vue框架 各指令和实例成员
前言:
Vue是前台框架,轻量级,主要用于web端;
类比:
Angular企业级,比较厚重;
React主要用于ios/安卓端。
总结:Vue结合了其他框架优点、轻量级、中文API、数据驱动,双向绑定,MVVM设计模式、组件化开发、单页面应用
ps:vue是js渐进式框架,根据开发需求们可以决定vue框架控制项目的具体方位,可为一个标签,亦可为一个页面,甚至可为整个项目
一、vue运用
1、导入:同jQuery方法,在script标签的src内
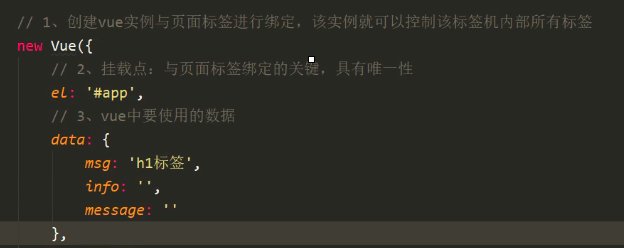
2、挂载点:
1)html与body不能作为挂载点
2)一个vue对象挂载点之后索引一个匹配结果,所以挂载点一般用id标识
3、数据:
1)用示例成员data为vue环境提供数据,数据采用字典{ }形式;
2)在插值表达式{{ }}中,直接书写数据的key来访问数据;
3)在外部通过接受实例的变量app,访问实例成员(实例成员都用$开头),间接访问到数据app.$data.info
4)在外部也可以通过实例变量app直接访问数据app.info
4、过滤器:
在插值表达式可以直接做简单运算
挂载点、数据、图示:
二、指令
1、文本指令
1)v-指令名="变量",变量是需要data提供数据值的(v-text="info")
2)v-指令名="常量",常量采用常量基本的语法,数字与布尔值等可以直接书写,字符串等需要特殊符号的需要添加
3)v-html可以解析 html 语法
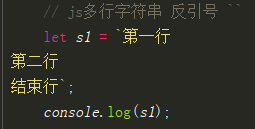
ps:js多行字符串,用反向``
2、事件指令
1)v-on:事件名="时间函数名" ;可以简写为@事件名="事件函数"。
2)事件传参:
@事件="方法" 默认传入事件对象 $event
@事件="方法()" 不传递任何参数
@事件="方法(参数...)" 只传递自定义参数
@事件="方法($event, 参数)" 自定义传参时传递事件对象

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
<style>
body {
/*页面文本不允许选择*/
user-select: none;
}
.low-num {
cursor: pointer;
}
.low-num:hover {
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- 事件指令:v-on:事件名="事件函数名" -->
<p class="low-num" v-on:click="lowNum">
<span>点击减一:</span>
<span>{{ num }}</span>
</p>
<p v-on:dblclick="dblAction">双击</p>
<!-- v-on:事件名="事件函数" 可以简写为 @事件名="事件函数" -->
<p @mouseover="overAction()">悬浮</p>
<p @mouseover="overAction(10)">悬浮1</p>
<p @mouseover="overAction(10, 20)">悬浮2</p>
<p @mouseover="overAction(10, 20, $event)">悬浮3</p>
<!-- 事件传参:
@事件='方法' 默认传入事件对象 $event
@事件='方法()' 不传递任何参数
@事件='方法(参数...)' 只传递自定义参数
@事件='方法($event, 参数...)' 自定义传参时传递事件对象
-->
</div>
</body>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
let app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
num: 99
},
methods: {
lowNum: function () {
// 在vue实例内部的方法中,使用变量
// alert(this.num)
this.num -= 1;
},
dblAction (ev) {
// alert('双击事件');
console.log(ev)
},
overAction(a, b, c) {
console.log(a, b, c)
}
}
})
</script>
</html>
3、属性指令
1)v-bind:属性名="变量" 可以简写:属性名="变量"
2)style样式属性绑定

<p :style="myStyle">样式绑定1</p> data: { myStyle: { backgroundColor: 'pink', color: 'deeppink', 'border-radius': '50%' },

<p :style="{backgroundColor: c1, color: c2, 'border-radius': '50%'}">样式绑定2</p>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
c1: 'cyan',
c2: 'tan',
}
3)class类属性绑定
<p :class="myc1">样式绑定3</p>
<p :class="[myc2,myc3,myc4,'bbb']">样式绑定4</p>
<p :class="{xxx:yyy}">样式绑定5</p>
样式绑定可以单个;
多个及直接字符串书写;
yyy为 ture/false

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>属性指令</title>
<style>
[index] {
color: orange;
}
.ccc {
background-color: yellowgreen;
color: greenyellow;
border-radius: 50%;
}
.ccc1 {
background-color: yellowgreen;
}
.ccc2 {
color: greenyellow;
}
.ccc3 {
border-radius: 50%;
}
.ttt {
background-color: gold;
color: orange;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!--1) 语法:v-bind:属性名="变量" -->
<p id="p1" class="p1" style="" title="" index="">属性指令1</p>
<p id="p2" v-bind:class="p1" style="" title="" index="">属性指令2</p>
<p v-bind:index="p1">自定义属性也可以被vue绑定1</p>
<!--2) v-bind:属性名="变量" 简写 :属性名="变量" -->
<p :index="p1">自定义属性也可以被vue绑定2</p>
<p :title="'文本提示'">悬浮文本提示</p>
<!--3) style样式属性绑定 -->
<p :style="myStyle">样式绑定1</p>
<p :style="{backgroundColor: c1, color: c2, 'border-radius': '50%'}">样式绑定2</p>
<!--4) class类属性绑定 -->
<p :class="myc1">样式绑定3</p>
<p :class="[myc2,myc3,myc4,'bbb']">样式绑定4</p>
<p :class="{xxx:yyy}">样式绑定5</p>
<!--案例:点击切换类名是否起作用-->
<p @click="clickAction" :class="{ttt:yyy}">点击切换类</p>
</div>
</body>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
p1: 'q1',
myStyle: {
backgroundColor: 'pink',
color: 'deeppink',
'border-radius': '50%'
},
c1: 'cyan',
c2: 'tan',
myc1: 'ccc ddd eee',
myc2: 'ccc1',
myc3: 'ccc2',
myc4: 'ccc3',
yyy: true, // false
},
methods: {
clickAction() {
this.yyy = !this.yyy;
}
}
})
</script>
</html>
4、表单指令
1)对表单标签value进行绑定操作变量,不能实时检测绑定的变量
2)表单标签的值有v-model="变量" 来绑定控制,操作的还是value,但是拥有实时变量值的检测
3)确认框
4)单选框
5)复选框

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
<style>
.p1 {
width: 500px;
height: 21px;
background-color: orange;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<form action="">
<!--1) 对表单标签value进行绑定操作变量,不能时时检测绑定的变量-->
<input class="inp1" type="text" :value="info">
<input class="inp2" type="text" :value="info">
<p class="p1">{{ info }}</p>
<hr>
<!--2) 表单标签的值有 v-model="变量" 来绑定控制,操作的还是value,但是拥有时时变量值的检测 -->
<input class="inp1" type="text" v-model="info">
<input class="inp2" type="text" v-model="info">
<p class="p1">{{ info }}</p>
<hr>
<!-- 2) v-model操作单独复选框 - 确认框 -->
是否同意:<input type="checkbox" name="agree" v-model="isAgree">
<!--是否同意:<input type="checkbox" name="agree" true-value="yes" false-value="no" v-model="isAgree">-->
<p>{{ isAgree }}</p>
<!-- 3) 单选框-->
性取向:
男 <input type="radio" name="sex" value="male" v-model="mysex">
女 <input type="radio" name="sex" value="female" v-model="mysex">
哇塞 <input type="radio" name="sex" value="others" v-model="mysex">
<p>{{ mysex }}</p>
<!-- 4) 复选框-->
兴趣爱好:
男 <input type="checkbox" name="hobbies" value="male" v-model="myhobbies">
女 <input type="checkbox" name="hobbies" value="female" v-model="myhobbies">
哇塞 <input type="checkbox" name="hobbies" value="others" v-model="myhobbies">
<p>{{ myhobbies }}</p>
<hr>
<input type="submit">
</form>
</div>
</body>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
info: '123',
isAgree: 0,
// isAgree: 'no',
mysex: 'others',
myhobbies: ['male', 'female']
}
})
</script>
</html>
ps:v-once指令(唯一锁定)、v-cloak指令(斗篷,取消页面渲染闪烁)

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
<style>
.box {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: orange;
}
.center {
text-align: center;
line-height: 200px;
}
.rcenter {
text-align: right;
line-height: 200px;
}
.right {
text-align: right;
}
.top {
line-height: 21px;
}
.bottom {
line-height: calc(400px - 21px);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<div class="box" :class="[c1, {right:r, top:t, bottom:b}]" @mouseover="a1" @mousedown="a2" @mouseup="a3" @mouseout="a4">{{ msg }}</div>
</div>
</body>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
methods: {
a1(){
this.msg = '被悬浮';
// 正中
this.c1 = 'center';
this.r = 0;
this.t = 0;
this.b = 0;
},
a2(){
this.msg = '被按下';
// 右上
this.r = 1;
this.t = 1;
this.b = 0;
},
a3(){
this.msg = '被抬起';
// 右中
this.c1 = 'rcenter';
this.r = 0;
this.t = 0;
this.b = 0;
},
a4(){
this.msg = '被移开';
// 右下
this.r = 1;
this.t = 0;
this.b = 1;
},
},
data: {
msg: '',
c1: '',
r:0,
t:0,
b:0,
}
})
</script>
</html>
5、条件指令v-if
1)v-show与v-if区别:两种都可以控制标签的显隐,绑定的值是布尔类型值,当都隐藏标签时前者以 display:none方式渲染,后者不渲染标签
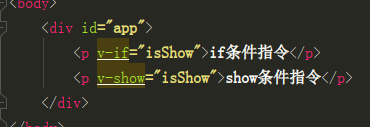
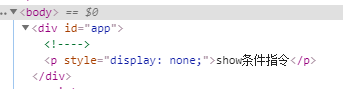
2)v-if、v-else-if、v-else;

<p>
<button @click="changeBox('rBox')" :class="showName == 'rBox' ? 'active' : ''">红</button>
<button @click="changeBox('yBox')" :class="showName == 'yBox' ? 'active' : ''">黄</button>
<button @click="changeBox('bBox')" :class="showName == 'bBox' ? 'active' : ''">蓝</button>
</p>
6、原义指令v-pre
v-pre 指令可以在vue控制范围内,形成局部vue不能控制的区域,类似于 r' 转义符的作用,是当前局部失去vue作用,表达原义
7、循环指令v-for
1)语句 v-for=" 元素 in 容器 "
2)针对循环遍历的标签,通过会提供key属性来优化渲染速度,但key的值必须是唯一
v-for="(ch , i) in str " : key = "ch + i" (用元素+索引拼接的key必定唯一)
3)循环字典
<p v-for="(ele , k, i) in dic"> {{ i }} {{ k }} : {{ ele }}</p>
8、todolist案例

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title></title> <style> li:hover { color: red; cursor: pointer; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <p> <input type="text" v-model="userMsg"> <button type="button" @click="sendMsg">留言</button> </p> <ul> <li v-for="(msg, index) in msgs" @click="deleteMsg(index)"> {{ msg }} </li> </ul> </div> </body> <script src="js/vue.js"></script> <script> new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { msgs: localStorage.msgs ? JSON.parse(localStorage.msgs) : [], // 所有留言 userMsg: '', // 用户留言 }, methods: { sendMsg() { // 留言事件 // 尾增 // this.msgs.push(this.userMsg); // 首增 // this.msgs.unshift(this.userMsg); let userMsg = this.userMsg; if (userMsg) { this.msgs.unshift(userMsg); // 渲染给页面 localStorage.msgs = JSON.stringify(this.msgs); // 同步到数据库 this.userMsg = ''; // 清空留言框 } }, deleteMsg(index) { // 开始索引 操作长度 操作的结果们 this.msgs.splice(index, 1) } } }) </script> <script> // localStorage['num'] = 10; // sessionStorage.num = 888; // console.log(localStorage.num); // localStorage.msgs = JSON.stringify(['1111', '2222']); // console.log(JSON.parse(localStorage.msgs)); // console.log(JSON.parse(localStorage.msgs)[0]); </script> </html>
三、实例成员
1、插值表达式符号

<div id="app"> {{ msg }} {[ msg ]} </div> <script> new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { msg: '12345' }, // delimiters: ['{{', '}}'], delimiters: ['{[', ']}'], }) </script>
2、计算属性 computed
1)computed是用来声明方法属性的
2)声明的方法属性不能在data中重复定义
3)方法属性必须在页面中渲染使用,才会对内部出现的所有变量进行监听

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title></title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <p @click="fn">{{ num }}</p> <p>十位:{{ parseInt(num / 10) }}</p> <p>个位:{{ num % 10 }}</p> <!-- 一个变量的值依赖多个变量,且依赖的任意一个变量发生改变,该变量都会改变 --> 十位:<input type="number" v-model="shi" min="0" max="9"> 个位:<input type="number" v-model="ge" min="0" max="9"> 结果:<b>{{ shi * 10 + +ge }}</b> 结果:<b>{{ result }}</b> </div> </body> <script src="js/vue.js"></script> <script> new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { num: 99, shi: '', ge: '', // result: 0, }, methods: { fn() { this.num -= 3; } }, // 1) computed是用来声明 方法属性 的 // 2) 声明的方法属性不能在data中重复定义 // 3) 方法属性必须在页面中渲染使用,才会对内部出现的所有变量进行监听 computed: { result() { // console.log('该方法被调用了'); // this.shi; // this.ge; return this.shi * 10 + +this.ge } } }) </script> </html>
3、属性监听 watch
1)watch为data中已存在的属性设置监听事件
2)监听的属性值发送改变,就会出发监听事件
3)监听事件的方法返回值没有任何意义

<div id="app"> 姓名:<input type="text" v-model="fullName"> 姓:<b>{{ firstName }}</b> 名:<b>{{ lastName }}</b> </div> </body> <script src="js/vue.js"></script> <script> new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { fullName: '', firstName: '', lastName: '', }, watch: { // fullName值改变,就会调用绑定的事件方法 fullName() { nameArr = this.fullName.split(''); this.firstName = nameArr[0]; this.lastName = nameArr[1]; } } }) </script>




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号