Java 线性表——ArrayList & LinkedList
数组
- 简单:数组是一种最简单的数据结构
- 占据连续内存:数组空间连续,按照申请的顺序存储,但是必须制定数组大小
- 数组空间效率低:数组中经常有空闲的区域没有得到充分的应用
- 操作麻烦:数组的增加和删除操作很麻烦
线性表
为了应对数组的缺点,可以使用线性表。
按物理结构划分:顺序存储结构(顺序表)、链式存储结构。
顺序表(ArrayList)
a1 是 a2 的前驱,ai+1 是 ai 的后继,a1 没有前驱,an 没有后继。
n 为线性表的长度 ,若 n==0 时,线性表为空表。
封装了数组:
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E> implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {
transient Object[] elementData;
private int size;
}
增(add)
// 直接在表尾添加
public boolean add(E e) {
modCount++;
add(e, elementData, size);
return true;
}
private void add(E e, Object[] elementData, int s) {
if (s == elementData.length)
elementData = grow();
elementData[s] = e;
size = s + 1;
}
// 插入
// 需要使用 System.arraycopy 把数据往后挪(位移)
public void add(int index, E element) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
modCount++;
final int s;
Object[] elementData;
if ((s = size) == (elementData = this.elementData).length)
elementData = grow();
System.arraycopy(elementData, index,
elementData, index + 1,
s - index);
elementData[index] = element;
size = s + 1;
}
rangeCheckForAdd 方法检查是否触发数组越界:
private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) {
if (index > size || index < 0)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
添加元素可能触发扩容:
最少扩一个,默认扩两倍。
private Object[] grow() {
return grow(size + 1);
}
private Object[] grow(int minCapacity) {
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
if (oldCapacity > 0 || elementData != DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
int newCapacity = ArraysSupport.newLength(oldCapacity,
minCapacity - oldCapacity, /* minimum growth */
oldCapacity >> 1 /* preferred growth */);
return elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
} else {
return elementData = new Object[Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity)];
}
}
删(remove)
public E remove(int index)
public boolean remove(Object o)
public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c)
public boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter)
public E remove(int index) {
Objects.checkIndex(index, size);
final Object[] es = elementData;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E oldValue = (E) es[index];
fastRemove(es, index);
return oldValue;
}
// 使用 System.arraycopy 位移
private void fastRemove(Object[] es, int i) {
modCount++;
final int newSize;
if ((newSize = size - 1) > i)
System.arraycopy(es, i + 1, es, i, newSize - i);
es[size = newSize] = null;
}
// 先找到索引,再删除
public boolean remove(Object o) {
final Object[] es = elementData;
final int size = this.size;
int i = 0;
found: {
if (o == null) {
for (; i < size; i++)
if (es[i] == null)
break found;
} else {
for (; i < size; i++)
if (o.equals(es[i]))
break found;
}
return false;
}
fastRemove(es, i);
return true;
}
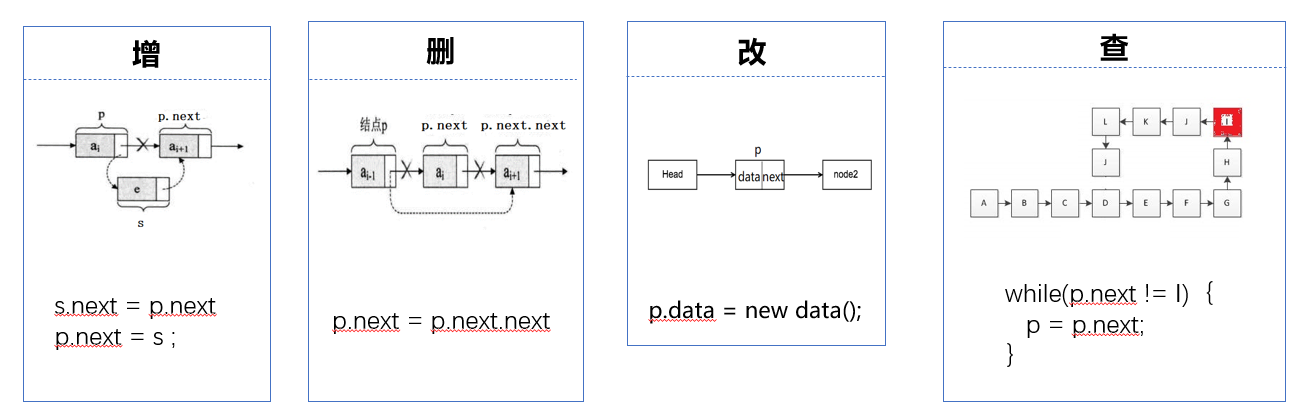
改(set)
public E set(int index, E element) {
Objects.checkIndex(index, size);
E oldValue = elementData(index);
elementData[index] = element;
return oldValue;
}
查(get、contains、indexOf)
public E get(int index) {
Objects.checkIndex(index, size);
return elementData(index);
}
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o) >= 0;
}
public int indexOf(Object o) {
return indexOfRange(o, 0, size);
}
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
return lastIndexOfRange(o, 0, size);
}
迭代器(Iterator)
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {
int cursor; // index of next element to return
int lastRet = -1; // index of last element returned; -1 if no such
int expectedModCount = modCount;
// prevent creating a synthetic constructor
Itr() {}
public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor != size;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor;
if (i >= size)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i + 1;
return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];
}
public void remove() {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet);
cursor = lastRet;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
@Override
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
final int size = ArrayList.this.size;
int i = cursor;
if (i < size) {
final Object[] es = elementData;
if (i >= es.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
for (; i < size && modCount == expectedModCount; i++)
action.accept(elementAt(es, i));
// update once at end to reduce heap write traffic
cursor = i;
lastRet = i - 1;
checkForComodification();
}
}
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
ArrayList 应用场景
- 优点:尾插效率高,支持随机访问。
- 缺点:中间插入或者删除效率低。
排序不要使用 ArrayList,经常增删改变位置不要用 ArrayList,效率很低。
只存放,随机访问,可以使用 ArrayList。
ArrayList 顺序删除节点要用迭代器从尾部往前删,如果从前往后删的话,会频繁触发 System.arraycopy。
遍历 ArrayList 尽量使用迭代器。
链表
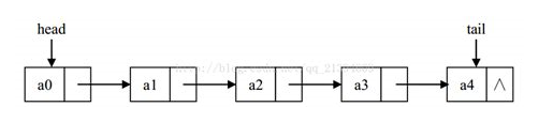
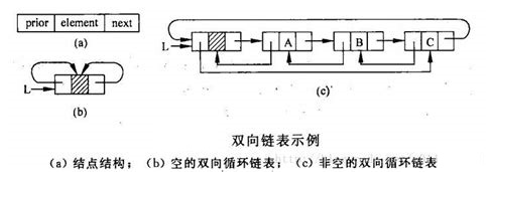
线性表的链式存储结构的特点是用一组任意的存储单元存储线性表的数据元素,这组存储单元可以是连续的,也可以是不连续的。分为:单循环链表、双向循环链表。

单链表
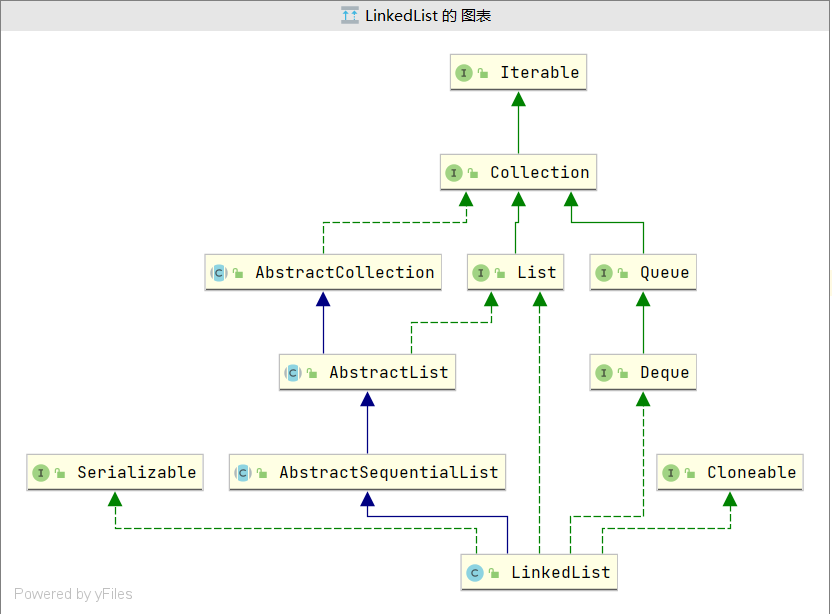
双链表(LinkedList)
public class LinkedList<E> extends AbstractSequentialList<E> implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {
transient int size = 0;
transient Node<E> first;
transient Node<E> last;
private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
}
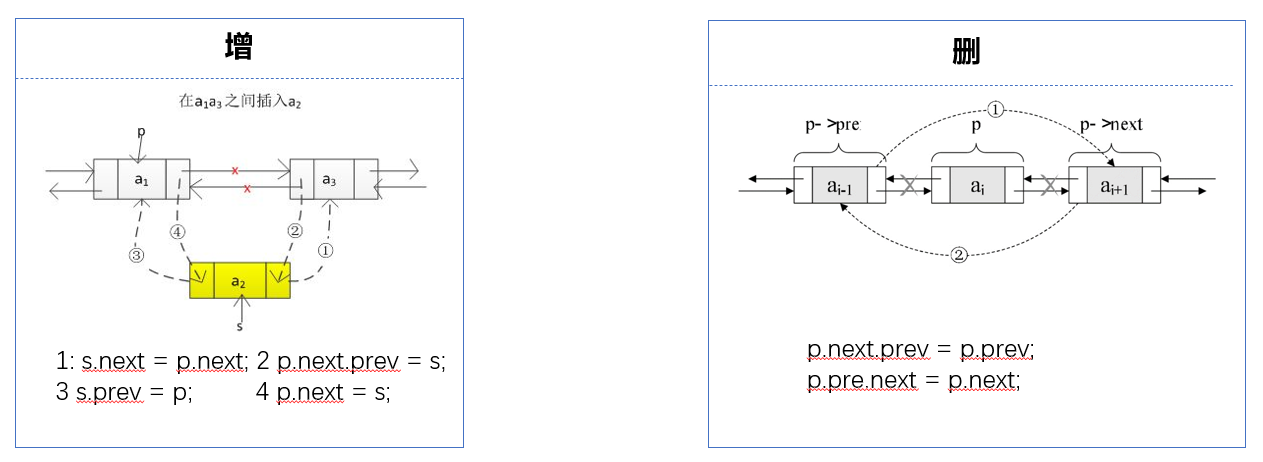
增(add)
public void addFirst(E e)
public void addLast(E e)
public boolean add(E e)
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c)
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c)
public void add(int index, E element)
public void add(int index, E element) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
if (index == size)
linkLast(element);
else
linkBefore(element, node(index));
}
void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) {
// assert succ != null;
final Node<E> pred = succ.prev;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ);
succ.prev = newNode;
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
Node<E> node(int index) {
// assert isElementIndex(index);
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
Node<E> x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
Node<E> x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}
删(remove)
public E removeFirst()
public E removeLast()
public boolean remove(Object o)
public E remove(int index)
public E remove()
public boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o)
public boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o)
public E remove(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return unlink(node(index));
}
E unlink(Node<E> x) {
// assert x != null;
final E element = x.item;
final Node<E> next = x.next;
final Node<E> prev = x.prev;
if (prev == null) {
first = next;
} else {
prev.next = next;
x.prev = null;
}
if (next == null) {
last = prev;
} else {
next.prev = prev;
x.next = null;
}
x.item = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
| 优点 | 缺点 | |
|---|---|---|
| 顺序表 | 存储空间连续 允许随机访问 尾插,尾删方便 |
插入删除效率低 长度固定 |
| 单链表 | 随意进行增删改 插入删除效率高 长度可以随意修改 |
内存不连续 不能随机查找 |
| 双链表 | 随意进行增删改 插入效率高 删除效率高 长度可以随意修改 查找效率比单链表快一倍 |
内存不连续,不能随机查找,但是效率比单链表快一倍 |
LinkedList 应用场景
排序、频繁增删
List
Enumeration 可以枚举(一次获得一个)Vector 中的元素。目前已被迭代器取代。但它还是使用在诸如 Vector 和 Properties 这些传统类所定义的方法中。
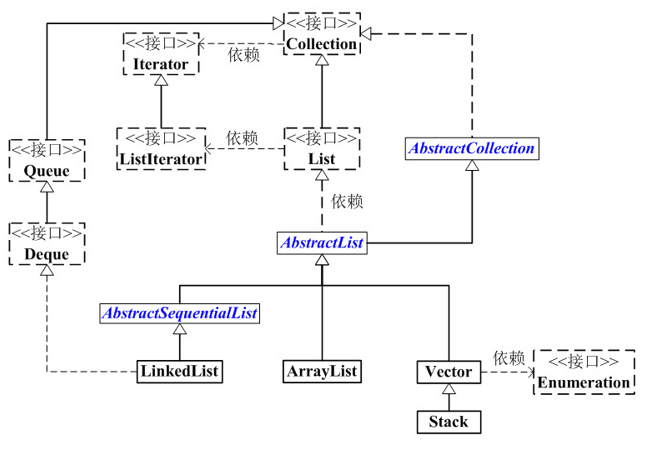
List是一个接口,它继承于Collection的接口。它代表着有序的队列。AbstractList是一个抽象类,它继承于AbstractCollectionAbstractList实现List接口中除size()、get(int location)之外的函数。AbstractSequentialList是一个抽象类,它继承于AbstractList.AbstractSequentialList实现了“链表中,根据index索引值操作链表的全部函数”。ArrayList, LinkedList, Vector, Stack是List的 4 个实现类。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号