Python自动化测试(五)
一、文件操作
""" 1、编写函数后要调用函数才会执行内部 2、函数的调用: 直接调用 在主函数里面调用:if __name__=='__main__' 3、写文件涉及中文需指定编码格式如UTF-8,读取时使用相同编码格式 """ def fileW(): # W模式 f=open(file='log.txt',mode='w') f.write('hello python') f.close() fileW() def fileA(): # A模式 f=open(file='log.txt',mode='a',encoding= "utf-8") f.write('HI GO语言') f.close() fileA()
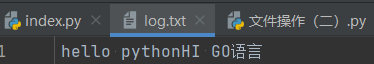
def readF(): f=open(file='log.txt',encoding='utf-8') # 读取文件内所有内容 print(f.read()) # 读取文件第一行 print(f.readline()) # 换行读取文件里面内容 for item in f.readlines(): print(item.strip) f.close() readF()
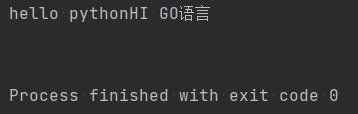
def filew(): with open('log.txt','w') as f: f.write('hi,go') def filea(): with open('log.txt','a',encoding='utf-8') as f: f.write('GO语言实践') def refdFile(): with open('log.txt' ,'r',encoding='utf-8') as f: print(f.read()) if __name__ == '__main__': filew() filea() refdFile()
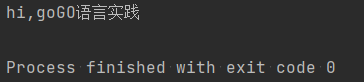
""" 文件操作步骤: 1、打开文件 2、对文件进行操作,读或者是写的操作 3、关闭文件 模式: r:读取 w:写,特点是先清空文件已有的内容,然后把新的内容写进去 a:写,在文件已有内容的基础之上增加新的内容 open(写) 1、查看被操作文件是否存在 2、若不存在,会自动创建文件 open(读) 1、查看被操作文件是否存在 2、如果不存在则抛出异常 """ f=open('log.txt', 'w') f.write('hello Python') f.close() f=open('log.txt','r') print(f.read()) f.close()
二、Json实战(序列化和反序列化)
import json list1=["go","Python"] # 对列表进行序列化 list_str=json.dumps(list1) # dumps()序列化:把内存中数据类型转化为字符串 print('对象:{0},数据类型:{1}'.format(list_str,type(list_str))) # 对列表进行反序列化 str_list=json.loads(list_str) # loads()反序列化:将字符串转Python对象 print('对象:{0},数据类型:{1}'.format(str_list,type(str_list))) """ format()格式化函数 "{} {}".format("hello", "world") # 不设置指定位置,按默认顺序 'hello world' "{0} {1}".format("hello", "world") # 设置指定位置 'hello world' "{1} {0} {1}".format("hello", "world") # 设置指定位置 'world hello world' """ # 元组序列化 tuple1=("go","Python") tuple_str=json.dumps(tuple1) print('对象:{0},数据类型:{1}'.format(tuple_str,type(tuple_str))) # 元组反序列化 str_tuple=json.loads(tuple_str) print('对象:{0},数据类型:{1}'.format(str_tuple,type(str_tuple))) # 字典序列化 dict1={"name":"admin","age":"15"} dict_str=json.dumps(dict1) print('对象:{0},数据类型:{1}'.format(dict_str,type(dict_str))) # 字典反序列 str_dict=json.loads(dict_str) print('对象:{0},数据类型:{1}'.format(str_dict,type(str_dict)))
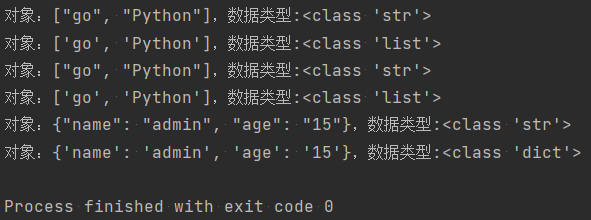
import json import requests r=requests.get( url='http://httpbin.org/get') # # 反序列化 print(json.loads(r.text)) print(json.loads(r.text)['url']) # 序列化 print(json.dumps(r.json(),indent=True,ensure_ascii=False)) # ensure_ascii表示是否要转为ASCII码,默认打开True,那么转为json后中文会变成ASCII编码,False中文还是中文,不会变为ASCII编码。
三、os实战(判断目录,文件,时间)
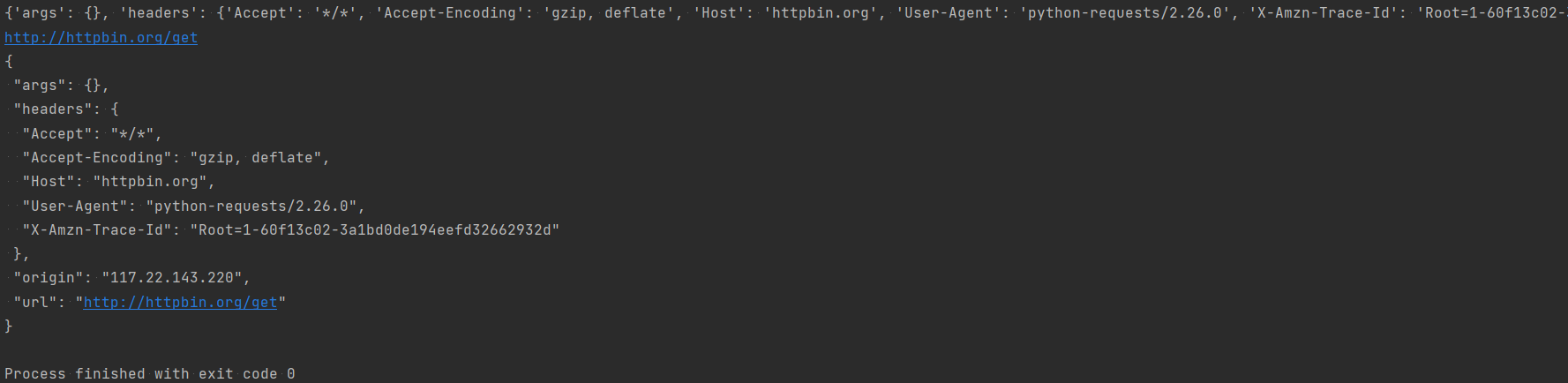
import os # 获取当前路径 print(os.path.dirname(__file__)) # 获取当前的上一路径 print(os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(__file__))) # 获取绝对路径 print(os.path.abspath(__file__)) # 获取当前时间 print(os.system('date'))
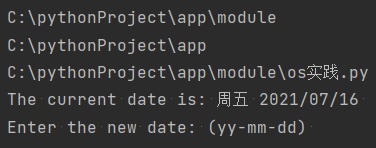
# 判断是否是目录 print(os.path.exists('log.txt')) # exists()判断文件是否存在 print(os.path.isfile('C:/pythonProject/app/module/os实践.py')) # isfile()判断某一对象(需提供绝对路径)是否为文件 base_dir=os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(__file__)) print(base_dir) filePath=os.path.join(base_dir,'data','login.json') with open(filePath,'r') as f: print(f.read())
四、异常
# try except else finally # try-->else-->finally # try-->except-->finally # 异常的父类是BaseException def divion(): try: return 10/1 except Exception as e: print(e.args[0]) else: print('try执行ok') finally: print('我无论不会显示异常') print(divion())

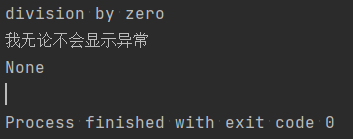
def divion(): try: return 10/0 except Exception as e: print(e.args[0]) else: print('try执行ok') finally: print('我无论不会显示异常') print(divion())
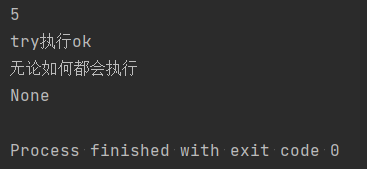
def add(a,b): try: print(a+b) except Exception as e: print(e.args[0]) else: print('try执行ok') finally: print('无论如何都会执行') print(add(2,3))
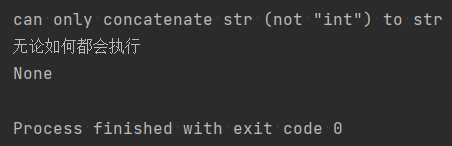
def add(a,b): try: print(a+b) except Exception as e: print(e.args[0]) else: print('try执行ok') finally: print('无论如何都会执行') print(add("#",3))
五、引入自定义包
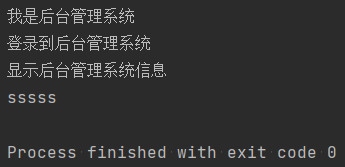
# import 包.模块 # import admin.adminSys.name # from 包.模块 import*(模块内所有对象) from admin.adminSys import * # from 包.包.模块 import*(模块内所有对象) from admin.a.info import * print(name) login() show() showInfo()

def showInfo(): print('sssss')
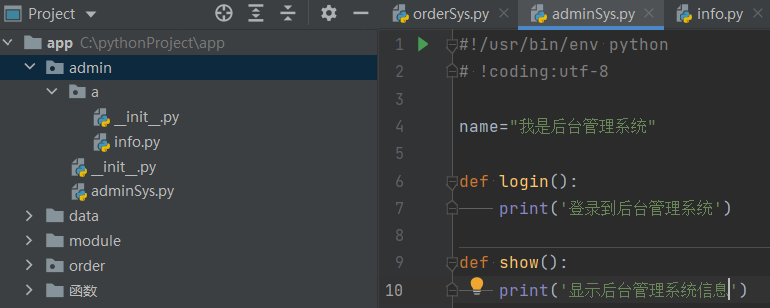
name="我是后台管理系统" def login(): print('登录到后台管理系统') def show(): print('显示后台管理系统信息')
pip3 install selenium
pip3 install requests
pip3 install django
pip3 install flask
安装对应组件



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号