Spring Boot 注解——@ConfigurationProperties
引言
我们习惯于将某些经常变化的东西放在配置文件中,为了方便,未来可能需要创建一些组件,注入到容器中。因此实现的场景就是将配置文件放在Bean中的指定属性中。
简介
@ConfigurationProperties是Springboot提供读取配置文件的一个注解。其对应的bean的后置处理器为ConfigurationPropertiesBindingPostProcessor
使用方法
@ConfigurationProperties的基本用法非常简单:我们为每个要捕获的外部属性提供一个带有字段的类。请注意以下几点:
- 前缀定义了哪些外部属性将绑定到类的字段上
- 根据 Spring Boot 宽松的绑定规则,类的属性名称必须与外部属性的名称匹配
- 我们可以简单地用一个值初始化字段作为一个默认值
- 类本身可以是包私有的
- 类的字段必须有公共 setter 方法
Spring宽松绑定规则(relaxed binding)
Spring使用一些宽松的绑定属性规则。因此,以下变体都将绑定到 hostName 属性上:
- mail.hostName = localhost
- mail.hostname = localhost
- mail.host_name = localhost
- mail.host-name = localhost
- mail.HOSTNAME = localhost
@Component和@ConfigurationProperties
- 在配置文件中放入需要配置的KV值
# 放入自定义配置
mycar:
brand: BYD
price: 100000
- 创建一个对应的自定义类
// 只有在容器中的组件,才能被赋值
@Component
// 将配置文件中对应属性的值赋值到对应的属性
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "mycar")
public class car {
/**
* 品牌
*/
private String bread;
/**
* 价格
*/
private Integer Price;
public String getBread() {
return this.bread;
}
public void setBread(String bread) {
this.bread = bread;
}
public Integer getPrice() {
return this.price;
}
public void setPrice(Integer price) {
this.price = price
}
}
- 结果
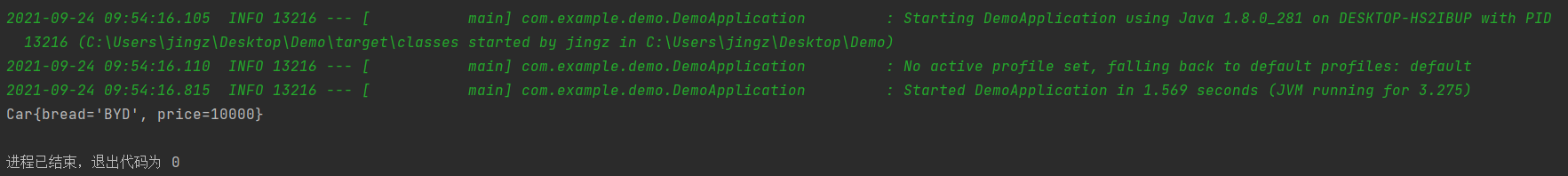
@EnableConfigurationProperties和@ConfigurationProperties
- 在配置文件中放入需要配置的KV值
# 放入自定义配置
mycar:
brand: BYD
price: 100000
- 创建一个对应的自定义类
// 只有在容器中的组件,才能被赋值
@Component
// 将配置文件中对应属性的值赋值到对应的属性
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "mycar")
public class car {
/**
* 品牌
*/
private String bread;
/**
* 价格
*/
private Integer Price;
public String getBread() {
return this.bread;
}
public void setBread(String bread) {
this.bread = bread;
}
public Integer getPrice() {
return this.price;
}
public void setPrice(Integer price) {
this.price = price
}
}
- 创建一个自定义配置类
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties(Car.class)
public class CarConfig {
}
- 结果
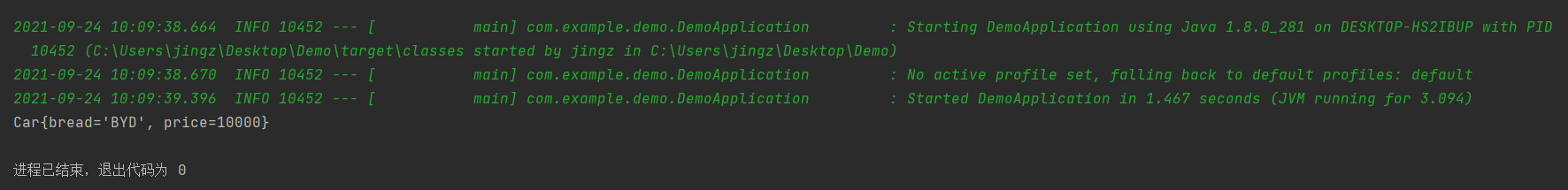
经过测试,在标注@Configuration的类上标注@EnableConfigurationProperties(xxx.class)也能够注入成功,因为@EnableConfigurationProperties(xxx.class)在程序启动的时候会将xxx.class进行一次组件注入。
@EnableConfigurationProperties(xxx.class)作用:
- 开启配置属性绑定功能
- 将指定的类自动导入容器中
文档解释:
当@EnableConfigurationProperties注解应用到你的@Configuration时,任何被@ConfigurationProperties注解的beans将自动被Environment属性配置。 这种风格的配置特别适合与SpringApplication的外部YAML配置进行配合使用。
注意事项
在使用@ConfigurationProperties这个注解的时候一定要搭配@Component或@EnableConfigurationProperties注解,否则会报错!!!
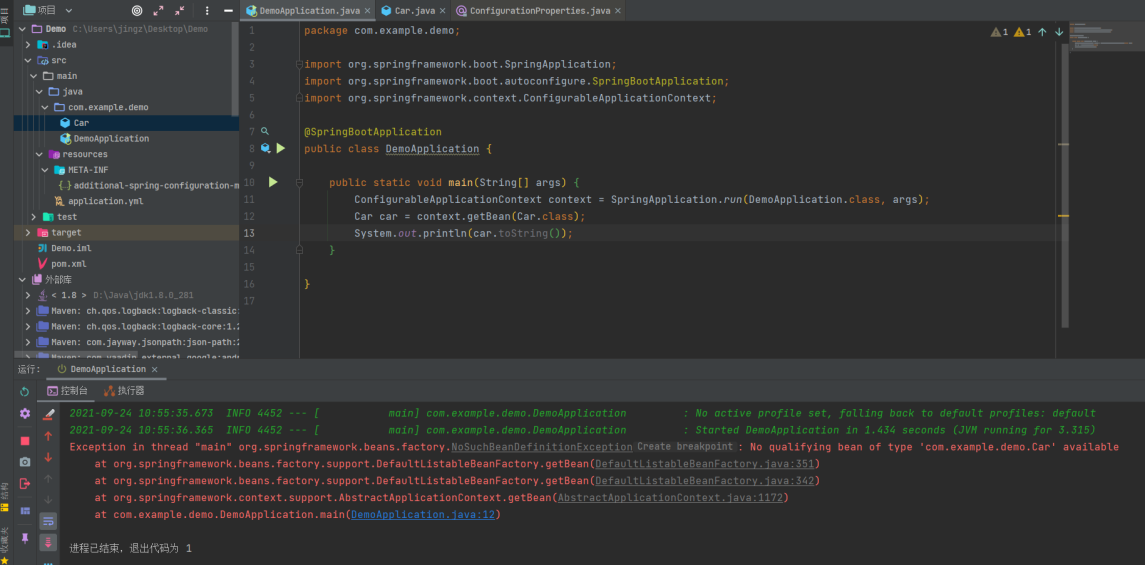
为什么呢?在前文提到过
Spring Boot需要先将标注@ConfigurationProperties注解的类注入到容器中,才能够将配置文件中的属性绑定到对应的Bean上,这一波操作全部基于Spring中强大的IOC机制。
源码解析
@Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Indexed
public @interface ConfigurationProperties {
/**
* 有效绑定到此对象的属性的前缀。一个有效的前缀由一个或多个用点分隔的单词定义(例如"acme.system.feature" )
*/
@AliasFor("prefix")
String value() default "";
/**
* 有效绑定到此对象的属性的前缀。一个有效的前缀由一个或多个用点分隔的单词定义(例如"acme.system.feature" )
*/
@AliasFor("value")
String prefix() default "";
/**
* 标志以指示绑定到此对象时应忽略无效字段。根据所使用的绑定器,无效意味着无效,
* 通常这意味着字段类型错误(或无法强制转换为正确类型)
*/
boolean ignoreInvalidFields() default false;
/**
* 标志以指示绑定到此对象时应忽略未知字段。未知字段可能表示属性中存在错误
*/
boolean ignoreUnknownFields() default true;
}
其背后的有一个名为ConfigurationPropertiesBindingPostProcessor的后置解析器,其中有两个重要的方法:
- register
- 作用:注入一个ConfigurationPropertiesBindingPostProcessor类型的BeanDefinition
- 源码实现:
/** * 生成一个ConfigurationPropertiesBindingPostProcessor Bean */ public static void register(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { Assert.notNull(registry, "Registry must not be null"); // 注册 ConfigurationPropertiesBindingPostProcessor 类型的 BeanDefinition if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(BEAN_NAME)) { BeanDefinition definition = BeanDefinitionBuilder .rootBeanDefinition(ConfigurationPropertiesBindingPostProcessor.class).getBeanDefinition(); definition.setRole(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE); registry.registerBeanDefinition(BEAN_NAME, definition); } // 注册 ConfigurationPropertiesBinder 和 ConfigurationPropertiesBinder.Factory 两个 BeanDefinition ConfigurationPropertiesBinder.register(registry); } - bind (最重要)
- 作用:将注解 @ConfigurationProperties 指定的外部配置属性项设置到目标对象 bean
- 源码实现:
/** * 将注解 @ConfigurationProperties 指定的外部配置属性项设置到目标对象 bean */ private void bind(ConfigurationPropertiesBean bean) { // 如果bean 为null 或者已经处理过,则直接跳过 if (bean == null || hasBoundValueObject(bean.getName())) { return; } Assert.state(bean.getBindMethod() == BindMethod.JAVA_BEAN, "Cannot bind @ConfigurationProperties for bean '" + bean.getName() + "'. Ensure that @ConstructorBinding has not been applied to regular bean"); try { // 通过ConfigurationPropertiesBinder(配置属性绑定器)将指定前缀的属性值设置到这个Bean 中, // 会借助 Conversion 类型转换器进行类型转换 this.binder.bind(bean); } catch (Exception ex) { throw new ConfigurationPropertiesBindException(bean, ex); } }
ConfigurationPropertiesBinder.bind()源码
BindResult<?> bind(ConfigurationPropertiesBean propertiesBean) {
// 获取需要绑定配置的
Bindable<?> target = propertiesBean.asBindTarget();
// 获取@ConfigurationProperties注解
ConfigurationProperties annotation = propertiesBean.getAnnotation();
// 获取用于绑定配置的处理器
BindHandler bindHandler = getBindHandler(target, annotation);
// 通过处理器绑定配置
return getBinder().bind(annotation.prefix(), target, bindHandler);
}
Binder.bind()源码:
private <T> T bind(ConfigurationPropertyName name, Bindable<T> target, BindHandler handler, Context context,
boolean allowRecursiveBinding, boolean create) {
try {
// 确定需要替换的目标,OnStart方法中只有一行return target,不知道是什么意思
Bindable<T> replacementTarget = handler.onStart(name, target, context);
if (replacementTarget == null) {
return handleBindResult(name, target, handler, context, null, create);
}
target = replacementTarget;
Object bound = bindObject(name, target, handler, context, allowRecursiveBinding);
return handleBindResult(name, target, handler, context, bound, create);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
return handleBindError(name, target, handler, context, ex);
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号