[转]Remoting之同步—异步调用
一. 前言
关于Remoting程序的调用效率问题,在刚做完项目中并未作为考虑因素加以考虑,无意中看到一篇关于Remoting的同步/异步调用方式的讨论的引论,于是打算对这个问题作一些解读,并通过程序来证明异步调用在提高Remoting效率方面的作用。
二. 简介
.NET Framework提供了三种调用远程对象的方法(不论是Server activated object, 或者是Client activated object), 你可以通过同步调用,异步调用,或者异步[OneWay]的方式来调用远程对象。
同步调用是一种基本的调用方式,在《Remoting随想》中涉及的所有的调用方式都是同步调用方式,客户端调用远程服务器端的方法如同调用本地方法一样。当服务器端接到客户端的调用请求后开始运行被调用的方法,而客户端必须的等待服务器端的方法执行完毕方可再发出请求。如果在远程方法调用过程中出现异常,则在你所调用的服务器端抛出异常。
异步调用分为两个步骤,第一个步骤是触发远程方法执行,而不必等待远程方法的返回值。客户端程序继续向下执行。当客户端收到被调用方法回复(response)后,这时须调用另一个专门用于检查服务器端是否已经执行完成了对客户端请求的业务;如果没有完成,则客户端等待,直到服务器端程序完成。在此过程中如果有异常发生,异常将会在被调用方法中出错的位置被抛出,即使你事先未被告知服务器端已在脱机状态下。
最后一种调用方式与前一种调用方式稍有不同,在[OneWay]调用方式下,若服务器端出现问题(如脱机,或者被调用方法未能完成业务功能),客户端程序(即调用方)将得不到返回值、异常原因。.NET Framework将试图在远端服务器端调用这个方法。
三.同步调用
前面已经提及,同步调用是.NET Framework的调用方法的通常方式。服务器端和被客户端直接通信,客户端程序将被阻塞,直到服务器端的方法运行完毕。如果服务器端不可用或者异常出现而无法满足客户段的需求,异常将会被抛出。
具体的各种Remoting部署方案可以参考我所写的《Remoting随想》那篇文章,采取任何一种类型都不会影响本文的讨论。这里我们列举一种是用接口的方式来说明同步/异步调用调用。接口的使用可以用关键字interface来定义一个接口,同样也可以用抽象类来实现。
3.1 接口定义
我们新建一个Class library工程,并在随后的服务器端和客户端添加对此DLL的引用。下面代码就是被引用DLL所需的接口定义。
定义RecordingManager.dll:
 using System;
using System;
 using System.Runtime.Remoting.Messaging;
using System.Runtime.Remoting.Messaging;
 namespace RecordingManager
namespace RecordingManager
 {
{
 public abstract class BaseRemoteObject : MarshalByRefObject
public abstract class BaseRemoteObject : MarshalByRefObject
 {
{
 public abstract DataSet GetRecordingsMe();
public abstract DataSet GetRecordingsMe();
 public abstract DataSet GetRecordingsYou();
public abstract DataSet GetRecordingsYou();
 }
}
 }
}

3.2 同步调用模式下的服务器端程序
 using System;
using System; using System.Runtime.Remoting.Messaging;
using System.Runtime.Remoting.Messaging; namespace RecordingManager
namespace RecordingManager {
{ public abstract class BaseRemoteObject : MarshalByRefObject
public abstract class BaseRemoteObject : MarshalByRefObject {
{ public abstract DataSet GetRecordingsMe();
public abstract DataSet GetRecordingsMe(); public abstract DataSet GetRecordingsYou();
public abstract DataSet GetRecordingsYou(); }
} }
}
新建一个控制台程序,在服务器端来实现接口定义的方法,这个实现接口的类可以与服务器端主程序写在一起,也可以单独写成一个类,我们这里单独写为一个类,这样逻辑更佳清楚。
 using System;
using System; using System.Data;
using System.Data; using System.Data.OracleClient;
using System.Data.OracleClient; using System.Runtime.Remoting;
using System.Runtime.Remoting; using RecordingManager;
using RecordingManager; using System.Runtime.Remoting.Messaging;
using System.Runtime.Remoting.Messaging; using System.Collections;
using System.Collections; namespace TcpServer
namespace TcpServer {
{  // Implementations of syncronized patterns.
// Implementations of syncronized patterns. // This class extends the abstract class "BaseRemoteObject".
// This class extends the abstract class "BaseRemoteObject". [Serializable]
[Serializable] public class SynRemotingServices : BaseRemoteObject
public class SynRemotingServices : BaseRemoteObject {
{  public SynRemotingServices()
public SynRemotingServices() {
{ System.Console.WriteLine("New Reference Added through a interface, syncronized!");
System.Console.WriteLine("New Reference Added through a interface, syncronized!"); }
}
 public override DataSet GetRecordingsMe()
public override DataSet GetRecordingsMe() {
{ DataSet ds = new DataSet();
DataSet ds = new DataSet(); try
try {
{  // simulate a long running action
// simulate a long running action Console.WriteLine("Get data from table 'ME', please wait
Console.WriteLine("Get data from table 'ME', please wait ");
"); // get data from database
// get data from database  String selectCmd = "select * from ME";
String selectCmd = "select * from ME";  OracleConnection myConnection = new OracleConnection(
OracleConnection myConnection = new OracleConnection( "Data Source = DB00; User Id = jakey; Password = jakey");
"Data Source = DB00; User Id = jakey; Password = jakey"); OracleDataAdapter myAdapter = new
OracleDataAdapter myAdapter = new  OracleDataAdapter(selectCmd, myConnection);
OracleDataAdapter(selectCmd, myConnection);
 myAdapter.Fill(ds, "ME");
myAdapter.Fill(ds, "ME");  Console.WriteLine("get datatable 'ME' from database successful!");
Console.WriteLine("get datatable 'ME' from database successful!");  }
}  catch(OracleException ex)
catch(OracleException ex) {
{ Console.WriteLine("Oracle error!" + ex.Message);
Console.WriteLine("Oracle error!" + ex.Message); }
} catch(RemotingException ex)
catch(RemotingException ex) {
{ Console.WriteLine("Remoting error!" + ex.Message);
Console.WriteLine("Remoting error!" + ex.Message); }
} catch(Exception ex)
catch(Exception ex) {
{ Console.WriteLine("Unknown error!" + ex.Message);
Console.WriteLine("Unknown error!" + ex.Message); }
} return ds;
return ds; }
} 
 public override DataSet GetRecordingsYou()
public override DataSet GetRecordingsYou() {
{ DataSet ds = new DataSet();
DataSet ds = new DataSet(); try
try {
{ // simulate a long running action
// simulate a long running action Console.WriteLine("Get data from table 'YOU', please wait
Console.WriteLine("Get data from table 'YOU', please wait ");
"); // get data from database
// get data from database  String selectCmd = "select * from YOU";
String selectCmd = "select * from YOU";  OracleConnection myConnection = new OracleConnection(
OracleConnection myConnection = new OracleConnection( "Data Source = DB00; User Id = jakey; Password = jakey");
"Data Source = DB00; User Id = jakey; Password = jakey"); OracleDataAdapter myAdapter = new
OracleDataAdapter myAdapter = new  OracleDataAdapter(selectCmd, myConnection);
OracleDataAdapter(selectCmd, myConnection); myAdapter.Fill(ds, "YOU");
myAdapter.Fill(ds, "YOU");  Console.WriteLine("get datatable 'YOU' from database successful!");
Console.WriteLine("get datatable 'YOU' from database successful!");  }
}  catch(OracleException ex)
catch(OracleException ex) {
{ Console.WriteLine("Oracle error!" + ex.Message);
Console.WriteLine("Oracle error!" + ex.Message); }
} catch(RemotingException ex)
catch(RemotingException ex) {
{ Console.WriteLine("Remoting error!" + ex.Message);
Console.WriteLine("Remoting error!" + ex.Message); }
} catch(Exception ex)
catch(Exception ex) {
{ Console.WriteLine("Unknown error!" + ex.Message);
Console.WriteLine("Unknown error!" + ex.Message); }
} return ds;
return ds; }
} }
} }
}
 using System;
using System;
 using System.Runtime.Remoting;
using System.Runtime.Remoting;
 using System.Runtime.Remoting.Channels;
using System.Runtime.Remoting.Channels;
 using System.Runtime.Remoting.Channels.Tcp;
using System.Runtime.Remoting.Channels.Tcp;
 using RecordingManager;
using RecordingManager;
 using System.Data.OracleClient;
using System.Data.OracleClient;
 using System.Data;
using System.Data;
 using System.Runtime.Remoting.Messaging;
using System.Runtime.Remoting.Messaging;
 using System.Collections;
using System.Collections;
 namespace TcpServer
namespace TcpServer
 {
{
 /// <summary>
/// <summary>
 /// Server application of remoting.
/// Server application of remoting.
 /// </summary>
/// </summary>
 class TcpServer
class TcpServer
 {
{
 /// <summary>
/// <summary>
 /// The main entry point for the application.
/// The main entry point for the application.
 /// </summary>
/// </summary>
 [STAThread]
[STAThread]
 public static void Main(string [] args)
public static void Main(string [] args)
 {
{
 try
try
 {
{
 //Normal method (use interface) start, synchronized patterns.
//Normal method (use interface) start, synchronized patterns.
 TcpChannel channel = new TcpChannel(8888);
TcpChannel channel = new TcpChannel(8888);
 ChannelServices.RegisterChannel(channel);
ChannelServices.RegisterChannel(channel);

 RemotingConfiguration.RegisterWellKnownServiceType
RemotingConfiguration.RegisterWellKnownServiceType
 (typeof(SynRemotingServices),//first parameter is the realization of method of the interface
(typeof(SynRemotingServices),//first parameter is the realization of method of the interface
 "myServer",//second parameter is the name of remote service name
"myServer",//second parameter is the name of remote service name
 WellKnownObjectMode.Singleton);//third parameter is type of activation type (server/client)
WellKnownObjectMode.Singleton);//third parameter is type of activation type (server/client)
 //WellKnownObjectMode.SingleCall,server instance object to each user
//WellKnownObjectMode.SingleCall,server instance object to each user
 //WellKnownObjectMode.SingleTone,there is only one instance to all user
//WellKnownObjectMode.SingleTone,there is only one instance to all user

 Console.WriteLine("Server Started");
Console.WriteLine("Server Started");
 Console.ReadLine();
Console.ReadLine();
 }
}

 catch( NullReferenceException nullExp )
catch( NullReferenceException nullExp )
 {
{
 Console.WriteLine( "Server null reference error!" + nullExp.Message );
Console.WriteLine( "Server null reference error!" + nullExp.Message );
 }
}
 catch( RemotingException remExp )
catch( RemotingException remExp )
 {
{
 Console.WriteLine( "Server remoting error!" + remExp.Message );
Console.WriteLine( "Server remoting error!" + remExp.Message );
 }
}
 catch(Exception x)
catch(Exception x)
 {
{
 Console.WriteLine("Server Other error:" + x.Message);
Console.WriteLine("Server Other error:" + x.Message);
 }
}
 }
}
 }
}
 }
}

3.3 同步调用模式下的客户端程序
 using System;
using System; using System.Runtime.Remoting;
using System.Runtime.Remoting; using System.Runtime.Remoting.Channels;
using System.Runtime.Remoting.Channels; using System.Runtime.Remoting.Channels.Tcp;
using System.Runtime.Remoting.Channels.Tcp; using RecordingManager;
using RecordingManager; using System.Data.OracleClient;
using System.Data.OracleClient; using System.Data;
using System.Data; using System.Runtime.Remoting.Messaging;
using System.Runtime.Remoting.Messaging;  using System.Collections;
using System.Collections; namespace TcpServer
namespace TcpServer {
{ /// <summary>
/// <summary> /// Server application of remoting.
/// Server application of remoting. /// </summary>
/// </summary> class TcpServer
class TcpServer {
{  /// <summary>
/// <summary> /// The main entry point for the application.
/// The main entry point for the application. /// </summary>
/// </summary> [STAThread]
[STAThread] public static void Main(string [] args)
public static void Main(string [] args)  {
{ try
try {
{ //Normal method (use interface) start, synchronized patterns.
//Normal method (use interface) start, synchronized patterns. TcpChannel channel = new TcpChannel(8888);
TcpChannel channel = new TcpChannel(8888); ChannelServices.RegisterChannel(channel);
ChannelServices.RegisterChannel(channel);
 RemotingConfiguration.RegisterWellKnownServiceType
RemotingConfiguration.RegisterWellKnownServiceType  (typeof(SynRemotingServices),//first parameter is the realization of method of the interface
(typeof(SynRemotingServices),//first parameter is the realization of method of the interface "myServer",//second parameter is the name of remote service name
"myServer",//second parameter is the name of remote service name WellKnownObjectMode.Singleton);//third parameter is type of activation type (server/client)
WellKnownObjectMode.Singleton);//third parameter is type of activation type (server/client) //WellKnownObjectMode.SingleCall,server instance object to each user
//WellKnownObjectMode.SingleCall,server instance object to each user  //WellKnownObjectMode.SingleTone,there is only one instance to all user
//WellKnownObjectMode.SingleTone,there is only one instance to all user
 Console.WriteLine("Server Started");
Console.WriteLine("Server Started"); Console.ReadLine();
Console.ReadLine();  }
}
 catch( NullReferenceException nullExp )
catch( NullReferenceException nullExp ) {
{ Console.WriteLine( "Server null reference error!" + nullExp.Message );
Console.WriteLine( "Server null reference error!" + nullExp.Message ); }
} catch( RemotingException remExp )
catch( RemotingException remExp ) {
{ Console.WriteLine( "Server remoting error!" + remExp.Message );
Console.WriteLine( "Server remoting error!" + remExp.Message ); }
}  catch(Exception x)
catch(Exception x) {
{ Console.WriteLine("Server Other error:" + x.Message);
Console.WriteLine("Server Other error:" + x.Message); }
} }
} }
} }
}
新建一个控制台程序,调用服务器端方法。
 using System;
using System; using System.Runtime.Remoting;
using System.Runtime.Remoting; using System.Runtime.Remoting.Channels.Tcp;
using System.Runtime.Remoting.Channels.Tcp; using System.Runtime.Remoting.Channels.Http;
using System.Runtime.Remoting.Channels.Http; using System.Runtime.Remoting.Channels;
using System.Runtime.Remoting.Channels; using System.Runtime.Remoting.Proxies;
using System.Runtime.Remoting.Proxies; using System.Data;
using System.Data; using System.Data.OracleClient;
using System.Data.OracleClient; using RecordingManager;
using RecordingManager;
 namespace synchronizeTest
namespace synchronizeTest {
{ /// <summary>
/// <summary> /// This class is used for synchronization test of remoting
/// This class is used for synchronization test of remoting  /// </summary>
/// </summary> class synchronizeClient
class synchronizeClient {
{ // Define a variable
// Define a variable private static DataSet myDataSet;
private static DataSet myDataSet; /// <summary>
/// <summary> /// The main entry point for the application.
/// The main entry point for the application. /// </summary>
/// </summary> [STAThread]
[STAThread] static void Main(string[] args)
static void Main(string[] args) {
{ // synchronization start
// synchronization start DateTime start = System.DateTime.Now;
DateTime start = System.DateTime.Now; int recordCount;
int recordCount; //Register channel
//Register channel TcpChannel tcpChannel = new TcpChannel();
TcpChannel tcpChannel = new TcpChannel(); ChannelServices.RegisterChannel(tcpChannel); // Carete a TCP client channel,
ChannelServices.RegisterChannel(tcpChannel); // Carete a TCP client channel, // this channel is not bind one port
// this channel is not bind one port
 RecordingManager.BaseRemoteObject myobj =
RecordingManager.BaseRemoteObject myobj =  (RecordingManager.BaseRemoteObject)Activator.GetObject // Server activated user GetObject()
(RecordingManager.BaseRemoteObject)Activator.GetObject // Server activated user GetObject() (typeof(RecordingManager.BaseRemoteObject)// First parameter is the remote object type,
(typeof(RecordingManager.BaseRemoteObject)// First parameter is the remote object type, ,"tcp://localhost:8888/myServer"); // Second parameter is the remote object's URI。
,"tcp://localhost:8888/myServer"); // Second parameter is the remote object's URI。
 Console.WriteLine("synchronizeClient.Main(): Reference to remoting obj. acquired");
Console.WriteLine("synchronizeClient.Main(): Reference to remoting obj. acquired");  // get data from table me
// get data from table me Console.WriteLine("synchronizeClient.Main(): Get data from table 'ME'");
Console.WriteLine("synchronizeClient.Main(): Get data from table 'ME'"); myDataSet = myobj.GetRecordingsMe();
myDataSet = myobj.GetRecordingsMe(); recordCount = myDataSet.Tables["ME"].Rows.Count;
recordCount = myDataSet.Tables["ME"].Rows.Count; Console.WriteLine("The counts of table 'ME' is: {0}", recordCount);
Console.WriteLine("The counts of table 'ME' is: {0}", recordCount);
 // get data from table you
// get data from table you Console.WriteLine("synchronizeClient.Main(): Get data from table 'YOU'");
Console.WriteLine("synchronizeClient.Main(): Get data from table 'YOU'"); myDataSet = myobj.GetRecordingsYou();
myDataSet = myobj.GetRecordingsYou(); recordCount = myDataSet.Tables["YOU"].Rows.Count;
recordCount = myDataSet.Tables["YOU"].Rows.Count; Console.WriteLine("The counts of table 'YOU' is: {0}", recordCount);
Console.WriteLine("The counts of table 'YOU' is: {0}", recordCount);
 DateTime end = System.DateTime.Now;
DateTime end = System.DateTime.Now; TimeSpan duration = end.Subtract(start);
TimeSpan duration = end.Subtract(start); Console.WriteLine("synchronizeClient.Main(): Execution took {0} seconds.",
Console.WriteLine("synchronizeClient.Main(): Execution took {0} seconds.", duration.Seconds);
duration.Seconds); // wait for any key press
// wait for any key press Console.ReadLine();
Console.ReadLine(); }
} }
}
编译程序,先启动服务器端程序,在启动客户段程序,我们可以看到如图所示的结果,客户端调用两个方法用了5秒钟的时间(Fig 3-1),我们注意观察服务器端程序控制台所示(Fig 3-2),服务器端的两个程序是先后被调用的,与客户端调用次序一致,这证明服务器端程序当第一个方法被调用执行完成后,第二个方法才开始执行。
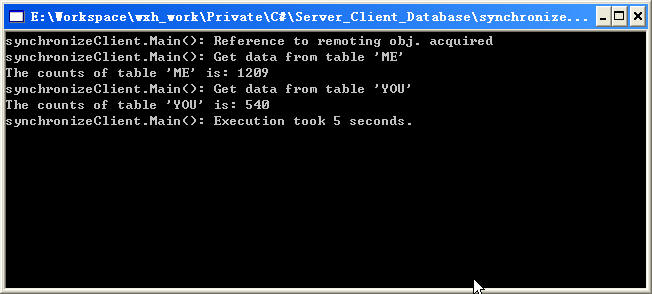
Fig 3- 1 同步调用时客户端程序控制台显示内容
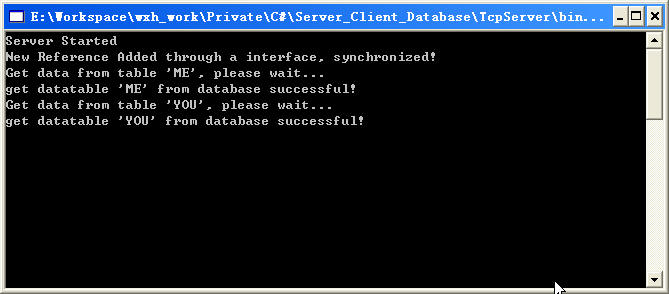
Fig 3- 2 同步调用时服务器端控制台显示内容
四.异步调用
在同步调用的例子里面我们可以看到,客户端程序独立调用服务器端的两个方法时,由于程序之间的相互等待导致了性能大打折扣。我们可以通过独立的线程(Thread)去分别调用它们,然而,即便是在.NET中使用线程很容易,但是这样做使得Remoting反而变得复杂,从而得不偿失。
.NET Framework提供了一种方法,叫做异步代理(asynchronous delegates),它容许方法以异步方式被调用。
服务器将异步操作拆分成两个逻辑部分:采用来自客户端的输入并调用异步操作的部分,向客户端提供异步操作结果的部分。
除了异步操作所需的输入外,第一部分还采用在完成异步操作时后要被调用的 AsyncCallback 委托。第一部分返回一个可等待的对象,该对象实现客户端使用的 IAsyncResult 接口来确定异步操作的状态。
服务器还使用它返回到客户端的可等待对象来维护与异步操作关联的任何状态。通过提供可等待的对象,客户端使用第二部分获取异步操作的结果。
4.1 异步调用模式下的客户端程序
异步调用模式下,接口定义和服务器端程序不作修改,客户端程序需要有较大变动。
 using System;
using System; using System.Runtime.Remoting;
using System.Runtime.Remoting; using System.Runtime.Remoting.Channels.Tcp;
using System.Runtime.Remoting.Channels.Tcp; using System.Runtime.Remoting.Channels.Http;
using System.Runtime.Remoting.Channels.Http; using System.Runtime.Remoting.Channels;
using System.Runtime.Remoting.Channels; using System.Runtime.Remoting.Proxies;
using System.Runtime.Remoting.Proxies; using System.Data;
using System.Data; using System.Data.OracleClient;
using System.Data.OracleClient; using Recording;
using Recording;
 namespace asynchronousClient
namespace asynchronousClient {
{ /// <summary>
/// <summary> /// This class is used for asynchronous test of remoting
/// This class is used for asynchronous test of remoting  /// </summary>
/// </summary> class asynchronousClient
class asynchronousClient {
{ // Define a variable
// Define a variable private static DataSet myDataSet;
private static DataSet myDataSet;
 // Define two delegate
// Define two delegate delegate DataSet GetDataTableMeDelegate();
delegate DataSet GetDataTableMeDelegate(); delegate DataSet GetDataTableYouDelegate();
delegate DataSet GetDataTableYouDelegate();
 /// <summary>
/// <summary> /// The main entry point for the application.
/// The main entry point for the application. /// </summary>
/// </summary> [STAThread]
[STAThread] static void Main(string[] args)
static void Main(string[] args) {
{  try
try {
{ // Using Asynchronous Delegates start
// Using Asynchronous Delegates start DateTime start = System.DateTime.Now;
DateTime start = System.DateTime.Now; int recordCount;
int recordCount;
 //Register channel
//Register channel TcpChannel tcpChannel = new TcpChannel();
TcpChannel tcpChannel = new TcpChannel(); ChannelServices.RegisterChannel(tcpChannel); // Carete a TCP client channel,
ChannelServices.RegisterChannel(tcpChannel); // Carete a TCP client channel, // this channel is not bind one port
// this channel is not bind one port
 RecordingManager.BaseRemoteObject myobj =
RecordingManager.BaseRemoteObject myobj =  (RecordingManager.BaseRemoteObject)Activator.GetObject // Server activated user GetObject()
(RecordingManager.BaseRemoteObject)Activator.GetObject // Server activated user GetObject() (typeof(RecordingManager.BaseRemoteObject)// First parameter is the remote object type,
(typeof(RecordingManager.BaseRemoteObject)// First parameter is the remote object type, ,"tcp://localhost:8888/myServer"); // Second parameter is the remote object's URI。
,"tcp://localhost:8888/myServer"); // Second parameter is the remote object's URI。
 Console.WriteLine("asynchronousClient.Main(): Reference to remoting obj. acquired");
Console.WriteLine("asynchronousClient.Main(): Reference to remoting obj. acquired");
 // get data from table me
// get data from table me Console.WriteLine("asynchronousClient.Main(): Get data from table 'ME'");
Console.WriteLine("asynchronousClient.Main(): Get data from table 'ME'"); GetDataTableMeDelegate meDelegate = new GetDataTableMeDelegate(myobj.GetRecordingsMe);
GetDataTableMeDelegate meDelegate = new GetDataTableMeDelegate(myobj.GetRecordingsMe); IAsyncResult meAsyncres = meDelegate.BeginInvoke(null, null);
IAsyncResult meAsyncres = meDelegate.BeginInvoke(null, null);
 // get data from table you
// get data from table you Console.WriteLine("asynchronousClient.Main(): Get data from table 'YOU'");
Console.WriteLine("asynchronousClient.Main(): Get data from table 'YOU'"); GetDataTableYouDelegate youDelegate = new GetDataTableYouDelegate(myobj.GetRecordingsYou);
GetDataTableYouDelegate youDelegate = new GetDataTableYouDelegate(myobj.GetRecordingsYou); IAsyncResult youAsyncres = youDelegate.BeginInvoke(null, null);
IAsyncResult youAsyncres = youDelegate.BeginInvoke(null, null);
 // get the counts of records
// get the counts of records Console.WriteLine("asynchronousClient.Main(): EndInvoke for me");
Console.WriteLine("asynchronousClient.Main(): EndInvoke for me"); myDataSet = meDelegate.EndInvoke(meAsyncres);
myDataSet = meDelegate.EndInvoke(meAsyncres); recordCount = myDataSet.Tables["ME"].Rows.Count;
recordCount = myDataSet.Tables["ME"].Rows.Count; Console.WriteLine("The counts of table 'ME' is: {0}", recordCount);
Console.WriteLine("The counts of table 'ME' is: {0}", recordCount);
 // get the counts of records
// get the counts of records Console.WriteLine("asynchronousClient.Main(): EndInvoke for you");
Console.WriteLine("asynchronousClient.Main(): EndInvoke for you"); myDataSet = youDelegate.EndInvoke(youAsyncres);
myDataSet = youDelegate.EndInvoke(youAsyncres); recordCount = myDataSet.Tables["YOU"].Rows.Count;
recordCount = myDataSet.Tables["YOU"].Rows.Count; Console.WriteLine("The counts of table 'YOU' is: {0}", recordCount);
Console.WriteLine("The counts of table 'YOU' is: {0}", recordCount);
 DateTime end = System.DateTime.Now;
DateTime end = System.DateTime.Now; TimeSpan duration = end.Subtract(start);
TimeSpan duration = end.Subtract(start); Console.WriteLine("asynchronousClient.Main(): Execution took {0} seconds.",
Console.WriteLine("asynchronousClient.Main(): Execution took {0} seconds.", duration.Seconds);
duration.Seconds); // Using Asynchronous Delegates end
// Using Asynchronous Delegates end }
} catch(Exception ex)
catch(Exception ex) {
{ Console.WriteLine("asynchronousClient.Main(): EXCEPTION during EndInvoke " + ex.Message);
Console.WriteLine("asynchronousClient.Main(): EXCEPTION during EndInvoke " + ex.Message); }
}  // wait for any key press
// wait for any key press  Console.ReadLine();
Console.ReadLine(); }
}  }
} }
}
编译程序,先启动服务器端程序,在启动客户段程序,我们可以看到如图所示的结果,客户端调用两个方法用了2秒钟的时间(Fig 4-1),我们注意观察服务器端程序控制台所示(Fig 4-2),服务器端的两个程序是同时被调用的,这证明服务器端程序当第一个方法被调用执行的同时,第二个方法也开始执行,这样就完成了异步调用。
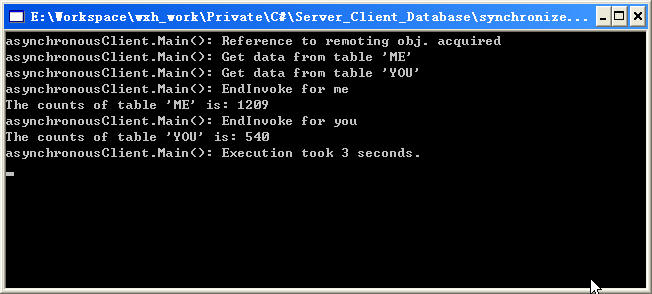
Fig 4- 1 异步调用时客户端程序控制台显示内容
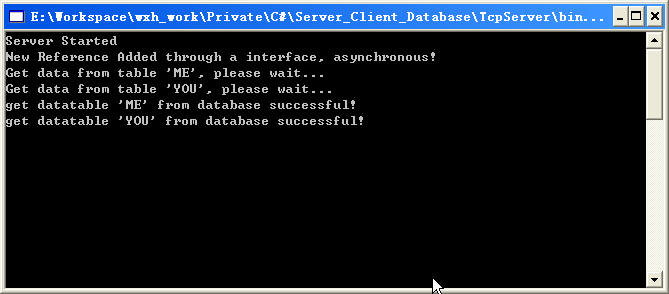
Fig 4- 2异步调时用服务器端控制台显示内容
五.异步[OneWay]调用
异步One-Way(单向)调用与异步调用稍有不同,.NET Framework并不保障One-Way调用方式的执行。此外,用这种调用方式的方法不能有返回值或out参数。客户端仍然可以用代理(delegate)来调用One-Way方法,但是EndIncoke()方法不会检查服务器端程序是否已经完成而直接退出。即便是服务器死机或脱机状态下异常也不会被抛出,客户端更是无法知道请求失败的原因。在一些不重要的记录日志或跟踪应用中,可以考虑采用异步One-Way调用,这样Remote method的执行情况就不会影响到其他业务代码的执行。
异步One-Way调用的实现很简单,只需要在接口定义的方法之前加上属性(attribute)[OneWay()]即可,其他程序不需要修改。
 public abstract class BaseRemoteObject : MarshalByRefObject
public abstract class BaseRemoteObject : MarshalByRefObject {
{ [OneWay()]
[OneWay()] public abstract DataSet GetRecordingsMe();
public abstract DataSet GetRecordingsMe(); public abstract DataSet GetRecordingsYou();
public abstract DataSet GetRecordingsYou(); }
}
注意:请始终牢记使用了异步One-Way调用方式时,客户端将忽视服务器端的返回值,并且不会去检查服务器端的运行状态。
六.小结
综合上述观点我们知道,的确,通过异步调用远程对象可以提高程序运行的效率,降低了由于某个方法的错误而造成整个应用程序崩溃的风险。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号