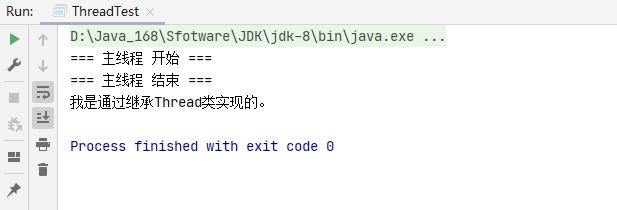
1、创建线程方式一:『继承Thread类』
/**
* 创建线程方式一:『继承Thread类』
*/
public class ThreadTest {
public static class MyThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("我是通过继承Thread类实现的。");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("=== 主线程 开始 ===");
MyThread myThread = new MyThread();
myThread.start();
System.out.println("=== 主线程 结束 ===");
}
}
![]()
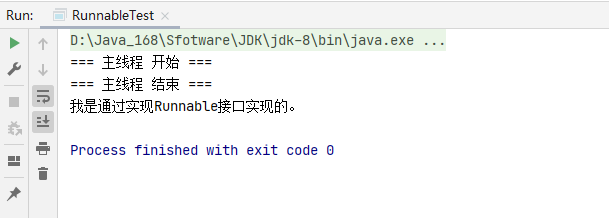
2、创建线程方式二:『实现Runnable接口』
/**
* 创建线程方式二:『实现Runnable接口』
*/
public class RunnableTest {
public static class MyRunnable implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("我是通过实现Runnable接口实现的。");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("=== 主线程 开始 ===");
MyRunnable myRunnable = new MyRunnable();
Thread thread = new Thread(myRunnable);
thread.start();
System.out.println("=== 主线程 结束 ===");
}
}
![]()
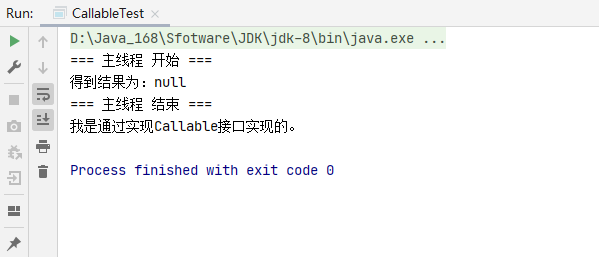
3、创建线程方式三:『实现CallTable接口』, 需要与FutureTask配合
/**
* 创建线程方式三:『实现CallTable接口』, 需要与FutureTask配合
*/
public class CallableTest {
public static class MyCallable implements Callable{
@Override
public Object call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("我是通过实现Callable接口实现的。");
return "中国,我爱你!";
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
System.out.println("=== 主线程 开始 ===");
MyCallable myCallable = new MyCallable();
FutureTask<String> futureTask = new FutureTask<>(myCallable);
Thread thread = new Thread(futureTask);
thread.start();
String result = null;
// result = futureTask.get(); // get()是阻塞等待的,只有线程执行结束才能获取到返回结果
System.out.println("得到结果为:" + result);
System.out.println("=== 主线程 结束 ===");
}
}
![]()
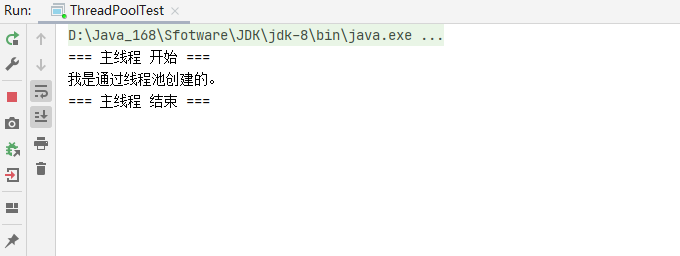
4、创建线程方式四:『通过线程池』,将任务提交给线程池
/**
* 创建线程方式四:『通过线程池』,将任务提交给线程池
*/
public class ThreadPoolTest {
// 创建一个指定线程数的线程池
public static ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
System.out.println("=== 主线程 开始 ===");
// executor.execute(() -> System.out.println("我是通过线程池创建的。")); // execute() 没有返回值
Future<String> future = executor.submit(() -> {return "我是通过线程池创建的。";}); // submit() 有返回值
System.out.println(future.get());
System.out.println("=== 主线程 结束 ===");
}
}
![]()



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号