算法day12-二叉树(2)
目录
- 二叉树的最大深度
- 二叉树的最小深度
- 扩展题
一、二叉树的最大深度
https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree?envType=problem-list-v2&envId=8At1GmaZ
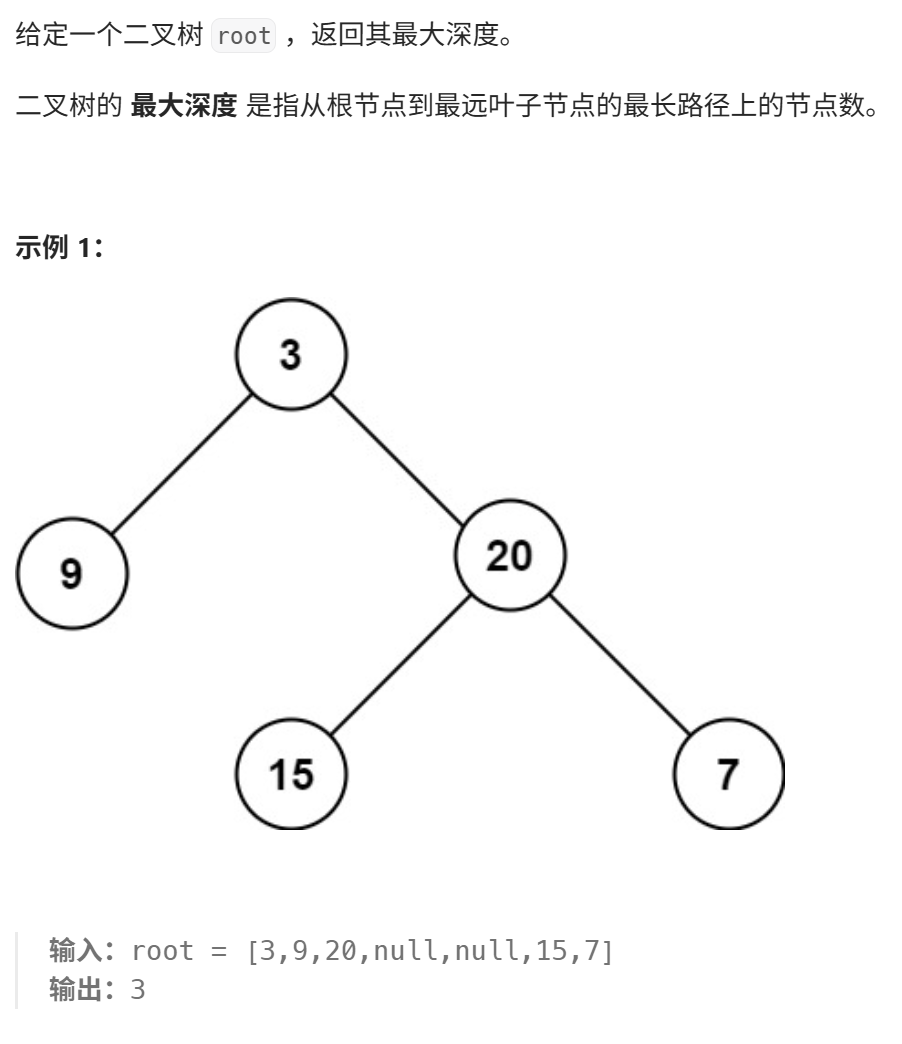
这道题可以用广度优先搜索/深度优先方法做。
1. 深度优先遍历(递归)
class Solution{ public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) { if(root == null){ return 0; } int leftDepth = maxDepth(root.left); int rightDepth = maxDepth(root.right); return Math.max(leftDepth, rightDepth) + 1; } }
1
/ \
2 3
/
4
递归展开过程:
maxDepth(1)
→ maxDepth(2)
→ maxDepth(4)
→ maxDepth(null) → return 0
→ maxDepth(null) → return 0
→ return max(0, 0) + 1 = 1
→ maxDepth of node 4 = 1
→ maxDepth(null) → return 0
→ return max(1, 0) + 1 = 2
→ maxDepth of node 2 = 2
→ maxDepth(3)
→ maxDepth(null) → return 0
→ maxDepth(null) → return 0
→ return max(0, 0) + 1 = 1
→ maxDepth of node 3 = 1
→ return max(2, 1) + 1 = 3
2. 广度优先遍历
class Solution { public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) { int depth = 0; if(root == null){ return 0; } Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>(); queue.offer(root); while(!queue.isEmpty()){ int size = queue.size(); for(int i=0; i<size; i++){ TreeNode cur = queue.poll(); if(cur.left != null) queue.offer(cur.left); if(cur.right != null) queue.offer(cur.right); } depth++; } return depth; } }
二、二叉树的最小深度
https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-depth-of-binary-tree?envType=problem-list-v2&envId=8At1GmaZ
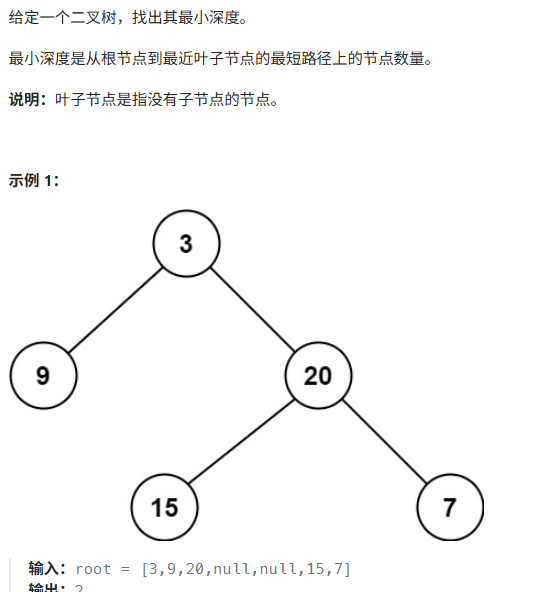
这道题求最短路径,用BFS,遇到第一个叶子节点就返回深度即可。
class Solution { public int minDepth(TreeNode root) { if(root == null){ return 0; } Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>(); queue.offer(root); int depth = 0; while(!queue.isEmpty()){ depth++; int size = queue.size(); for(int i=0; i<size; i++){ TreeNode cur = queue.poll(); if(cur.left == null && cur.right == null){ return depth; } if(cur.left != null) queue.offer(cur.left); if(cur.right != null) queue.offer(cur.right); } } return depth; } }
三、扩展题(都是BFS的扩展题)
1. 二叉树的右视图
https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-right-side-view/?envType=problem-list-v2&envId=8At1GmaZ
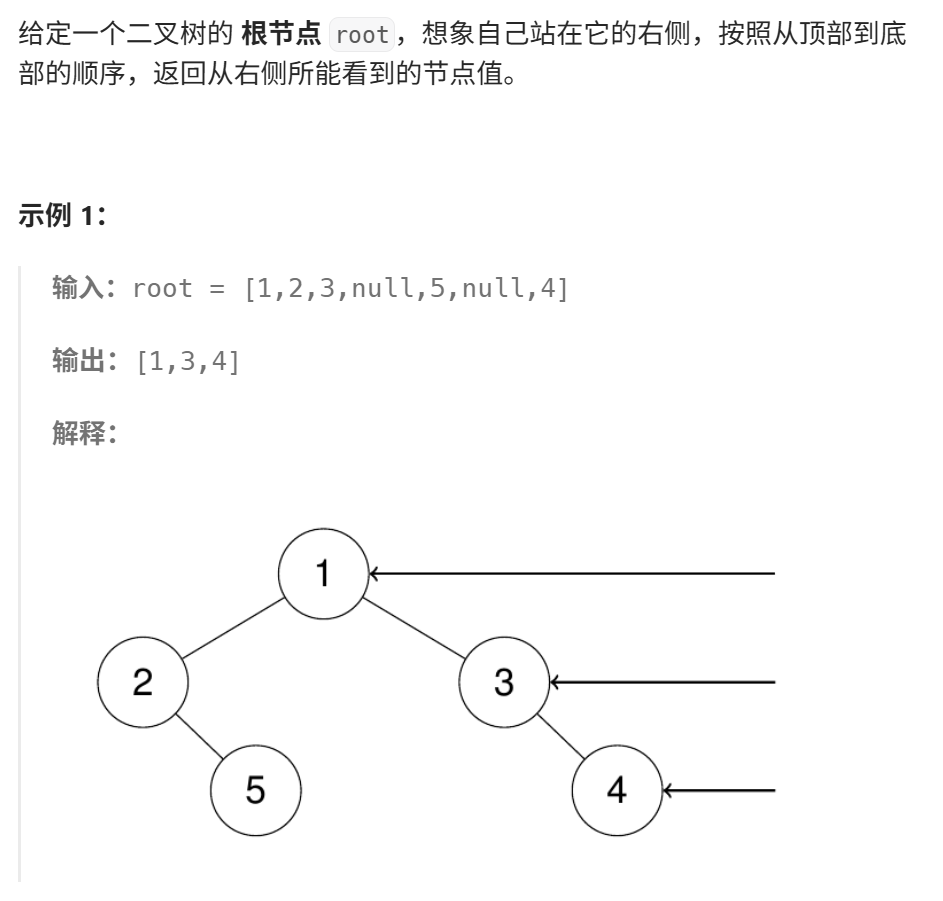
这道题可以用BFS来做,也就是当层序遍历到每一层的最后一个节点时,将这个节点加入结果即可。
class Solution { public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) { List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>(); if(root == null){ return res; } Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>(); queue.offer(root); while(!queue.isEmpty()){ int size = queue.size(); for(int i = 0; i<size; i++){ TreeNode cur = queue.poll(); if(i == size-1){ res.add(cur.val); } if(cur.left != null) queue.offer(cur.left); if(cur.right != null) queue.offer(cur.right); } } return res; } }
2. 二叉树的层平均值
https://leetcode.cn/problems/average-of-levels-in-binary-tree/description/?envType=problem-list-v2&envId=8At1GmaZ
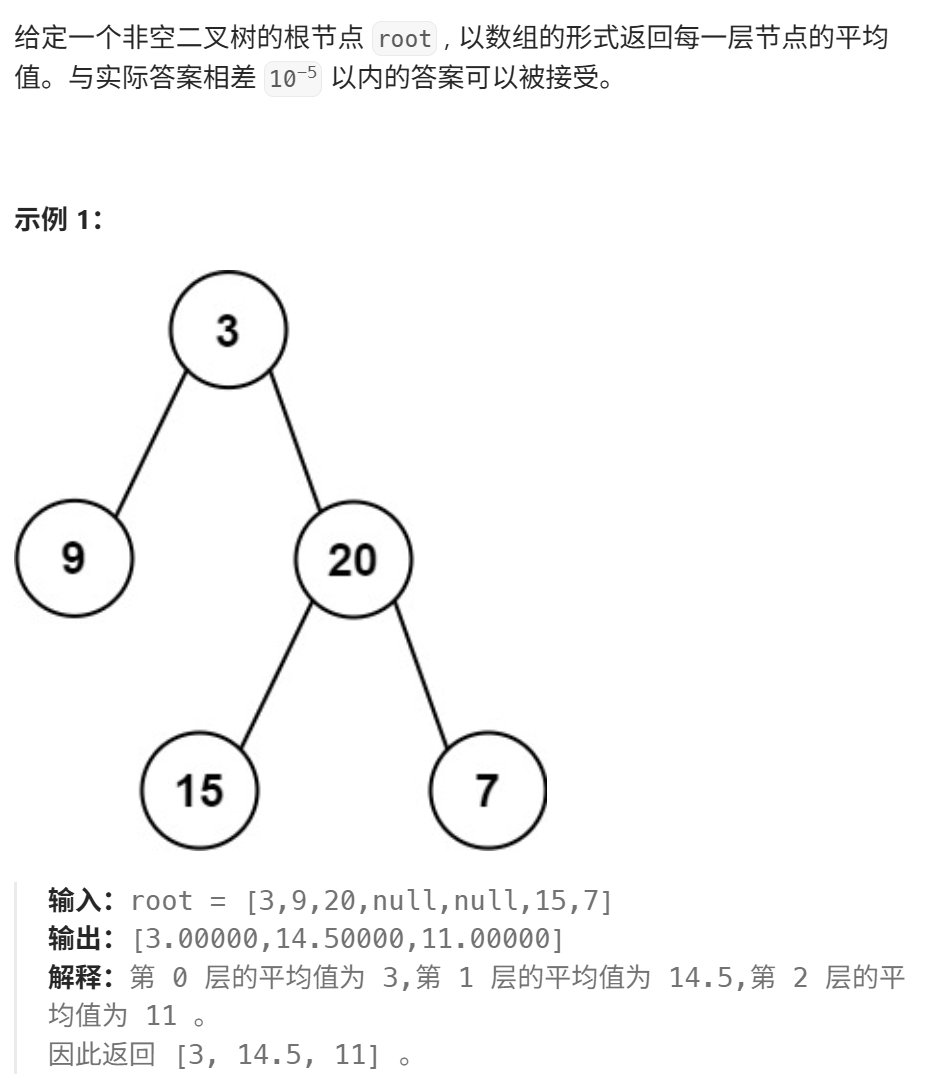
class Solution { public List<Double> averageOfLevels(TreeNode root) { List<Double> res = new ArrayList<>(); if(root == null){ return res; } Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>(); queue.offer(root); Double sum = 0.00; Double avg = 0.00; while(!queue.isEmpty()){ sum = 0.00; avg = 0.00; int size = queue.size(); for(int i=0; i<size; i++){ TreeNode cur = queue.poll(); sum += cur.val; if(cur.left != null) queue.offer(cur.left); if(cur.right != null) queue.offer(cur.right); } avg = sum / size; res.add(avg); } return res; } }
3. N叉树的层序遍历
https://leetcode.cn/problems/n-ary-tree-level-order-traversal/?envType=problem-list-v2&envId=8At1GmaZ
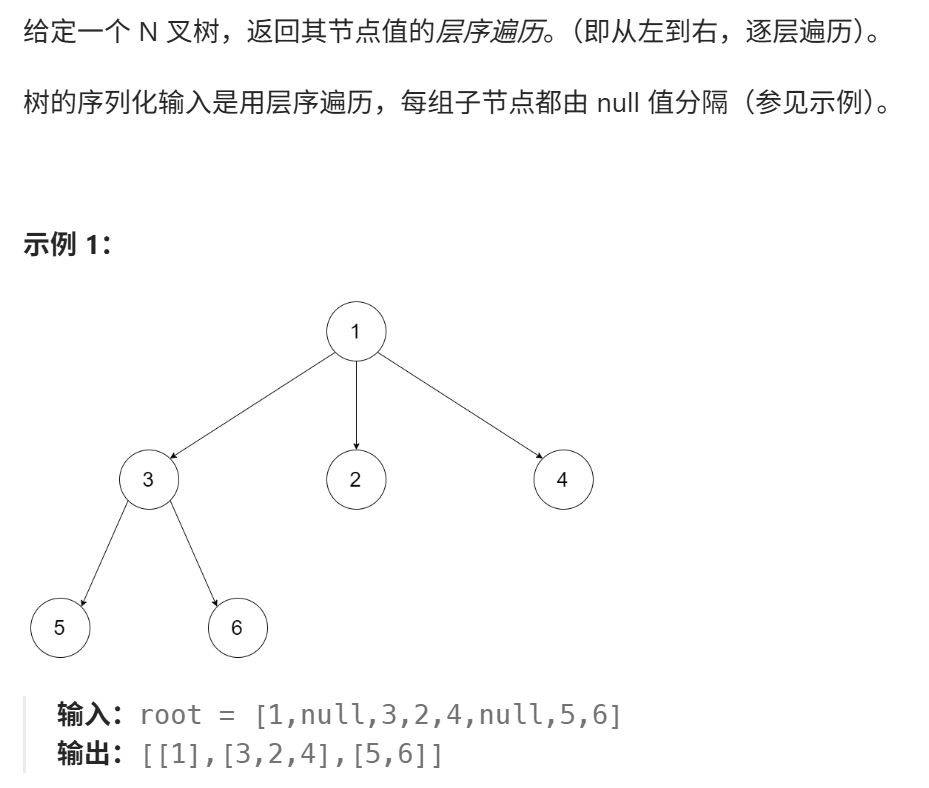
class Node { public int val; public List<Node> children; public Node() {} public Node(int _val) { val = _val; } public Node(int _val, List<Node> _children) { val = _val; children = _children; } }; class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(Node root) { List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>(); if(root == null){ return res; } Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>(); queue.offer(root); while(!queue.isEmpty()){ List<Integer> level = new ArrayList<>(); int size = queue.size(); for(int i=0; i<size; i++){ Node cur = queue.poll(); level.add(cur.val); for(Node node : cur.children){ queue.offer(node); } } res.add(level); } return res; } }
4. 在每个树行中找最大值
https://leetcode.cn/problems/populating-next-right-pointers-in-each-node/description/?envType=problem-list-v2&envId=8At1GmaZ
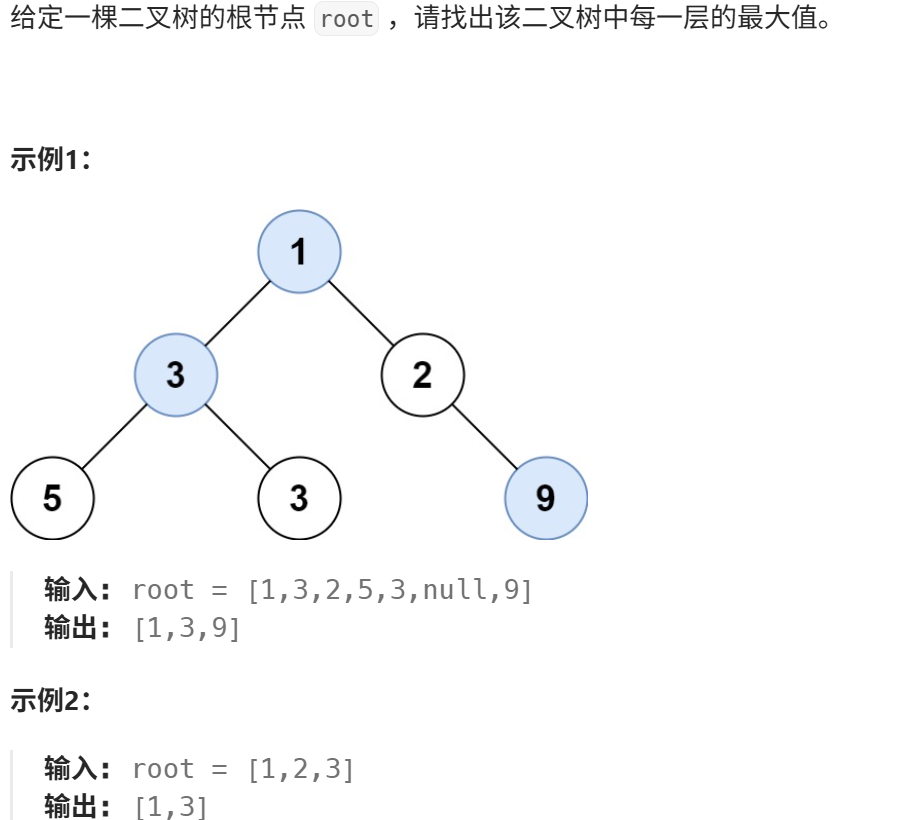
class Solution { public List<Integer> largestValues(TreeNode root) { List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>(); if(root == null){ return res; } Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>(); queue.offer(root); int maxLevel = Integer.MIN_VALUE; while(!queue.isEmpty()){ maxLevel = Integer.MIN_VALUE; int size = queue.size(); for(int i = 0; i < size; i++){ TreeNode cur = queue.poll(); maxLevel = Math.max(maxLevel, cur.val); if(cur.left != null) queue.offer(cur.left); if(cur.right != null) queue.offer(cur.right); } res.add(maxLevel); } return res; } }
5. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
https://leetcode.cn/problems/populating-next-right-pointers-in-each-node?envType=problem-list-v2&envId=8At1GmaZ
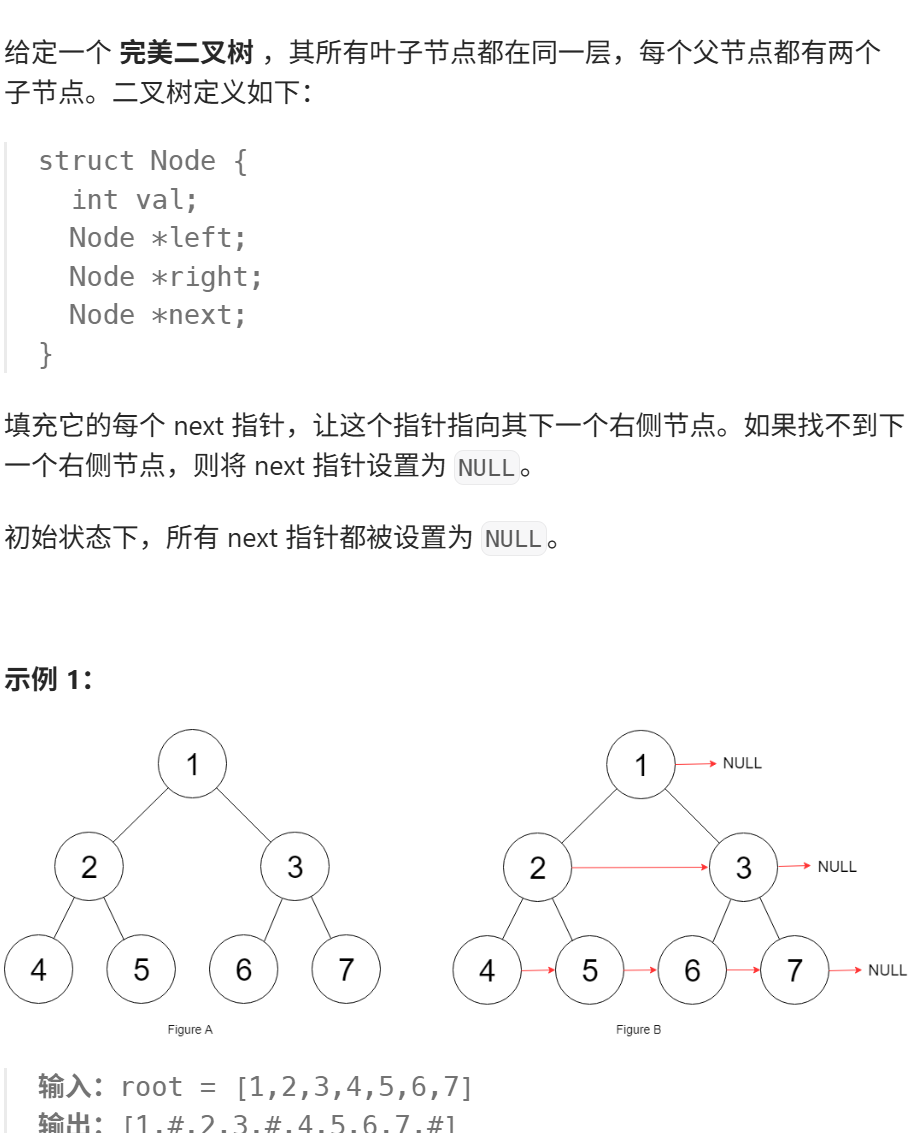
主要思路: 这段代码使用层序遍历(BFS)的方法,通过队列按层访问二叉树的每个节点,在每层中依次将节点的 next 指针指向其右侧的节点(即队列中的下一个节点),如果是该层的最后一个节点则指向 null,同时将左右子节点加入队列,用于处理下一层。该方法可用于普通二叉树,时间复杂度为O(N)。
/* // Definition for a Node. class Node { public int val; public Node left; public Node right; public Node next; public Node() {} public Node(int _val) { val = _val; } public Node(int _val, Node _left, Node _right, Node _next) { val = _val; left = _left; right = _right; next = _next; } }; */ class Solution { public Node connect(Node root) { if(root == null){ return root; } Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>(); queue.offer(root); while(!queue.isEmpty()){ int size = queue.size(); for(int i =0; i<size; i++){ Node cur = queue.poll(); if(i == size-1){ cur.next = null; }else{ cur.next = queue.peek(); } if(cur.left!=null) queue.offer(cur.left); if(cur.right != null) queue.offer(cur.right); } } return root; } }
6. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点
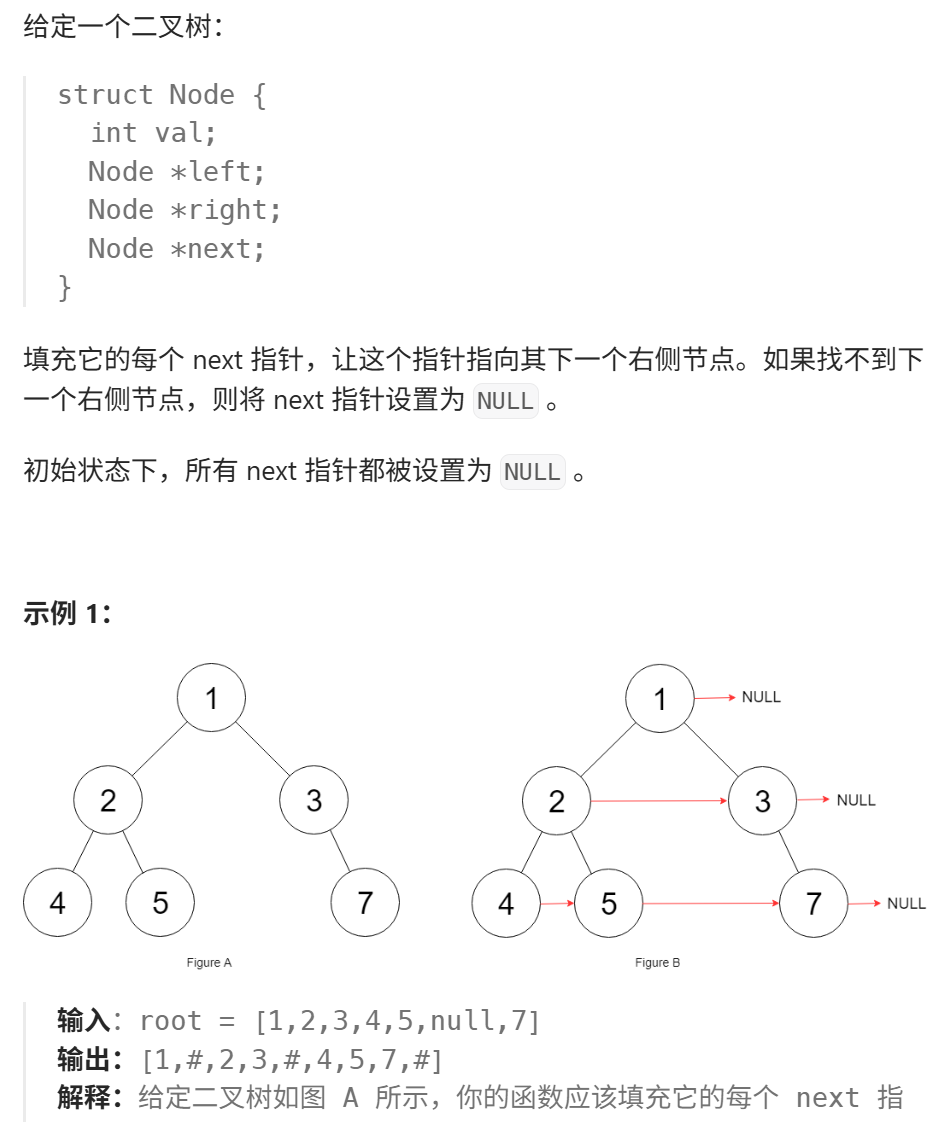
代码同上。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号