24种设计模式学习笔记之命令模式
命令模式----行为型模式
命令模式将“请求”封装成对象,以便使用不同的请求、队列或者日志来参数化其他对象。命令模式也支持可撤销的操作。
这种说法比较难以理解,换种说法就是指:
在软件系统中,“行为请求者”与“行为实现者”通常呈现一种“紧耦合”。但在某些场合,比如要对行为进行“记录、撤销/重做、事务”等处理,这种无法抵御变化的紧耦合是不合适的。
在这种情况下,如何将“行为请求者”与“行为实现者”解耦?将一组行为抽象为对象,实现二者之间的松耦合。这就是命令模式(Command Pattern)。
UMl 图
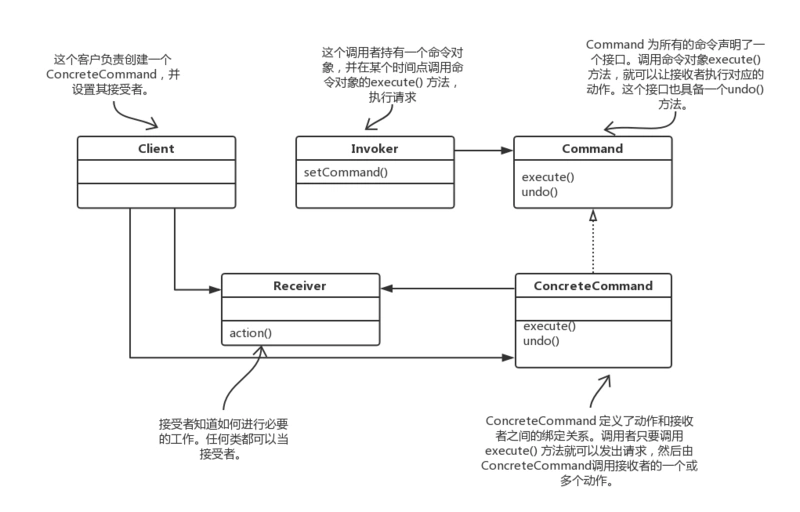
组成结构:
- 命令接口 (Command):定义命令的接口,声明执行的方法。
- 具体命令 (ConcreteCommand):命令接口实现对象,是“虚”的实现;通常会持有接收者,并调用接收者的功能来完成命令要执行的操作。
- 接受者 (Receiver):接收者,真正执行命令的对象。任何类都可能成为一个接收者,只要它能够实现命令要求实现的相应功能。
- 调用者 (Invoker):要求命令对象执行请求,通常会持有命令对象,可以持有很多的命令对象。这个是客户端真正触发命令并要求命令执行相应操作的地方,也就是说相当于使用命令对象的入口。
- 客户 (Client):创建具体的命令对象,并且设置命令对象的接收者。注意这个不是我们常规意义上的客户端,而是在组装命令对象和接收者,或许,把这个 Client 称为装配者会更好理解,因为真正使用命令的客户端是从 Invoker 来触发执行。
代码
/** * 接收者,真正执行命令的对象 * * 电灯提供打开和关闭的功能 * */ public class Light { void on(){ System.out.println("Light is on!"); } void off(){ System.out.println("Light is off!"); } }
/** * 命令接口 * 所有的命令对象都应该实现的接口,提供了一个执行的方法。 */ public interface Command { void execute(); }
/** * * 具体命令 LightOffCommand 类 * * **/ public class LightOffCommand implements Command { Light light; public LightOffCommand(Light light){ this.light = light; } /** * 调用电灯关闭的方法 */ @Override public void execute() { light.off(); } }
/** * * 具体命令 * **/ public class LightOnCommand implements Command{ Light light; /** * 通过构造器实力化 light 对象,在 execute() 方法中调用其对应的打开与关闭方法 * * @param light 电灯对象 */ public LightOnCommand(Light light){ this.light = light; } /** * 调用电灯打开的方法 */ @Override public void execute() { light.on(); } }
/** * * 调用者 RemoteControl 类 (遥控器) * */ public class RemoteControl { Command onCommand; Command offComand; public RemoteControl(){} /** * 传入一组命令 * * @param onCommand 打开电灯的命令对象 * @param offComand 关闭电灯的命令对象 */ public void setCommand(Command onCommand, Command offComand){ this.onCommand = onCommand; this.offComand = offComand; } /** * 打开电灯的按钮,通过 onCommand 调用 execute() 方法 */ public void onButtonWasPushed(){ //execute() 方法中封装了打开电灯的方法 onCommand.execute(); } /** * 关闭电灯的按钮,通过 offComand 调用 execute() 方法 */ public void offButtonWasPushed(){ //execute() 方法中封装了关闭电灯的方法 offComand.execute(); } }
运行
/** * * 客户 RemoteLoader 类 * */ public class RemoteLoader { public static void main(String[] args) { // 定义一个远程遥控器 RemoteControl remoteControl = new RemoteControl(); // 定义一个电灯对象 Light light = new Light(); // 打开电灯的命令对象 Command onCommand = new LightOnCommand(light); // 关闭电灯的命令对象 Command offCommand = new LightOffCommand(light); remoteControl.setCommand(onCommand,offCommand); remoteControl.onButtonWasPushed(); remoteControl.offButtonWasPushed(); } }
使用场景
- 系统需要将请求调用者和请求接收者解耦,使得调用者和接收者不直接交互。
- 系统需要在不同的时间指定请求、将请求排队和执行请求。
- 系统需要支持命令的撤销 (Undo) 操作和恢复 (Redo) 操作。
- 系统需要将一组操作组合在一起,即支持宏命令。
优点
- 降低对象之间的耦合度。
- 新的命令可以很容易地加入到系统中。
- 可以比较容易地设计一个组合命令。
- 调用同一方法实现不同的功能。
缺点
使用命令模式可能会导致某些系统有过多的具体命令类。因为针对每一个命令都需要设计一个具体命令类,因此某些系统可能需要大量具体命令类,这将影响命令模式的使用。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号