数据结构与算法(八)
哈希表
哈希表是一种数据结构,不是算法。
Google 上机题场景
有一个公司,当有新的员工来报道时,要求将该员工的信息加入 (id,性别,年龄,住址..), 当输入该员工的 id 时,要求查
找到该员工的 所有信息。
要求:不使用数据库、尽量节省内存、速度越快越好。
那么这道题,就可以使用哈希表
基本介绍
散列表(Hash table),也叫哈希表。是根据 关键码值(key value) 而直接进行访问的数据结构。
也就是说,它 通过关键码值映射到表中的一个位置来访问记录,以加快查找的速度。这个映射函数叫做 散列函数,存放记录的数组叫做 散列表 。
它的由来如下图所述:
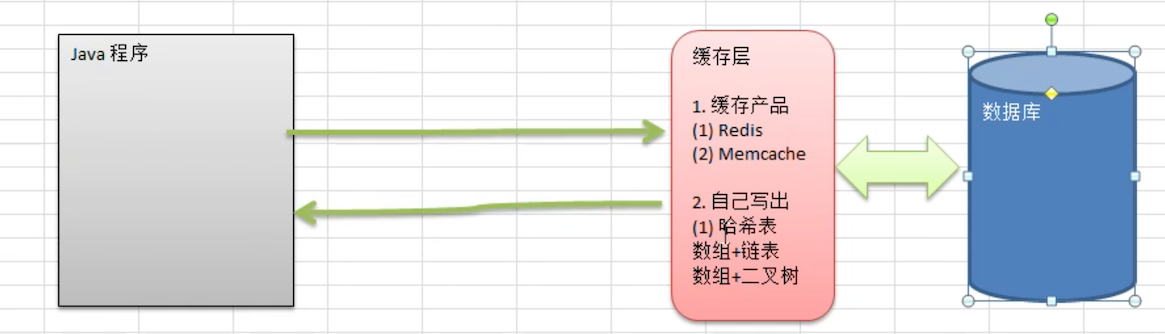
在早些年代,没有缓存产品出现,或则在某些场景中使用缓存产品太重了,就自己写缓存实现:
- 哈希表 + 链表
- 数组 + 二叉树
哈希表在内存中的结构就如下图所示:
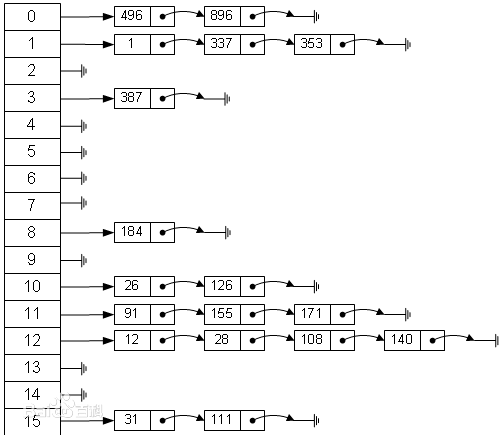
如上所述:
-
左侧有 15 个元素的数组(可以用数组实现),就是一个表
-
该表中存放的是一个链表
-
通过 散列函数,计算出一个位置,然后在把数据存储到这个链表上
比如上面有 15 个,可以计算出散列值后,再取模。
111 % 15,就定位在了某一个元素位置上。
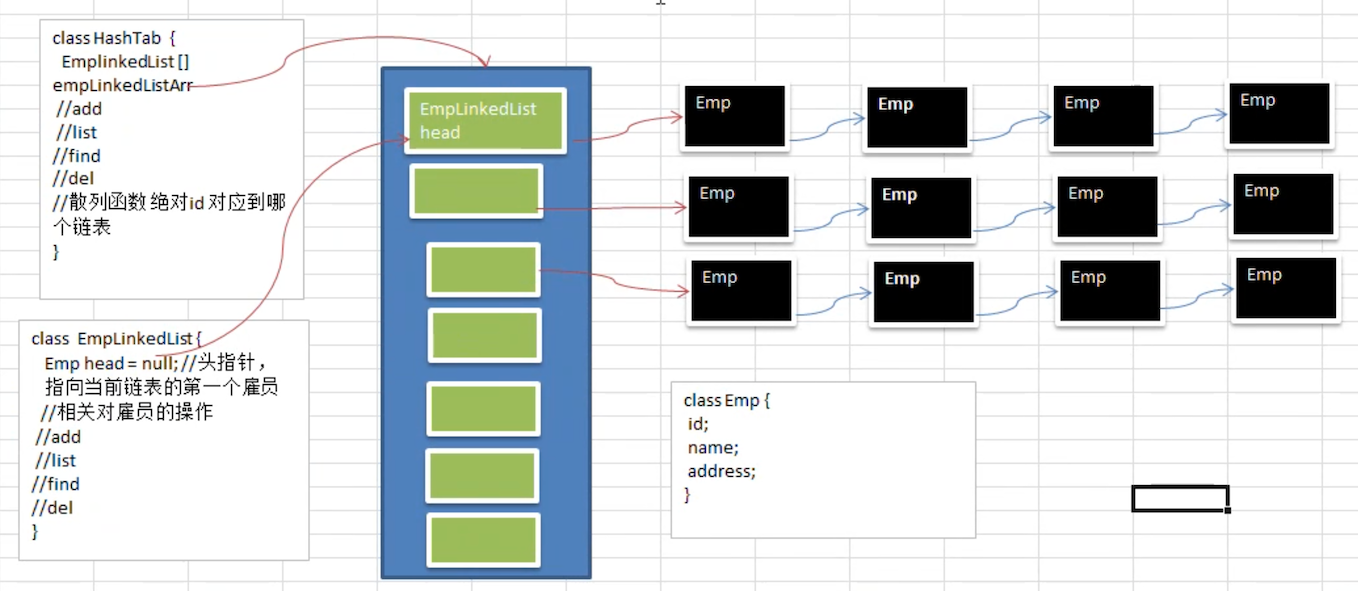
思路分析
-
HashTab:哈希表,也就是上图蓝色区块
要实现 add、list、find、del 函数,至少还需要 散列函数,用来决定 id 对应到哪个链表
-
EmpLinkedList:链表
对相关雇员的操作
代码实现
//定义员工类
class Employee{
public int no;
public String name;
public Employee next;//下一个节点的位置,默认为null
public Employee(int no, String name) {
this.no = no;
this.name = name;
}
}
//定义链表
class EmpLinkedList{
private Employee head;//头结点,指向链表第一个元素
//添加
public void add(Employee e){
if(head == null){
//说明添加为第一次
head = e;
}else{
//将其添加到链表结尾
Employee curEmp = head;
while(true){
if(curEmp.next == null){
break;
}
curEmp = curEmp.next;
}
curEmp.next = e;
}
}
//遍历链表
public void list(){
if(head == null){
System.out.println("当前链表为空");
return;
}
Employee curEmp = head;
while(true){
System.out.printf("=> 编号:%d 名字:%s\t",curEmp.no,curEmp.name);
if(curEmp.next == null){
break;
}
curEmp = curEmp.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
//查找指定元素
public Employee findById(int no){
if(head == null){
return null;
}
Employee curEmp = head;
while(true){
if(curEmp.no == no){//找到了
break;
}
if(curEmp.next == null){//没有找到
curEmp = null;
break;
}
curEmp = curEmp.next;
}
return curEmp;
}
//删除员工信息
public boolean delete(int no){
if(head == null){
return false;
}
//先判断第一个是不是要删除的元素
if(head.no == no){
if(head.next == null){
//只有一个元素
head = null;
}else{
head = head.next;
}
return true;
}else{//删除的元素不是第一个
Employee curEmp = head;
while(true){
if(curEmp.next == null){
return false;
}
if(curEmp.next.no == no){
curEmp.next = curEmp.next.next;
return true;
}
curEmp = curEmp.next;//指针后移
}
}
}
}
//哈希表
class HashTab{
private EmpLinkedList[] empLinkedListArray;//存储数据的链表数组
private int size;//哈希表中数组的大小
public HashTab(int size){
this.size = size;
empLinkedListArray = new EmpLinkedList[size];
//进行初始化
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++){
empLinkedListArray[i] = new EmpLinkedList();
}
}
//哈希表散列函数
public int hashFun(int no){
return no%size;
}
//添加元素
public void add(Employee e){
//先找到在哈希表中的位置
int hashIndex = hashFun(e.no);
empLinkedListArray[hashIndex].add(e);
}
//遍历元素
public void list(){
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++){
System.out.print("第"+(i+1)+"链表: \t");
empLinkedListArray[i].list();
}
}
//查找元素,没有找到返回为null
public Employee findById(int no){
int hashIndex = hashFun(no);
Employee employee = empLinkedListArray[hashIndex].findById(no);
return employee;
}
//删除指定编号员工,删除成功返回true,失败返回false
public boolean delete(int no){
int hashIndex = hashFun(no);
boolean flag = empLinkedListArray[hashIndex].delete(no);
return flag;
}
}
代码测试
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
HashTab hashTab = new HashTab(7);
String index = null;
boolean flag = true;
while(flag){
System.out.println("add 添加员工");
System.out.println("show 显示员工");
System.out.println("find 查找员工");
System.out.println("delete 删除员工");
System.out.println("exit 退出系统");
System.out.println("请输入指令:");
index = scanner.next();
switch(index){
case "add":
System.out.println("请输入员工id:");
int id = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入员工名字:");
String name = scanner.next();
Employee e = new Employee(id,name);
hashTab.add(e);
break;
case "show":
hashTab.list();
break;
case "find":
System.out.println("请输入要查找的员工id:");
id = scanner.nextInt();
e = hashTab.findById(id);
if(e != null){//找到
System.out.printf("找到员工编号:%d,名字为%s\n",e.no,e.name);
}else{
System.out.printf("没有找到员工编号%d的员工\n",id);
}
break;
case "delete":
System.out.println("请输入删除员工编号:");
id = scanner.nextInt();
boolean delFlag = hashTab.delete(id);
if(delFlag){
System.out.printf("删除员工%d成功\n",id);
}else{
System.out.printf("删除员工%d失败\n",id);
}
break;
case "exit":
scanner.close();
flag = false;
break;
default:
System.out.println("输入指令有误,重新输入!");
break;
}
}
System.out.println("测试程序退出");


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号