数组
1、数组概述
![image-20220118163501724]()
2、数组的声明创建
![image-20220118163532315]()
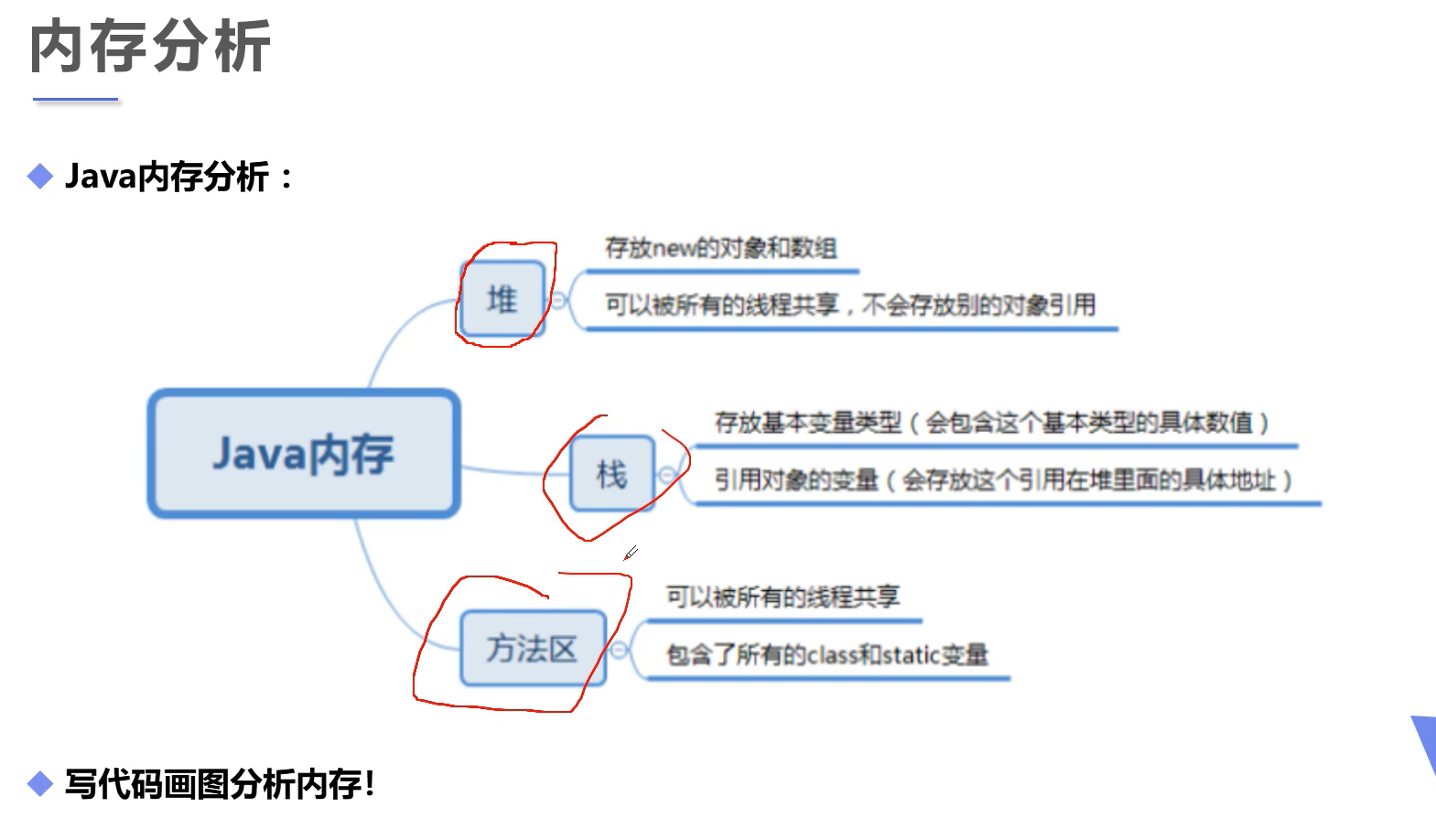
内存分析
![image-20220118164847756]()
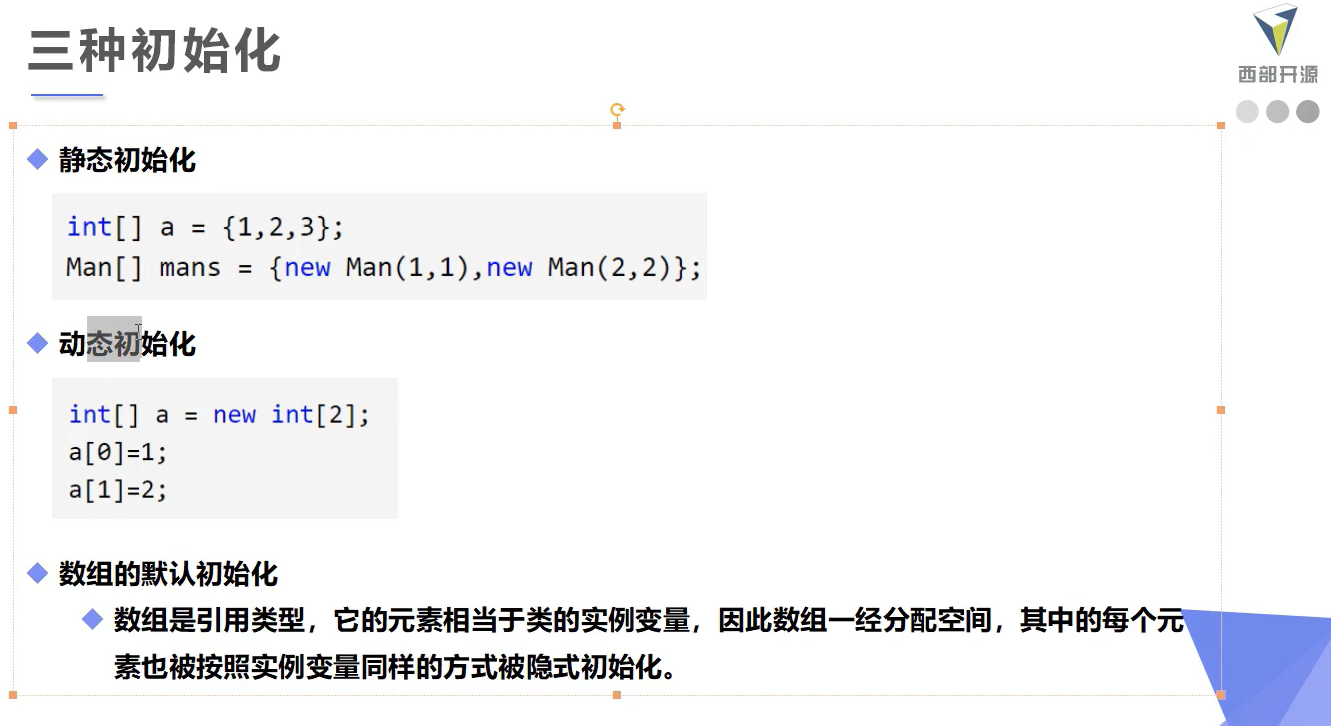
数组三种初始化
![image-20220118165203017]()
数组的是个基本特点
![image-20220118164737419]()
数组边界
![image-20220118170324295]()
报错代码
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 8
at com.kuang.array.ArrayDemo02.main(ArrayDemo02.java:10)
3、数组使用
![image-20220118173350789]()
For-Each循环
package com.kuang.array;
public class ArrayDemo04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arrays = {1,2,3,4,5};
//JDK1.5,没有下标
for(int array : arrays){
System.out.println(array);
}
}
}
![结果]()
数组作为方法入参
package com.kuang.array;
public class ArrayDemo04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arrays = {1,2,3,4,5};
printArray(arrays);
}
//打印数组元素
public static void printArray(int[] arrays){
for (int i = 0; i < arrays.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arrays[i]+" ");
}
}
}
![image-20220119134038445]()
数组作为返回值
package com.kuang.array;
public class ArrayDemo04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arrays = {1,2,3,4,5};
int[] recerse = reverse(arrays);
printArray(recerse);
}
//打印数组元素
public static void printArray(int[] arrays){
for (int i = 0; i < arrays.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arrays[i]+" ");
}
}
//反转数组
public static int[] reverse(int[] arrays){
int[] result = new int[arrays.length];
//反转的操作
for (int i = 0 , j = result.length-1; i < arrays.length; i++,j--) {
result[j] = arrays[i];
}
return result;
}
}
![image-20220119134140262]()
4、多维数组
![image-20220119134430436]()
5、Arrays类
![image-20220119142733194]()
冒泡排序
![image-20220119143456532]()
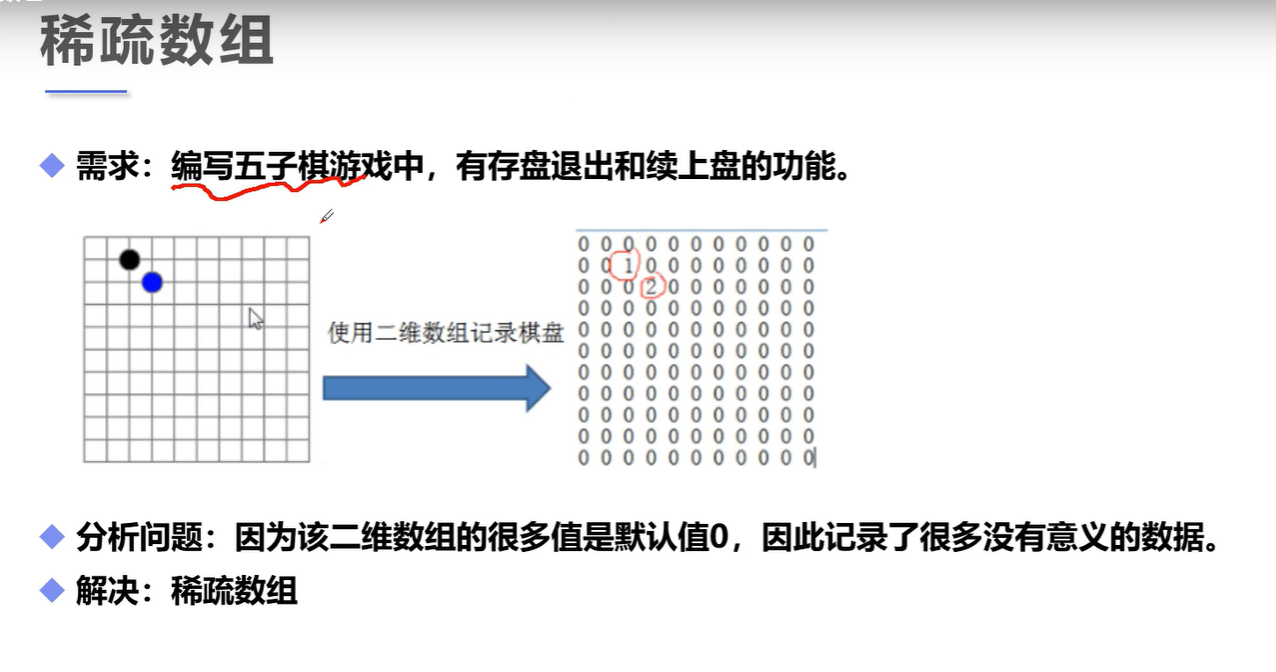
6、稀疏数组
![image-20220119161229729]()
package com.kuang.array;
public class ArrayDemo08 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1、创建一个二维数组11*11 0:没有棋子 1:黑棋 2:白旗
int[][] array1 = new int[11][11];
array1[1][2] = 1;
array1[2][3] = 2;
//输出原始数组
System.out.println("输出原始的数组");
for(int[] ints : array1){
for (int anInt : ints) {
System.out.print(anInt+"\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println("=====================");
//转换为稀疏数组保存
//获取有效值的个数
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 11; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 11; j++) {
if (array1[i][j] != 0) {
sum++;
}
}
}
System.out.println("有效值的个数:"+sum);
//2、创建一个稀疏数组
int[][] array2 = new int[sum+1][3];
array2[0][0] = 11;
array2[0][1] = 11;
array2[0][2] = sum;
//遍历二维数组,将非零的值,存放稀疏数组中
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < array1.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < array1[i].length; j++) {
if (array1[i][j] != 0) {
count++;
array2[count][0] = i;
array2[count][1] = j;
array2[count][2] = array1[i][j];
}
}
}
//输出稀疏数组
System.out.println("稀疏数组");
for (int i = 0; i < array2.length; i++) {
System.out.println(array2[i][0]+"\t"+array2[i][1]+"\t"+array2[i][2]+"\t");
}
System.out.println("=====================");
System.out.println("还原");
//1、读取稀疏数组
int[][] array3 = new int[array2[0][0]][array2[0][1]];
//2、给其中的元素还原它的值
for (int i = 1; i < array2.length; i++) {
array3[array2[i][0]][array2[i][1]] = array2[i][2];
}
//3、打印
System.out.println("输出还原的数组");
for (int[] ints : array3) {
for (int anInt : ints) {
System.out.print(anInt+"\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
![image-20220119161318939]()













 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号