Thread
public synchronized void start() {//方法加锁,同一时间start只能被调用一次 /**0状态值对应状态“NEW” * A zero status value corresponds to state "NEW". */ if (threadStatus != 0)//如果线程的状态不是处于尚未启动的状态,则报错 throw new IllegalThreadStateException(); /* Notify the group that this thread is about to be started * so that it can be added to the group's list of threads * and the group's unstarted count can be decremented. */ group.add(this); boolean started = false; try { start0(); started = true; } finally { try { if (!started) { group.threadStartFailed(this); } } catch (Throwable ignore) { /* do nothing. If start0 threw a Throwable then it will be passed up the call stack */ } } }
void add(Thread t) { synchronized (this) { if (destroyed) {//如果已经被销毁,则报错 throw new IllegalThreadStateException(); } if (threads == null) {//如果线程组为null threads = new Thread[4];//初始化一个线程组 } else if (nthreads == threads.length) {//如果线程的个数和线程组的个数相等,则进行扩容,扩容为原来的2倍 threads = Arrays.copyOf(threads, nthreads * 2); } threads[nthreads] = t; // This is done last so it doesn't matter in case the // thread is killed nthreads++; // The thread is now a fully fledged member of the group, even // though it may, or may not, have been started yet. It will prevent // the group from being destroyed so the unstarted Threads count is // decremented. nUnstartedThreads--;//未启动的线程减1 } }
Stop方法(已被弃用,有固有的不安全因素)
该方法具有固有的不安全性。用 Thread.stop 来终止线程将释放它已经锁定的所有监视器(作为沿堆栈向上传播的未检查 ThreadDeath 异常的一个自然后果)。如果以前受这些监视器保护的任何对象都处于一种不一致的状态,则损坏的对象将对其他线程可见,这有可能导致任意的行为。stop 的许多使用都应由只修改某些变量以指示目标线程应该停止运行的代码来取代。目标线程应定期检查该变量,并且如果该变量指示它要停止运行,则从其运行方法依次返回。如果目标线程等待很长时间(例如基于一个条件变量),则应使用 interrupt 方法来中断该等待。
@Deprecated public final void stop() { SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager(); if (security != null) { checkAccess(); if (this != Thread.currentThread()) { security.checkPermission(SecurityConstants.STOP_THREAD_PERMISSION); } } // A zero status value corresponds to "NEW", it can't change to // not-NEW because we hold the lock. if (threadStatus != 0) { resume(); // Wake up thread if it was suspended; no-op otherwise } // The VM can handle all thread states stop0(new ThreadDeath()); }
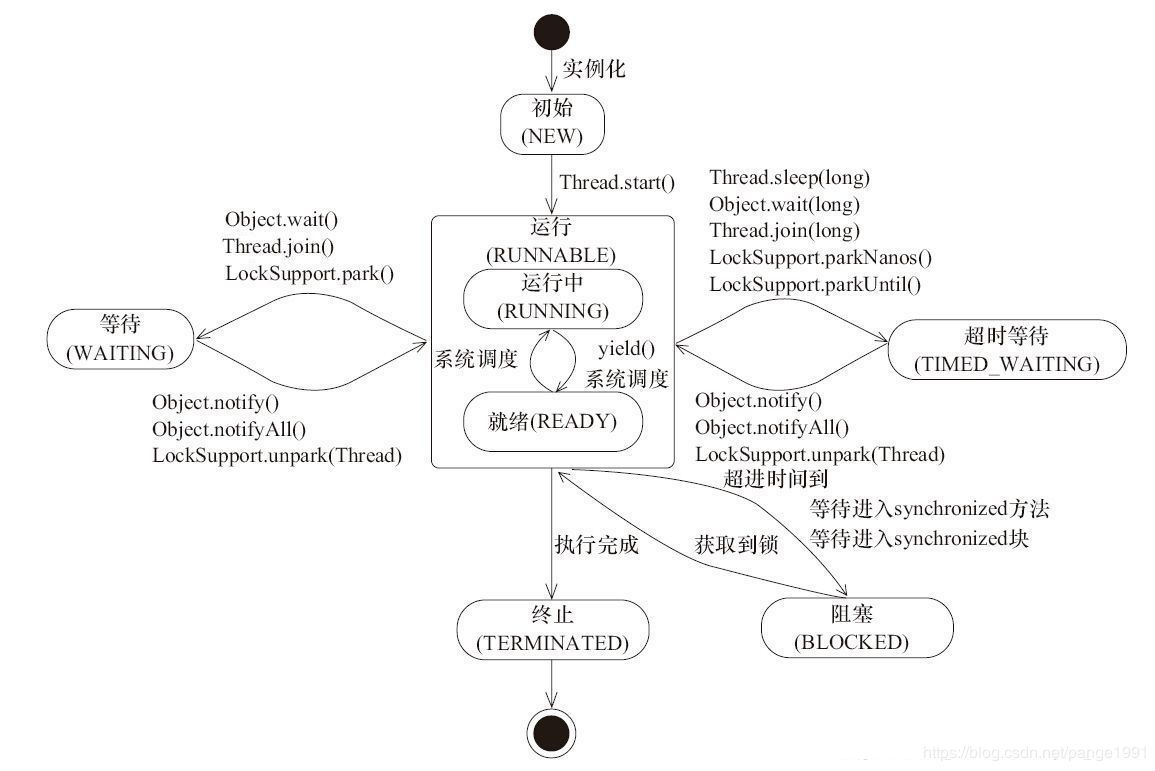
线程的6种状态
NEW,//新建状态
RUNNABLE,//可运行状态
BLOCKED,//阻塞状态
WAITING,//等待状态
TIMED_WAITING,//时间等待状态
TERMINATED;//终止状态


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号