doc-llm-autotest 基于大模型的文档自动化测试平台:worker服务的可靠性增强
一、可靠性分析
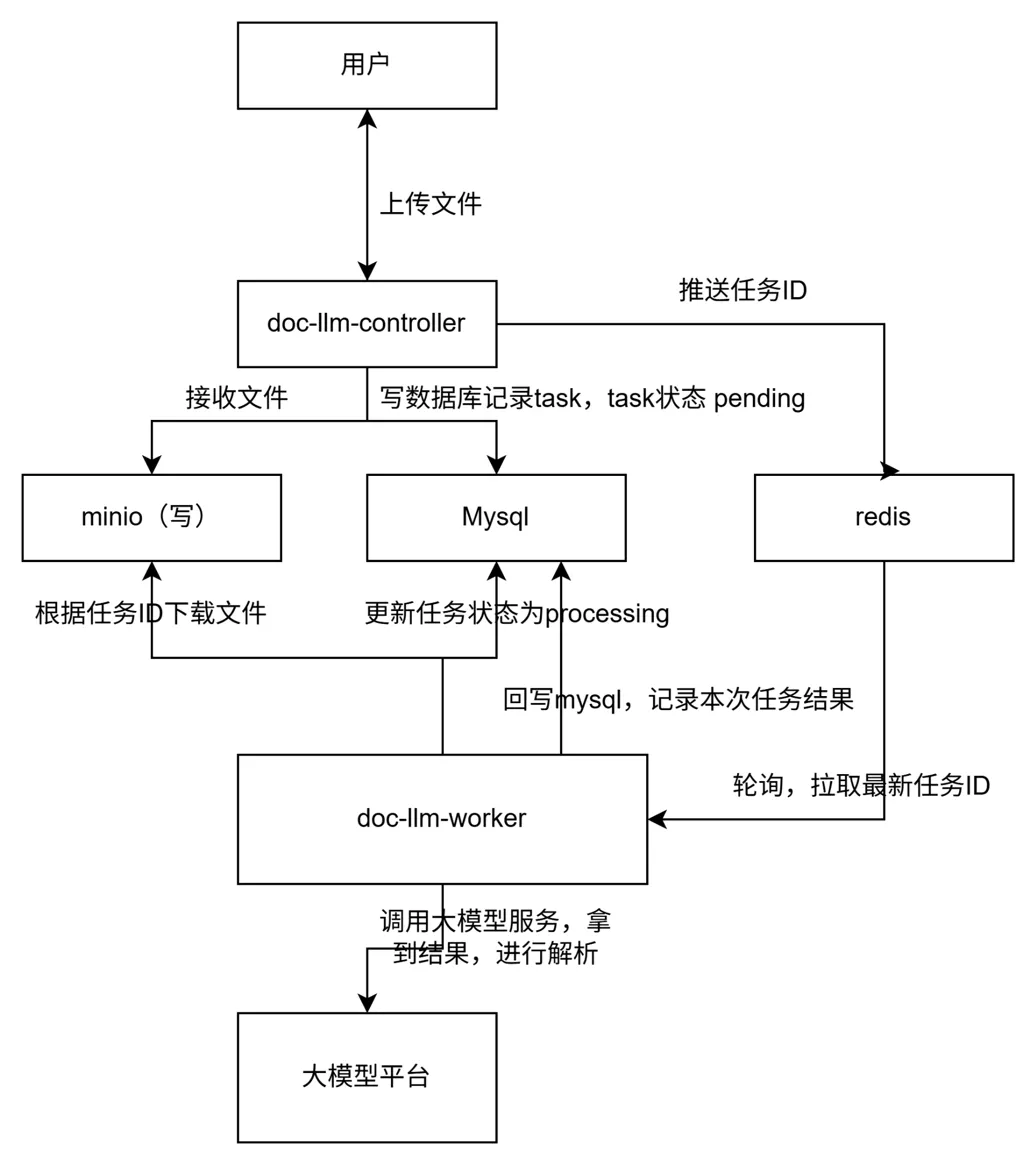
从架构图上,我们可以看出worker调用大模型服务过程中,会发生阻塞等待,如果此时worker异常容器挂掉了,那么此次任务状态会一直为processing,并且因为redis关联task_id的消息已经被消费了,那么这个任务就无法被识别出来重试。
基于这个场景分析,我们要补充巡检服务,去定时重启处于超时并且状态为processing的任务,此时服务可以从mysql捞任务表,但考虑到性能等影响,我们选择在redis构建新的processing队列,存储正在执行的task_id,构建processing_ts队列存储开始处理时间,巡检服务访问redis的processing队列、processing_ts队列来更新状态异常的任务。
适配worker服务逻辑:设置原子操作保证worker取任务+放入processing不会被中断。
二、逻辑实现
1. doc_llm_test_worker补充原子操作将task从ready移动到processing,记录开始执行的时间
TASK_QUEUE_READY_KEY = "docllm:queue:ready" TASK_QUEUE_PROCESSING_KEY = "docllm:queue:processing" TASK_PROCESSING_TS_KEY = "docllm:hash:processing_ts" def worker_loop(): """文档检查任务 worker 主循环""" logging.info("doc_llm_test_worker started, waiting for tasks...") while True: try: raw_item = redis_client.brpoplpush(TASK_QUEUE_READY_KEY, TASK_QUEUE_PROCESSING_KEY, timeout=10) if not raw_item: time.sleep(5) continue # 没有任务,就继续下一轮 try: payload_str = raw_item.decode("utf-8") data = json.loads(payload_str) task_id = int(data["task_id"]) except Exception as e: logging.exception(f"invalid processing queue item: {raw_item!r}") redis_client.lrem(TASK_QUEUE_PROCESSING_KEY, 1, raw_item) continue start_ts = int(time.time()) redis_client.hset(TASK_PROCESSING_TS_KEY, task_id, start_ts) try: process_task(task_id) finally: redis_client.lrem(TASK_QUEUE_PROCESSING_KEY, 1, raw_item) redis_client.hdel(TASK_PROCESSING_TS_KEY, task_id) except Exception: logging.exception("unexpected error in worker loop, sleep 3s") time.sleep(3)
2.补充巡检服务,定时重启处于超时并且状态为processing的任务,需要做到重新入队 + 状态恢复流程
设置参数 PROCESSING_TIMEOUT_SECONDS = 600
判断逻辑:
now_ts - start_ts > PROCESSING_TIMEOUT_SECONDS
该任务视为:
-
worker 处理失败(worker 崩了/卡死)
-
需要重新 pending
-
丢回 ready 队列给新的 worker
适配task_service,提供给巡检服务同步改数据库任务状态
def mark_task_processing(task_id: int) -> bool: """worker 刚拿到任务时调用:pending -> processing""" with get_session() as session: stmt = ( update(TaskDocLLM).where( TaskDocLLM.task_id == task_id, TaskDocLLM.status == TaskStatus.pending ).values( status=TaskStatus.processing, processing_started_at=func.now() ) ) result = session.execute(stmt) session.commit() return result.rowcount == 1 def reclaim_task(task_id: int, timeout_dt) -> bool: """ 将超时的任务重新放回队列 :param timeout_dt: datetime对象,代表“必须早于此时间才会被恢复” """ with get_session() as session: stmt = ( update(TaskDocLLM).where( TaskDocLLM.task_id == task_id, TaskDocLLM.status == TaskStatus.processing, TaskDocLLM.processing_started_at < timeout_dt ).values( status=TaskStatus.pending, retry_count=TaskDocLLM.retry_count + 1, processing_started_at=None, result=None ) ) result = session.execute(stmt) session.commit() return result.rowcount == 1
新增巡检函数reaper_loop,筛选超时任务,恢复状态,其中要做到:
-
扫描处理中的任务(在 processing 队列)
-
查看 start_ts 是否超时
-
原子重置数据库的任务状态 ,然后再重入 ready 队列
且reaper也需要保证假设有多个worker的情况下,其他worker的巡检进程不会同时抢占同一个状态为processing的任务,否则可能会导致重复入队。所以用到了reclaim_task的原子 UPDATE。
def reaper_loop(): """巡检 processing 队列,恢复超时的任务""" logging.info("doc_llm_reaper started, interval=%ss, timeout=%ss", REAPER_INTERVAL_SECONDS, PROCESSING_TIMEOUT_SECONDS) while True: try: now_ts = int(time.time()) timeout_border_ts = now_ts - PROCESSING_TIMEOUT_SECONDS timeout_threshold_dt = datetime.utcnow() - timedelta(seconds=PROCESSING_TIMEOUT_SECONDS) items = redis_client.lrange(TASK_QUEUE_PROCESSING_KEY, 0, -1) if not items: time.sleep(REAPER_INTERVAL_SECONDS) continue for raw in items: try: payload_str = raw.decode("utf-8") payload = json.loads(payload_str) task_id = payload.get("task_id") task_name = payload.get("task_name") except Exception: redis_client.lrem(TASK_QUEUE_PROCESSING_KEY, 1, raw) continue start_ts_raw = redis_client.hget(TASK_PROCESSING_TS_KEY, task_id) if start_ts_raw is None: continue start_ts = int(start_ts_raw) if start_ts > timeout_border_ts: continue logging.warning(f"doc_llm_reaper: task {task_id} seems stuck, start_ts={start_ts}, now_ts={now_ts}") ok = task_service.reclaim_task(task_id, timeout_threshold_dt) if not ok: continue redis_client.lrem(TASK_QUEUE_PROCESSING_KEY, 1, raw) redis_client.hdel(TASK_PROCESSING_TS_KEY, task_id) new_payload = json.dumps( {"task_id": task_id, "task_name": task_name}, ensure_ascii=False ) redis_client.lpush(TASK_QUEUE_READY_KEY, new_payload) logging.info(f"doc_llm_reaper: task {task_id} reclaimed and requeued to READY") except Exception: logging.exception("unexpected error in reaper loop, sleep 3s") time.sleep(REAPER_INTERVAL_SECONDS)
在主进程之外,起一个线程循环跑巡检:
def start_reaper_thread(): reaper_thread = threading.Thread(target=reaper_loop, name="doc_llm_reaper", daemon=True) reaper_thread.start() return reaper_thread if __name__ == "__main__": setup_logging() init_llm() start_reaper_thread() worker_loop()
三、测试验证
我们构造场景让worker在处理一条任务的时候主动挂掉,此时环境有一条mysql状态为processing的task,并且redis的doc_llm:task_queue:ready没有这条task_id关联的消息,只有doc_llm:task_queue:processing,doc_llm:hash:processing_ts队列有值。
这相当于这次任务被消费了,但worker异常导致任务丢失,如果没有巡检,我们就只能主动删除这条不会被触发的任务。但我们期望重启后的巡检进程reaper_loop能够检测到异常,并让这条任务重新入队,设置的超时时间是10分钟。
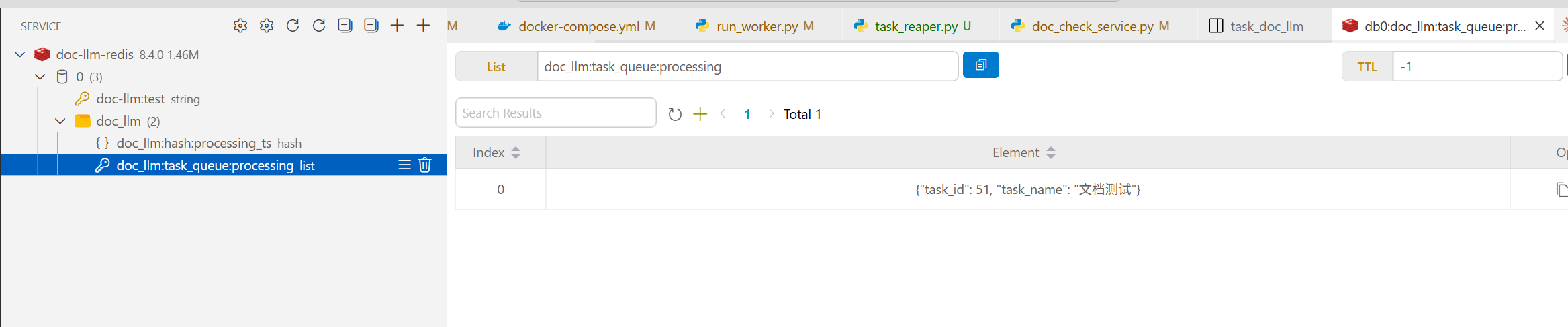
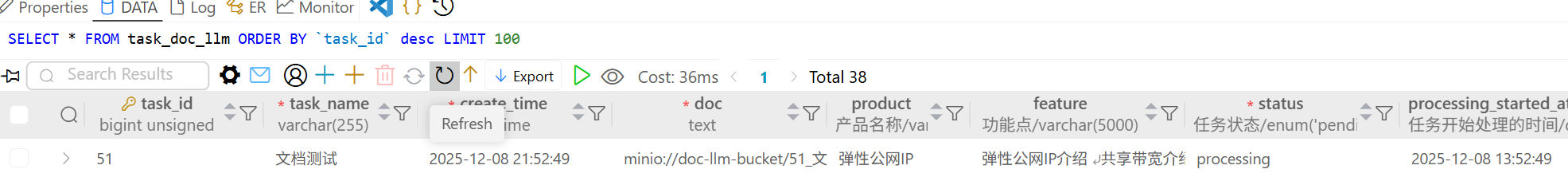
现在重启worker,并开启巡检服务:
查看日志,显示51这条任务被巡检出来,重新进入测试:
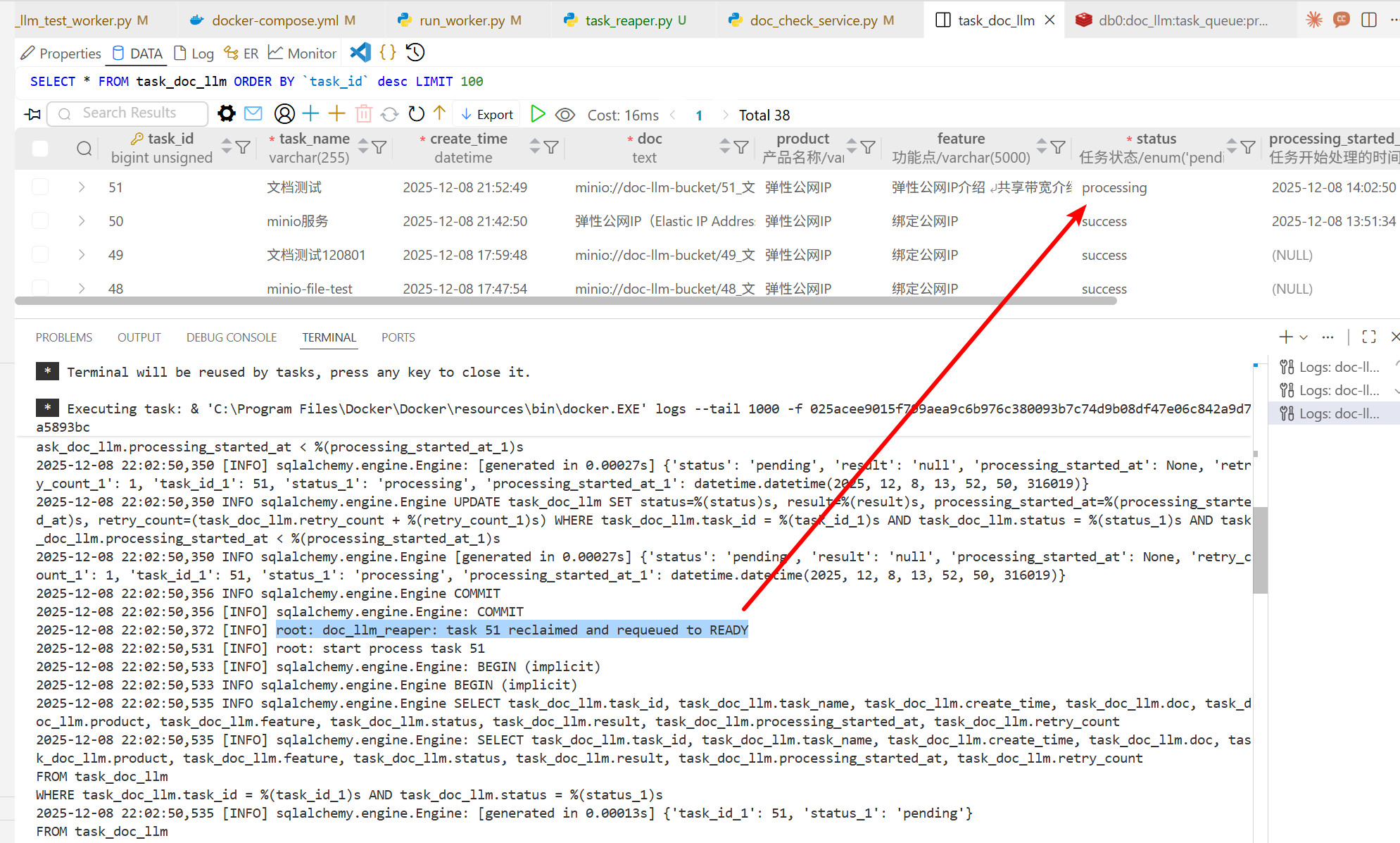
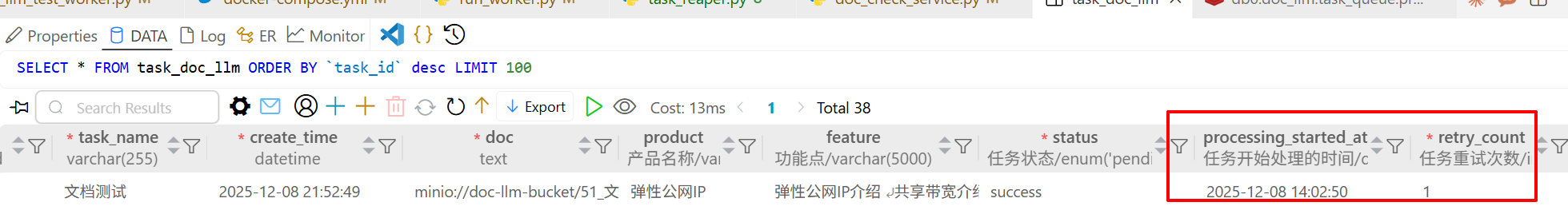
任务最终被执行,数据库记录了重试次数、时间等信息,这就说明巡检服务是有效的



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号