原题https://www.patest.cn/contests/pat-t-practise/1011:

Sample Input:
8 3 0 0 1 0 1 1 3 0 0 1 1 0 1 3 0 0 1 0 1 1 3 0 0 1 1 0 2 4 0 4 1 4 1 0 0 0 4 4 0 4 1 0 1 0 0 3 0 0 1 1 0 1 4 2 3 1 4 1 7 2 7 5 10 10 10 12 12 12 14 11 14 10 3 28 35 29 35 29 37 3 7 9 8 11 8 9 5 87 26 92 26 92 23 90 22 87 22 5 0 0 2 0 1 1 1 2 0 2 4 0 0 1 1 2 1 2 0 4 0 0 0 1 1 1 2 0 4 0 0 0 1 1 1 2 0
Sample Output:
YES NO YES YES YES YES NO YES
题目大意说的就是给了两个可能经过90度倍数旋转、镜像、平移的多边形,判断它们是否是由一个垂直于坐标轴的矩形用一条直线切分而成的。
此题有两种思路:
1.枚举旋转、镜像情况,找出两个多边形两条平行且相等的边作为公共边,“焊接”为一个新的多边形,再判断这个多边形是否为矩形且垂直于坐标轴
2.进行分类讨论,有三角形+三角形,三角形+四边形,三角形+五边形,四边形+四边形几种情况
我所用的当然是第一种做法,避免了这些分支情况。
这种做法的难点主要是焊接的过程,需要删去3点共线的中间点,并且一开始最好能把凹多边形的情况排除,再根据一定的顶点时针顺序规则,就可以防止焊接时两个多边形相交的情况。
简单的示意图:
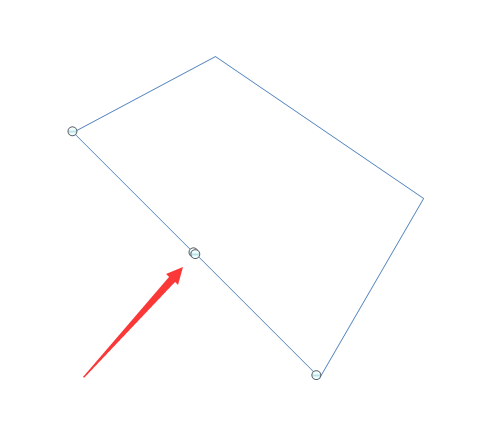
图1:三点共线,需要剔除中间这个,方便后续的矩形判断
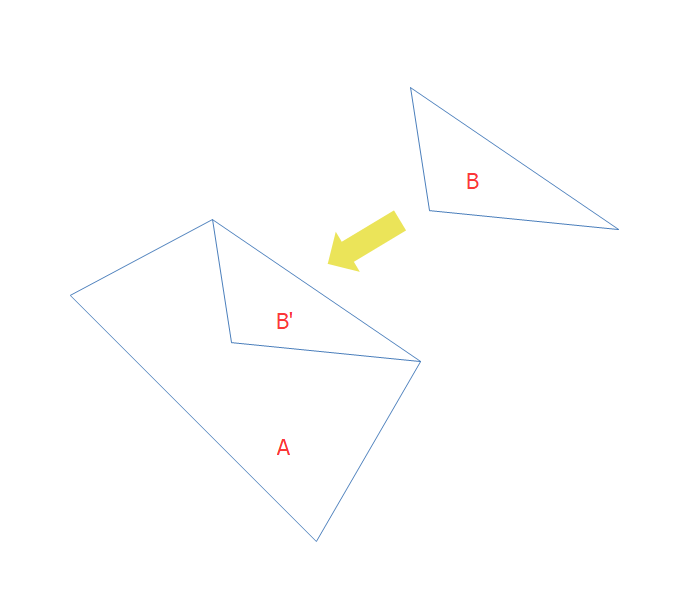
图2:我们不希望看到的情况,B平移为B',与A相交
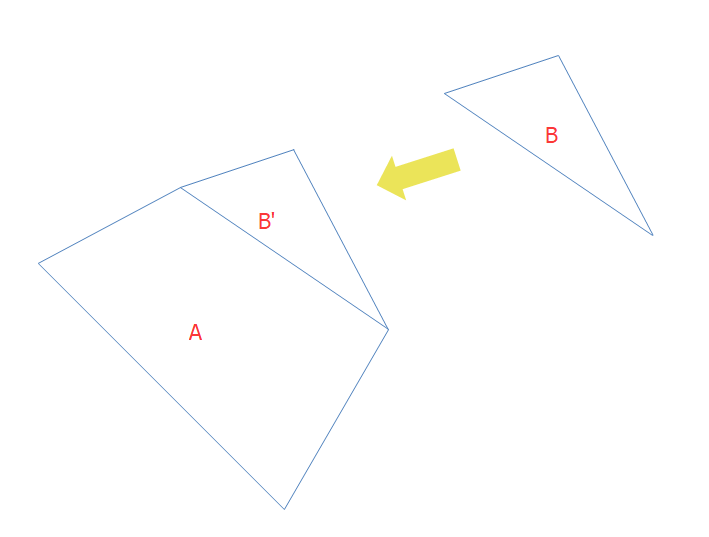
图3:正常情况
虽然搜了各种情况,效率还是可以的
#include "stdafx.h" #include <stdlib.h> #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include<string> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; class Vector2D { public: Vector2D() { } void rotate(int angle) {//点绕(0,0)旋转 long long x0 = x; long long y0 = y; if (angle == 0) { } else if (angle == 90) { x = -y0; y = x0; } else if (angle == 180) { x = -x0; y = -y0; } else if (angle == 270) { x = y0; y = -x0; } } Vector2D(long long x, long long y) { this->x = x; this->y = y; } long long x = 0; long long y = 0; bool parrallel2axis() {//向量是否垂直于坐标轴 if (x == 0 || y == 0) { return true; } return false; } static long long chaji(Vector2D a, Vector2D b) {//叉积 return a.x*b.y - b.x*a.y; } static bool is_shun_clock(Vector2D p1, Vector2D p2, Vector2D p3) {//三点是否符合顺时针 Vector2D a = p1 - p2; Vector2D b = p2 - p3; if (chaji(a, b)<0) { return true; } return false; } Vector2D operator-(Vector2D b) { return Vector2D(x - b.x, y - b.y); } Vector2D operator+(Vector2D b) { return Vector2D(x + b.x, y + b.y); } bool operator==(Vector2D v) { if (x == v.x&&y == v.y) { return true; } return false; } long long operator*(Vector2D b) {//点积 return x*b.x + y*b.y; } long long length_square() {//长度的平方 return x*x + y*y; } }; class Polygon { public: vector<Vector2D> points; //输入处理后都用顺时针存放 Vector2D vct_edg(int i) {//取第i条边到下一条边的向量 return Vector2D(points[(i + 1) % points.size()] - points[i]); } void get_all_edge_lengthsquare(vector<long long>& edges_lengthsquare) { int n = points.size(); edges_lengthsquare.resize(n); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { Vector2D now_vct = points[(i + 1) % n] - points[i]; edges_lengthsquare[i] = (now_vct.length_square()); } } static bool all_the_same(vector<long long>& a, vector<long long>& b, int n) { for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { if (a[i] != b[i]) { return false; } } return true; } void find_zhijiaos_point_index(vector<Vector2D>& ans_points) { //获取多边形中的所有直角角点 ans_points.resize(0); int n = points.size(); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { Vector2D& p1 = points[(i - 1 + n) % n]; Vector2D& p2 = points[i]; Vector2D& p3 = points[(i + 1) % n]; if ((p2 - p1)*(p3 - p2) == 0) { ans_points.push_back(p2); } } } void try_invert2clock() {//尝试把点弄成顺时针顺序 //处理后并不确保一定不是凹多边形 if (Vector2D::is_shun_clock(points[0], points[1], points[2])) { } else { vector<Vector2D> points_ = points; for (int i = 0; i < points.size(); i++) { points[i] = points_[points.size() - 1 - i]; } } } int next_point(int i) {//某点的顺时针下一点 return (i + 1) % points.size(); } int last_point(int i) {//某点的顺时针下一点(逆时针下一点) return (i - 1 + points.size()) % points.size(); } bool check_shunshizhen() { //如果不是所有点满足顺时针return false; for (int i = 0; i < points.size(); i++) { if (!Vector2D::is_shun_clock(points[last_point(i)], points[i], points[next_point(i)])) { return false; } } return true; } void mirror_me() {//随便哪条轴都是镜像,反正后面要旋转,坐标不重要反正要平移 for (int i = 0; i < points.size(); i++) { points[i].x = -points[i].x; } try_invert2clock();//镜像操作会导致不是顺时针,要弄回来 } void rotate_me(int angle) { for (int i = 0; i < points.size(); i++) { points[i].rotate(angle); } } int insert_point(Vector2D& p, int index_b4) {//index_b4是指插在那个点后面(顺时针的下一位) int index_maybe = next_point(index_b4); points.insert(points.begin() + index_maybe, p); int index_return = index_maybe; return index_return; } void trans_me(Vector2D vct_trans) { for (int i = 0; i < points.size(); i++) { points[i] = points[i] + vct_trans; } } bool three_point_in_line(Vector2D& a, Vector2D& b, Vector2D& c) {//三点是否共线 if (Vector2D::chaji(b - a, c - b) == 0) { //用叉积判断其实不能确保b是加在a,c之间的,不过之前排除了凹多边形的情况了 return true; } return false; } void delete_extra_points() {//删除由于共线多余的点 vector<bool> point_2_delete(points.size(), false); for (int i = 0; i < points.size(); i++) { int i_b4 = last_point(i); int i_next = next_point(i); Vector2D p = points[i]; Vector2D p_b4 = points[i_b4]; Vector2D p_next = points[i_next];//按理说不会出现p不在中间却共线,因为都是凸的 if (three_point_in_line(p_b4, p, p_next)) { point_2_delete[i] = true; } } vector<Vector2D> points_new; for (int i = 0; i < points.size(); i++) { if (point_2_delete[i]) { } else { points_new.push_back(points[i]); } } points = points_new; } static Polygon try_combine(Polygon a, int i_a, Polygon b, int i_b) { //给定两个多边形以及它们各自公共边起点下标,拼接成一个新的多边形 int i_a_next = a.next_point(i_a); int i_b_next = b.next_point(i_b); Vector2D vct_trans = a.points[i_a] - b.points[i_b_next]; b.trans_me(vct_trans); Polygon& ans = a; int p2insert = b.next_point(i_b_next); int index_b4 = i_a; while (p2insert != i_b) { index_b4 = ans.insert_point(b.points[p2insert], index_b4); p2insert = b.next_point(p2insert); } ans.delete_extra_points(); return ans; } static bool can_combine(Polygon& a, Polygon& b) { if (!a.check_shunshizhen() || !b.check_shunshizhen()) { return false; } for (int jx = 0; jx < 2; jx++) {//是否镜像枚举 Polygon a_jx = a; Polygon b_jx = b; if (jx == 1) { b_jx.mirror_me(); } for (int anglenow = 0; anglenow < 360; anglenow += 90) {//旋转角度枚举 Polygon a_jx_rot = a_jx; Polygon b_jx_rot = b_jx; b_jx_rot.rotate_me(anglenow); for (int i_a = 0; i_a < a_jx_rot.points.size(); i_a++) { Vector2D& pa1 = a_jx_rot.points[i_a]; Vector2D& pa2 = a_jx_rot.points[a_jx_rot.next_point(i_a)]; for (int i_b = 0; i_b < b_jx_rot.points.size(); i_b++) { Vector2D& pb1 = b_jx_rot.points[i_b]; Vector2D& pb2 = b_jx_rot.points[b_jx_rot.next_point(i_b)]; if ((pa2 - pa1) == (pb1 - pb2)) { //这里要注意后面是pb1 - pb2,与a要反一反, //恰好确保了两个多边形相背而不会相交 Polygon ans_now = try_combine(a_jx_rot, i_a, b_jx_rot, i_b); if (ans_now.is_rect()) { if (ans_now.vct_edg(0).parrallel2axis()) return true; } } } } } } return false; } bool is_rect() {//是不是矩形 vector<Vector2D> zhijiao_points; find_zhijiaos_point_index(zhijiao_points); if (zhijiao_points.size() == 4 && points.size() == 4) { return true; } return false; } }; void myinput(int& n, vector<Polygon>& polys) { cin >> n; polys.resize(2 * n); int k = 0; long long xnow = 0, ynow = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 2 * n; i++) { cin >> k; Polygon& poly = polys[i]; poly.points.resize(k); for (int j = 0; j < k; j++) { cin >> xnow >> ynow; poly.points[j] = Vector2D(xnow, ynow); } poly.try_invert2clock(); } } int main() { vector<Polygon> polys; int n = 0; myinput(n, polys); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { Polygon& p1 = polys[2 * i]; Polygon& p2 = polys[2 * i + 1]; if (Polygon::can_combine(p1, p2)) cout << "YES" << "\n"; else cout << "NO" << "\n"; } system("pause"); return 0; }


