三角法TRIANGLE阈值
图像处理之三角法图像二值化
三角法求阈值最早见于Zack的论文《Automatic measurement of sister chromatid exchange frequency》主要是用于染色体的研究,该方法是使用直方图数据,基于纯几何方法来寻找最佳阈值,它的成立条件是假设直方图最大波峰在靠近最亮的一侧,然后通过三角形求得最大直线距离,根据最大直线距离对应的直方图灰度等级即为分割阈值,图示如下: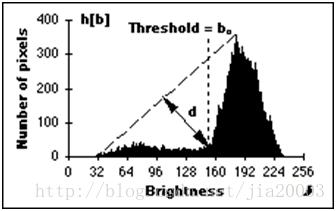
对上图的详细解释:
在直方图上从最高峰处bmx到最暗对应直方图bmin(p=0)%构造一条直线,从bmin处开始计算每个对应的直方图b到直线的垂直距离,知道bmax为止,其中最大距离对应的直方图位置即为图像二值化对应的阈值T。
扩展情况:
有时候最大波峰对应位置不在直方图最亮一侧,而在暗的一侧,这样就需要翻转直方图,翻转之后求得值,用255减去即得到为阈值T。扩展情况的直方图表示如下:
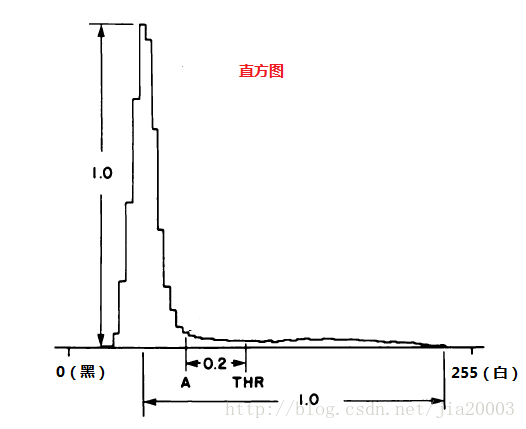
代码:
/* 8. 图像转灰度 9. 计算图像灰度直方图 10. 寻找直方图中两侧边界 11. 寻找直方图最大值 12. 检测是否最大波峰在亮的一侧,否则翻转 13. 计算阈值得到阈值T,如果翻转则255-T //三角法图像二值化 */ void* Triangle(QImage &image,QImage &otpImage) { int width = image.width(); int height = image.height(); int i = 0,j = 0; int gray; int temp = 0; bool isflipped = false; QVector<int> histogram(256); //直方图 for(int row = 0; row < height; row++) { for(int col = 0; col<width; col++) { gray = qGray(image.pixel(col,row)); histogram[gray] ++; } } //3. 寻找直方图中两侧边界 int left_bound = 0; int right_bound = 0; int max = 0; int max_index = 0; //左侧为零的位置 for(i = 0; i<256; i++) { if(histogram[i]>0) { left_bound = i; break; } } //直方图为零的位置 if(left_bound > 0) { left_bound --; } //直方图右侧为零的位置 for(i = 255; i>0; i--) { if(histogram[i]>0) { right_bound = i; break; } } //直方图为零的地方 if(right_bound >0) { right_bound++; } //4. 寻找直方图最大值 for(i = 0; i<256;i++) { if(histogram[i] > max) { max = histogram[i]; max_index = i; } } //判断最大值是否在最左侧,如果是则不用翻转 //因为三角法二值化只能适用于最大值在最右侧 if(max_index - left_bound < right_bound - max_index) { isflipped = true; i = 0; j = 255; while( i < j ) { // 左右交换 temp = histogram[i]; histogram[i] = histogram[j]; histogram[j] = temp; i++; j--; } left_bound = 255-right_bound; max_index = 255-max_index; } // 计算求得阈值 double thresh = left_bound; double a, b, dist = 0, tempdist; a = max; b = left_bound-max_index; for( i = left_bound+1; i <= max_index; i++ ) { // 计算距离 - 不需要真正计算 tempdist = a*i + b*histogram[i]; if( tempdist > dist) { dist = tempdist; thresh = i; } } thresh--; // 对已经得到的阈值T,如果前面已经翻转了,则阈值要用255-T if( isflipped ) { thresh = 255-thresh; } //二值化 Threshold(image,otpImage,thresh); return 0; }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号