算法——链表总结及扩展题
目录
扩展题
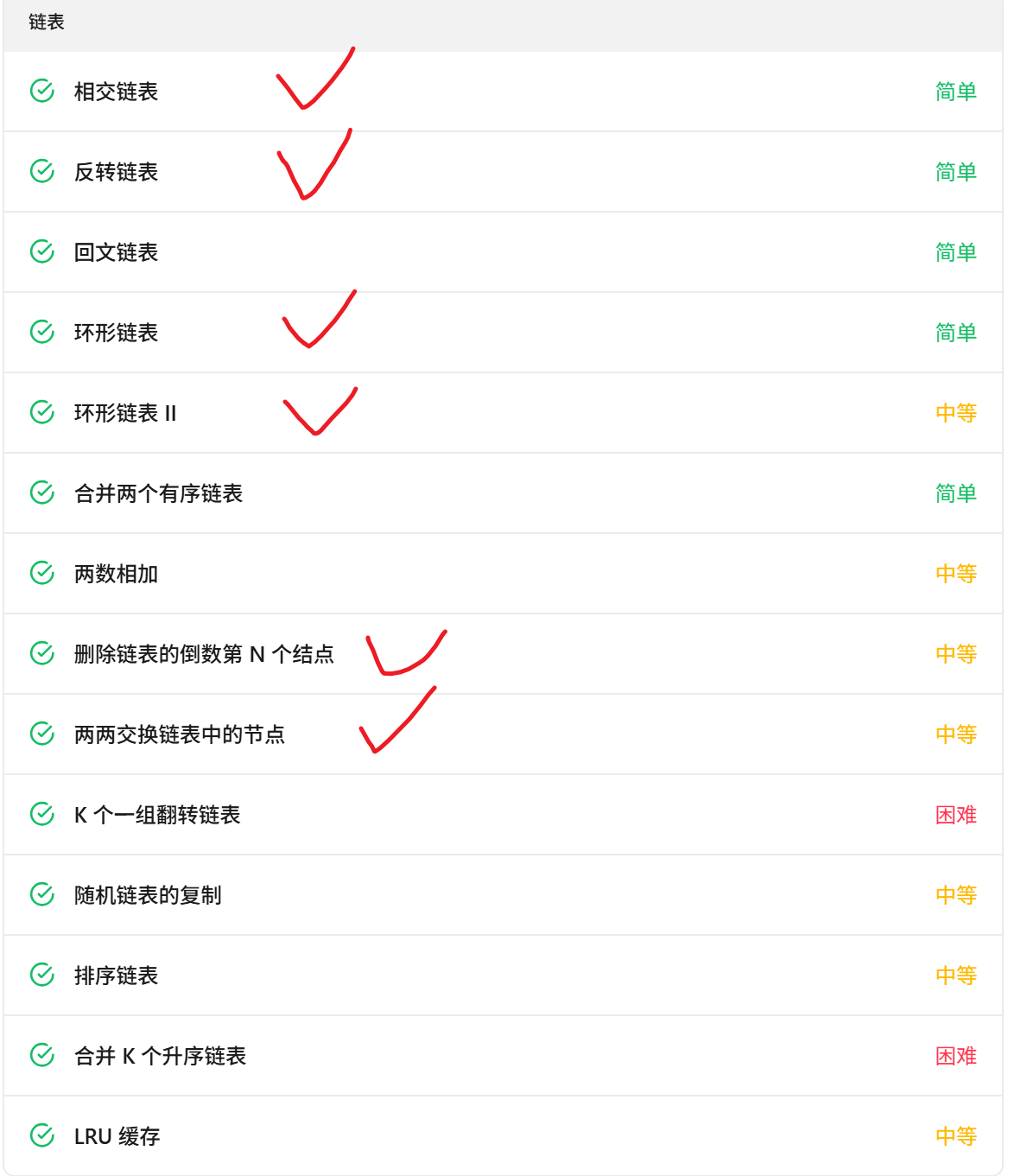
下图中打勾的题目为前两个专题中已经做过的,接下来我们就来联系一下剩余的题目。
- 回文链表234. 回文链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
- 21. 合并两个有序链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
- 2. 两数相加 - 力扣(LeetCode)
- 25. K 个一组翻转链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
- 138. 随机链表的复制 - 力扣(LeetCode)
- 148. 排序链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
- 23. 合并 K 个升序链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
- 146. LRU 缓存 - 力扣(LeetCode)
一、回文链表

思路:我刚开始的做法是把整个节点入栈,但这样是不对的!!应该只用把节点的值入栈即可。回文:倒着和正着是一样的,这就可以先把所有节点入栈(后进先出),然后第二次遍历逐个比较栈顶元素(出栈的顺序跟本身顺序相反)
代码:
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode() {} * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } * } */ class Solution { public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) { //借助栈来做 Deque<Integer> stack = new LinkedList<>(); ListNode cur = head; //第一次遍历 while(cur != null){ stack.push(cur.val); cur = cur.next; } //第二次遍历 cur = head; while(cur != null){ if(stack.pop() != cur.val){ return false; //只要有一个不一样,就不是回文 } cur = cur.next; } return stack.isEmpty(); } } //时间复杂度:O(N) //空间复杂度:O(N)
二、合并两个有序链表
class Solution { public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) { ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(); ListNode p1 = list1; ListNode p2 = list2; ListNode cur = dummyHead; while(p1!=null && p2!=null){ if(p1.val <= p2.val){ cur.next = p1; cur = cur.next; p1 = p1.next; }else{ cur.next = p2; cur = cur.next; p2 = p2.next; } } while(p1!=null){ //若此时list1还没遍历完,则把剩下的链到新链上 cur.next = p1; cur = cur.next; p1 = p1.next; } while(p2!=null){ cur.next = p2; cur = cur.next; p2 = p2.next; } return dummyHead.next; } }
//时间复杂度:O(N+M)
//空间复杂度:O(1)
三、两数相加
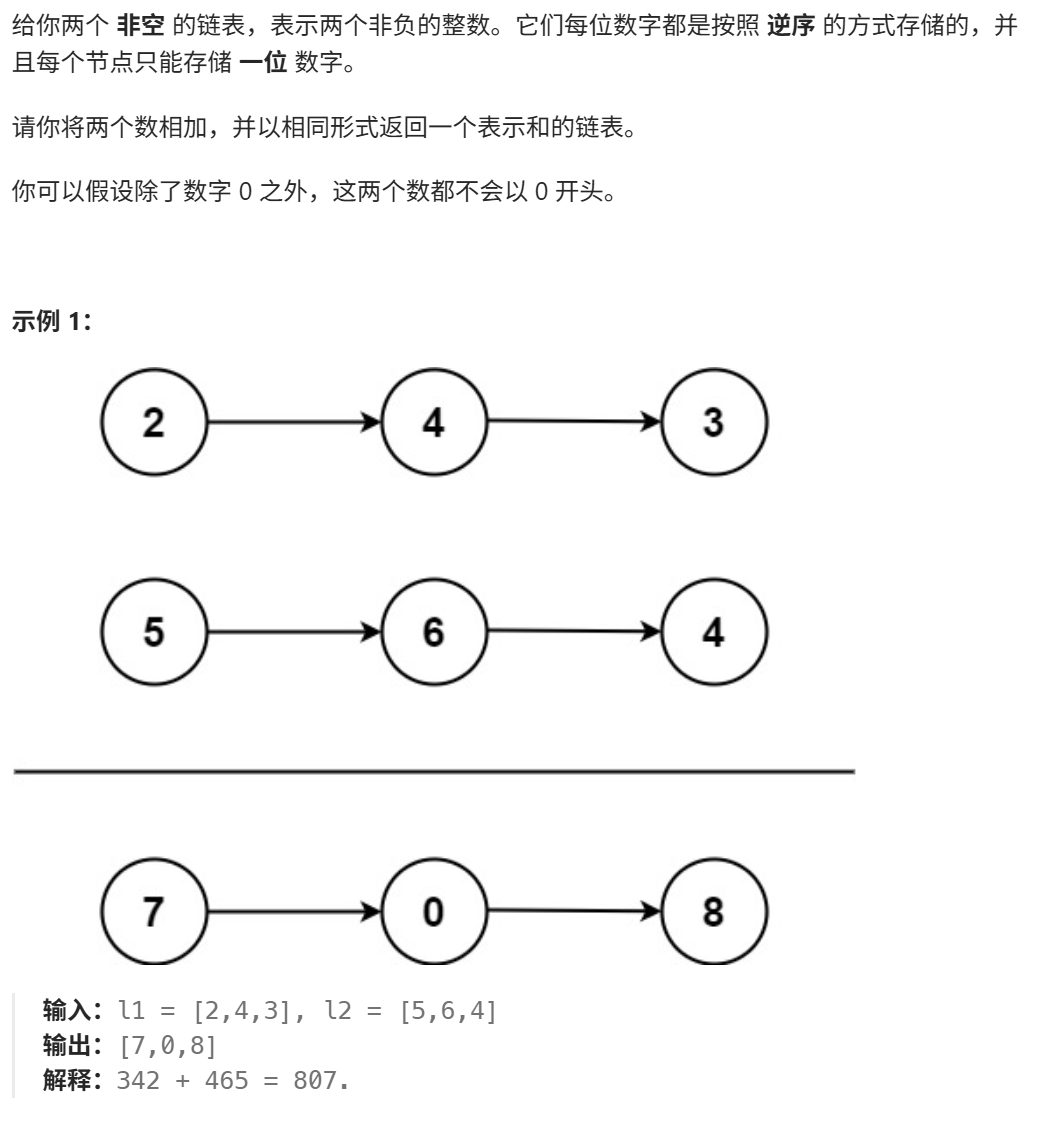
class Solution { public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) { ListNode dummy = new ListNode(); ListNode cur = dummy; int carry = 0; //进位 while(l1!=null || l2!=null || carry!=0){ if(l1!=null){ carry += l1.val; l1 = l1.next; } if(l2!=null){ carry += l2.val; l2 = l2.next; } cur.next = new ListNode(carry % 10); //每个节点保存一个数位 cur = cur.next; carry /= 10; //新的进位 } return dummy.next; } } //时间复杂度:O(N+M) //空间复杂度:O(1)
四、K个一组翻转链表【需要重点理解,指针指向】
这道题和前面的两两交换链表的题目类似。
class Solution { public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) { ListNode dummy = new ListNode(); //虚拟头节点 dummy.next = head; int n = 0; for(ListNode cur = head; cur != null; cur = cur.next){ //统计有多少个组 n++; } ListNode cur = head, pre = null; ListNode p0 = dummy; for(; n >= k; n -= k){ for(int i=0; i<k; i++){ ListNode nxt = cur.next; //存下cur的下一个位置 cur.next = pre; //cur指向前一个 pre = cur; cur = nxt; } ListNode tmp = p0.next; p0.next = pre; tmp.next = cur; p0 = tmp; } return dummy.next; } } //时间复杂度:O(N) //空间复杂度:O(1)
五、随机链表的复制
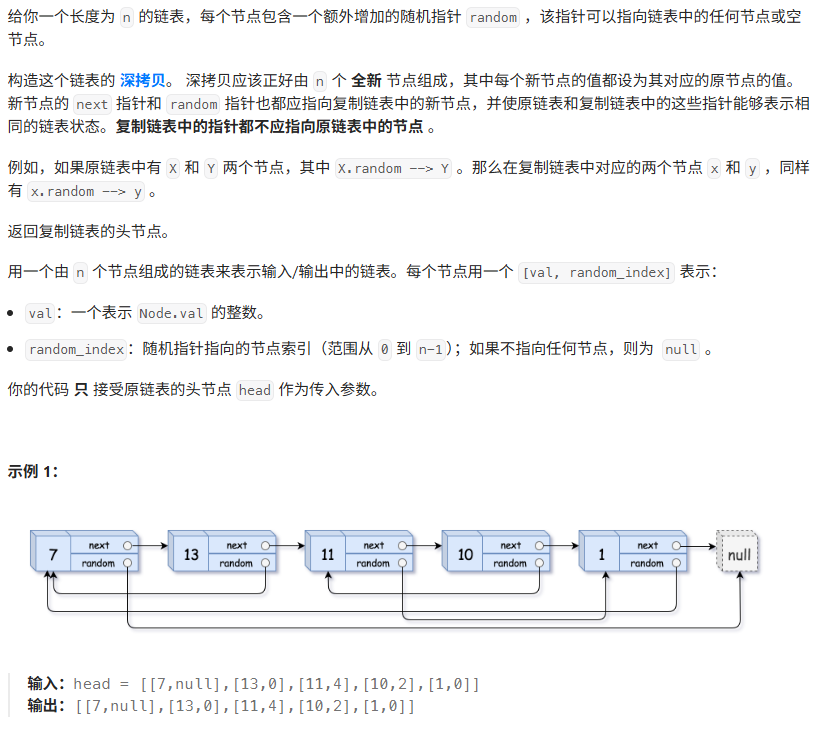
这道题的意思是,除了指向下一个节点之外,还会指向一个随机的索引。我们要把这个链表复制下来。
class Solution { public Node copyRandomList(Node head) { //使用哈希表的方式将原节点与拷贝节点一一对应 if(head == null) return null; Node cur = head; Map<Node, Node> map = new HashMap<>(); //先把所有节点放到map中 while(cur != null){ map.put(cur, new Node(cur.val)); cur = cur.next; } cur = head; //链接上拷贝后的节点 while(cur != null){ map.get(cur).next = map.get(cur.next); map.get(cur).random = map.get(cur.random); cur = cur.next; } return map.get(head); } } //时间复杂度:O(N) //空间复杂度:O(N)
六、排序链表【需要重点理解,分治】
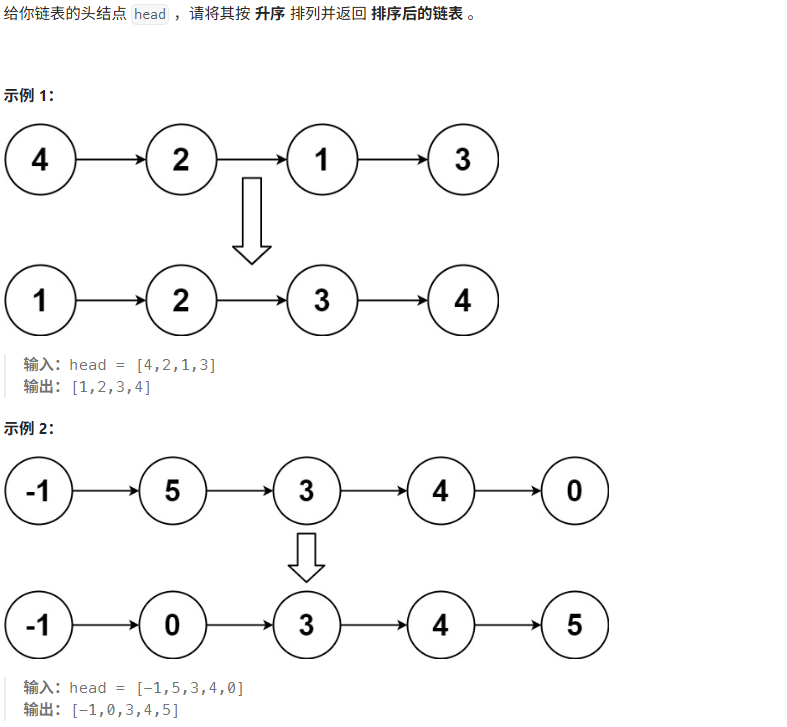
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode() {} * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } * } */ class Solution { public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) { if(head == null || head.next == null){ return head; } ListNode middle = findMiddle(head); //找到链表的中点 ListNode rightHead = middle.next; middle.next = null; //断开链表 ListNode left = sortList(head); ListNode right = sortList(rightHead); return mergeList(left, right); } public static ListNode findMiddle(ListNode head){ ListNode fast = head.next; ListNode slow = head; while(fast != null && fast.next != null){ fast = fast.next.next; slow = slow.next; } return slow; } public static ListNode mergeList(ListNode left, ListNode right){ ListNode dummy = new ListNode(); ListNode cur = dummy; while(left != null && right != null){ if(left.val <= right.val){ cur.next = left; left = left.next; }else{ cur.next = right; right = right.next; } cur = cur.next; } cur.next = left == null ? right : left; return dummy.next; } } //时间复杂度:O(nlogn) //空间复杂度:O(logn),每一层只用了常数个常量
七、合并K个升序链表【需要重点理解】
先合并前两个,然后把合并后的链表跟后一个再合并。
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode() {} * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } * } */ class Solution { public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) { ListNode ans = null; for(int i=0; i<lists.length; i++){ //两个合并 ans = mergeTwoList(ans, lists[i]); } return ans; } public ListNode mergeTwoList(ListNode a, ListNode b){ if(a==null || b==null){ //若有一个为空,则直接等于对方 return a == null ? b : a; } ListNode dummy = new ListNode(); ListNode cur = dummy, p1 = a, p2 = b; while(p1 != null && p2 != null){ if(p1.val < p2.val){ cur.next = p1; p1 = p1.next; }else{ cur.next = p2; p2 = p2.next; } cur = cur.next; } cur.next = p1 == null ? p2 : p1; return dummy.next; } } //时间复杂度:O(n*k) //空间复杂度:O()
还有一个做法是分治,左半部分和右半部分分别合并。
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode() {} * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } * } */ class Solution { public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) { return mergeKLists(lists, 0, lists.length); } public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists, int i ,int j){ int m = j-i; if(m==0){ return null; } if(m==1){ //无需合并,直接返回 return lists[i]; } ListNode left = mergeKLists(lists, i, i + m/2); //合并左半部分 ListNode right = mergeKLists(lists, i+m/2, j); //合并右半部分 return mergeTwoList(left, right); } public ListNode mergeTwoList(ListNode a, ListNode b){ if(a==null || b==null){ //若有一个为空,则直接等于对方 return a == null ? b : a; } ListNode dummy = new ListNode(); ListNode cur = dummy, p1 = a, p2 = b; while(p1 != null && p2 != null){ if(p1.val < p2.val){ cur.next = p1; p1 = p1.next; }else{ cur.next = p2; p2 = p2.next; } cur = cur.next; } cur.next = p1 == null ? p2 : p1; return dummy.next; } } //时间复杂度:O(nlogk) //空间复杂度:O(logk)
八、LRU缓存



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号