实验四
实验任务1
源代码GradeCalc.hpp
1 #pragma once 2 #include <vector> 3 #include <array> 4 #include <string> 5 class GradeCalc { 6 public: 7 GradeCalc(const std::string& cname); 8 void input(int n); // 录入n个成绩 9 void output() const; // 输出成绩 10 void sort(bool ascending = false); // 排序 (默认降序) 11 int min() const; // 返回最低分(如成绩未录入,返回-1) 12 int max() const; // 返回最高分 (如成绩未录入,返回-1) 13 double average() const; // 返回平均分 (如成绩未录入,返回0.0) 14 void info(); // 输出课程成绩信息 15 private: 16 void compute(); // 成绩统计 17 private: 18 std::string course_name; // 课程名 19 std::vector<int> grades; // 课程成绩 20 std::array<int, 5> counts; // 保存各分数段人数([0, 60), [60, 70), [70, 80), [80,90), [90, 100] 21 std::array<double, 5> rates; // 保存各分数段人数占比 22 bool is_dirty; // 脏标记,记录是否成绩信息有变更 23 };
源代码GradeCalc.cpp
#include <algorithm> #include <array> #include <cstdlib> #include <iomanip> #include <iostream> #include <numeric> #include <string> #include <vector> #include "GradeCalc.hpp" GradeCalc::GradeCalc(const std::string& cname) :course_name{ cname }, is_dirty{ true } { counts.fill(0); rates.fill(0); } void GradeCalc::input(int n) { if (n < 0) { std::cerr << "无效输入! 人数不能为负数\n"; std::exit(1); } grades.reserve(n); int grade; for (int i = 0; i < n;) { std::cin >> grade; if (grade < 0 || grade > 100) { std::cerr << "无效输入! 分数须在[0,100]\n"; continue; } grades.push_back(grade); ++i; } is_dirty = true; // 设置脏标记:成绩信息有变更 } void GradeCalc::output() const { for (auto grade : grades) std::cout << grade << ' '; std::cout << std::endl; } void GradeCalc::sort(bool ascending) { if (ascending) std::sort(grades.begin(), grades.end()); else std::sort(grades.begin(), grades.end(), std::greater<int>()); } int GradeCalc::min() const { if (grades.empty()) return -1; auto it = std::min_element(grades.begin(), grades.end()); return *it; } int GradeCalc::max() const { if (grades.empty()) return -1; auto it = std::max_element(grades.begin(), grades.end()); return *it; } double GradeCalc::average() const { if (grades.empty()) return 0.0; double avg = std::accumulate(grades.begin(), grades.end(), 0.0) / grades.size(); return avg; } void GradeCalc::info() { if (is_dirty) compute(); std::cout << "课程名称:\t" << course_name << std::endl; std::cout << "平均分:\t" << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << average() << std::endl; std::cout << "最高分:\t" << max() << std::endl; std::cout << "最低分:\t" << min() << std::endl; const std::array<std::string, 5> grade_range{ "[0, 60) ", "[60, 70)", "[70, 80)", "[80, 90)", "[90, 100]" }; for (int i = grade_range.size() - 1; i >= 0; --i) std::cout << grade_range[i] << "\t: " << counts[i] << "人\t" << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << rates[i] * 100 << "%\n"; } void GradeCalc::compute() { if (grades.empty()) return; counts.fill(0); rates.fill(0.0); // 统计各分数段人数 for (auto grade : grades) { if (grade < 60) ++counts[0]; // [0, 60) else if (grade < 70) ++counts[1]; // [60, 70) else if (grade < 80) ++counts[2]; // [70, 80) else if (grade < 90) ++counts[3]; // [80, 90) else ++counts[4]; // [90, 100] } // 统计各分数段比例 for (int i = 0; i < rates.size(); ++i) rates[i] = counts[i] * 1.0 / grades.size(); is_dirty = false; // 更新脏标记 }
源代码demo1.cpp
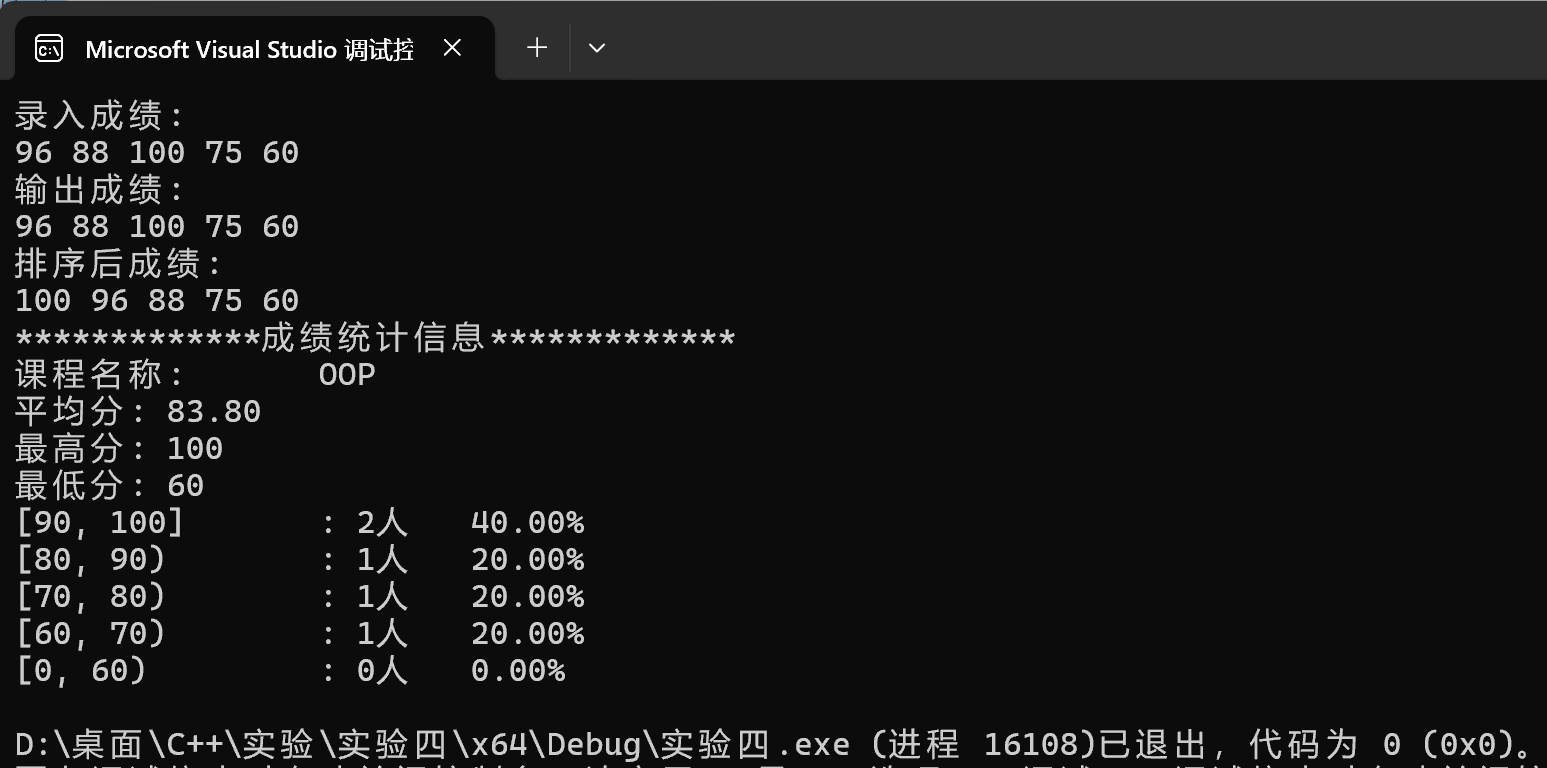
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include "GradeCalc.hpp" void test() { GradeCalc c1("OOP"); std::cout << "录入成绩:\n"; c1.input(5); std::cout << "输出成绩:\n"; c1.output(); std::cout << "排序后成绩:\n"; c1.sort(); c1.output(); std::cout << "*************成绩统计信息*************\n"; c1.info(); } int main() { test(); }
运行测试结果截图
答:std::string course_name; // 存储课程名称字符串
std::vector<int> grades; // 动态存储所有学生的成绩数据
std::array<int, 5> counts; // 固定大小数组,保存各分数段人数
std::array<double, 5> rates; // 固定大小数组,保存各分数段人数占比
GradeCalc c("OOP"); c.inupt(5); c.push_back(97); // 不合法
答:不合法。因为 push_back 是 std::vector 类的公有成员函数,而不是 GradeCalc 类的公有接口。c.push_back(97) 试图直接操作 GradeCalc 类的私有成员变量 grades,这违反了类的封装性原则,编译器会报错,因为 GradeCalc 类没有名为 push_back 的公有成员函数。
1 double median; 2 this->sort();//使用类实现的排序方法对成绩进行降序排序 3 int n = grades.size(); 4 if (n % 2 != 0) 5 median = grades[n / 2];//当成绩个数为奇数时中位数即为正中间的数 6 else 7 median = (grades[n / 2 - 1] + grades[n / 2]) / 2;//当成绩个数为偶数时中位数为中间两个数的平均值 8 std::cout << "中位数:\t" << median << std::endl;
实现效果如下
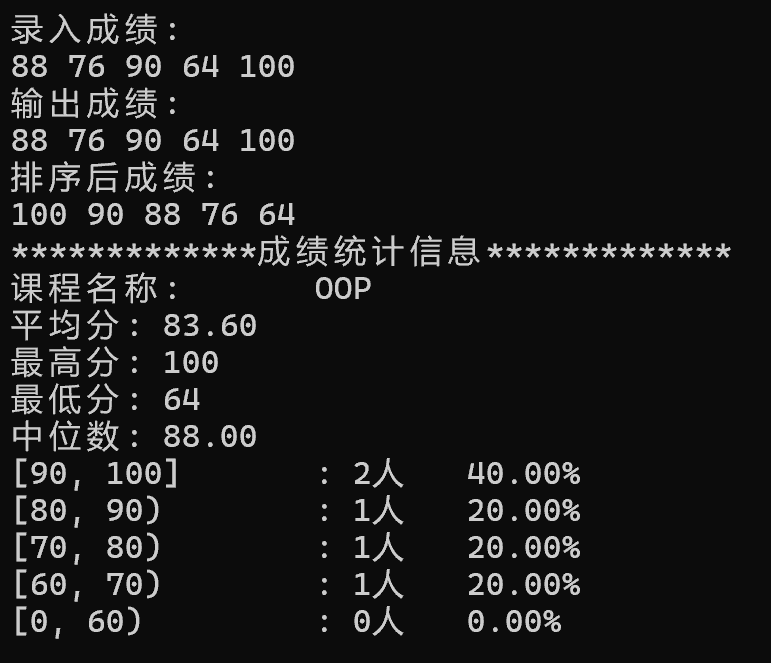
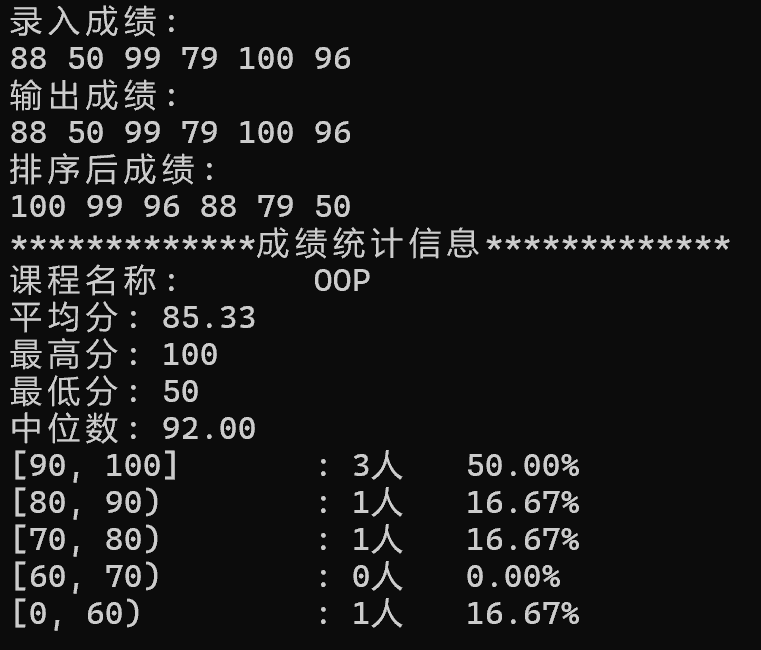
答:在 compute 函数中,counts.fill(0) 和 rates.fill(0) 这两行代码不能去掉。它们的作用是在每次计算前清零统计数组,确保结果基于当前成绩数据。如果去掉这两行,在多次调用 input 更新成绩的场景下会引发统计错误。例如先输入一批成绩查看统计,再输入第二批成绩时,由于 counts 和 rates 保留了上一次的结果,新统计会在旧数据上累加,导致输出错误的分析报告。
1 #pragma once 2 #include <array> 3 #include <string> 4 #include <vector> 5 class GradeCalc: private std::vector<int> { 6 public: 7 GradeCalc(const std::string &cname); 8 void input(int n); // 录入n个成绩 9 void output() const; // 输出成绩 10 void sort(bool ascending = false); // 排序 (默认降序) 11 int min() const; // 返回最低分 12 int max() const; // 返回最高分 13 double average() const; // 返回平均分 14 void info(); // 输出成绩统计信息 15 private: 16 void compute(); // 计算成绩统计信息 17 private: 18 std::string course_name; // 课程名 19 std::array<int, 5> counts; // 保存各分数段人数([0, 60), [60, 70), [70, 80), [80, 20 90), [90, 100] 21 std::array<double, 5> rates; // 保存各分数段占比 22 bool is_dirty; // 脏标记,记录是否成绩信息有变更 23 };
源代码GradeCalc.cpp
1 #include <algorithm> 2 #include <array> 3 #include <cstdlib> 4 #include <iomanip> 5 #include <iostream> 6 #include <numeric> 7 #include <string> 8 #include <vector> 9 #include "GradeCalc.hpp" 10 11 12 GradeCalc::GradeCalc(const std::string& cname) : course_name{ cname }, is_dirty{ true } { 13 counts.fill(0); 14 rates.fill(0); 15 } 16 void GradeCalc::input(int n) { 17 if (n < 0) { 18 std::cerr << "无效输入! 人数不能为负数\n"; 19 return; 20 } 21 this->reserve(n); 22 int grade; 23 for (int i = 0; i < n;) { 24 std::cin >> grade; 25 if (grade < 0 || grade > 100) { 26 std::cerr << "无效输入! 分数须在[0,100]\n"; 27 continue; 28 } 29 this->push_back(grade); 30 ++i; 31 } 32 is_dirty = true; 33 } 34 void GradeCalc::output() const { 35 for (auto grade : *this) 36 std::cout << grade << ' '; 37 std::cout << std::endl; 38 } 39 void GradeCalc::sort(bool ascending) { 40 if (ascending) 41 std::sort(this->begin(), this->end()); 42 else 43 std::sort(this->begin(), this->end(), std::greater<int>()); 44 } 45 int GradeCalc::min() const { 46 if (this->empty()) 47 return -1; 48 return *std::min_element(this->begin(), this->end()); 49 } 50 int GradeCalc::max() const { 51 if (this->empty()) 52 return -1; 53 return *std::max_element(this->begin(), this->end()); 54 } 55 double GradeCalc::average() const { 56 if (this->empty()) 57 return 0.0; 58 double avg = std::accumulate(this->begin(), this->end(), 0.0) / this->size(); 59 return avg; 60 } 61 void GradeCalc::info() { 62 if (is_dirty) 63 compute(); 64 std::cout << "课程名称:\t" << course_name << std::endl; 65 std::cout << "平均分:\t" << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << average() << 66 std::endl; 67 std::cout << "最高分:\t" << max() << std::endl; 68 std::cout << "最低分:\t" << min() << std::endl; 69 const std::array<std::string, 5> grade_range{ "[0, 60) ", 70 "[60, 70)", 71 "[70, 80)", 72 "[80, 90)", 73 "[90, 100]" }; 74 for (int i = grade_range.size() - 1; i >= 0; --i) 75 std::cout << grade_range[i] << "\t: " << counts[i] << "人\t" 76 << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << rates[i] * 100 << "%\n"; 77 } 78 void GradeCalc::compute() { 79 if (this->empty()) 80 return; 81 counts.fill(0); 82 rates.fill(0); 83 // 统计各分数段人数 84 for (int grade : *this) { 85 if (grade < 60) 86 ++counts[0]; // [0, 60) 87 else if (grade < 70) 88 ++counts[1]; // [60, 70) 89 else if (grade < 80) 90 ++counts[2]; // [70, 80) 91 else if (grade < 90) 92 ++counts[3]; // [80, 90) 93 else 94 ++counts[4]; // [90, 100] 95 } 96 // 统计各分数段比例 97 for (int i = 0; i < rates.size(); ++i) 98 rates[i] = counts[i] * 1.0 / this->size(); 99 is_dirty = false; 100 }
源代码demo2.cpp
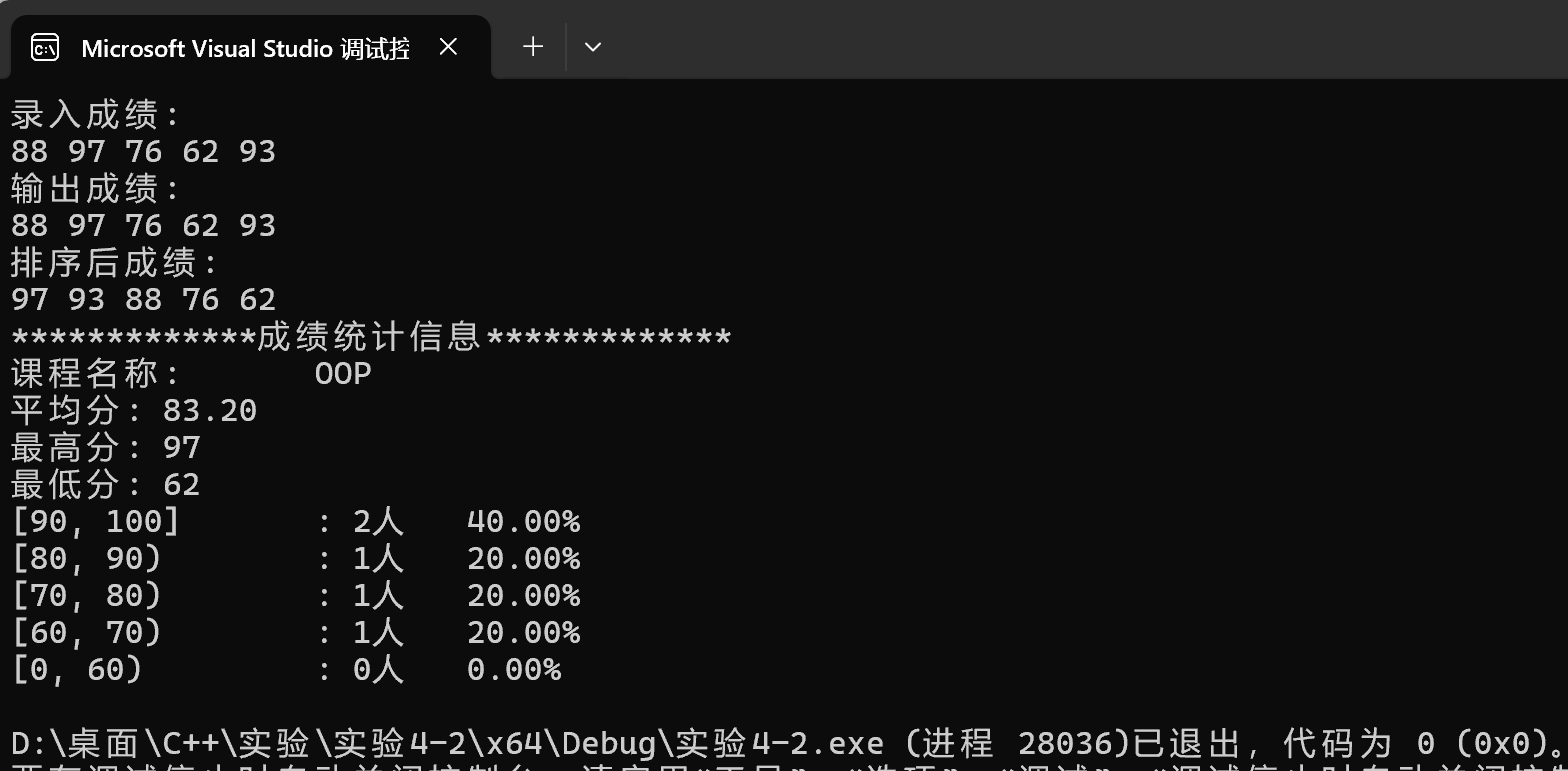
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 #include "GradeCalc.hpp" 4 void test() { 5 GradeCalc c1("OOP"); 6 std::cout << "录入成绩:\n"; 7 c1.input(5); 8 std::cout << "输出成绩:\n"; 9 c1.output(); 10 std::cout << "排序后成绩:\n"; 11 c1.sort(); c1.output(); 12 std::cout << "*************成绩统计信息*************\n"; 13 c1.info(); 14 } 15 int main() { 16 test(); 17 }
运行结果测试截图
问题1:继承关系识别
写出 GradeCalc 类声明体现"继承"关系的完整代码行。
答:
class GradeCalc : private std::vector<int>
问题2:接口暴露理解
当前继承方式下,基类 vector<int> 的接口会自动成为 GradeCalc 的接口吗?
如在 test 模块中这样用,能否编译通过?用一句话解释原因。
GradeCalc c("OOP"); c.input(5); c.push_back(97); // 不合法
答:(1)不会,由于 GradeCalc 采用了私有继承,基类 std::vector<int> 的所有公共和保护成员在子类 GradeCalc 外部都会被视为私有成员。因此,基类的接口不会自动成为 GradeCalc 的公共接口。
(2)不能编译通过,因为GradeCalc 是私有继承自 std::vector<int>,基类的公共方法 push_back 在 GradeCalc 外部被视为私有成员。
问题3:数据访问差异
对比继承方式与组合方式内部实现数据访问的一行典型代码。说明两种方式下的封装差异带来的数据访问接口差异。
// 组合方式 for (auto grade : grades) // 通过成员变量 grades 直接访问数据 // 略 // 继承方式 for (int grade : *this) // 通过继承的迭代器接口间接访问数据 // 略
答: 组合方式:数据完全封装在类内部,外部只能通过公有成员函数访问,数据保护性更强。
继承方式:虽然使用私有继承限制了外部直接访问基类接口,但类内部可以像使用自己的成员一样使用继承的功能,代码更简洁,但耦合度更高。
问题4:组合 vs. 继承方案选择
你认为组合方案和继承方案,哪个更适合成绩计算这个问题场景?简洁陈述你的结论和理由。
答:组合方案更适合成绩计算场景,因为成绩计算的核心是业务逻辑(统计、分析、排序),因此它和vector不会是一种is-a关系。组合方案提供更好的封装性,避免与标准容器的过度耦合,使GradeCalc保持纯粹的业务类身份,未来更容易扩展或更换数据结构。
实验任务三
源代码Graph.hpp
1 #pragma once 2 #include <string> 3 #include <vector> 4 enum class GraphType { circle, triangle, rectangle }; 5 // Graph类定义 6 class Graph { 7 public: 8 virtual void draw() {} 9 virtual ~Graph() = default; 10 }; 11 // Circle类声明 12 class Circle : public Graph { 13 public: 14 void draw(); 15 }; 16 // Triangle类声明 17 class Triangle : public Graph { 18 public: 19 void draw(); 20 }; 21 // Rectangle类声明 22 class Rectangle : public Graph { 23 public: 24 void draw(); 25 }; 26 // Canvas类声明 27 class Canvas { 28 public: 29 void add(const std::string& type); // 根据字符串添加图形 30 void paint() const; // 使用统一接口绘制所有图形 31 ~Canvas(); // 手动释放资源 32 private: 33 std::vector<Graph*> graphs; 34 }; 35 // 4. 工具函数 36 GraphType str_to_GraphType(const std::string& s); // 字符串转枚举类型 37 Graph* make_graph(const std::string& type); // 创建图形,返回堆对象指针
源代码Graph.cpp
1 #include <algorithm> 2 #include <cctype> 3 #include <iostream> 4 #include <string> 5 #include "Graph.hpp" 6 // Circle类实现 7 void Circle::draw() { std::cout << "draw a circle...\n"; } 8 // Triangle类实现 9 void Triangle::draw() { std::cout << "draw a triangle...\n"; } 10 // Rectangle类实现 11 void Rectangle::draw() { std::cout << "draw a rectangle...\n"; } 12 // Canvas类实现 13 void Canvas::add(const std::string& type) { 14 Graph* g = make_graph(type); 15 if (g) 16 graphs.push_back(g); 17 } 18 19 void Canvas::paint() const { 20 for (Graph* g : graphs) 21 g->draw(); 22 } 23 Canvas::~Canvas() { 24 for (Graph* g : graphs) 25 delete g; 26 } 27 // 工具函数实现 28 // 字符串 → 枚举转换 29 GraphType str_to_GraphType(const std::string& s) { 30 std::string t = s; 31 std::transform(s.begin(), s.end(), t.begin(), 32 [](unsigned char c) { return std::tolower(c); }); 33 if (t == "circle") 34 return GraphType::circle; 35 if (t == "triangle") 36 return GraphType::triangle; 37 if (t == "rectangle") 38 return GraphType::rectangle; 39 return GraphType::circle; // 缺省返回 40 } 41 // 创建图形,返回堆对象指针 42 Graph* make_graph(const std::string& type) { 43 switch (str_to_GraphType(type)) { 44 case GraphType::circle: return new Circle; 45 case GraphType::triangle: return new Triangle; 46 case GraphType::rectangle: return new Rectangle; 47 default: return nullptr; 48 } 49 }
源代码demo3.cpp
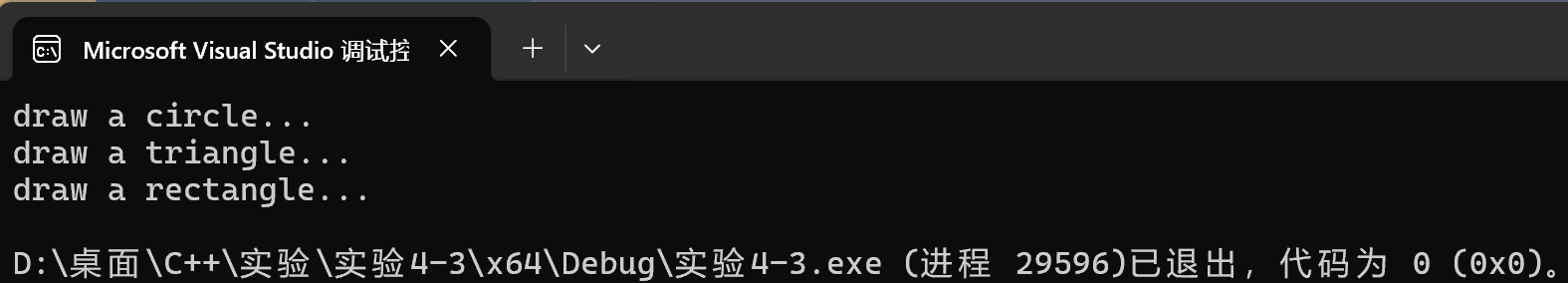
1 #include <string> 2 #include "Graph.hpp" 3 void test() { 4 Canvas canvas; 5 canvas.add("circle"); 6 canvas.add("triangle"); 7 canvas.add("rectangle"); 8 canvas.paint(); 9 } 10 11 int main() { 12 test(); 13 }
运行结果测试截图
问题1:对象关系识别
(1)写出Graph.hpp中体现"组合"关系的成员声明代码行,并用一句话说明被组合对象的功能。
(2)写出Graph.hpp中体现"继承"关系的类声明代码行。
答:(1)体现"组合"关系的成员声明代码行
std::vector<Graph*> graphs;
功能:用于存储所有添加到画布上的图形对象的指针。
(2)体现"继承"关系的类声明代码行
class Circle : public Graph{ class Triangle : public Graph{ class Rectangle : public Graph{
问题2:多态机制观察
(1) Graph 中的 draw 若未声明成虚函数, Canvas::paint() 中 g->draw() 运行结果会有何不同?
(2)若 Canvas 类 std::vector<Graph*> 改成 std::vector<Graph> ,会出现什么问题?
(3)若 ~Graph() 未声明成虚函数,会带来什么问题?
答:(1)如果draw未声明为虚函数,Canvas::paint()中的g->draw()将始终调用基类Graph的draw方法,而不会调用具体子类的draw方法,导致输出全为空。

(2)如果改为存储实际对象而不是指针,当存入Circle、Triangle等派生类对象时会发生对象切片,只保留基类Graph部分,丢失派生类的特有属性和行为,导致draw方法的多态性也会失效。
(3)如果基类析构函数不是虚函数,当通过基类指针删除派生类对象时,只会调用基类的析构函数,而不会调用派生类的析构函数,导致派生类特有的资源无法正确释放,造成内存泄漏。
问题3:扩展性思考
若要新增星形 Star ,需在哪些文件做哪些改动?逐一列出。
答:(1)Graph.hpp
enum class GraphType { circle, triangle, rectangle, star };//新增枚举值
class Star : public Graph {//新增Star类 public: void draw(); };
(2)Graph.cpp
void Star::draw() { std::cout << "draw a star...\n"; }//Star类draw方法实现
GraphType str_to_GraphType(const std::string& s) {//扩展字符串转换函数 // 在现有条件判断中新增: if (t == "star") return GraphType::star; }
Graph* make_graph(const std::string& type) {//扩展工厂函数 switch (str_to_GraphType(type)) { // 在switch case中新增: case GraphType::star: return new Star; } }
(3)demo3.cpp
canvas.add("star"); // 添加星形
问题4:资源管理
观察 make_graph 函数和 Canvas 析构函数:
(1) make_graph 返回的对象在什么地方被释放?
(2)使用原始指针管理内存有何利弊?
答:(1)当 Canvas 对象生命周期结束时,其析构函数会遍历动态数组中的所有指针,并对每个指针执行 delete 操作,从而释放 make_graph 动态分配的内存。
(2)优点:性能开销小,执行效率高。
缺点:安全性差,必须手动调用 delete,易导致内存泄漏。
实验任务4
问题描述
设计一个毛绒玩具管理系统,能够管理不同类型的电子毛绒玩具,每种玩具具有独特的特异功能,通过统一的接口进行管理和功能展示。
对象关系
继承关系:CharacterToy, AnimalToy, SmartToy 继承自抽象基类 Toy
组合关系:ToyFactory 包含 std::vector<Toy*> 管理所有玩具
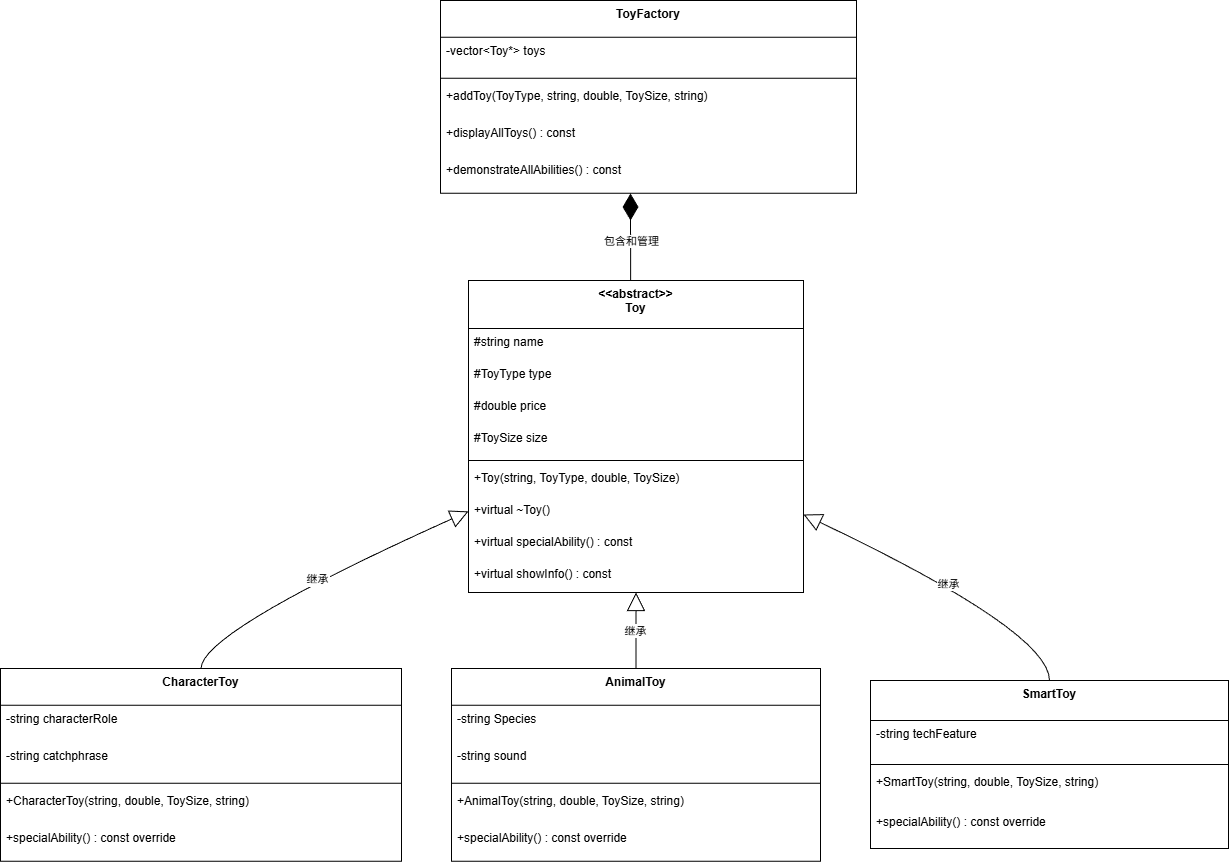
源代码Toy.hpp
1 #pragma once 2 #include <string> 3 #include <iostream> 4 #include<vector> 5 // 玩具类型 6 enum class ToyType {character,animal,smart}; 7 // 玩具大小 8 enum class ToySize {small,medium,large,extra_large}; 9 10 // 抽象基类 Toy 11 class Toy { 12 public: 13 Toy(const std::string& name, ToyType type, double price, ToySize size); 14 virtual ~Toy() = default; 15 16 virtual void specialAbility() const; 17 virtual void showInfo() const; 18 19 protected: 20 std::string name; 21 ToyType type; 22 double price; 23 ToySize size; 24 }; 25 26 // 人物型玩具 27 class CharacterToy : public Toy { 28 public: 29 CharacterToy(const std::string& name, double price, ToySize size, const std::string& role); 30 void specialAbility() const override; 31 32 private: 33 std::string characterRole; 34 std::string catchphrase; 35 }; 36 37 // 动物型玩具 38 class AnimalToy : public Toy { 39 public: 40 AnimalToy(const std::string& name, double price, ToySize size, const std::string& species); 41 void specialAbility() const override; 42 43 private: 44 std::string Species; 45 std::string sound; 46 }; 47 48 // 智能型玩具 49 class SmartToy : public Toy { 50 public: 51 SmartToy(const std::string& name, double price, ToySize size, const std::string& tech); 52 void specialAbility() const override; 53 private: 54 std::string techFeature; 55 }; 56 57 // 玩具工厂类 58 class ToyFactory { 59 public: 60 void addToy(ToyType type, const std::string& name, double price, ToySize size, const std::string& role); 61 void displayAllToys() const; 62 void demonstrateAllAbilities() const; 63 64 private: 65 std::vector<Toy*> toys; 66 }; 67 68 // 4. 工具函数 69 std::string getTypeString(ToyType type); 70 std::string getSizeString(ToySize size);
源代码Toy.cpp
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<string> 3 #include"Toy.hpp" 4 using namespace std; 5 6 // Toy 基类实现 7 Toy::Toy(const std::string& name, ToyType type, double price, ToySize size):name(name),type(type),price(price),size(size){} 8 void Toy::specialAbility() const { 9 cout << name << " performs a special ability." << endl; 10 } 11 void Toy::showInfo() const { 12 cout << name << " | " << getTypeString(type) << " | " << getSizeString(size)<< " | $" << price << endl; 13 } 14 15 // CharacterToy 实现 16 CharacterToy::CharacterToy(const string& name, double price, ToySize size, const string& role) 17 : Toy(name, ToyType::character, price, size), characterRole(role) { 18 19 // 根据角色设置不同的台词 20 if (role == "IronMan") { 21 catchphrase = "I am Iron Man!"; 22 } 23 else if (role == "Luffy") { 24 catchphrase = "我是要成为海贼王的男人!"; 25 } 26 else if (role == "灰太狼") { 27 catchphrase = "我一定会回来的!"; 28 } 29 else if (role == "Conan") { 30 catchphrase = "真相只有一个!"; 31 } 32 else { 33 catchphrase = "Hello! I'm " + name + ", your " + role + " friend!"; 34 } 35 } 36 37 void CharacterToy::specialAbility() const { 38 cout << catchphrase << endl; 39 } 40 41 // AnimalToy 实现 42 AnimalToy::AnimalToy(const string& name, double price, ToySize size, const string& species) 43 : Toy(name, ToyType::animal, price, size), Species(species) { 44 45 // 根据动物种类设置声音 46 if (species == "Dog") sound = "Woof Woof! "; 47 else if (species == "Cat") sound = "Meow! "; 48 else if (species == "Lion") sound = "Roar! "; 49 else if (species == "Cow") sound = "Moo! "; 50 else if (species == "Sheep") sound = "Baa! "; 51 else if (species == "Duck") sound = "Quack! "; 52 else sound = "Grrr!"; 53 } 54 55 void AnimalToy::specialAbility() const { 56 cout << sound << endl; 57 } 58 59 // SmartToy 实现 60 SmartToy::SmartToy(const string& name, double price, ToySize size, const string& tech) 61 : Toy(name, ToyType::smart, price, size), techFeature(tech) { 62 } 63 64 void SmartToy::specialAbility() const { 65 if (techFeature == "Voice") { 66 cout << "Hello! I'm your voice-activated smart toy!'" << endl; 67 } 68 else if (techFeature == "Story") { 69 cout << "Once upon a time, in a magical land...'" << endl; 70 } 71 else if (techFeature == "Music") { 72 cout << "Twinkle Twinkle Little Star" << endl; 73 } 74 else if (techFeature == "Quiz") { 75 cout << "What is 2 + 2? The answer is 4!'" << endl; 76 } 77 else if (techFeature == "Weather") { 78 cout << "Today's weather is sunny and warm!'" << endl; 79 } 80 else { 81 cout << "I'm your smart " << techFeature << " toy!'" << endl; 82 } 83 } 84 85 // ToyFactory 实现 86 void ToyFactory::addToy(ToyType type, const string& name, double price, ToySize size, const string& feature) { 87 switch (type) { 88 case ToyType::character: 89 toys.push_back(new CharacterToy(name, price, size, feature)); 90 break; 91 case ToyType::animal: 92 toys.push_back(new AnimalToy(name, price, size, feature)); 93 break; 94 case ToyType::smart: 95 toys.push_back(new SmartToy(name, price, size, feature)); 96 break; 97 } 98 } 99 100 void ToyFactory::displayAllToys() const { 101 cout << "=== All Toys' information in Factory (" << toys.size() << " items) ===" << endl; 102 if (toys.empty()) { 103 cout << "No toys in factory." << endl; 104 return; 105 } 106 for (size_t i = 0; i < toys.size(); ++i) { 107 cout << i + 1 << "、"; 108 toys[i]->showInfo(); 109 } 110 cout << "==========================================\n" << endl; 111 } 112 113 void ToyFactory::demonstrateAllAbilities() const { 114 cout << "\n=== Demonstrating Special Abilities ===" << endl; 115 if (toys.empty()) { 116 cout << "No toys to demonstrate." << endl; 117 return; 118 } 119 120 for (size_t i = 0; i < toys.size(); ++i) { 121 cout << i + 1 << ". "; 122 toys[i]->specialAbility(); 123 } 124 cout << "======================================\n" << endl; 125 } 126 127 // 工具函数实现 128 string getTypeString(ToyType type) { 129 switch (type) { 130 case ToyType::character: return "Character"; 131 case ToyType::animal: return "Animal"; 132 case ToyType::smart: return "Smart"; 133 default: return "Unknown"; 134 } 135 } 136 137 string getSizeString(ToySize size) { 138 switch (size) { 139 case ToySize::small: return "Small"; 140 case ToySize::medium: return "Medium"; 141 case ToySize::large: return "Large"; 142 case ToySize::extra_large: return "Extra Large"; 143 default: return "Unknown"; 144 } 145 }
源代码demo4.cpp
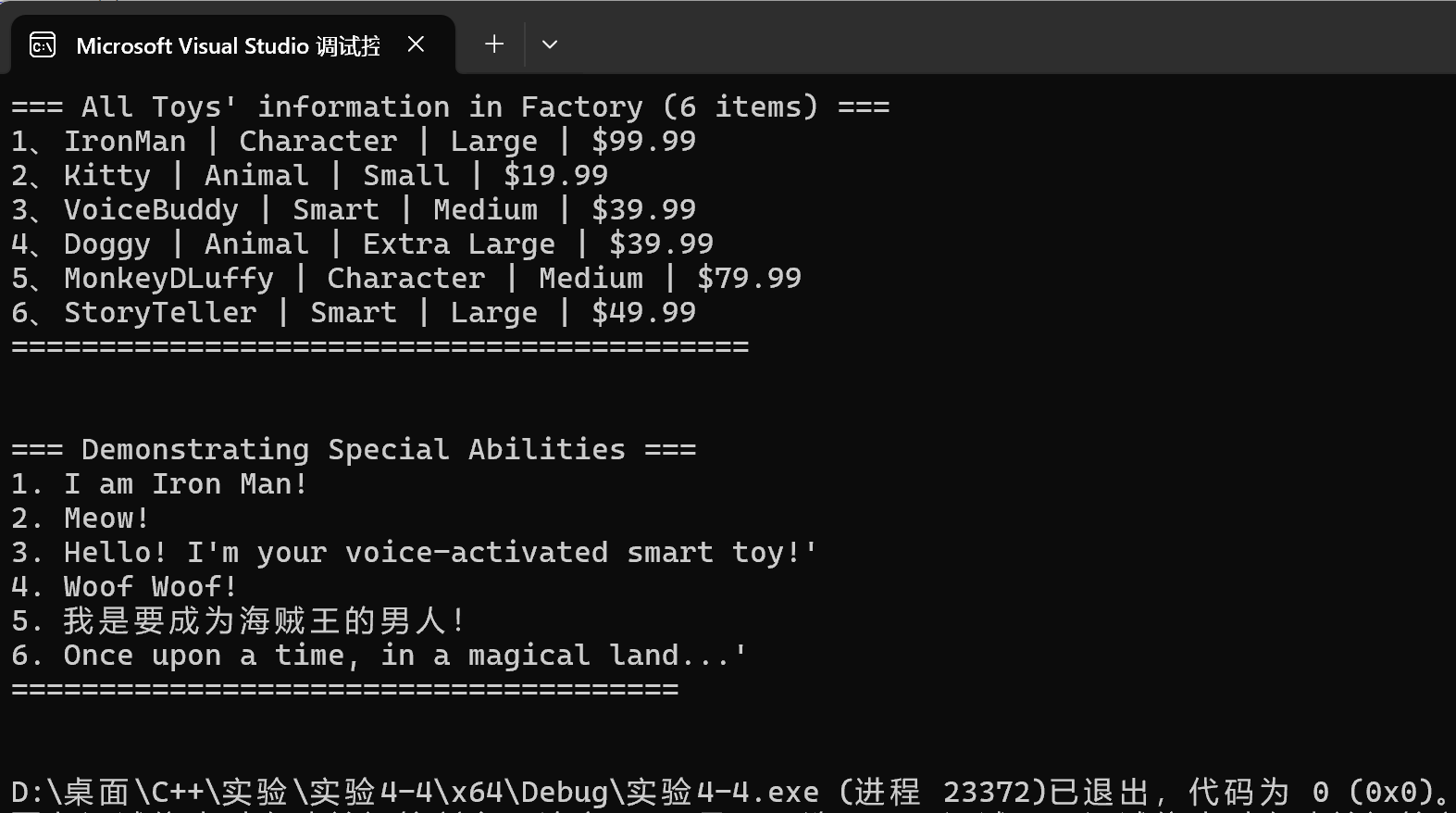
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include "Toy.hpp" 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 void test() { 7 8 ToyFactory factory; 9 10 factory.addToy(ToyType::character, "IronMan", 99.99, ToySize::large, "IronMan"); 11 factory.addToy(ToyType::animal, "Kitty", 19.99, ToySize::small, "Cat"); 12 factory.addToy(ToyType::smart, "VoiceBuddy", 39.99, ToySize::medium, "Voice"); 13 factory.addToy(ToyType::animal, "Doggy", 39.99, ToySize::extra_large, "Dog"); 14 factory.addToy(ToyType::character, "MonkeyDLuffy", 79.99, ToySize::medium, "Luffy"); 15 factory.addToy(ToyType::smart, "StoryTeller", 49.99, ToySize::large, "Story"); 16 17 // 显示所有玩具信息 18 factory.displayAllToys(); 19 20 // 演示所有特殊功能 21 factory.demonstrateAllAbilities(); 22 } 23 24 int main() 25 { 26 test(); 27 }
运行结果测试截图





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号