![]()
![]()
/**
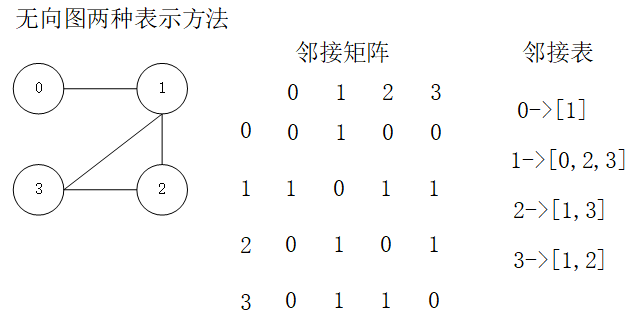
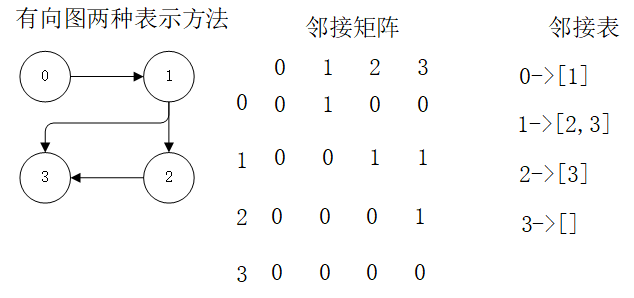
* 二维数组实现 图的邻接矩阵
*/
public class DenseGraph {
private int n; //图的节点
private int m; //图的边
private boolean directed; //是否为有向图或无向图
private int[][] arr;
public DenseGraph(int n, boolean directed){
this.n = n;
this.m = 0;
this.directed = directed;
this.arr = new int[n][n];
}
//向邻接矩阵中新增一条边
public void addEdge(int v, int w){
if((v >=0 && v < n) && (w >= 0 && w < n)){
if(hasEdge(v,w) == 1){
return;
}
arr[v][w] = 1;
if(!this.directed){
arr[w][v] = 1;
}
m ++;
}
}
//判断两个节点中是否以及存在边
public int hasEdge(int v, int w){
if((v >=0 && v < n) && (w >= 0 && w < n)){
return arr[v][w];
}
return 0;
}
//获取当前图中的节点数
public int getN(){
return n;
}
//获取当前图中的边数
public int getM(){
return m;
}
public void print(){
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i ++){
for (int j = 0; j < arr[i].length; j ++){
System.out.print(arr[i][j]);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
DenseGraph denseGraph = new DenseGraph(4,false);
denseGraph.addEdge(0,1);
denseGraph.addEdge(1,2);
denseGraph.addEdge(1,3);
denseGraph.addEdge(2,3);
denseGraph.print();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("边的个数 " + denseGraph.getM());
}
}
/**
* 使用Map实现图的邻接表
*/
public class DenseGraph2 {
private int n; //图的节点
private int m; //图的边
private boolean directed; //是否为有向图或无向图
private Map<Integer, List<Integer>> map;
public DenseGraph2(int n, boolean directed){
this.n = n;
this.m = 0;
this.directed = directed;
this.map = new HashMap<>();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++) {
map.put(i,new ArrayList<>());
}
}
public int getN() {
return n;
}
public int getM(){
return m;
}
public void addEdge(int v, int w){
if((v >= 0 && v < n) && (w >= 0 && w < n)){
if(hasEdge(v,w)){
return;
}
if(this.map.get(v).size() > 0){
this.map.get(v).add(w);
}else {
List<Integer> arr = new ArrayList<>();
arr.add(w);
map.put(v,arr);
}
if(!this.directed){
if(this.map.get(w).size() > 0){
this.map.get(w).add(v);
}else {
List<Integer> arr2 = new ArrayList<>();
arr2.add(v);
map.put(w,arr2);
}
}
m ++;
}
}
public boolean hasEdge(int v, int w){
if((v >= 0 && v < n) && (w >= 0 && w < n)){
List<Integer> list = this.map.get(v);
if(list.size() >0 && list.contains(w)){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public void print(){
Set<Integer> keySet = map.keySet();
for(Integer key : keySet){
System.out.println(key + "->" + map.get(key));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
DenseGraph2 denseGraph2 = new DenseGraph2(4,false);
denseGraph2.addEdge(0,1);
denseGraph2.addEdge(1,2);
denseGraph2.addEdge(1,3);
denseGraph2.addEdge(2,3);
denseGraph2.print();
}
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号