css3 学习
css3学习
初识css
css选择器(重点加难点)
cascading style sheet 层叠级联样式表
表现:美化网页
F12:审查元素
规范:
基本入门
css代码与html代码写在一起:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>First css</title>
<!-- 规范,<style> 可以编写css的代码,每一个声明最好使用分号结尾;
语法:
选择器{
声明1;
声明2;
声明3;
}
-->
<style>
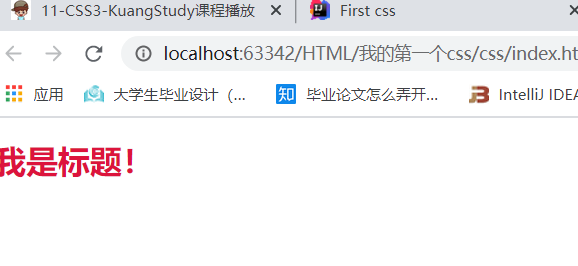
h1{
color: crimson;
/* 使标题颜色变为红色*/
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>我是标题!</h1>
</body>
</html>
css代码与html5分离
html5:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>First css</title>
<!-- 规范,<style> 可以编写css的代码,每一个声明最好使用分号结尾;
语法:
选择器{
声明1;
声明2;
声明3;
}
-->
<!-- 用link连接 css与html5-->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="Style.css">
</head>
<body>
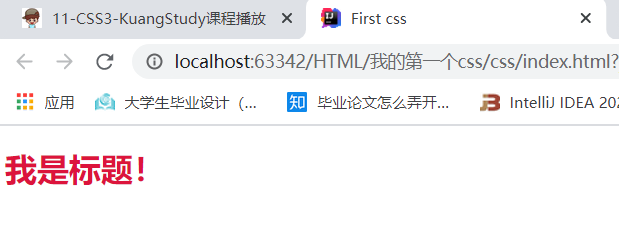
<h1>我是标题!</h1>
</body>
</html>
css:
h1{
color: crimson;
/* 使标题颜色变为红色*/
}
注:两个代码处入同级目录
css的优势:
1.内容和表现分离
2.网页结构表现统一,可以复用
3.样式十分丰富
4.利于SEO,容易被搜索引擎收录
四种css导入方式
1.内部样式:css代码与html代码写在一起:1
2.外部样式:css代码与html5分离:2
3.行内样式:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<!--行内样式 在标签元素中,编写一个style属性,编写样式即可-->
<h1 style="color: brown">这是一个标题</h1>
</body>
</html>
优先级:就近原则 谁离这个元素近就用谁
外部样式两种写法:
链接式:
<link rel="stylesheet" href="Style.css">
导入式:
<style>
@import url(Style.css);
</style>
选择器
三种基本选择器
作用:选择页面上的某一个或某一类元素
1.标签选择器
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
h1{
/*标签选择器 会选到这个页面上所有的这个标签的元素
*/
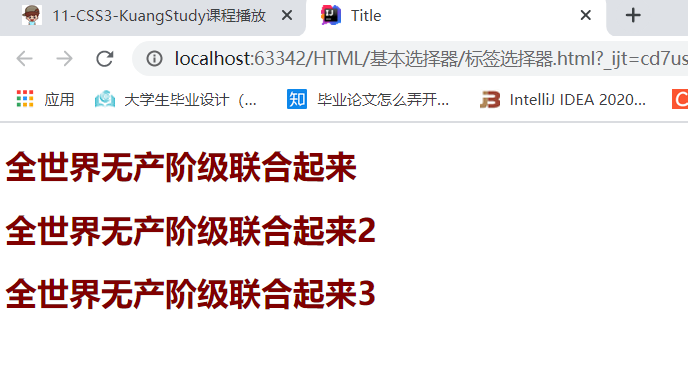
color: maroon;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
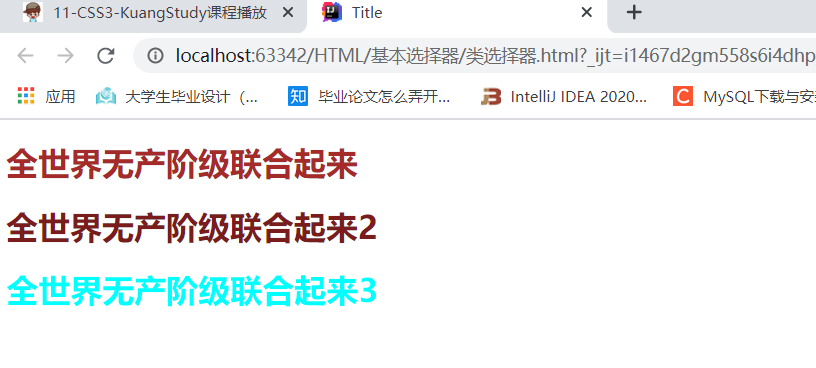
<h1>全世界无产阶级联合起来</h1>
<h1>全世界无产阶级联合起来2</h1>
<h1>全世界无产阶级联合起来3</h1>
</body>
</html>
2.类选择器 class
好处:可以多个标签归类,是同一个class可以复用(不同标签也可)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
/* 类选择器的格式 。class的名称{}*/
.name1{
color: brown;
}
.name2{
color: #7b1c1c;
}
.name3{
color: aqua;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1 class="name1">全世界无产阶级联合起来1</h1>
<h1 class="name2">全世界无产阶级联合起来2</h1>
<h1 class="name3">全世界无产阶级联合起来3</h1>
</body>
</html>
3.id 选择器
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
/* id选择器:id必须保证全局唯一!(即 不可重名)
#id名称{}
不遵循就近原则,固定的
id选择器 >class选择器 >标签选择器
*/
#style1{
color: #7d7b30;
}
#style2{
color: #e24040;
}
.style3{
color: #498ba5;
}
h1{
color: #1a22bd;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
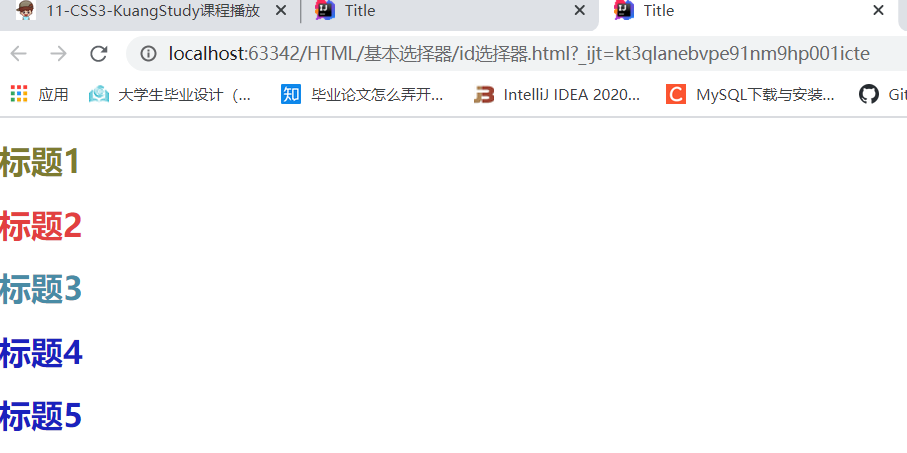
<h1 id="style1">标题1</h1>
<h1 id="style2">标题2</h1>
<h1 class="style3">标题3</h1>
<h1>标题4</h1>
<h1>标题5</h1>
</body>
</html>
层次选择器
1.后代选择器:某个元素后面的全部
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
/* 后代选择器 * body+ 空格 +p*/
body p{
background: maroon;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
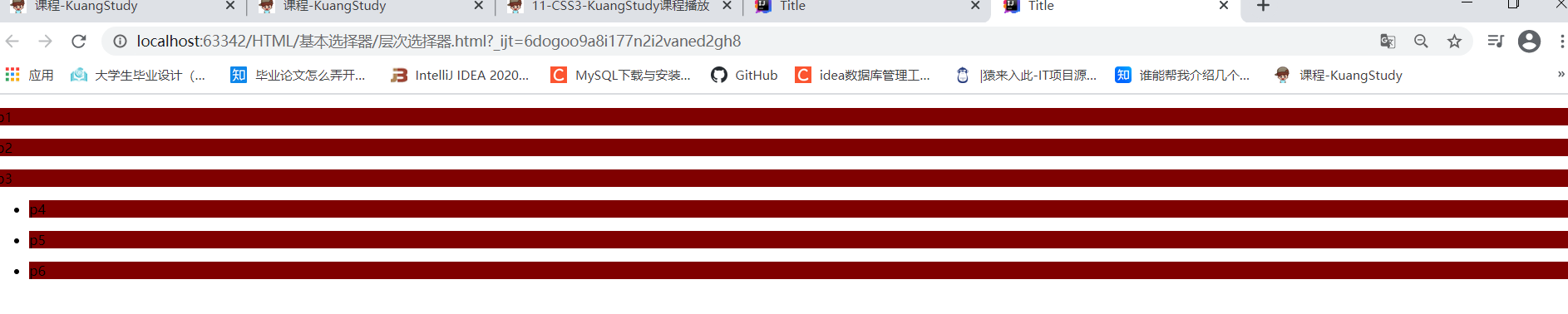
<p>p1</p>
<p>p2</p>
<p>p3</p>
<ul>
<li>
<p>p4</p>
</li>
<li>
<p>p5</p>
</li>
<li>
<p>p6</p>
</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
2.子选择器
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
/* 子选择器 只对一代可用(子) */
body>p{
background: blue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
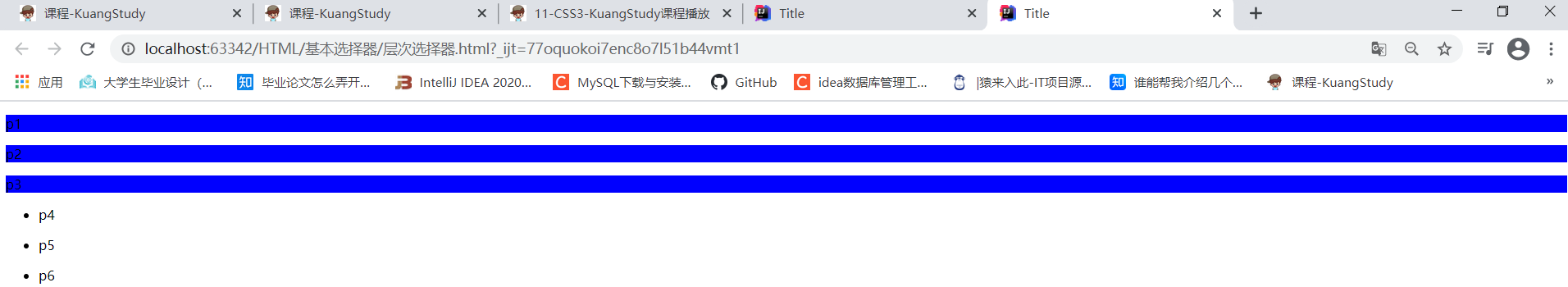
<p>p1</p>
<p>p2</p>
<p>p3</p>
<ul>
<li>
<p>p4</p>
</li>
<li>
<p>p5</p>
</li>
<li>
<p>p6</p>
</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
3.相邻兄弟选择器:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
/* 相邻兄弟选择器 只有一个(向下) */
.active+p{
background: cyan;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>p1</p>
<p class="active">p2</p>
<p>p3</p>
<ul>
<li>
<p>p4</p>
</li>
<li>
<p>p5</p>
</li>
<li>
<p>p6</p>
</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
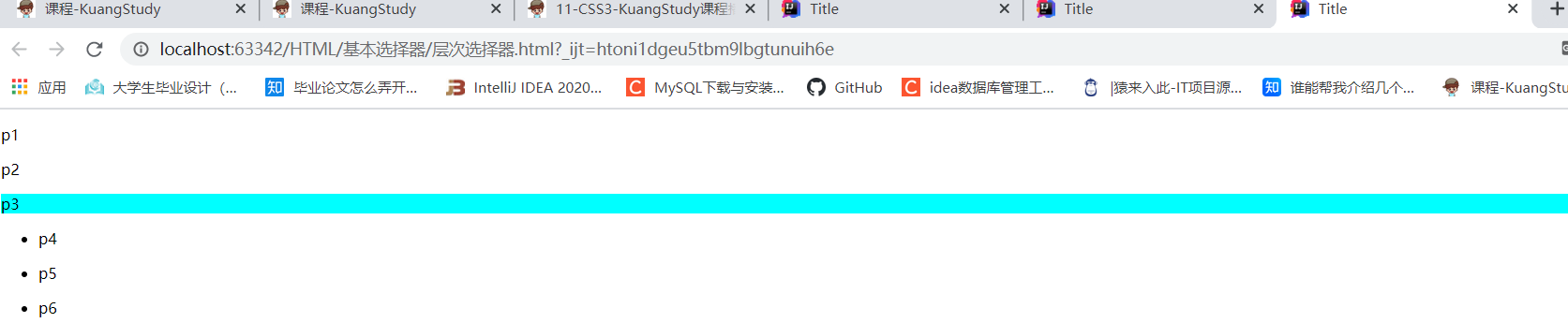
4.通用兄弟选择器
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
/* 通用兄弟选择器 (向下)之后所有的兄弟 */
.active~p{
background: cyan;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>p1</p>
<p class="active">p2</p>
<p>p3</p>
<ul>
<li>
<p>p4</p>
</li>
<li>
<p>p5</p>
</li>
<li>
<p>p6</p>
</li>
</ul>
<p>p7</p>
<p>p8</p>
</body>
</html>
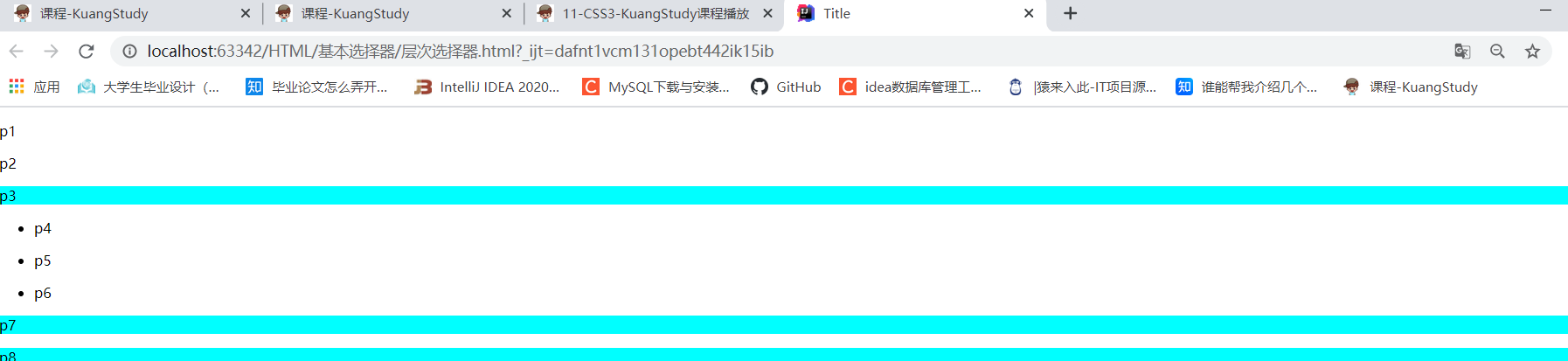
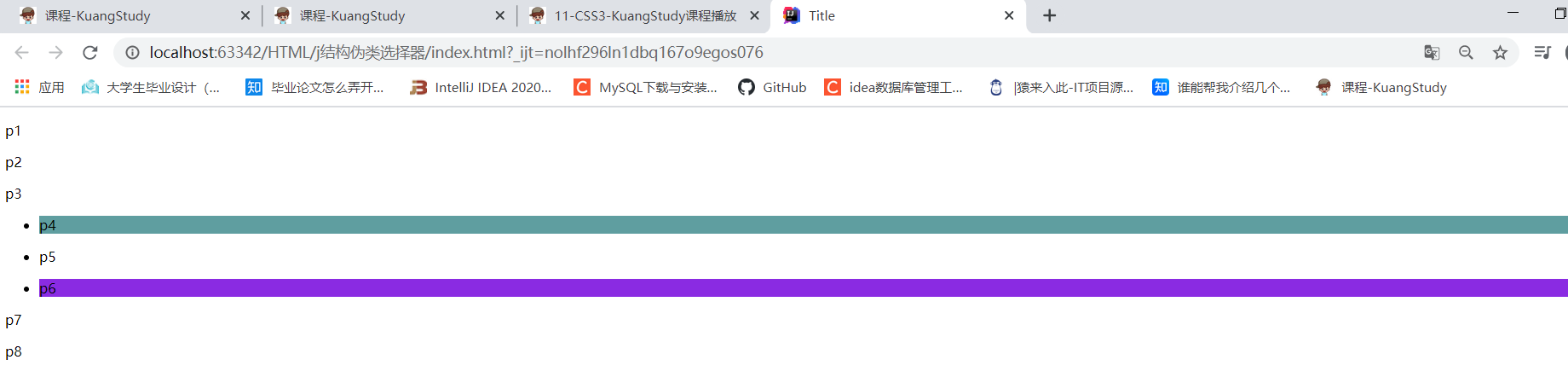
结构伪类选择器:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<!-- 避免使用.class id选择器-->
<style>
/* ul的第一个元素 */
ul li:first-child{
background: cadetblue;
}
/* ul的最后一个元素 */
ul li:last-child{
background: blueviolet;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>p1</p>
<p>p2</p>
<p>p3</p>
<ul>
<li>
<p>p4</p>
</li>
<li>
<p>p5</p>
</li>
<li>
<p>p6</p>
</li>
</ul>
<p>p7</p>
<p>p8</p>
</body>
</html>
伪类:条件
属性选择器(常用)
id 加 class 结合
代码部分:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
.demo a {
float: left;
display: block;
width: 20px;
height: 20px;
border-radius: 10px;
background: blue;
text-align: center;
color: cadetblue;
text-decoration: none;
margin-right: 5px;
}
/* 存在id属性的元素 a[]{} */
/* a[id]{
background: chartreuse;
} */
/* id属性为 niubi元素 a */
/*a[id=niubi]{
background: fuchsia;
}*/
/* class中只有link属性的元素 */
/* a[class=links]{
background: deepskyblue;
}*/
/* class中有link属性的元素 */
/*a[class*=links]{
background: deepskyblue;
}*/
/*选择href中以www开头的属性
a[href^=https]{
background: #c7c746;
}*/
/* 选择以jpg结尾的元素 */
a[href$=jpg]{
background: deeppink;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p class="demo">
<a href="https://www.xiaowei.com"id="niubi" class="links first">1</a>
<a href="" class="links" target="_blank" title="test">2</a>
<a href="images/xiong.jpg" class="links title">3</a>
<a href="i/we.jpg" style="target: behind">4</a>
<a href="https://www.jd.com" about="">5</a>
<a href="d/d.png" accesskey="">6</a>
<a href="q/we.gif" id="niubi2">7</a>
<a href="xiaowei.pdf">8</a>
</p>
</body>
</html>
1.id属性元素
2.具体id名属性元素
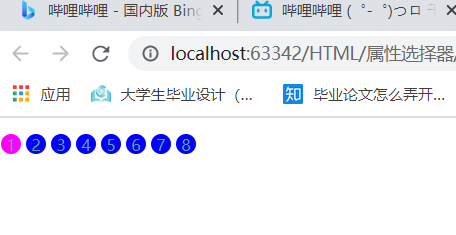
3.class中只有links属性元素
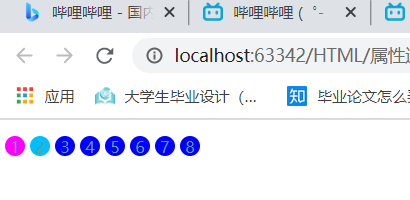
3.class属性中有links属性的元素
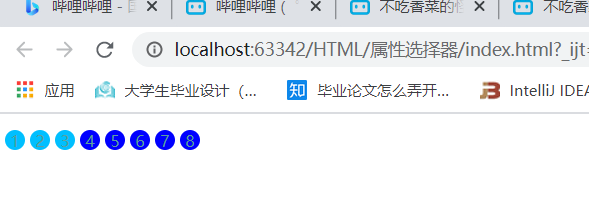
注意:注意在使用过程中 = 与 *= 的区别
4.选中href 中以http 开头的属性:
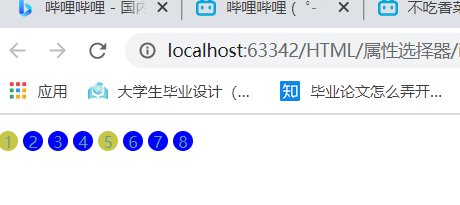
5.选中以jpg结尾的属性:
美化网页元素
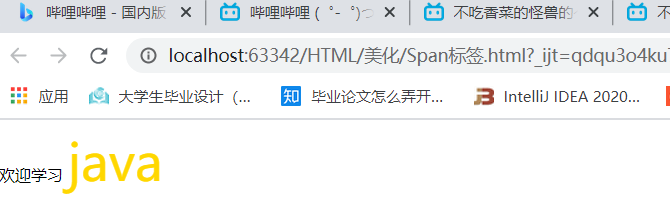
span标签:重点要突出的字用span标签圈起来
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
#xiao{
color: gold;
font-size: 50px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
欢迎学习 <span id="xiao">java</span>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
body{
font-size: medium;
/*
font-family:设置所有字体
font-size:字体大小
font-weight:字体粗细
color:字体颜色
*/
font-family: 幼圆;
color: fuchsia;
}
h1{
font-size: 50px;
}
.p1{
font-weight: bold;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
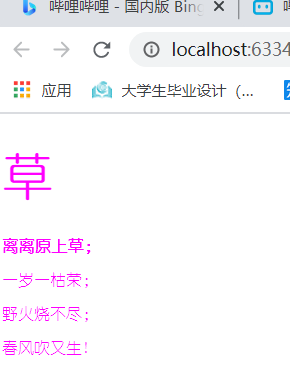
<h1>草</h1>
<p class="p1">离离原上草;</p>
<p>一岁一枯荣;</p>
<p>野火烧不尽;</p>
<p>春风吹又生!</p>
</body>
</html>
文本样式
1.颜色
2.文本对齐方式
3.首行缩进
4.行高
5.装饰
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<!-- 颜色:color
RGB:0~f
RGBA:A:0~1 透明度
文本居中:text-align: center;居右,居左同理
-->
<style>
h1{
color: rgba(0,256,0,0.5);
text-align: center;
}
.p1{
/*首行缩进两个字符 */
text-indent: 2em;
}
.p3{
/*行高与块高度一致就可以上下居中*/
background: #e24040;
height: 50px;
line-height: 50px;
}
.p2{
/*下划线*/
text-decoration: underline;
/*中划线
text-decoration: line-through;
*/
/*上划线
text-decoration: overline;
*/
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
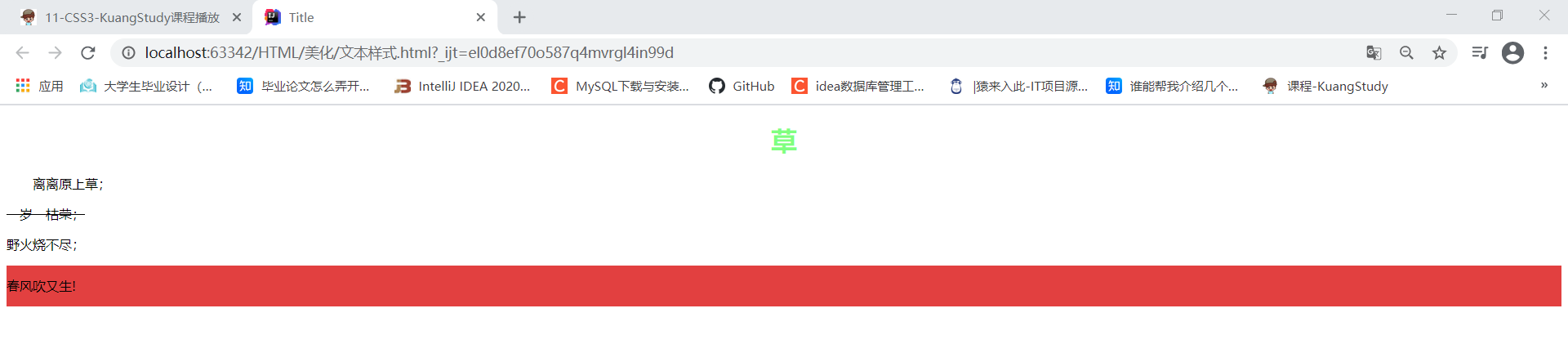
<h1>草</h1>
<p class="p1">离离原上草;</p>
<p class="p2">一岁一枯荣;</p>
<p>野火烧不尽;</p>
<p class="p3">春风吹又生!</p>
</body>
</html>
超链接伪类
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
a{
/*祛除下划线*/
text-decoration: none;
/*默认颜色*/
color: #ff0303;
}
/*鼠标悬浮颜色 超链接伪类*/
a:hover{
color: gold;
font-size: 50px;
}
/*鼠标按住未释放状态*/
a:active{
color: deepskyblue;
}
/*访问过后*/
a:visited{
color: yellow;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<a href="#">
<img src="java.jpg" alt="">
</a>
<p>
<a href="#">JAVA编程思想</a>
</p>
<p>
<a href="#">作者:牛逼</a>
</p>
</body>
</html>
列表样式

背景图像应用及渐变
代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>列表样式</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css" type="text/css">
</head>
<div id="nav">
<body>
<h2 class="title">商品种类</h2>
<ul>
<li><a href="#">图书</a> <a href="#">音像</a> <a href="#">数字商品</a> </li>
<li><a href="#">电脑</a> <a href="#">笔记本</a> <a href="#">手机</a> </li>
<li><a href="#">充电包</a> <a href="#">充电器</a> <a href="#">电池</a> </li>
<li><a href="#">耳机</a> <a href="#">数据线</a> <a href="#">键盘</a> </li>
<li><a href="#">鼠标</a> <a href="#">打火机</a> <a href="#">香烟</a> </li>
<li><a href="#">牛奶</a> <a href="#">面包</a> <a href="#">水果</a> </li>
</ul>
</body>
</div>
</html>
#nav{
width: 300px;
}
.title
{
font-size: 18px;
font-weight: bold;
text-indent: 1em;
line-height: 35px;
/*颜色 图片 图片位置 平铺方式*/
background: red url("down.jpg " )250px 15px no-repeat;
}
/*ul li*/
/*list-style:
none:去掉原点
circle:空心圆
deciml:数字
square:正方形
*/
ul{
background: rgba(255,106,127,0.19);
}
ul li{
height: 30px;
list-style: none;
text-indent: 1em;
background-image: url("右.jpg");
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-position: 240px 2px;
}
a{
text-decoration: none;
font-size: 14px;
color: black;
}
a:hover{
color: orange;
text-decoration: underline;
}
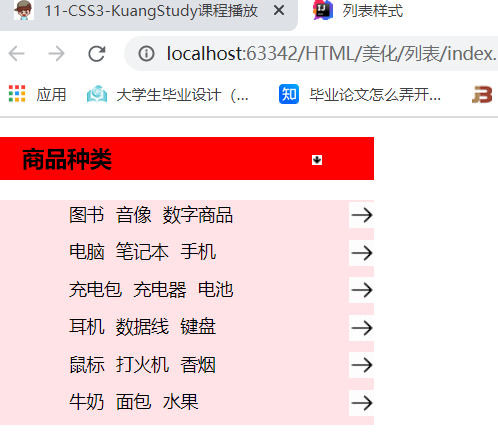
运行效果:
渐变:
参考网站:http://www.hepou.com/peise/grabient.html
盒子模型
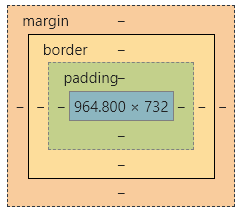
margin:外边距
padding:内边距
border:边框
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
/*body总有一个默认的外边距 margin 0 初始化*/
h1,ul,li,a,body{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
text-decoration: none;
}
/*border 粗细 样式 颜色*/
#box{
width: 300px;
border: 1px solid red;
}
/*form 标签选择器*/
form{
background:#ff0303;
}
/* div下的第一个type 的input框 */
div:nth-of-type(1)>input{
border: 5px solid black;
}
div:nth-of-type(2)>input{
border: 4px dashed blue;
}
div:nth-of-type(3)>input{
border: 3px solid rosybrown;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="box">
<h2>会员登陆</h2>
<form action="#">
<div>
<span>用户名:</span>
<input type="text">
</div>
<div>
<span>密 码:</span>
<input type="text">
</div>
<div>
<span>邮 箱:</span>
<input type="text">
</div>
</form>
</div>
</body>
</html>
内外边距及div居中
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
/*body总有一个默认的外边距 margin 0 初始化*/
h1,ul,li,a,body{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
text-decoration: none;
}
/*border 粗细 样式 颜色*/
#box{
width: 300px;
border: 1px solid red;
/* padding:10px 15px :上下10px 左右15px */
/*padding:10px 15px 17px 19:(顺时针) 上右中下 */
}
/*form 标签选择器*/
form{
background:#ff0303;
}
input{
margin: 0 auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="box">
<h2>会员登陆</h2>
<form action="#">
<div>
<span>用户名:</span>
<input type="text">
</div>
<div>
<span>密 码:</span>
<input type="text">
</div>
<div>
<span>邮 箱:</span>
<input type="text">
</div>
</form>
</div>
</body>
</html>
浮动
标准文档流
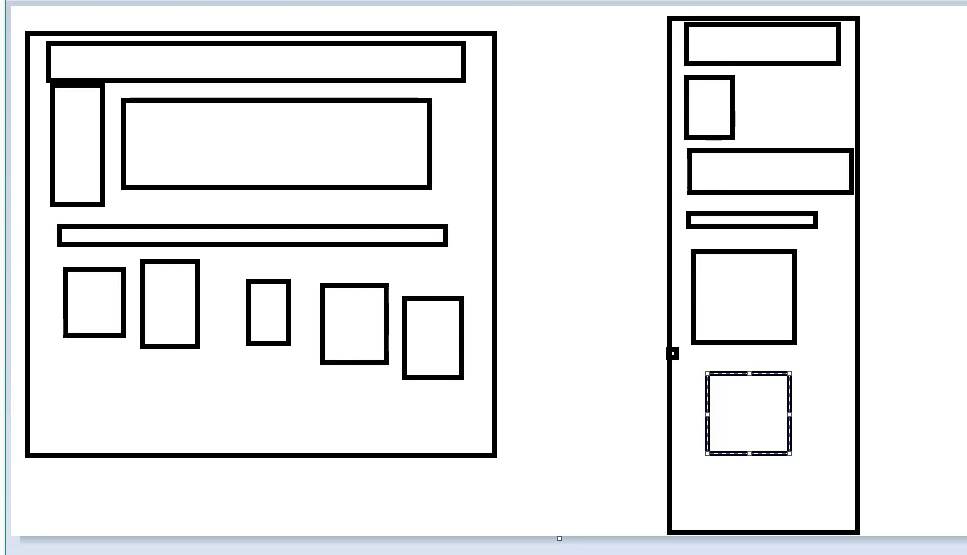
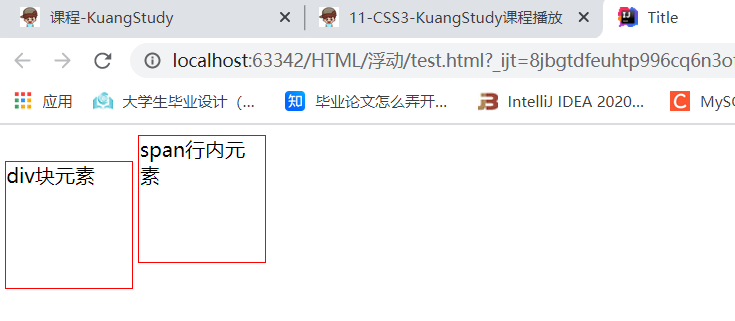
块级元素:独占一行
h1~h6 p 列表
行内元素:不独占一行
span a img strong...
行内元素可以包含在块级元素,块级元素不能包含在行内元素
display
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
div{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border: 1px solid red;
display: inline-block;
}
span{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border: 1px solid red;
/* display:block :块元素
inline:行内元素
inline-block:是块元素,但是可以内联在一行
*/
display: inline-block;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>div块元素</div>
<span>span行内元素</span>
</body>
</html>
float
左右浮动
<html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>菜鸟教程(runoob.com)</title> <style> img { float:left; } </style> </head> ```html <html> <head> <style type="text/css"> img { float:right } </style> </head> <body>在下面的段落中,我们添加了一个样式为 float:right 的图像。结果是这个图像会浮动到段落的右侧。
 This is some text. This is some text. This is some text.
This is some text. This is some text. This is some text.
This is some text. This is some text. This is some text.
This is some text. This is some text. This is some text.
This is some text. This is some text. This is some text.
This is some text. This is some text. This is some text.
This is some text. This is some text. This is some text.
This is some text. This is some text. This is some text.
This is some text. This is some text. This is some text.
This is some text. This is some text. This is some text.
This is some text. This is some text. This is some text.
This is some text. This is some text. This is some text.
This is some text. This is some text. This is some text.
This is some text. This is some text. This is some text.
This is some text. This is some text. This is some text.
This is some text. This is some text. This is some text.
This is some text. This is some text. This is some text.
This is some text. This is some text. This is some text.
This is some text. This is some text. This is some text.
This is some text. This is some text. This is some text.

**`父级边框塌陷问题`**
1.增加父级元素的高度
2.增加一个空的div标签,清除浮动
3.overflow解决溢出问题
*在父级元素增加一个overflow:hidden 属性*
4.父类添加一个伪类:after
```html
#father:after{
content:'';
display:block;
clear;both;
}

定位
相对定位
*相对于原来位置进行指定的偏移,相对定位任在标准文件流中,原来的位置任被保留
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
#father{
margin: 10px;
padding: 5px;
font-size: 12px;
line-height: 25px;
}
#first{
background:#1a22bd;
border: 2px dashed #1a22ff;
position: relative; /*相对定位*/
left:-20px;
}
#second{
background:#1affbd;
border: 2px dashed #1affff;
position: relative;
top:-20px;/*上移20个像素*/
}
#third{
background:#ff22bd;
border: 2px dashed #ff22ff;
position: relative;
right: -20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="father">
<div id="first">第一个盒子</div>
<div id="second">第二个盒子</div>
<div id="third">第三个盒子</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
题:
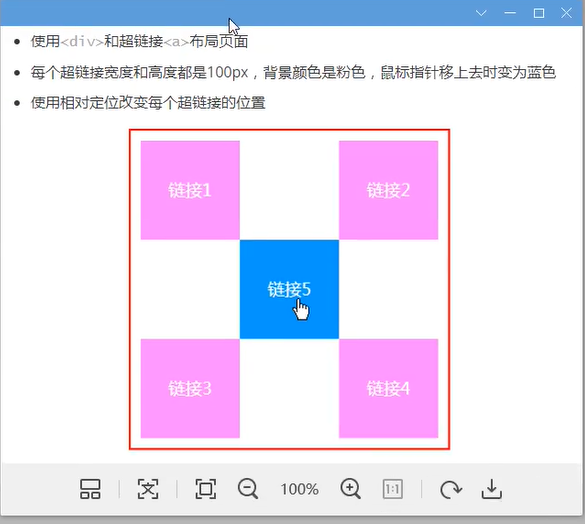

绝对定位:
定位:基于xxx定位,上下左右
1.没有父级元素定位的前提下,相对于浏览器定位
2.假设父级元素存在定位,我们通常会相对父级元素进行偏移
3.绝对定位使元素的位置与文档流无关,因此不占据空间
固定定位:
fixed
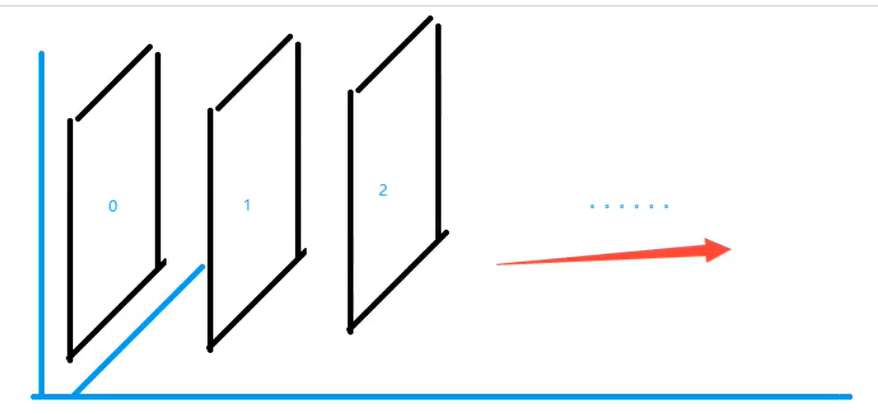
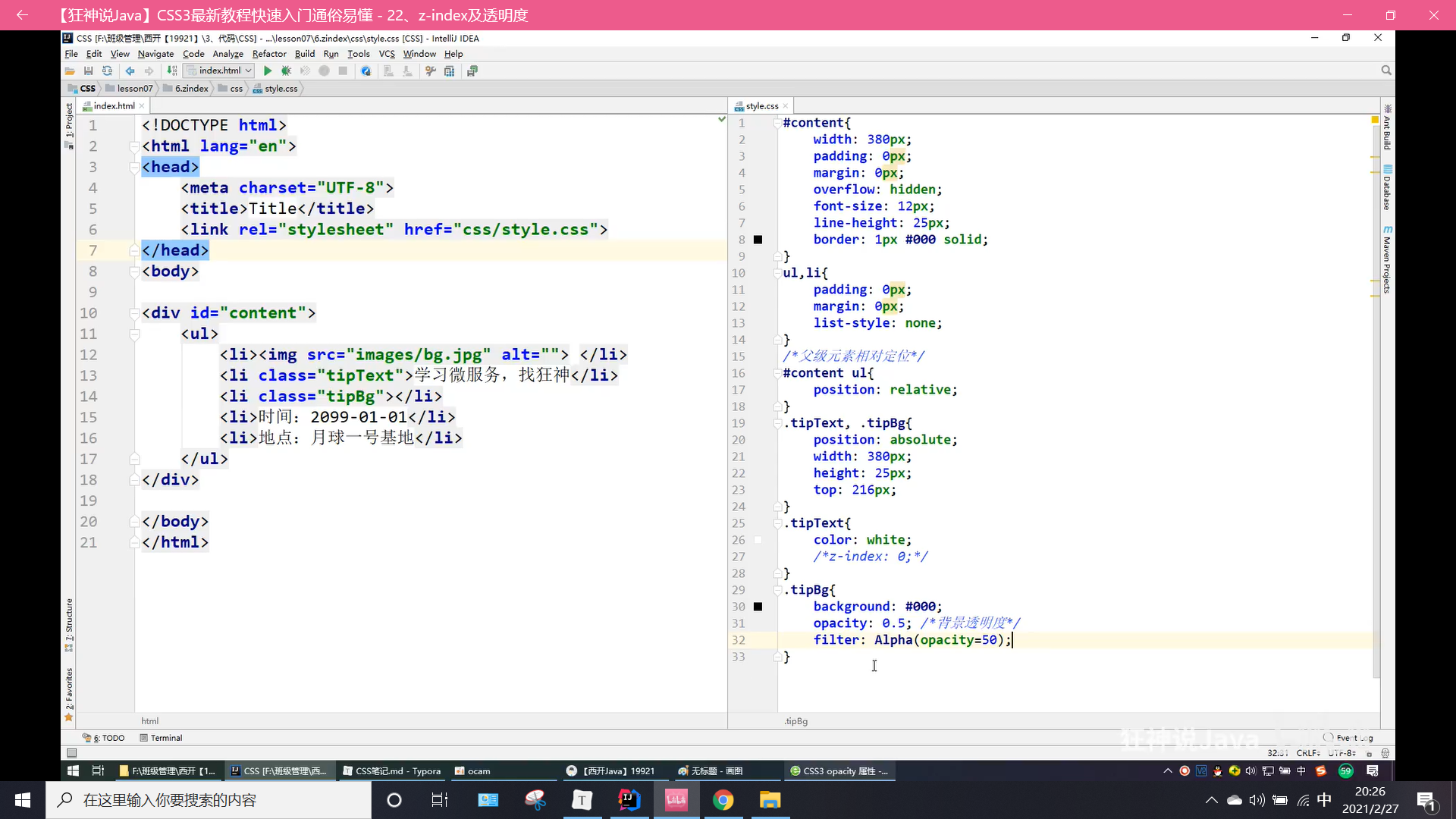
z-index
图层:




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号