面向对象编程(OOP)
1、初始面向对象
面向过程&&面向对象
![image-20220119161700049]()
什么是面向对象
![image-20220119182420608]()
2、方法回顾和加深
![image-20220119184221280]()
静态方法与非静态方法
package com.kuang.oop.Demo01;
////学生类
//public class Student {
// //静态方法 static
// public static void say(){
// System.out.println("学生说话了");
// }
//
//}
public class Student {
//非静态方法
public void say() {
System.out.println("学生说话了");
}
}
package com.kuang.oop.Demo01;
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//静态方法 static
// Student.say();
//非静态方法
//实例化这个类
Student student = new Student();
student.say();
}
//和类一起加载的
public static void a(){
// b();
}
//类实例化 之后才存在
public void b(){
}
}
形参和实参
package com.kuang.oop.Demo01;
public class Demo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//实际参数和形式参数的类型要对应
int add = Demo03.add(1,2);
System.out.println(add);
}
public static int add(int a,int b){
return a+b;
}
}
值传递和引用传递
值传递
package com.kuang.oop.Demo01;
//值传递
public class Demo04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 1;
System.out.println(a);//1
Demo04.change(a);
System.out.println(a);//1
}
//返回值为空
public static void change(int a){
a = 10;
}
}
引用传递
package com.kuang.oop.Demo01;
//应用传递:传递一个对象
public class Demo05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person person = new Person();
System.out.println(person.name);//null
Demo05.change(person);
System.out.println(person.name);//小许
}
public static void change(Person person){
//person是一个对象:指向的 ---> Person person = new Person();这是一个具体的人,可以改变属性!
person.name = "小许";
}
}
//定义了一个Person类,有一个属性:name
class Person{
String name;//null
}
3、对象的创建分析
类和对象的关系
![image-20220119194129393]()
创建和初始化对象
![image-20220119203045955]()
类的初始化
package com.kuang.oop.Demo02;
//学生类
public class Student {
//属性:字段
String name;//null
int age;//0
//方法
public void study(){
System.out.println(this.name+"在学习");
}
}
//Person-->身高、体重、年龄、国籍、祖籍
//学程序好? 对世界进行更好的建模!---宅! 音乐,旅游,出国
/*
//类:抽象的,实例化
//类实例化后会返回一个自己的对象!
//student对象就是一个Student类的具体实例!
Student xiaoming = new Student();
Student xiaohong = new Student();
xiaoming.name = "小明";
xiaoming.age = 3;
System.out.println(xiaoming.name);
System.out.println(xiaoming.age);
xiaohong.name = "小红";
xiaohong.age = 3;
System.out.println(xiaoming.name);
System.out.println(xiaoming.age);
xiaoming.study();
xiaohong.study();
*/
构造器
package com.kuang.oop.Demo02;
//alt+ insert 构造快捷键 ********
//java --->class
public class Person {
//一个类即使什么都不写,它也会存在一个方法
//显示的定义构造器
String name;
int age;
//实例化初始值
//1、使用new关键字,必须要有构造器
public Person() {
}
//有参构造:一旦定义了有参构造,无参就必须显示定义
public Person(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
/*
//new 实例化了一个对象
Person person = new Person("kuangshen");
System.out.println(person.name);//null 小许
}
构造器:
1. 和类名相同
2. 没有返回值
作用:
1. new 本质在调用构造方法
2. 初始化对象的值
注意点:
1. 定义有参构造之后,如果想使用无参构造,显示的定义一个无参的构造
Alt+ Insert
this. =
*/
}
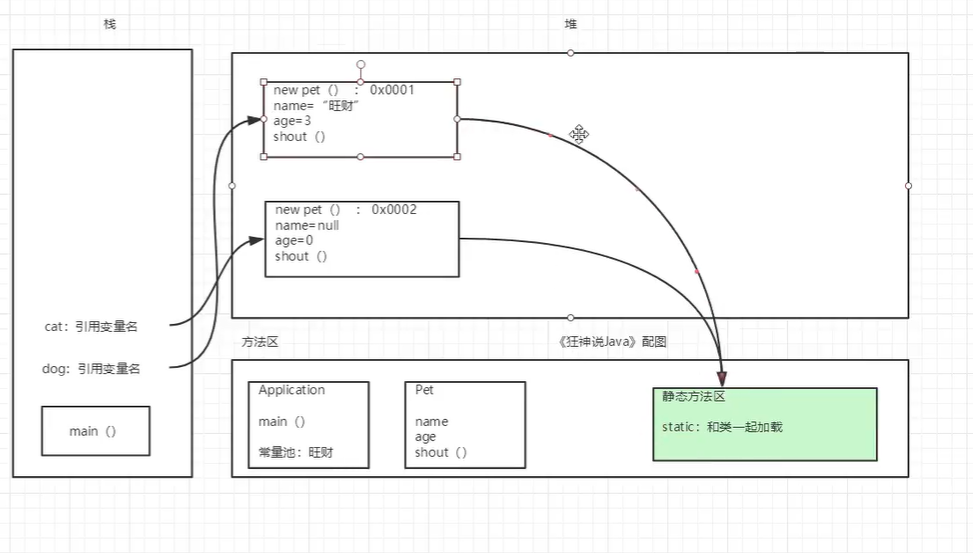
创建对象内存分析
![image-20220119215543365]()
package com.kuang.oop.Demo03;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Pet dog = new Pet();
dog.name = "旺财";
dog.age = 3;
dog.shout();
System.out.println(dog.name);
System.out.println(dog.age);
Pet cat = new Pet();
}
}
package com.kuang.oop.Demo03;
public class Pet {
String name;
int age;
//无参构造
public void shout(){
System.out.println("叫了一声");
}
}
简单小结类与对象
package com.kuang.oop.Demo03;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Pet dog = new Pet();
// dog.name = "旺财";
// dog.age = 3;
// dog.shout();
//
// System.out.println(dog.name);
// System.out.println(dog.age);
// Pet cat = new Pet();
/*
1.类与对象
类是一个模板:抽象,对象是一个具体的实例
2.方法
定义、调用
3.对应的引用
引用类型: 基本类型(8)
对象是通过引用来完成操作的:栈 --->堆
4.属性:字段Field 成员变量
默认初始化
数字: 0 0.0
char: u0000
boolean: false
引用: null
修饰符 属性类型 属性名 = 属性值
5.对象的创建和使用
- 必须使用new 关键字创造对象, 构造器 Person kuangshen = new Person();
- 对象的属性 kuangshen.name
- 对象的方法 kuangshen.sleep()
6.类
静态的属性 属性
动态的行为 方法
·封装、集成、多态·
*/
}
}
4、面向对象三大特征
封装
![image-20220217190232139]()
封装的意义
1.提高程序的安全性,保护数据
2.隐藏代码的实现细节
3.统一接口
4.系统的可维护性增加了
package com.kuang.oop.Demo04;
//类
public class Student {
//属性私有
private String name;//名字
private int id; //学号
private char sex; //性别
private int age; //年龄
//提供一些可以操作这个属性的方法!
// 提供一些public 的get、set方法
//get 获得这个数据
public String getName(){
return this.name;
}
//set 给这个数据设置值
public void setName(String name){
this.name = name;
}
//alt + insert
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public char getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(char sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
if(age>120||age<0){ //不合法
this.age = 3;
}else {
this.age = age;
}
}
}
//main方法
package com.kuang.oop.Demo04;
import com.kuang.oop.Demo04.Student;
/*
1.提高程序的安全性,保护数据
2.隐藏代码的实现细节
3.统一接口
4.系统的可维护性增加了
*/
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1 = new Student();
s1.setName("小许");
//方法名,参数列表(重载)
System.out.println(s1.getName());
s1.setAge(25);//不合法的
System.out.println(s1.getAge());
}
}
继承
![image-20220217194152808]()
注意点
super注意点:
1. super调用父类的构造方法,
2. super 必须只能出现在子类的方法或者构造方法中!
3. super和 this不能同时调用构造方法!
对比 this:
代表的对象不同:
this:本身调用者这个对象
super:代表父类对象的引用
前提
this:没哟继承也可以使用
super:只能在继承条件才可以使用
构造方法
this() ;本类的构造
super():父类的构造!
重写:需要有继承关系,子类重写父类的方法!
1.方法名必须相同
2.参数列表列表必须相同
3.修饰符:范围可以扩大但不能缩小; public>Protected>Default>private
4.抛出的异常:范围,可以被缩小,但不能扩大; ClassNotFoundException --> Exception(大)
重写,子类的方法和父类必要一致;方法体不同!
为什么需要重写:
1.父类的功能,子类不一定需要,或者不一定满足!
Alt + Insert : override;
package com.kuang.oop.Demo05;
//在java中,所有的类,都默认直接或者间接继承Object
//Person 人 : 父类
public class Person /*extends Object*/ {
// //public
// //protected
// //default
// //private
// private int money = 1_0000_0000;
//
// public void say(){
// System.out.println("说了一句话");
// }
//
// public int getMoney() {
// return money;
// }
//
// public void setMoney(int money) {
// this.money = money;
// }
public Person() {
System.out.println("Person无参执行了");
}
protected String name = "xiaoxu";
//私有的东西无法被继承
// private void print(){
public void print(){
System.out.println("Person");
}
}
package com.kuang.oop.Demo05;
//学生 is 人: 派生类 : 子类
//子类继承了父类,就会拥有父类的全部方法!
public class Student extends Person {
//Ctrl + H
public Student() {
//隐藏代码:调用了父类的无参构造
super();//调用父类的构造器(子类this也一样),必须要在子类的第一行
System.out.println("Student无参执行了");
}
// public Student(String name){
// this.name = name;
// }
private String name = "hanzige";
public void print(){
System.out.println("Student");
}
public void test1(){
print();//Student
this.print();//Student
super.print();//Person
}
public void test(String name){
System.out.println(name);//许
System.out.println(this.name);//hanzige
System.out.println(super.name);//xiaoxu
}
}
package com.kuang.oop.Demo05;
//老师 is 人: 派生类 : 子类
public class Teacher extends Person {
}
package com.kuang.oop.Demo05;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Student student = new Student();
// student.say();
// System.out.println(student.money);
// Student student = new Student();
// student.test("许");
// student.test1();
//静态方法和非静态方法区别很大!
//静态方法的调用只和左边,定义的数据类型有关
//非静态:重写
A a = new A();
a.test();//A
//父类的引用指向子类
B b = new A();//子类重写了父类的方法
b.test();//B
}
}
重写
package com.kuang.oop.Demo05;
//继承
public class A extends B {
//Override 重写
@Override //注解:有功能的注释!
public void test() {
System.out.println("A=>test");
}
}
package com.kuang.oop.Demo05;
//重写都是方法的重写,和属性无关
public class B {
public void test(){
System.out.println("B=>test");
}
}
/*
//静态方法和非静态方法区别很大!
//静态方法的调用只和左边,定义的数据类型有关
//非静态:重写
A a = new A();
a.test();//A
//父类的引用指向子类
B b = new A();//子类重写了父类的方法
b.test();//B
*/









 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号