算法day04-链表篇(2)
训练目录
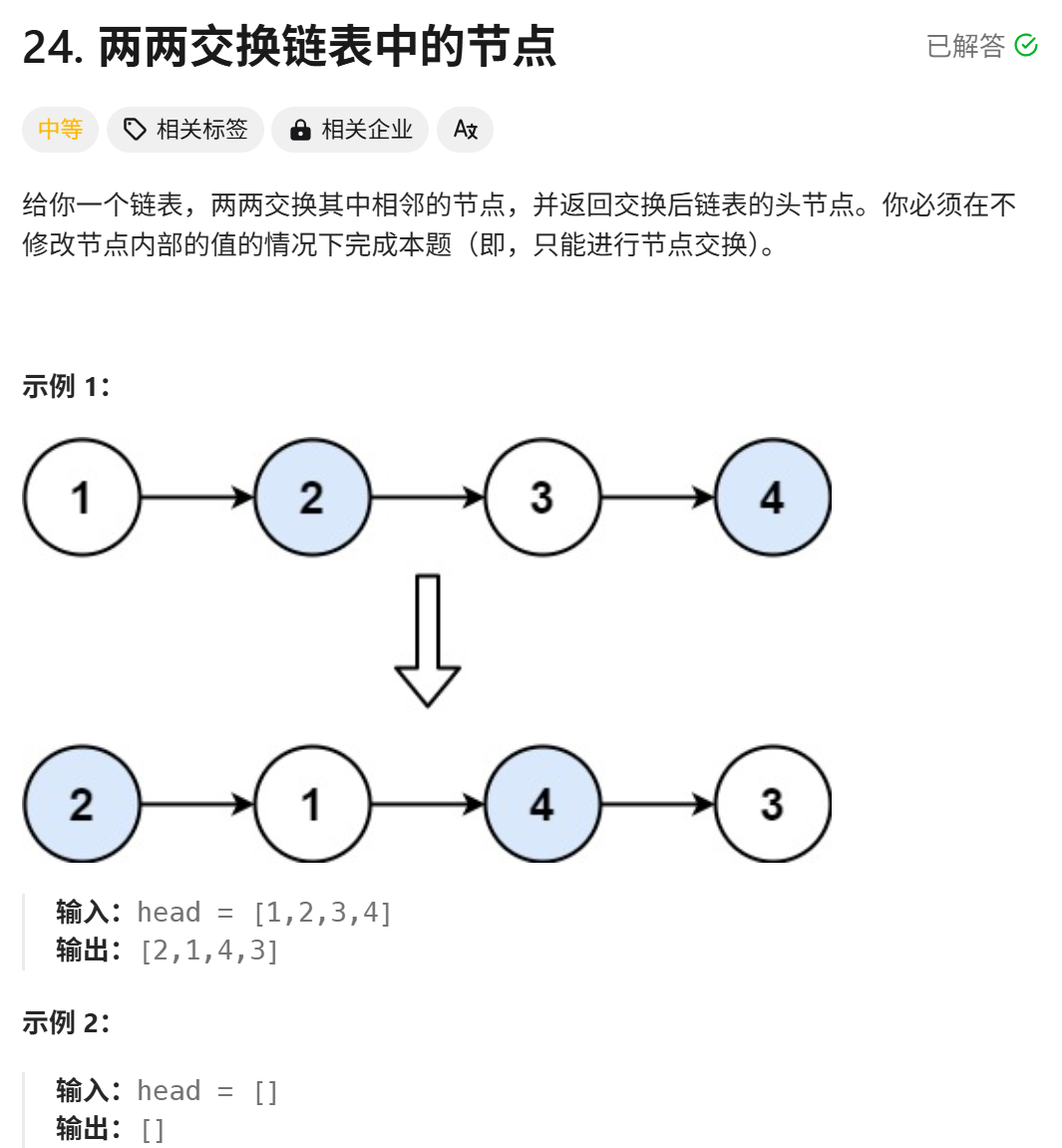
- 24题两两交换链表中的节点
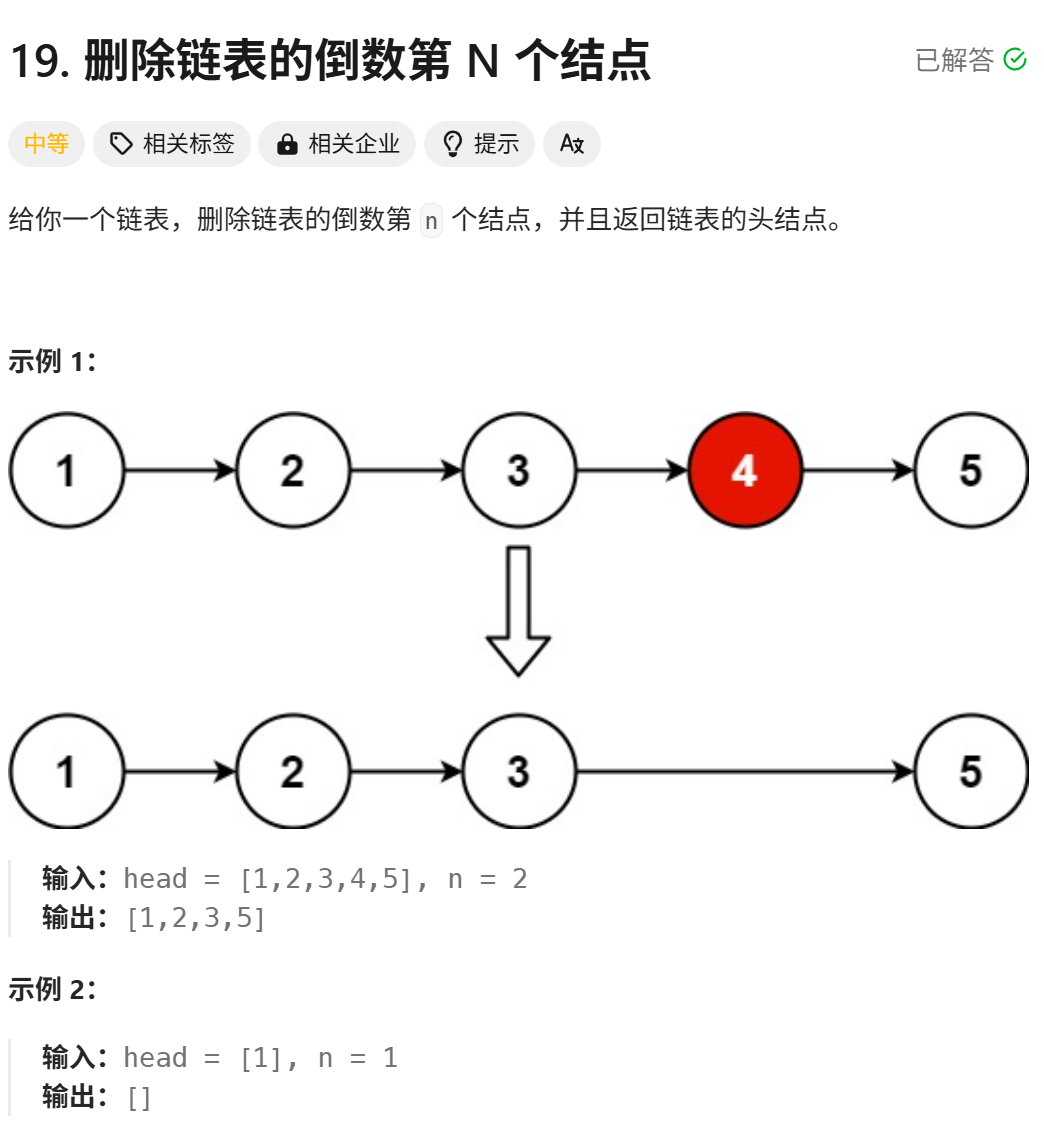
- 19题 删除链表的倒数第N个节点
- 面试题 链表相交
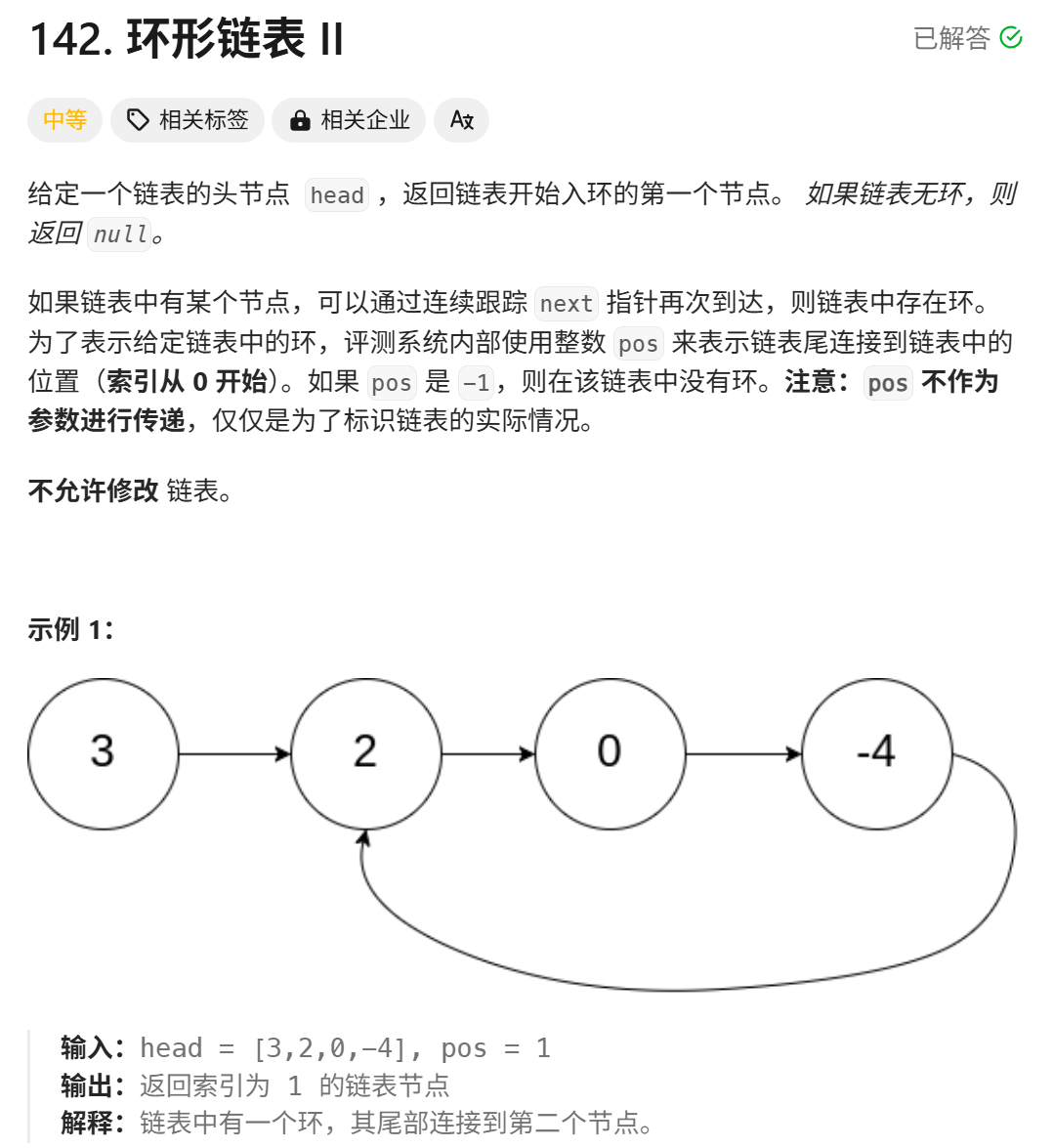
- 142题 环形链表II
一、两两交换链表中的节点【交换节点】
这道题可以参考k个一组反转链表的操作。也可以就用两个节点交换的做法。
1 /** 2 * Definition for singly-linked list. 3 * public class ListNode { 4 * int val; 5 * ListNode next; 6 * ListNode() {} 7 * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } 8 * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } 9 * } 10 */ 11 class Solution { 12 public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) { 13 ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(); 14 dummyHead.next = head; 15 ListNode p0 = dummyHead; 16 int k = 0; 17 for(ListNode cur = head; cur != null; cur = cur.next){ 18 k++; //统计链表的总长度 19 } 20 ListNode cur = head, pre = null; 21 for(; k>=2; k = k-2){ 22 for(int i=0; i<2; i++){ 23 ListNode nxt = cur.next; 24 cur.next = pre; 25 pre = cur; 26 cur = nxt; 27 } 28 ListNode tmp = p0.next; 29 p0.next = pre; 30 tmp.next = cur; 31 p0 = tmp; 32 } 33 return dummyHead.next; 34 } 35 }
//时间复杂度:O(N)
//空间复杂度:O(1)
卡哥做法:
class Solution { public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) { ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(); dummyHead.next = head; ListNode cur = dummyHead; //cur指向要操作两个节点的前一个 while(cur.next != null && cur.next.next != null){ //顺序不能反! ListNode tmp = cur.next; //这里要存一下cur的下一个(1的地址) ListNode tmp1 = cur.next.next.next; //存2的下一个地址(3的地址) cur.next = cur.next.next; //cur指向2 cur.next.next = tmp; //2指向1 tmp.next = tmp1; //1指向3 cur = cur.next.next; //cur往后移两位 } return dummyHead.next; } }
【相关题目】
- 反转链表
- k个一组反转链表
二、删除链表的倒数第N个节点【删除节点】
这道题我的思考是:比较朴素的做法是先统计这条链总共有多少个元素,然后再次遍历找到这个节点,然后删除。但有一种方法可以只用遍历一次链表:快慢指针,先让快指针走n+1步,这样当快指针走到结尾的时候,慢指针的下一个刚好指向要删除的节点(注意这里要记录要删除节点的上一个,所以我这里的做法是先让快指针走n+1步)。
1 /** 2 * Definition for singly-linked list. 3 * public class ListNode { 4 * int val; 5 * ListNode next; 6 * ListNode() {} 7 * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } 8 * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } 9 * } 10 */ 11 class Solution { 12 public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) { 13 ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(); 14 dummyHead.next = head; 15 ListNode slow = dummyHead; 16 ListNode fast = dummyHead; 17 for(int i=0; i<=n; i++){ 18 fast = fast.next; //fast先走n步 19 } 20 while(fast != null){ 21 fast = fast.next; 22 slow = slow.next; 23 } 24 //最后slow的位置是要删除位置的前一个 25 slow.next = slow.next.next; 26 return dummyHead.next; 27 } 28 } 29 //时间复杂度:O(N) 30 //空间复杂度:O(1)
三、链表相交
面试题 02.07. 链表相交 - 力扣(LeetCode)

土法子:
1 /** 2 * Definition for singly-linked list. 3 * public class ListNode { 4 * int val; 5 * ListNode next; 6 * ListNode(int x) { 7 * val = x; 8 * next = null; 9 * } 10 * } 11 */ 12 public class Solution { 13 public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) { 14 ListNode cur = headA; 15 Set<ListNode> set = new HashSet<>(); 16 while(cur != null){ 17 set.add(cur); 18 cur = cur.next; 19 } 20 ListNode tmp = headB; 21 while(tmp != null){ 22 if(set.contains(tmp)){ 23 return tmp; 24 }else{ 25 tmp = tmp.next; 26 } 27 } 28 return null; 29 } 30 } 31 //时间复杂度:O(N) 32 //空间复杂度:O(N)
巧妙做法:可以利用数学做法,A走完headA+A头节点到相交节点的位置(这里也可能为空,也就是两条链没有相交的情况) = B走完headA+B头节点到相交节点的位置。
1 /** 2 * Definition for singly-linked list. 3 * public class ListNode { 4 * int val; 5 * ListNode next; 6 * ListNode(int x) { 7 * val = x; 8 * next = null; 9 * } 10 * } 11 */ 12 public class Solution { 13 public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) { 14 ListNode pA = headA; 15 ListNode pB = headB; 16 while(pA != pB){ 17 if(pA == null){ 18 pA = headB; 19 }else{ 20 pA = pA.next; 21 } 22 if(pB == null){ 23 pB = headA; 24 }else{ 25 pB = pB.next; 26 } 27 } 28 return pA; 29 } 30 } 31 //时间复杂度:O(N) 32 //空间复杂度:O(1)
四、环形链表II【快慢指针】
我的思考:可以用一个hashset来记录访问过的节点,如果没访问过就加入set,访问过的话就返回当前这个节点,表示成环的节点。
1 /** 2 * Definition for singly-linked list. 3 * class ListNode { 4 * int val; 5 * ListNode next; 6 * ListNode(int x) { 7 * val = x; 8 * next = null; 9 * } 10 * } 11 */ 12 public class Solution { 13 public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) { 14 Set<ListNode> set = new HashSet<>(); 15 ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(); 16 dummyHead.next = head; 17 ListNode cur = dummyHead.next; 18 while(cur != null){ 19 if(set.contains(cur)){ 20 return cur; 21 }else{ 22 set.add(cur); //如果不存在则加进set 23 cur = cur.next; 24 } 25 } 26 return null; 27 } 28 } 29 //时间复杂度:O(N) 30 //空间复杂度:O(N)
还有一种做法是用快慢指针,但这里难点在于如何推断成环节点的位置。在慢指针进入环里的第一圈就被快指针遇到了。
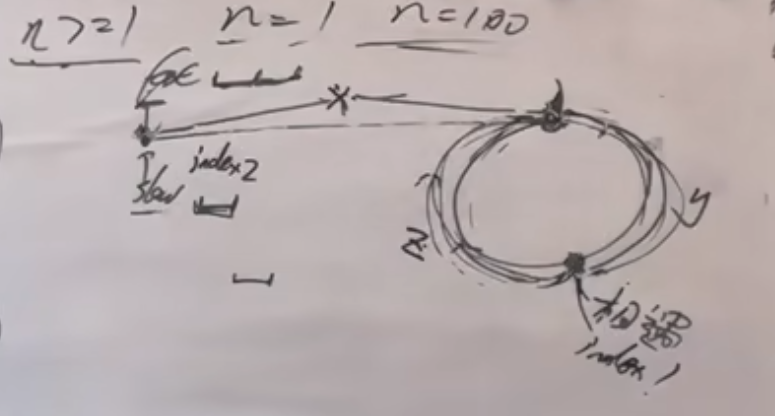

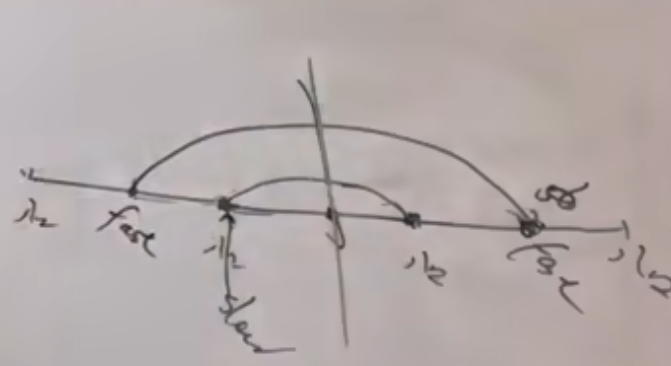
public class Solution { public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) { //快慢指针,快指针走两步,慢指针走一步。如果有环的话,快指针一定可以追上慢指针(因为快指针相对慢指针是走一步) ListNode fast = head; ListNode slow = head; while(fast != null && fast.next != null){ fast = fast.next.next; //快指针向后走两步 slow = slow.next; //慢指针向后走一步 if(fast == slow){ ListNode index1 = fast; //在相遇点 ListNode index2 = head; //在头节点 while(index1 != index2){ index1 = index1.next; index2 = index2.next; } return true; //return index1; } } return false; //没找到环,return null; } } //时间复杂度:O(N) //空间复杂度:O(1)
【相关题目】
- 判断链表是否有环(同上面的快慢指针题解)



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号