BeanFactoryPostProcessor & BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor——执行时机
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor继承自BeanFactoryPostProcessor。
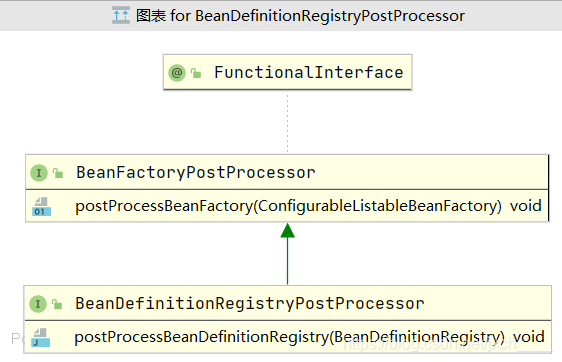
BeanFactoryPostProcessor
@FunctionalInterface
public interface BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException;
}
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
public interface BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor extends BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException;
}
执行时机:抽象的来看就是 BeanFactory加载完Bean定义后,实例化Bean之前执行。
从代码角度就是AbstractApplicationContext#refresh中的invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);语句(以下代码的第22行)
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
StartupStep contextRefresh = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.refresh");
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
StartupStep beanPostProcess = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.beans.post-process");
// 执行时机
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
beanPostProcess.end();
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
} catch // ...
finally // ...
}
}
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors
protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors());
// ...
}
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate#invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors
public static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
// 流程过于复杂,就全部省略了
if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) {
// ...
boolean reiterate = true;
while (reiterate) {
// ... BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry, beanFactory.getApplicationStartup());
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
}
// Now, invoke the postProcessBeanFactory callback of all processors handled so far.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory);
} else {
// Invoke factory processors registered with the context instance.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactoryPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
// 排序 按顺序执行
// implement PriorityOrdered ...
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// implement Ordered ...
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// all other BeanFactoryPostProcessors ...
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(nonOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
beanFactory.clearMetadataCache();
}
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors——调用BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口
private static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(Collection<? extends BeanFactoryPostProcessor> postProcessors, ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) {
StartupStep postProcessBeanFactory = beanFactory.getApplicationStartup().start("spring.context.bean-factory.post-process").tag("postProcessor", postProcessor::toString);
// 在此处调用 BeanFactoryPostProcessor
postProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
postProcessBeanFactory.end();
}
}
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors——调用BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口
private static void invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(Collection<? extends BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> postProcessors, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, ApplicationStartup applicationStartup) {
for (BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) {
StartupStep postProcessBeanDefRegistry = applicationStartup.start("spring.context.beandef-registry.post-process").tag("postProcessor", postProcessor::toString);
// 在此处调用 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
postProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);
postProcessBeanDefRegistry.end();
}
}
所以可以看出先调用BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,后调用BeanFactoryPostProcessor,而BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor继承自BeanFactoryPostProcessor。
所以抽象的来看,执行时机是在 BeanFactory加载完Bean定义后,实例化Bean之前。且先执行BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法,再执行BeanFactoryPostProcessor的postProcessBeanFactory方法。
如果在postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法中增加一个bean定义,那么在postProcessBeanFactory方法中是可以拿到的。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号