NOT EXISTS idx_product_name ON product (product_name); -- 商品名称模糊查询索引
CREATE INDEX IF NOT EXISTS idx_product_category ON product (category_id); -- 分类过滤索引
(2)商品自定义关联表(人工干预用)
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS product_custom_relation (
relation_id BIGSERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
main_product_id BIGINT NOT NULL, -- 主商品ID(如“大料”的ID)
related_product_id BIGINT NOT NULL, -- 关联商品ID(如“花椒”的ID)
custom_weight FLOAT NOT NULL DEFAULT 1.0, -- 自定义权重(0-10,越高排序越靠前)
is_active BOOLEAN NOT NULL DEFAULT TRUE, -- 是否生效
create_time TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
-- 外键约束(确保关联商品存在)
FOREIGN KEY (main_product_id) REFERENCES product(product_id),
FOREIGN KEY (related_product_id) REFERENCES product(product_id),
-- 唯一约束(避免重复关联)
UNIQUE (main_product_id, related_product_id)
);
-- 关联表索引(加速人工关联查询)
CREATE INDEX IF NOT EXISTS idx_main_product ON product_custom_relation (main_product_id, is_active);
四、核心代码实现(Python)
1. 环境依赖
pip install fastapi uvicorn psycopg2-binary sqlalchemy sentence-transformers elasticsearch pandas2. 工具类封装
(1)向量生成工具(Sentence-BERT 中文模型)
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer
class VectorGenerator:
"""语义向量生成器(单例模式,避免重复加载模型)"""
_instance = None
def __new__(cls, model_name: str = "uer/sbert-base-chinese-nli"):
if cls._instance is None:
cls._instance = super().__new__(cls)
# 加载中文预训练模型(兼顾语义准确性与速度)
cls._instance.model = SentenceTransformer(model_name)
return cls._instance
def text_to_vector(self, text: str) -> list[float]:
"""将文本(商品名称/搜索词)转化为768维向量"""
if not text.strip():
raise ValueError("输入文本不能为空")
# 生成向量并转为列表(适配pgvector存储格式)
vector = self.model.encode(text, convert_to_tensor=False)
return vector.tolist()
# 实例化(全局唯一)
vector_generator = VectorGenerator()(2)PostgreSQL+pgvector 交互工具
from sqlalchemy import create_engine, text
from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker
from typing import List, Dict
class PGVectorClient:
def __init__(self, db_url: str):
"""初始化PG客户端(支持向量查询与分区表操作)"""
self.engine = create_engine(db_url)
self.Session = sessionmaker(bind=self.engine)
def get_similar_products(self,
query_vector: list[float],
category_id: int = None,
filter_product_ids: List[int] = None, # ES过滤后的商品ID列表
top_k: int = 20) -> List[Dict]:
"""
按向量相似度查询商品(核心方法)
:param query_vector: 搜索词向量
:param category_id: 商品分类ID(可选,进一步过滤)
:param filter_product_ids: ES过滤后的商品ID(必选,减少计算量)
:param top_k: 返回Top N结果
"""
session = self.Session()
try:
# 基础SQL:计算余弦相似度(1 - 向量距离 = 相似度,范围0-1)
base_sql = """
SELECT
p.product_id, p.product_name, p.price, p.stock,
1 - (p.product_vec <=> :query_vec) AS similarity_score
FROM product p
WHERE 1=1
"""
params = {"query_vec": query_vector, "top_k": top_k}
# 条件1:ES过滤后的商品ID(必选)
if filter_product_ids and len(filter_product_ids) > 0:
base_sql += " AND p.product_id = ANY(:filter_ids)"
params["filter_ids"] = filter_product_ids
# 条件2:分类过滤(可选)
if category_id:
base_sql += " AND p.category_id = :category_id"
params["category_id"] = category_id
# 完整SQL:按相似度降序,限制结果数量
full_sql = f"{base_sql} ORDER BY similarity_score DESC LIMIT :top_k"
result = session.execute(text(full_sql), params).mappings().all()
return [dict(row) for row in result]
finally:
session.close()
def get_custom_related(self, main_product_id: int) -> List[Dict]:
"""获取人工自定义关联的商品(如“大料”关联“花椒、八角”)"""
session = self.Session()
try:
sql = """
SELECT
p.product_id, p.product_name, p.price, p.stock,
r.custom_weight AS similarity_score, -- 人工权重作为相似度分数
'人工关联' AS match_type
FROM product_custom_relation r
JOIN product p ON r.related_product_id = p.product_id
WHERE r.main_product_id = :main_id AND r.is_active = TRUE
ORDER BY r.custom_weight DESC
"""
result = session.execute(text(sql), {"main_id": main_product_id}).mappings().all()
return [dict(row) for row in result]
finally:
session.close()
def add_custom_relation(self, main_id: int, related_id: int, weight: float = 1.0) -> bool:
"""添加人工关联规则(如“大料”→“花椒”)"""
session = self.Session()
try:
# 避免重复关联
exists = session.execute(
text("SELECT 1 FROM product_custom_relation WHERE main_product_id=:m AND related_product_id=:r"),
{"m": main_id, "r": related_id}
).scalar()
if exists:
return False

