BLOG-2
(1)前言:
本次题目PTA题目集、超星作业、期中考试的题量适当,难度中等,PTA主要涉及到的知识点是类与类之间的关系,超星作业涉及到的知识点是单链表与双链表,期中考试涉及到的知识点是继承、多态和容器。其中PTA题目集04中的点线形系列三角形计算和题目集06点线形系列凸四边形的计算较为困难,并且这两道题有许多情况需要讨论,因此较为复杂。
(2)设计与分析:
下面重点对几道题进行解析:
1、题目集04:7-3 点线形系列3-三角形的计算
用户输入一组选项和数据,进行与三角形有关的计算。选项包括:
1:输入三个点坐标,判断是否是等腰三角形、等边三角形,判断结果输出true/false,两个结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。
2:输入三个点坐标,输出周长、面积、重心坐标,三个参数之间以一个英文空格分隔,坐标之间以英文","分隔。
3:输入三个点坐标,输出是钝角、直角还是锐角三角形,依次输出三个判断结果(true/false),以一个英文空格分隔,
4:输入五个点坐标,输出前两个点所在的直线与三个点所构成的三角形相交的交点数量,如果交点有两个,则按面积大小依次输出三角形被直线分割成两部分 的面积。若直线与三角形一条线重合,输出"The point is on the edge of the triangle"
5:输入四个点坐标,输出第一个是否在后三个点所构成的三角形的内部(输出in the triangle/outof triangle)。
必须使用射线法,原理:由第一个点往任一方向做一射线,射线与三角形的边的交点(不含点本身)数量如果为1,则在三角形内部。如果交点有两个或0 个,则在三角形之外。若点在三角形的某条边上,输出"on the triangle"
分析:这道题主要的难点在于选项四和选项五,选项一中若有两条边相等则为等腰三角形且第三条边与这两条边中的一条相等即为等边三角形,选项二中可用海伦公式求出三角形的面积。重心的横纵坐标用输入的三个点的横纵坐标的平均值求出。选项三根据三角形三条边的长度来判断。选项四需要考虑直线是否过三角形的顶点。选项五使用射线法来判断点是否在三角形内,即从该点垂直或水平方向做一条射线,若该射线与三角形的交点有且只有一个,则该点在三角形内部,否则在三角形外部。
判断三角形类型:
public int typeOfQuadrilateral() { int flag; double l1,l2,l3,l4; double k1,k2,k3,k4; l1 = Length(x1,y1,x2,y2); l2 = Length(x1,y1,x4,y4); l3 = Length(x2,y2,x3,y3); l4 = Length(x3,y3,x4,y4); k1 = Slope(x1,y1,x2,y2); k2 = Slope(x1,y1,x4,y4); k3 = Slope(x2,y2,x3,y3); k4 = Slope(x3,y3,x4,y4); if((x1==x4&&x2==x3)||(x1==x2&&x3==x4)) { if(l1==l2&&l1==l3&&l1==l4) { if((x1==x4&&x2==x3&&y1==y2&&y3==y4)||(x1==x2&&x3==x4&&y1==y4&&y2==y3)) { flag = 3; } else { flag = 1; } } else { flag = 2; } } else if(k1*k2==-1||k1*k3==-1||k3*k4==-1||k2*k4==-1) { if(l1==l2&&l1==l3&&l1==l4) { flag = 3; } else { flag = 2; } } else { flag = 1; } return flag; }
判断点是否在三角形内部:
public boolean intheQuadrilateral() { double l1,l2,l3,l4,l5,l6,l7,l8,l; double a1,a2,a3,a4,a5,a6,area; if(chonghe()) { if(x2==x3&&y2==y3) { l1 = Length(x2,y2,x4,y4); l2 = Length(x2,y2,x5,y5); l3 = Length(x4,y4,x5,y5); l4 = Length(x1,y1,x2,y2); l5 = Length(x1,y1,x4,y4); l6 = Length(x1,y1,x5,y5); } else if(x2==x4&&y2==y4) { l1 = Length(x2,y2,x3,y3); l2 = Length(x2,y2,x5,y5); l3 = Length(x3,y3,x5,y5); l4 = Length(x1,y1,x2,y2); l5 = Length(x1,y1,x3,y3); l6 = Length(x1,y1,x5,y5); } else if(x2==x5&&y2==y5) { l1 = Length(x2,y2,x3,y3); l2 = Length(x2,y2,x4,y4); l3 = Length(x3,y3,x4,y4); l4 = Length(x1,y1,x2,y2); l5 = Length(x1,y1,x3,y3); l6 = Length(x1,y1,x4,y4); } else if(x3==x4&&y3==y4) { l1 = Length(x2,y2,x3,y3); l2 = Length(x2,y2,x5,y5); l3 = Length(x3,y3,x5,y5); l4 = Length(x1,y1,x2,y2); l5 = Length(x1,y1,x3,y3); l6 = Length(x1,y1,x5,y5); } else if(x3==x5&&y3==y5) { l1 = Length(x2,y2,x3,y3); l2 = Length(x2,y2,x4,y4); l3 = Length(x3,y3,x4,y4); l4 = Length(x1,y1,x2,y2); l5 = Length(x1,y1,x3,y3); l6 = Length(x1,y1,x4,y4); } else { l1 = Length(x2,y2,x3,y3); l2 = Length(x2,y2,x4,y4); l3 = Length(x3,y3,x4,y4); l4 = Length(x1,y1,x2,y2); l5 = Length(x1,y1,x3,y3); l6 = Length(x1,y1,x4,y4); } area = Area(l1,l2,l3); a1 = Area(l1,l4,l5); a2 = Area(l2,l4,l6); a3 = Area(l3,l5,l6); if(Math.abs(a1+a2+a3-area)<1e-10) { return true; } } else { l1 = Length(x2,y2,x3,y3); l2 = Length(x3,y3,x4,y4); l3 = Length(x4,y4,x5,y5); l4 = Length(x2,y2,x5,y5); l5 = Length(x1,y1,x2,y2); l6 = Length(x1,y1,x3,y3); l7 = Length(x1,y1,x4,y4); l8 = Length(x1,y1,x5,y5); l = Length(x2,y2,x4,y4); a1 = Area(l1,l5,l6); a2 = Area(l2,l6,l7); a3 = Area(l3,l7,l8); a4 = Area(l4,l5,l8); a5 = Area(l1,l2,l); a6 = Area(l3,l4,l); if(Math.abs((a1+a2+a3+a4)-(a5+a6))<1e-10) { return true; } } return false; }
类图:

2、题目集06:7-2 点线形系列4-凸四边形的计算
用户输入一组选项和数据,进行与四边形有关的计算。
以下四边形顶点的坐标要求按顺序依次输入,连续输入的两个顶点是相邻顶点,第一个和最后一个输入的顶点相邻。
选项包括:
1:输入四个点坐标,判断是否是四边形、平行四边形,判断结果输出true/false,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。
2:输入四个点坐标,判断是否是菱形、矩形、正方形,判断结果输出true/false,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。 若四个点坐标无法构成四边形,输出"not a quadrilateral"
3:输入四个点坐标,判断是凹四边形(false)还是凸四边形(true),输出四边形周长、面积,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。 若四个点坐标无法构成四边形,输出"not a quadrilateral"
4:输入六个点坐标,前两个点构成一条直线,后四个点构成一个四边形或三角形,输出直线与四边形(也可能是三角形)相交的交点数量。如果交点有两个,再按面积从小到大输出四边形(或三角形)被直线分割成两部分的面积(不换行)。若直线与四边形或三角形的一条边线重合,输出"The line is coincide with one of the lines"。若后四个点不符合四边形或三角形的输入,输出"not a quadrilateral or triangle"。
后四个点构成三角形的情况:假设三角形一条边上两个端点分别是x、y,边线中间有一点z,另一顶点s:
1)符合要求的输入:顶点重复或者z与xy都相邻,如x x y s、x z y s、x y x s、s x y y。此时去除冗余点,保留一个x、一个y。
2) 不符合要求的输入:z 不与xy都相邻,如z x y s、x z s y、x s z y
5:输入五个点坐标,输出第一个是否在后四个点所构成的四边形(限定为凸四边形,不考虑凹四边形)或三角形(判定方法见选项4)的内部(若是四边形输出in the quadrilateral/outof the quadrilateral,若是三角形输出in the triangle/outof the triangle)。如果点在多边形的某条边上,输出"on the triangle或者on the quadrilateral"。若后四个点不符合四边形或三角形,输出"not a quadrilateral or triangle"。
分析:这道题主要的难点在于选项三判断是凹四边形还是凸四边形,选项四中直线与多边形的交点数量与分割成两部分的面积和判断输入是否符合要求,选项五判断点的位置。选项一若四个点中没有三个点共线即为四边形,若对边平行且相等则为平行四边形,选项二若四边形四条边长相等则为菱形若有一个角是直角则为矩形,若有一个角是直角且四条边相等则为正方形。选项三根据面积来判断是是凹四边形还是凸四边形。选项五使用射线法来判断。
类图:

判断四边形的形状:
public int typeOfQuadrilateral() { int flag; double l1,l2,l3,l4; double k1,k2,k3,k4; l1 = Length(x1,y1,x2,y2); l2 = Length(x1,y1,x4,y4); l3 = Length(x2,y2,x3,y3); l4 = Length(x3,y3,x4,y4); k1 = Slope(x1,y1,x2,y2); k2 = Slope(x1,y1,x4,y4); k3 = Slope(x2,y2,x3,y3); k4 = Slope(x3,y3,x4,y4); if((x1==x4&&x2==x3)||(x1==x2&&x3==x4)) { if(l1==l2&&l1==l3&&l1==l4) { if((x1==x4&&x2==x3&&y1==y2&&y3==y4)||(x1==x2&&x3==x4&&y1==y4&&y2==y3)) { flag = 3; } else { flag = 1; } } else { flag = 2; } } else if(k1*k2==-1||k1*k3==-1||k3*k4==-1||k2*k4==-1) { if(l1==l2&&l1==l3&&l1==l4) { flag = 3; } else { flag = 2; } } else { flag = 1; } return flag; }
判断点的位置:
public boolean intheQuadrilateral() { double l1,l2,l3,l4,l5,l6,l7,l8,l; double a1,a2,a3,a4,a5,a6,area; if(chonghe()) { if((x2==x3&&y2==y3)||(x3>=Math.min(x2, x4)&&x3<=Math.max(x2, x4)&&y3>=Math.min(y2, y4)&&y3<=Math.max(y2, y4))) { l1 = Length(x2,y2,x4,y4); l2 = Length(x2,y2,x5,y5); l3 = Length(x4,y4,x5,y5); l4 = Length(x1,y1,x2,y2); l5 = Length(x1,y1,x4,y4); l6 = Length(x1,y1,x5,y5); } else if((x2==x4&&y2==y4)||(x4>=Math.min(x3, x5)&&x4<=Math.max(x3, x5)&&y4>=Math.min(y3, y5)&&y4<=Math.max(y3, y5))) { l1 = Length(x2,y2,x3,y3); l2 = Length(x2,y2,x5,y5); l3 = Length(x3,y3,x5,y5); l4 = Length(x1,y1,x2,y2); l5 = Length(x1,y1,x3,y3); l6 = Length(x1,y1,x5,y5); } else if(x2==x5&&y2==y5) { l1 = Length(x2,y2,x3,y3); l2 = Length(x2,y2,x4,y4); l3 = Length(x3,y3,x4,y4); l4 = Length(x1,y1,x2,y2); l5 = Length(x1,y1,x3,y3); l6 = Length(x1,y1,x4,y4); } else if(x3==x4&&y3==y4) { l1 = Length(x2,y2,x3,y3); l2 = Length(x2,y2,x5,y5); l3 = Length(x3,y3,x5,y5); l4 = Length(x1,y1,x2,y2); l5 = Length(x1,y1,x3,y3); l6 = Length(x1,y1,x5,y5); } else if(x3==x5&&y3==y5) { l1 = Length(x2,y2,x3,y3); l2 = Length(x2,y2,x4,y4); l3 = Length(x3,y3,x4,y4); l4 = Length(x1,y1,x2,y2); l5 = Length(x1,y1,x3,y3); l6 = Length(x1,y1,x4,y4); } else { l1 = Length(x2,y2,x3,y3); l2 = Length(x2,y2,x4,y4); l3 = Length(x3,y3,x4,y4); l4 = Length(x1,y1,x2,y2); l5 = Length(x1,y1,x3,y3); l6 = Length(x1,y1,x4,y4); } area = Area(l1,l2,l3); a1 = Area(l1,l4,l5); a2 = Area(l2,l4,l6); a3 = Area(l3,l5,l6); if(Math.abs(a1+a2+a3-area)<1e-10) { return true; } } else { l1 = Length(x2,y2,x3,y3); l2 = Length(x3,y3,x4,y4); l3 = Length(x4,y4,x5,y5); l4 = Length(x2,y2,x5,y5); l5 = Length(x1,y1,x2,y2); l6 = Length(x1,y1,x3,y3); l7 = Length(x1,y1,x4,y4); l8 = Length(x1,y1,x5,y5); l = Length(x2,y2,x4,y4); a1 = Area(l1,l5,l6); a2 = Area(l2,l6,l7); a3 = Area(l3,l7,l8); a4 = Area(l4,l5,l8); a5 = Area(l1,l2,l); a6 = Area(l3,l4,l); if(Math.abs((a1+a2+a3+a4)-(a5+a6))<1e-10) { return true; } } return false; }
3、单链表:
java的单链表与C语言的单链表大同小异,链表是以节点的方式来存储,是链式存储,每个节点包含 data 域, next 域:指向下一个节点。
类图:
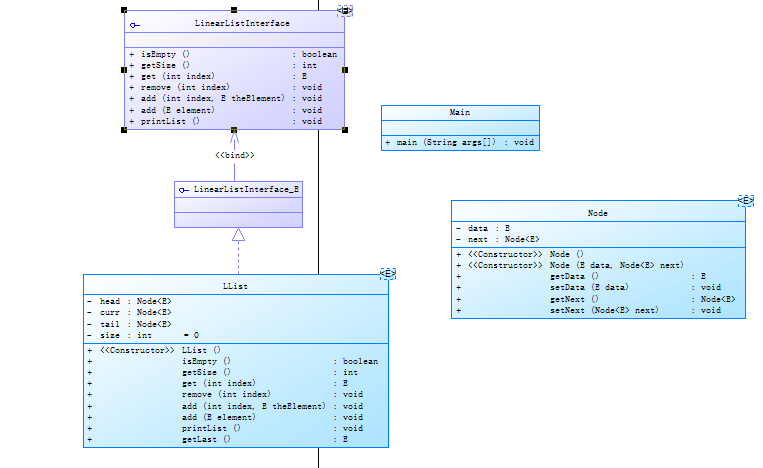
接口:
package 单链表; public interface LinearListInterface<E> { public boolean isEmpty(); //链表是否为空 public int getSize(); //链表的长度 public E get(int index); //链表中index位置的数 public void remove(int index); //删除index位置的数 public void add(int index, E theElement); //将index位置的数改为theElement public void add(E element); //添加element public void printList(); //输出链表 }
Node节点:
package 单链表; public class Node<E> { private E data; private Node<E> next; public Node() { } public Node(E data, Node<E> next) { super(); this.data = data; this.next = next; } public E getData() { return data; } public void setData(E data) { this.data = data; } public Node<E> getNext() { return next; } public void setNext(Node<E> next) { this.next = next; } }
List链表操作:
(1)判断链表是否为空:
public boolean isEmpty() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return this.size == 0; }
(2)判断链表长度:
public int getSize() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return this.size; }
(3)添加节点:
public void add(int index, E theElement) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub if(index < 1 || index > this.size + 1) { return ; } Node<E> curr = new Node<>(); curr.setData(theElement); curr.setNext(null); if(this.size == 0) { head.setNext(curr); tail = curr; }else if(index == this.size + 1) { tail.setNext(curr); tail = curr; }else { Node<E> tempNode = head; for(int i = 1; i < index;i++) { tempNode = tempNode.getNext(); } curr.setNext(tempNode.getNext()); tempNode.setNext(curr); } this.size ++; } @Override public void add(E element) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub this.add(this.size + 1,element); }
(4)删除节点:
public void remove(int index) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub if(index < 1 || index > this.size) { return ; } curr = head; if(index == 1) { curr = head.getNext(); head.setNext(curr.getNext()); }else { for(int i = 1;i < index; i++) { curr = curr.getNext(); } curr.setNext(curr.getNext().getNext()); } if(index == this.size) { tail = curr; } this.size --; }
(5)获取指定节点数值:
public E get(int index) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub if(index < 1 || index > this.size) { return null; } curr = head; for(int i = 0; i < index; i ++) { curr = curr.getNext(); } return curr.getData(); }
(6)输出链表:
public void printList() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub curr = head.getNext(); for(int i = 1; i <= this.size;i ++) { System.out.print(curr.getData() + " "); curr = curr.getNext(); } System.out.println(""); }
4、双链表:
双链表与单链表的区别在于双链表允许元素双向遍历,删除的时间复杂度比单链表低,但是双链表消耗的内存较大。
类图:
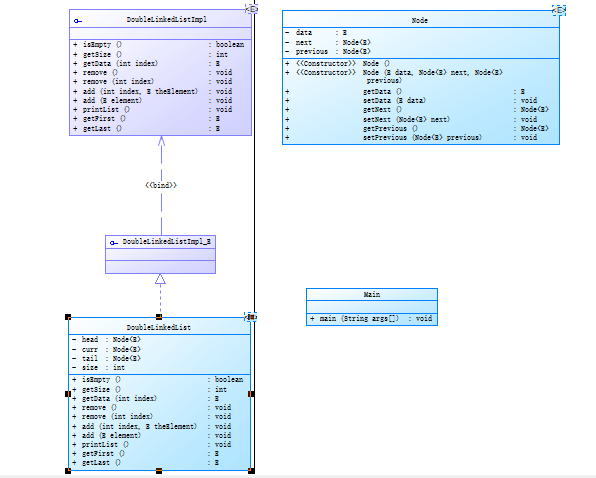
接口:
package 双链表; public interface DoubleLinkedListImpl<E> { /** * 判断链表是否为空 * @return */ public boolean isEmpty(); //判断链表是否为空 /** * 获取当前链表节点数量 * @return 节点数 */ public int getSize(); /** * 获取链表中第index个位置的节点的data值 * @param index:节点在链表中的位置 * @return:返回该节点的data值 */ public E getData(int index); /** * 删除链表最后一个节点 */ public void remove(); /** *删除链表中第index位置的节点 * @param index:节点在链表中的位置 */ public void remove(int index); /** * 在链表的第index个位置之前插入一个节点,值为theElement,index∈[1,size] * @param index:插入节点在链表中的位置 * @param theElement:新插入节点的data值 */ public void add(int index, E theElement); /** * 在链表尾插入节点,插入节点data值为element * @param element */ public void add(E element); /** * 输出链表 */ public void printList(); /** * 获取第一个节点的data值 * @return */ public E getFirst(); /** * 获取链表最后一个节点的data值 * @return */ public E getLast(); }
Node节点:
package 双链表; public class Node<E> { private E data;//数据域,类型为泛型E private Node<E> next;//后继引用(指针) private Node<E> previous;//前驱引用(指针) public Node() { super(); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } public Node(E data, Node<E> next, Node<E> previous) { super(); this.data = data; this.next = next; this.previous = previous; } public E getData() { return data; } public void setData(E data) { this.data = data; } public Node<E> getNext() { return next; } public void setNext(Node<E> next) { this.next = next; } public Node<E> getPrevious() { return previous; } public void setPrevious(Node<E> previous) { this.previous = previous; } }
链表操作:
(1)判断链表是否为空:
public boolean isEmpty() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return this.size==0; }
(2)判断链表长度:
public int getSize() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return this.size; }
(3)添加节点:
public void add(int index, E theElement) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub if(index < 1 || index > this.size + 1) { return ; } Node<E> current = new Node<>(); current.setData(theElement); current.setNext(null); if(this.size == 0) { head = current; tail = current; }else if(index == this.size + 1) { tail.setNext(current); current.setPrevious(tail); tail = current; }else { Node<E> tempNode = head; for(int i = 1; i < index-1;i++) { tempNode = tempNode.getNext(); } tempNode.getNext().setPrevious(current); current.setPrevious(tempNode); current.setNext(tempNode.getNext()); tempNode.setNext(current); } this.size++; } @Override public void add(E element) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub this.add(this.size + 1,element); }
(4)删除节点:
public void remove(int index) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub if(index < 1 || index > this.size) { return ; } curr = head; if(index == 1) { curr = head.getNext(); head.setNext(curr.getNext()); curr.setPrevious(null); }else if(index == this.size) { tail = curr; }else { for(int i = 1;i < index-1; i++) { curr = curr.getNext(); } curr.setNext(curr.getNext().getNext()); curr.getNext().getNext().setPrevious(curr); } this.size --; }
(5)获取指定节点数值:
public E getData(int index) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub if(index < 1 || index > this.size) { return null; } curr = head; for(int i = 0; i < index-1; i ++) { curr = curr.getNext(); } return curr.getData(); }
(6)获取链表第一个值:
public E getFirst() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return head.getData(); }
(7)获取链表最后一个值:
public E getLast() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return tail.getData(); }
(8)输出链表:
public void printList() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub curr = head; for(int i = 1; i <= this.size;i ++) { System.out.print(curr.getData() + " "); curr = curr.getNext(); } System.out.println(""); }
5、期中考试难度中等,三道题为迭代关系,主要考了继承、多态、容器。
一、继承:继承就是子类继承父类的特征和行为,使得子类对象(实例)具有父类的实例域和方法,或子类从父类继承方法,使得子类具有父类相同的行为。
二、多态:多态是面向对象程序设计(OOP)的一个重要特征,指同一个实体同时具有多种形式,即同一个对象,在不同时刻,代表的对象不一样,指的是对象的多种形态。
三、容器:在Java当中,如果有一个类专门用来存放其它类的对象,这个类就叫做容器,或者就叫做集合,集合就是将若干性质相同或相近的类对象组合在一起而形成的一个整体。
类图:
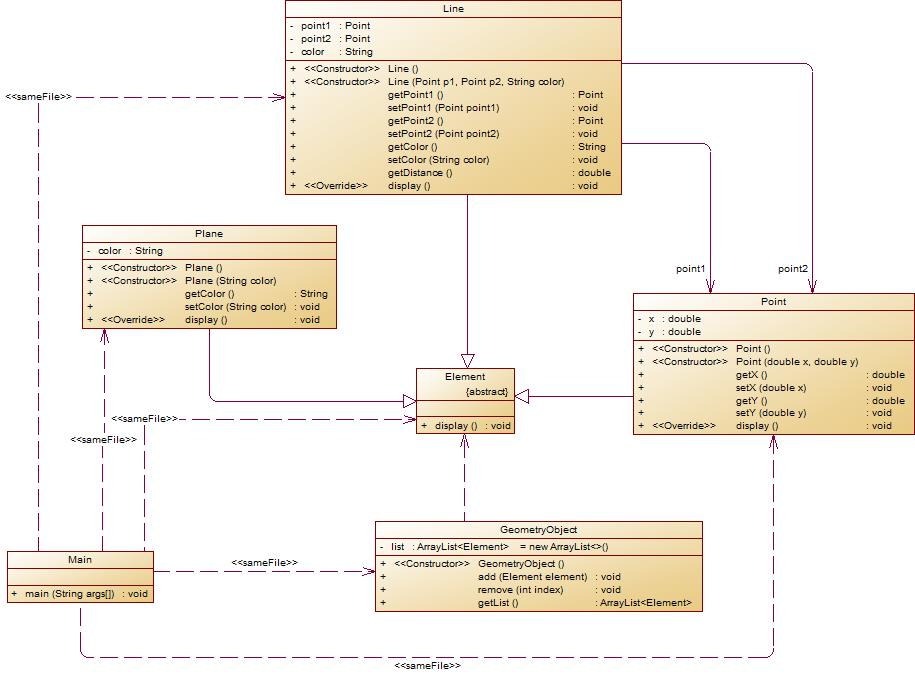
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); GeometryObject g = new GeometryObject(); int choice = input.nextInt(); while(choice != 0) { switch(choice) { case 1://insert Point object into list double x = input.nextDouble(); double y = input.nextDouble(); Point point = new Point(x,y); g.add(point); break; case 2://insert Line object into list double x1 = input.nextDouble(); double y1 = input.nextDouble(); double x2 = input.nextDouble(); double y2 = input.nextDouble(); String color = input.next(); Point point1 = new Point(x1,y1); Point point2 = new Point(x2,y2); Line line = new Line(point1,point2,color); g.add(line); break; case 3://insert Plane object into list String color1 = input.next(); Plant plant = new Plant(color1); g.add(plant); break; case 4://delete index - 1 object from list int index = input.nextInt(); if(index>=0&&index<=g.getList().size()) { g.remove(index); } break; } choice = input.nextInt(); } for(int i=0;i<g.list.size();i++) { g.getList().get(i).display(); } } } abstract class Element{ abstract public void display(); } class Point extends Element{ private double x,y; public Point() { super(); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } public Point(double x, double y) { super(); this.x = x; this.y = y; } public double getX() { return x; } public void setX(double x) { this.x = x; } public double getY() { return y; } public void setY(double y) { this.y = y; } public void display() { System.out.println("(" + String.format("%.2f",x) + "," + String.format("%.2f",y) + ")"); } } class Line extends Element{ private Point point1 = new Point(); private Point point2 = new Point(); private String color; public Line() { super(); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } public Line(Point point1, Point point2, String color) { super(); this.point1 = point1; this.point2 = point2; this.color = color; } public Point getPoint1() { return point1; } public void setPoint1(Point point1) { this.point1 = point1; } public Point getPoint2() { return point2; } public void setPoint2(Point point2) { this.point2 = point2; } public String getColor() { return color; } public void setColor(String color) { this.color = color; } public void display() { double x1 = point1.getX(), y1 = point1.getY(), x2 = point2.getX(), y2 = point2.getY(); double length = Math.sqrt(Math.pow((x1-x2),2)+Math.pow((y1-y2),2)); System.out.println("The line's color is:" + color); System.out.println("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:"); point1.display(); System.out.println("The line's end point's Coordinate is:"); point2.display(); System.out.println("The line's length is:" + String.format("%.2f",length)); } } class Plant extends Element{ private String color; public Plant() { super(); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } public Plant(String color) { super(); this.color = color; } public String getColor() { return color; } public void setColor(String color) { this.color = color; } public void display() { System.out.println("The Plane's color is:" + color); } } class GeometryObject{ ArrayList<Element> list = new ArrayList<>(); public GeometryObject() { super(); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } public void add(Element element) { list.add(element); } public void remove(int index) { list.remove(index-1); } public ArrayList<Element> getList(){ return list; } }
(3)采坑心得:
1、在写题之前要先规划好这道题所需要的类、属性、方法等,如果在写题时想到那么改起来会很麻烦。
2、在提交之前可以对代码进行测试,否则可能会出现提交之后一个测试点都没对的情况。
3、利用java的封装、继承、多态的特性,可以在写题之前设计一个较好地方案,写题时思路就比较清晰明了。
(4)改进建议:
在判断多边形时可以添加Point类与Line类以简化代码的复杂度。判断输入格式是否正确可以使用正则表达式。
(5)总结:
通过这几次PTA作业、超星作业以及期中考试,我懂得了类与类之间的关系,学会了单链表与双链表的操作,同时掌握了继承、多态、容器的定义以及使用方法。

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号