字母表数据结构
package string;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut;
public class Alphabet {
public static final Alphabet BINARY = new Alphabet("01");
public static final Alphabet OCTAL = new Alphabet("01234567");
public static final Alphabet DECIMAL = new Alphabet("0123456789");
public static final Alphabet HEXADECIMAL = new Alphabet("0123456789ABCDEF");
public static final Alphabet DNA = new Alphabet("ACGT");
public static final Alphabet LOWERCASE = new Alphabet("abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz");
public static final Alphabet UPPERCASE = new Alphabet("ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ");
public static final Alphabet PROTEIN = new Alphabet("ACDEFGHIKLMNPQRSTVWY");
public static final Alphabet BASE64 = new Alphabet("ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz0123456789+/");
public static final Alphabet ASCII = new Alphabet(128);
public static final Alphabet EXTENDED_ASCII = new Alphabet(256);
public static final Alphabet UNICODE16 = new Alphabet(65536);
private char[] alphabet; // the characters in the alphabet
private int[] inverse; // indices
private final int R; // the radix of the alphabet
public Alphabet(String alpha) {
// check that alphabet contains no duplicate chars
boolean[] unicode = new boolean[Character.MAX_VALUE];
for (int i = 0; i < alpha.length(); i++) {
char c = alpha.charAt(i);
if (unicode[c])
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal alphabet: repeated character = '" + c + "'");
unicode[c] = true;
}
alphabet = alpha.toCharArray();
R = alpha.length();
inverse = new int[Character.MAX_VALUE];
for (int i = 0; i < inverse.length; i++)
inverse[i] = -1;
// can't use char since R can be as big as 65,536
for (int c = 0; c < R; c++)
inverse[alphabet[c]] = c;
}
private Alphabet(int radix) {
this.R = radix;
alphabet = new char[R];
inverse = new int[R];
// can't use char since R can be as big as 65,536
for (int i = 0; i < R; i++)
alphabet[i] = (char) i;
for (int i = 0; i < R; i++)
inverse[i] = i;
}
public Alphabet() {
this(256);
}
public boolean contains(char c) {
return inverse[c] != -1;
}
@Deprecated
public int R() {
return R;
}
public int radix() {
return R;
}
public int lgR() {
int lgR = 0;
for (int t = R-1; t >= 1; t /= 2)
lgR++;
return lgR;
}
public int toIndex(char c) {
if (c >= inverse.length || inverse[c] == -1) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Character " + c + " not in alphabet");
}
return inverse[c];
}
public int[] toIndices(String s) {
char[] source = s.toCharArray();
int[] target = new int[s.length()];
for (int i = 0; i < source.length; i++)
target[i] = toIndex(source[i]);
return target;
}
public char toChar(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= R) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("index must be between 0 and " + R + ": " + index);
}
return alphabet[index];
}
public String toChars(int[] indices) {
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder(indices.length);
for (int i = 0; i < indices.length; i++)
s.append(toChar(indices[i]));
return s.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] encoded1 = Alphabet.BASE64.toIndices("NowIsTheTimeForAllGoodMen");
String decoded1 = Alphabet.BASE64.toChars(encoded1);
StdOut.println(decoded1);
int[] encoded2 = Alphabet.DNA.toIndices("AACGAACGGTTTACCCCG");
String decoded2 = Alphabet.DNA.toChars(encoded2);
StdOut.println(decoded2);
int[] encoded3 = Alphabet.DECIMAL.toIndices("01234567890123456789");
String decoded3 = Alphabet.DECIMAL.toChars(encoded3);
StdOut.println(decoded3);
}
}
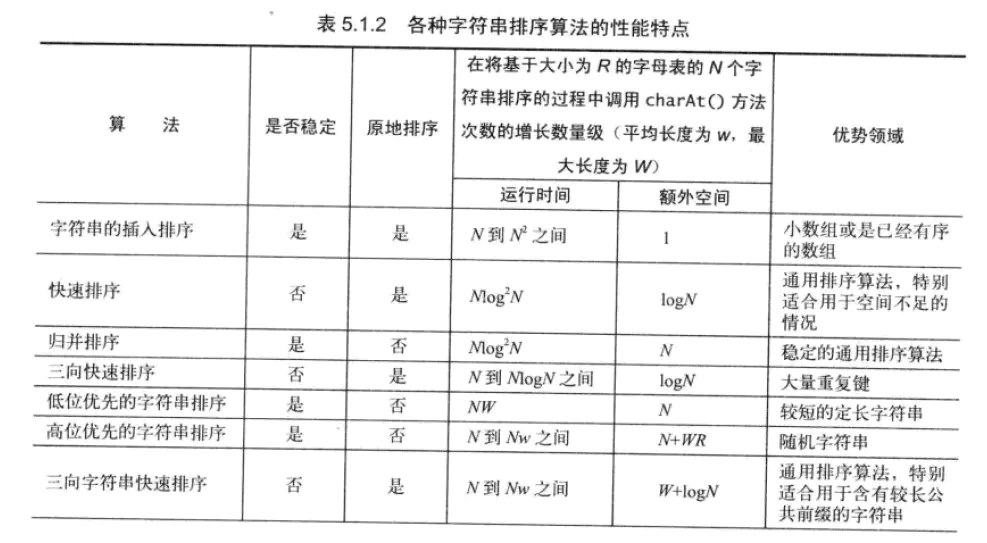
一.字符串排序
1.键索引计数法
2.低位优先的字符串排序(字符串长度相同)
package string;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdIn;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut;
public class LSD {
private static final int BITS_PER_BYTE = 8;
private LSD() { }
public static void sort(String[] a, int w) {
int n = a.length;
int R = 256; // extend ASCII alphabet size
String[] aux = new String[n];
for (int d = w-1; d >= 0; d--) {
// sort by key-indexed counting on dth character
// compute frequency counts
int[] count = new int[R+1];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
count[a[i].charAt(d) + 1]++;
// compute cumulates
for (int r = 0; r < R; r++)
count[r+1] += count[r];
// move data
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
aux[count[a[i].charAt(d)]++] = a[i];
// copy back
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
a[i] = aux[i];
}
}
public static void sort(int[] a) {
final int BITS = 32; // each int is 32 bits
final int R = 1 << BITS_PER_BYTE; // each bytes is between 0 and 255
final int MASK = R - 1; // 0xFF
final int w = BITS / BITS_PER_BYTE; // each int is 4 bytes
int n = a.length;
int[] aux = new int[n];
for (int d = 0; d < w; d++) {
// compute frequency counts
int[] count = new int[R+1];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int c = (a[i] >> BITS_PER_BYTE*d) & MASK;
count[c + 1]++;
}
// compute cumulates
for (int r = 0; r < R; r++)
count[r+1] += count[r];
// for most significant byte, 0x80-0xFF comes before 0x00-0x7F
if (d == w-1) {
int shift1 = count[R] - count[R/2];
int shift2 = count[R/2];
for (int r = 0; r < R/2; r++)
count[r] += shift1;
for (int r = R/2; r < R; r++)
count[r] -= shift2;
}
// move data
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int c = (a[i] >> BITS_PER_BYTE*d) & MASK;
aux[count[c]++] = a[i];
}
// copy back
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
a[i] = aux[i];
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] a = StdIn.readAllStrings();
int n = a.length;
// check that strings have fixed length
int w = a[0].length();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
assert a[i].length() == w : "Strings must have fixed length";
// sort the strings
sort(a, w);
// print results
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
StdOut.println(a[i]);
}
}
3.高位优先的字符串排序
package string;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdIn;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut;
public class MSD {
private static final int BITS_PER_BYTE = 8;
private static final int BITS_PER_INT = 32; // each Java int is 32 bits
private static final int R = 256; // extended ASCII alphabet size
private static final int CUTOFF = 15; // cutoff to insertion sort
// do not instantiate
private MSD() { }
public static void sort(String[] a) {
int n = a.length;
String[] aux = new String[n];
sort(a, 0, n-1, 0, aux);
}
// return dth character of s, -1 if d = length of string
private static int charAt(String s, int d) {
assert d >= 0 && d <= s.length();
if (d == s.length()) return -1;
return s.charAt(d);
}
// sort from a[lo] to a[hi], starting at the dth character
private static void sort(String[] a, int lo, int hi, int d, String[] aux) {
// cutoff to insertion sort for small subarrays
if (hi <= lo + CUTOFF) {
insertion(a, lo, hi, d);
return;
}
// compute frequency counts
int[] count = new int[R+2];
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++) {
int c = charAt(a[i], d);
count[c+2]++;
}
// transform counts to indicies
for (int r = 0; r < R+1; r++)
count[r+1] += count[r];
// distribute
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++) {
int c = charAt(a[i], d);
aux[count[c+1]++] = a[i];
}
// copy back
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++)
a[i] = aux[i - lo];
// recursively sort for each character (excludes sentinel -1)
for (int r = 0; r < R; r++)
sort(a, lo + count[r], lo + count[r+1] - 1, d+1, aux);
}
// insertion sort a[lo..hi], starting at dth character
private static void insertion(String[] a, int lo, int hi, int d) {
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++)
for (int j = i; j > lo && less(a[j], a[j-1], d); j--)
exch(a, j, j-1);
}
// exchange a[i] and a[j]
private static void exch(String[] a, int i, int j) {
String temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
}
// is v less than w, starting at character d
private static boolean less(String v, String w, int d) {
// assert v.substring(0, d).equals(w.substring(0, d));
for (int i = d; i < Math.min(v.length(), w.length()); i++) {
if (v.charAt(i) < w.charAt(i)) return true;
if (v.charAt(i) > w.charAt(i)) return false;
}
return v.length() < w.length();
}
public static void sort(int[] a) {
int n = a.length;
int[] aux = new int[n];
sort(a, 0, n-1, 0, aux);
}
// MSD sort from a[lo] to a[hi], starting at the dth byte
private static void sort(int[] a, int lo, int hi, int d, int[] aux) {
// cutoff to insertion sort for small subarrays
if (hi <= lo + CUTOFF) {
insertion(a, lo, hi, d);
return;
}
// compute frequency counts (need R = 256)
int[] count = new int[R+1];
int mask = R - 1; // 0xFF;
int shift = BITS_PER_INT - BITS_PER_BYTE*d - BITS_PER_BYTE;
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++) {
int c = (a[i] >> shift) & mask;
count[c + 1]++;
}
// transform counts to indicies
for (int r = 0; r < R; r++)
count[r+1] += count[r];
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++) {
int c = (a[i] >> shift) & mask;
aux[count[c]++] = a[i];
}
// copy back
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++)
a[i] = aux[i - lo];
// no more bits
if (d == 4) return;
// recursively sort for each character
if (count[0] > 0)
sort(a, lo, lo + count[0] - 1, d+1, aux);
for (int r = 0; r < R; r++)
if (count[r+1] > count[r])
sort(a, lo + count[r], lo + count[r+1] - 1, d+1, aux);
}
// TODO: insertion sort a[lo..hi], starting at dth character
private static void insertion(int[] a, int lo, int hi, int d) {
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++)
for (int j = i; j > lo && a[j] < a[j-1]; j--)
exch(a, j, j-1);
}
// exchange a[i] and a[j]
private static void exch(int[] a, int i, int j) {
int temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] a = StdIn.readAllStrings();
int n = a.length;
sort(a);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
StdOut.println(a[i]);
}
}
4.三向字符串快速排序
package string;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdIn;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdRandom;
public class Quick3string {
private static final int CUTOFF = 15; // cutoff to insertion sort
// do not instantiate
private Quick3string() { }
public static void sort(String[] a) {
StdRandom.shuffle(a);
sort(a, 0, a.length-1, 0);
assert isSorted(a);
}
// return the dth character of s, -1 if d = length of s
private static int charAt(String s, int d) {
assert d >= 0 && d <= s.length();
if (d == s.length()) return -1;
return s.charAt(d);
}
// 3-way string quicksort a[lo..hi] starting at dth character
private static void sort(String[] a, int lo, int hi, int d) {
// cutoff to insertion sort for small subarrays
if (hi <= lo + CUTOFF) {
insertion(a, lo, hi, d);
return;
}
int lt = lo, gt = hi;
int v = charAt(a[lo], d);
int i = lo + 1;
while (i <= gt) {
int t = charAt(a[i], d);
if (t < v) exch(a, lt++, i++);
else if (t > v) exch(a, i, gt--);
else i++;
}
// a[lo..lt-1] < v = a[lt..gt] < a[gt+1..hi].
sort(a, lo, lt-1, d);
if (v >= 0) sort(a, lt, gt, d+1);
sort(a, gt+1, hi, d);
}
// sort from a[lo] to a[hi], starting at the dth character
private static void insertion(String[] a, int lo, int hi, int d) {
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++)
for (int j = i; j > lo && less(a[j], a[j-1], d); j--)
exch(a, j, j-1);
}
// exchange a[i] and a[j]
private static void exch(String[] a, int i, int j) {
String temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
}
// is v less than w, starting at character d
// DEPRECATED BECAUSE OF SLOW SUBSTRING EXTRACTION IN JAVA 7
// private static boolean less(String v, String w, int d) {
// assert v.substring(0, d).equals(w.substring(0, d));
// return v.substring(d).compareTo(w.substring(d)) < 0;
// }
// is v less than w, starting at character d
private static boolean less(String v, String w, int d) {
assert v.substring(0, d).equals(w.substring(0, d));
for (int i = d; i < Math.min(v.length(), w.length()); i++) {
if (v.charAt(i) < w.charAt(i)) return true;
if (v.charAt(i) > w.charAt(i)) return false;
}
return v.length() < w.length();
}
// is the array sorted
private static boolean isSorted(String[] a) {
for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++)
if (a[i].compareTo(a[i-1]) < 0) return false;
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// read in the strings from standard input
String[] a = StdIn.readAllStrings();
int n = a.length;
// sort the strings
sort(a);
// print the results
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
StdOut.println(a[i]);
}
}
二.单词查找树
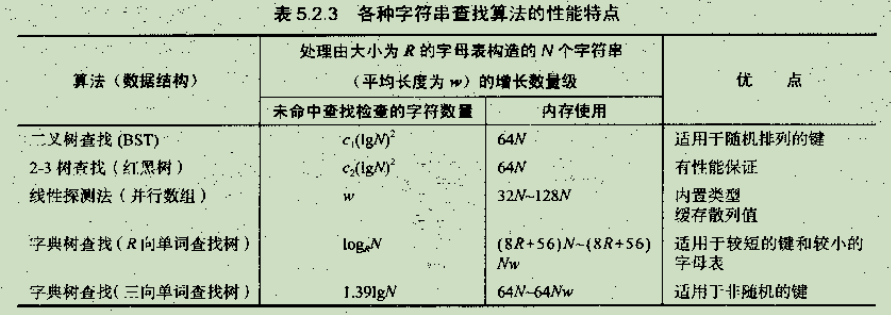
1.基于单词查找树的符号表
package string;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.Queue;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdIn;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut;
public class TrieST<Value> {
private static final int R = 256; // extended ASCII
private Node root; // root of trie
private int n; // number of keys in trie
private static class Node {
private Object val;
private Node[] next = new Node[R];
}
public TrieST() {
}
public Value get(String key) {
if (key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument to get() is null");
Node x = get(root, key, 0);
if (x == null) return null;
return (Value) x.val;
}
public boolean contains(String key) {
if (key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument to contains() is null");
return get(key) != null;
}
private Node get(Node x, String key, int d) {
if (x == null) return null;
if (d == key.length()) return x;
char c = key.charAt(d);
return get(x.next[c], key, d+1);
}
public void put(String key, Value val) {
if (key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("first argument to put() is null");
if (val == null) delete(key);
else root = put(root, key, val, 0);
}
private Node put(Node x, String key, Value val, int d) {
if (x == null) x = new Node();
if (d == key.length()) {
if (x.val == null) n++;
x.val = val;
return x;
}
char c = key.charAt(d);
x.next[c] = put(x.next[c], key, val, d+1);
return x;
}
public int size() {
return n;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size() == 0;
}
public Iterable<String> keys() {
return keysWithPrefix("");
}
public Iterable<String> keysWithPrefix(String prefix) {
Queue<String> results = new Queue<String>();
Node x = get(root, prefix, 0);
collect(x, new StringBuilder(prefix), results);
return results;
}
private void collect(Node x, StringBuilder prefix, Queue<String> results) {
if (x == null) return;
if (x.val != null) results.enqueue(prefix.toString());
for (char c = 0; c < R; c++) {
prefix.append(c);
collect(x.next[c], prefix, results);
prefix.deleteCharAt(prefix.length() - 1);
}
}
public Iterable<String> keysThatMatch(String pattern) {
Queue<String> results = new Queue<String>();
collect(root, new StringBuilder(), pattern, results);
return results;
}
private void collect(Node x, StringBuilder prefix, String pattern, Queue<String> results) {
if (x == null) return;
int d = prefix.length();
if (d == pattern.length() && x.val != null)
results.enqueue(prefix.toString());
if (d == pattern.length())
return;
char c = pattern.charAt(d);
if (c == '.') {
for (char ch = 0; ch < R; ch++) {
prefix.append(ch);
collect(x.next[ch], prefix, pattern, results);
prefix.deleteCharAt(prefix.length() - 1);
}
}
else {
prefix.append(c);
collect(x.next[c], prefix, pattern, results);
prefix.deleteCharAt(prefix.length() - 1);
}
}
public String longestPrefixOf(String query) {
if (query == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument to longestPrefixOf() is null");
int length = longestPrefixOf(root, query, 0, -1);
if (length == -1) return null;
else return query.substring(0, length);
}
// returns the length of the longest string key in the subtrie
// rooted at x that is a prefix of the query string,
// assuming the first d character match and we have already
// found a prefix match of given length (-1 if no such match)
private int longestPrefixOf(Node x, String query, int d, int length) {
if (x == null) return length;
if (x.val != null) length = d;
if (d == query.length()) return length;
char c = query.charAt(d);
return longestPrefixOf(x.next[c], query, d+1, length);
}
public void delete(String key) {
if (key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument to delete() is null");
root = delete(root, key, 0);
}
private Node delete(Node x, String key, int d) {
if (x == null) return null;
if (d == key.length()) {
if (x.val != null) n--;
x.val = null;
}
else {
char c = key.charAt(d);
x.next[c] = delete(x.next[c], key, d+1);
}
// remove subtrie rooted at x if it is completely empty
if (x.val != null) return x;
for (int c = 0; c < R; c++)
if (x.next[c] != null)
return x;
return null;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// build symbol table from standard input
TrieST<Integer> st = new TrieST<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; !StdIn.isEmpty(); i++) {
String key = StdIn.readString();
st.put(key, i);
}
// print results
if (st.size() < 100) {
StdOut.println("keys(\"\"):");
for (String key : st.keys()) {
StdOut.println(key + " " + st.get(key));
}
StdOut.println();
}
StdOut.println("longestPrefixOf(\"shellsort\"):");
StdOut.println(st.longestPrefixOf("shellsort"));
StdOut.println();
StdOut.println("longestPrefixOf(\"quicksort\"):");
StdOut.println(st.longestPrefixOf("quicksort"));
StdOut.println();
StdOut.println("keysWithPrefix(\"shor\"):");
for (String s : st.keysWithPrefix("shor"))
StdOut.println(s);
StdOut.println();
StdOut.println("keysThatMatch(\".he.l.\"):");
for (String s : st.keysThatMatch(".he.l."))
StdOut.println(s);
}
}
2.基于三向单词查找树的符号表
package string;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.Queue;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdIn;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut;
public class TST<Value> {
private int n; // size
private Node<Value> root; // root of TST
private static class Node<Value> {
private char c; // character
private Node<Value> left, mid, right; // left, middle, and right subtries
private Value val; // value associated with string
}
public TST() {
}
public int size() {
return n;
}
public boolean contains(String key) {
if (key == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument to contains() is null");
}
return get(key) != null;
}
public Value get(String key) {
if (key == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("calls get() with null argument");
}
if (key.length() == 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("key must have length >= 1");
Node<Value> x = get(root, key, 0);
if (x == null) return null;
return x.val;
}
// return subtrie corresponding to given key
private Node<Value> get(Node<Value> x, String key, int d) {
if (x == null) return null;
if (key.length() == 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("key must have length >= 1");
char c = key.charAt(d);
if (c < x.c) return get(x.left, key, d);
else if (c > x.c) return get(x.right, key, d);
else if (d < key.length() - 1) return get(x.mid, key, d+1);
else return x;
}
public void put(String key, Value val) {
if (key == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("calls put() with null key");
}
if (!contains(key)) n++;
else if(val == null) n--; // delete existing key
root = put(root, key, val, 0);
}
private Node<Value> put(Node<Value> x, String key, Value val, int d) {
char c = key.charAt(d);
if (x == null) {
x = new Node<Value>();
x.c = c;
}
if (c < x.c) x.left = put(x.left, key, val, d);
else if (c > x.c) x.right = put(x.right, key, val, d);
else if (d < key.length() - 1) x.mid = put(x.mid, key, val, d+1);
else x.val = val;
return x;
}
public String longestPrefixOf(String query) {
if (query == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("calls longestPrefixOf() with null argument");
}
if (query.length() == 0) return null;
int length = 0;
Node<Value> x = root;
int i = 0;
while (x != null && i < query.length()) {
char c = query.charAt(i);
if (c < x.c) x = x.left;
else if (c > x.c) x = x.right;
else {
i++;
if (x.val != null) length = i;
x = x.mid;
}
}
return query.substring(0, length);
}
public Iterable<String> keys() {
Queue<String> queue = new Queue<String>();
collect(root, new StringBuilder(), queue);
return queue;
}
public Iterable<String> keysWithPrefix(String prefix) {
if (prefix == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("calls keysWithPrefix() with null argument");
}
Queue<String> queue = new Queue<String>();
Node<Value> x = get(root, prefix, 0);
if (x == null) return queue;
if (x.val != null) queue.enqueue(prefix);
collect(x.mid, new StringBuilder(prefix), queue);
return queue;
}
// all keys in subtrie rooted at x with given prefix
private void collect(Node<Value> x, StringBuilder prefix, Queue<String> queue) {
if (x == null) return;
collect(x.left, prefix, queue);
if (x.val != null) queue.enqueue(prefix.toString() + x.c);
collect(x.mid, prefix.append(x.c), queue);
prefix.deleteCharAt(prefix.length() - 1);
collect(x.right, prefix, queue);
}
public Iterable<String> keysThatMatch(String pattern) {
Queue<String> queue = new Queue<String>();
collect(root, new StringBuilder(), 0, pattern, queue);
return queue;
}
private void collect(Node<Value> x, StringBuilder prefix, int i, String pattern, Queue<String> queue) {
if (x == null) return;
char c = pattern.charAt(i);
if (c == '.' || c < x.c) collect(x.left, prefix, i, pattern, queue);
if (c == '.' || c == x.c) {
if (i == pattern.length() - 1 && x.val != null) queue.enqueue(prefix.toString() + x.c);
if (i < pattern.length() - 1) {
collect(x.mid, prefix.append(x.c), i+1, pattern, queue);
prefix.deleteCharAt(prefix.length() - 1);
}
}
if (c == '.' || c > x.c) collect(x.right, prefix, i, pattern, queue);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// build symbol table from standard input
TST<Integer> st = new TST<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; !StdIn.isEmpty(); i++) {
String key = StdIn.readString();
st.put(key, i);
}
// print results
if (st.size() < 100) {
StdOut.println("keys(\"\"):");
for (String key : st.keys()) {
StdOut.println(key + " " + st.get(key));
}
StdOut.println();
}
StdOut.println("longestPrefixOf(\"shellsort\"):");
StdOut.println(st.longestPrefixOf("shellsort"));
StdOut.println();
StdOut.println("longestPrefixOf(\"shell\"):");
StdOut.println(st.longestPrefixOf("shell"));
StdOut.println();
StdOut.println("keysWithPrefix(\"shor\"):");
for (String s : st.keysWithPrefix("shor"))
StdOut.println(s);
StdOut.println();
StdOut.println("keysThatMatch(\".he.l.\"):");
for (String s : st.keysThatMatch(".he.l."))
StdOut.println(s);
}
}
三.子字符串查找

1.Knuth-Morris-Pratt字符串查找算法
package string;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut;
public class KMP {
private final int R; // the radix
private int[][] dfa; // the KMP automoton
private char[] pattern; // either the character array for the pattern
private String pat; // or the pattern string
public KMP(String pat) {
this.R = 256;
this.pat = pat;
// build DFA from pattern
int m = pat.length();
dfa = new int[R][m];
dfa[pat.charAt(0)][0] = 1;
for (int x = 0, j = 1; j < m; j++) {
for (int c = 0; c < R; c++)
dfa[c][j] = dfa[c][x]; // Copy mismatch cases.
dfa[pat.charAt(j)][j] = j+1; // Set match case.
x = dfa[pat.charAt(j)][x]; // Update restart state.
}
}
public KMP(char[] pattern, int R) {
this.R = R;
this.pattern = new char[pattern.length];
for (int j = 0; j < pattern.length; j++)
this.pattern[j] = pattern[j];
// build DFA from pattern
int m = pattern.length;
dfa = new int[R][m];
dfa[pattern[0]][0] = 1;
for (int x = 0, j = 1; j < m; j++) {
for (int c = 0; c < R; c++)
dfa[c][j] = dfa[c][x]; // Copy mismatch cases.
dfa[pattern[j]][j] = j+1; // Set match case.
x = dfa[pattern[j]][x]; // Update restart state.
}
}
public int search(String txt) {
// simulate operation of DFA on text
int m = pat.length();
int n = txt.length();
int i, j;
for (i = 0, j = 0; i < n && j < m; i++) {
j = dfa[txt.charAt(i)][j];
}
if (j == m) return i - m; // found
return n; // not found
}
public int search(char[] text) {
// simulate operation of DFA on text
int m = pattern.length;
int n = text.length;
int i, j;
for (i = 0, j = 0; i < n && j < m; i++) {
j = dfa[text[i]][j];
}
if (j == m) return i - m; // found
return n; // not found
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String pat = args[0];
String txt = args[1];
char[] pattern = pat.toCharArray();
char[] text = txt.toCharArray();
KMP kmp1 = new KMP(pat);
int offset1 = kmp1.search(txt);
KMP kmp2 = new KMP(pattern, 256);
int offset2 = kmp2.search(text);
// print results
StdOut.println("text: " + txt);
StdOut.print("pattern: ");
for (int i = 0; i < offset1; i++)
StdOut.print(" ");
StdOut.println(pat);
StdOut.print("pattern: ");
for (int i = 0; i < offset2; i++)
StdOut.print(" ");
StdOut.println(pat);
}
}
2.Boyer-Moore字符串匹配算法
package string;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut;
public class BoyerMoore {
private final int R; // the radix
private int[] right; // the bad-character skip array
private char[] pattern; // store the pattern as a character array
private String pat; // or as a string
public BoyerMoore(String pat) {
this.R = 256;
this.pat = pat;
// position of rightmost occurrence of c in the pattern
right = new int[R];
for (int c = 0; c < R; c++)
right[c] = -1;
for (int j = 0; j < pat.length(); j++)
right[pat.charAt(j)] = j;
}
public BoyerMoore(char[] pattern, int R) {
this.R = R;
this.pattern = new char[pattern.length];
for (int j = 0; j < pattern.length; j++)
this.pattern[j] = pattern[j];
// position of rightmost occurrence of c in the pattern
right = new int[R];
for (int c = 0; c < R; c++)
right[c] = -1;
for (int j = 0; j < pattern.length; j++)
right[pattern[j]] = j;
}
public int search(String txt) {
int m = pat.length();
int n = txt.length();
int skip;
for (int i = 0; i <= n - m; i += skip) {
skip = 0;
for (int j = m-1; j >= 0; j--) {
if (pat.charAt(j) != txt.charAt(i+j)) {
skip = Math.max(1, j - right[txt.charAt(i+j)]);
break;
}
}
if (skip == 0) return i; // found
}
return n; // not found
}
public int search(char[] text) {
int m = pattern.length;
int n = text.length;
int skip;
for (int i = 0; i <= n - m; i += skip) {
skip = 0;
for (int j = m-1; j >= 0; j--) {
if (pattern[j] != text[i+j]) {
skip = Math.max(1, j - right[text[i+j]]);
break;
}
}
if (skip == 0) return i; // found
}
return n; // not found
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String pat = args[0];
String txt = args[1];
char[] pattern = pat.toCharArray();
char[] text = txt.toCharArray();
BoyerMoore boyermoore1 = new BoyerMoore(pat);
BoyerMoore boyermoore2 = new BoyerMoore(pattern, 256);
int offset1 = boyermoore1.search(txt);
int offset2 = boyermoore2.search(text);
// print results
StdOut.println("text: " + txt);
StdOut.print("pattern: ");
for (int i = 0; i < offset1; i++)
StdOut.print(" ");
StdOut.println(pat);
StdOut.print("pattern: ");
for (int i = 0; i < offset2; i++)
StdOut.print(" ");
StdOut.println(pat);
}
}
3.Rabin-Karp指纹字符串查找算法
package string;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.Random;
public class RabinKarp {
private String pat; // the pattern // needed only for Las Vegas
private long patHash; // pattern hash value
private int m; // pattern length
private long q; // a large prime, small enough to avoid long overflow
private int R; // radix
private long RM; // R^(M-1) % Q
public RabinKarp(char[] pattern, int R) {
this.pat = String.valueOf(pattern);
this.R = R;
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Operation not supported yet");
}
public RabinKarp(String pat) {
this.pat = pat; // save pattern (needed only for Las Vegas)
R = 256;
m = pat.length();
q = longRandomPrime();
// precompute R^(m-1) % q for use in removing leading digit
RM = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= m-1; i++)
RM = (R * RM) % q;
patHash = hash(pat, m);
}
// Compute hash for key[0..m-1].
private long hash(String key, int m) {
long h = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++)
h = (R * h + key.charAt(j)) % q;
return h;
}
// Las Vegas version: does pat[] match txt[i..i-m+1] ?
private boolean check(String txt, int i) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++)
if (pat.charAt(j) != txt.charAt(i + j))
return false;
return true;
}
// Monte Carlo version: always return true
// private boolean check(int i) {
// return true;
//}
public int search(String txt) {
int n = txt.length();
if (n < m) return n;
long txtHash = hash(txt, m);
// check for match at offset 0
if ((patHash == txtHash) && check(txt, 0))
return 0;
// check for hash match; if hash match, check for exact match
for (int i = m; i < n; i++) {
// Remove leading digit, add trailing digit, check for match.
txtHash = (txtHash + q - RM*txt.charAt(i-m) % q) % q;
txtHash = (txtHash*R + txt.charAt(i)) % q;
// match
int offset = i - m + 1;
if ((patHash == txtHash) && check(txt, offset))
return offset;
}
// no match
return n;
}
// a random 31-bit prime
private static long longRandomPrime() {
BigInteger prime = BigInteger.probablePrime(31, new Random());
return prime.longValue();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String pat = args[0];
String txt = args[1];
RabinKarp searcher = new RabinKarp(pat);
int offset = searcher.search(txt);
// print results
StdOut.println("text: " + txt);
// from brute force search method 1
StdOut.print("pattern: ");
for (int i = 0; i < offset; i++)
StdOut.print(" ");
StdOut.println(pat);
}
}
四.正则表达式
package string;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.*;
public class NFA {
private Digraph graph; // digraph of epsilon transitions
private String regexp; // regular expression
private final int m; // number of characters in regular expression
public NFA(String regexp) {
this.regexp = regexp;
m = regexp.length();
Stack<Integer> ops = new Stack<Integer>();
graph = new Digraph(m+1);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int lp = i;
if (regexp.charAt(i) == '(' || regexp.charAt(i) == '|')
ops.push(i);
else if (regexp.charAt(i) == ')') {
int or = ops.pop();
// 2-way or operator
if (regexp.charAt(or) == '|') {
lp = ops.pop();
graph.addEdge(lp, or+1);
graph.addEdge(or, i);
}
else if (regexp.charAt(or) == '(')
lp = or;
else assert false;
}
// closure operator (uses 1-character lookahead)
if (i < m-1 && regexp.charAt(i+1) == '*') {
graph.addEdge(lp, i+1);
graph.addEdge(i+1, lp);
}
if (regexp.charAt(i) == '(' || regexp.charAt(i) == '*' || regexp.charAt(i) == ')')
graph.addEdge(i, i+1);
}
if (ops.size() != 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid regular expression");
}
public boolean recognizes(String txt) {
DirectedDFS dfs = new DirectedDFS(graph, 0);
Bag<Integer> pc = new Bag<Integer>();
for (int v = 0; v < graph.V(); v++)
if (dfs.marked(v)) pc.add(v);
// Compute possible NFA states for txt[i+1]
for (int i = 0; i < txt.length(); i++) {
if (txt.charAt(i) == '*' || txt.charAt(i) == '|' || txt.charAt(i) == '(' || txt.charAt(i) == ')')
throw new IllegalArgumentException("text contains the metacharacter '" + txt.charAt(i) + "'");
Bag<Integer> match = new Bag<Integer>();
for (int v : pc) {
if (v == m) continue;
if ((regexp.charAt(v) == txt.charAt(i)) || regexp.charAt(v) == '.')
match.add(v+1);
}
dfs = new DirectedDFS(graph, match);
pc = new Bag<Integer>();
for (int v = 0; v < graph.V(); v++)
if (dfs.marked(v)) pc.add(v);
// optimization if no states reachable
if (pc.size() == 0) return false;
}
// check for accept state
for (int v : pc)
if (v == m) return true;
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String regexp = "(" + args[0] + ")";
String txt = args[1];
NFA nfa = new NFA(regexp);
StdOut.println(nfa.recognizes(txt));
}
}
五.数据压缩
1.霍夫曼压缩
package string;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.BinaryStdIn;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.BinaryStdOut;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.MinPQ;
public class Huffman {
// alphabet size of extended ASCII
private static final int R = 256;
// Do not instantiate.
private Huffman() { }
// Huffman trie node
private static class Node implements Comparable<Node> {
private final char ch;
private final int freq;
private final Node left, right;
Node(char ch, int freq, Node left, Node right) {
this.ch = ch;
this.freq = freq;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
// is the node a leaf node?
private boolean isLeaf() {
assert ((left == null) && (right == null)) || ((left != null) && (right != null));
return (left == null) && (right == null);
}
// compare, based on frequency
public int compareTo(Node that) {
return this.freq - that.freq;
}
}
public static void compress() {
// read the input
String s = BinaryStdIn.readString();
char[] input = s.toCharArray();
// tabulate frequency counts
int[] freq = new int[R];
for (int i = 0; i < input.length; i++)
freq[input[i]]++;
// build Huffman trie
Node root = buildTrie(freq);
// build code table
String[] st = new String[R];
buildCode(st, root, "");
// print trie for decoder
writeTrie(root);
// print number of bytes in original uncompressed message
BinaryStdOut.write(input.length);
// use Huffman code to encode input
for (int i = 0; i < input.length; i++) {
String code = st[input[i]];
for (int j = 0; j < code.length(); j++) {
if (code.charAt(j) == '0') {
BinaryStdOut.write(false);
}
else if (code.charAt(j) == '1') {
BinaryStdOut.write(true);
}
else throw new IllegalStateException("Illegal state");
}
}
// close output stream
BinaryStdOut.close();
}
// build the Huffman trie given frequencies
private static Node buildTrie(int[] freq) {
// initialze priority queue with singleton trees
MinPQ<Node> pq = new MinPQ<Node>();
for (char c = 0; c < R; c++)
if (freq[c] > 0)
pq.insert(new Node(c, freq[c], null, null));
// merge two smallest trees
while (pq.size() > 1) {
Node left = pq.delMin();
Node right = pq.delMin();
Node parent = new Node('\0', left.freq + right.freq, left, right);
pq.insert(parent);
}
return pq.delMin();
}
// write bitstring-encoded trie to standard output
private static void writeTrie(Node x) {
if (x.isLeaf()) {
BinaryStdOut.write(true);
BinaryStdOut.write(x.ch, 8);
return;
}
BinaryStdOut.write(false);
writeTrie(x.left);
writeTrie(x.right);
}
// make a lookup table from symbols and their encodings
private static void buildCode(String[] st, Node x, String s) {
if (!x.isLeaf()) {
buildCode(st, x.left, s + '0');
buildCode(st, x.right, s + '1');
}
else {
st[x.ch] = s;
}
}
public static void expand() {
// read in Huffman trie from input stream
Node root = readTrie();
// number of bytes to write
int length = BinaryStdIn.readInt();
// decode using the Huffman trie
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
Node x = root;
while (!x.isLeaf()) {
boolean bit = BinaryStdIn.readBoolean();
if (bit) x = x.right;
else x = x.left;
}
BinaryStdOut.write(x.ch, 8);
}
BinaryStdOut.close();
}
private static Node readTrie() {
boolean isLeaf = BinaryStdIn.readBoolean();
if (isLeaf) {
return new Node(BinaryStdIn.readChar(), -1, null, null);
}
else {
return new Node('\0', -1, readTrie(), readTrie());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
if (args[0].equals("-")) compress();
else if (args[0].equals("+")) expand();
else throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal command line argument");
}
}
2.LZW算法的压缩
package string;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.BinaryStdIn;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.BinaryStdOut;
public class LZW {
private static final int R = 256; // number of input chars
private static final int L = 4096; // number of codewords = 2^W
private static final int W = 12; // codeword width
// Do not instantiate.
private LZW() { }
public static void compress() {
String input = BinaryStdIn.readString();
TST<Integer> st = new TST<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < R; i++)
st.put("" + (char) i, i);
int code = R+1; // R is codeword for EOF
while (input.length() > 0) {
String s = st.longestPrefixOf(input); // Find max prefix match s.
BinaryStdOut.write(st.get(s), W); // Print s's encoding.
int t = s.length();
if (t < input.length() && code < L) // Add s to symbol table.
st.put(input.substring(0, t + 1), code++);
input = input.substring(t); // Scan past s in input.
}
BinaryStdOut.write(R, W);
BinaryStdOut.close();
}
public static void expand() {
String[] st = new String[L];
int i; // next available codeword value
// initialize symbol table with all 1-character strings
for (i = 0; i < R; i++)
st[i] = "" + (char) i;
st[i++] = ""; // (unused) lookahead for EOF
int codeword = BinaryStdIn.readInt(W);
if (codeword == R) return; // expanded message is empty string
String val = st[codeword];
while (true) {
BinaryStdOut.write(val);
codeword = BinaryStdIn.readInt(W);
if (codeword == R) break;
String s = st[codeword];
if (i == codeword) s = val + val.charAt(0); // special case hack
if (i < L) st[i++] = val + s.charAt(0);
val = s;
}
BinaryStdOut.close();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
if (args[0].equals("-")) compress();
else if (args[0].equals("+")) expand();
else throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal command line argument");
}
}





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号