GPU CUDA G.4 优化内存复用
G.4 优化内存复用
CUDA通过两种方式实现内存复用:
‣ 图内复用:基于虚拟地址分配的虚拟内存与物理内存复用(类似流顺序分配器机制)
‣ 图间复用:通过虚拟别名技术实现物理内存复用,不同图可将相同物理内存映射到各自的独立虚拟地址
G.4.1 图内地址复用
CUDA可能通过为生命周期不重叠的不同内存分配分配相同虚拟地址范围来实现图内内存复用。由于虚拟地址可能被重复使用,指向具有非重叠生命周期的不同分配的指针不保证具有唯一性。
下图展示了新增分配节点(2)如何复用依赖节点(1)释放的地址空间:
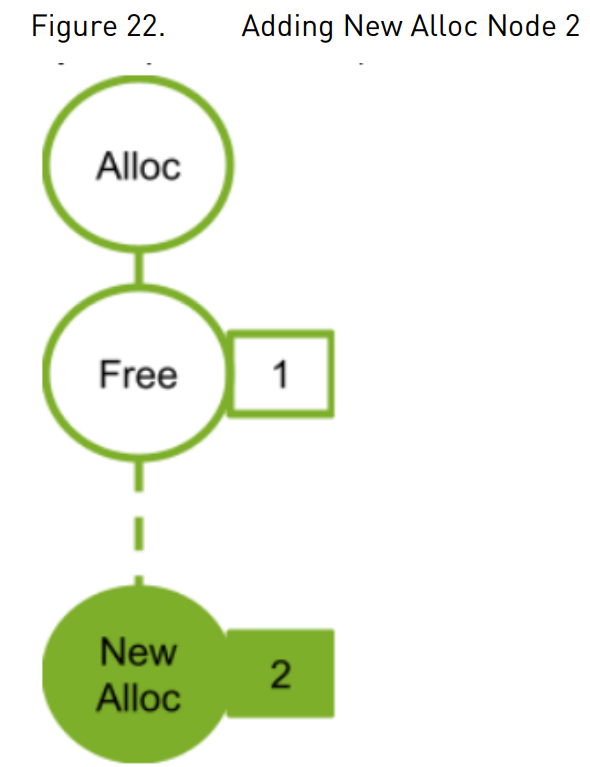
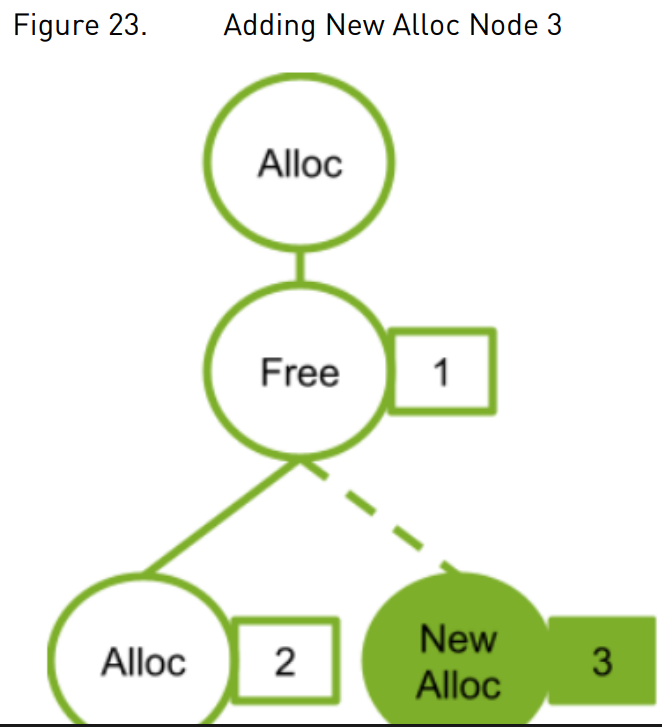
下图展示了新增分配节点(4)的情况。由于该新分配节点不依赖于释放节点(2),因此无法复用原分配节点(2)关联的地址空间。若分配节点(2)复用了释放节点(1)所释放的地址,则新分配节点(3)将需要分配新的地址空间。

cudaMemAllocNodeParams params = {};
params.poolProps.allocType = cudaMemAllocationTypePinned;
params.poolProps.location.type = cudaMemLocationTypeDevice;
// specify device 1 as the resident device
params.poolProps.location.id = 1;
params.bytesize = size;
// allocate an allocation resident on device 1 accessible from device 1
cudaGraphAddMemAllocNode(&allocNode, graph, NULL, 0, ¶ms);
accessDescs[2];
// boilerplate for the access descs (only ReadWrite and Device access supported by
the add node api)
accessDescs[0].flags = cudaMemAccessFlagsProtReadWrite;
accessDescs[0].location.type = cudaMemLocationTypeDevice;
accessDescs[1].flags = cudaMemAccessFlagsProtReadWrite;
accessDescs[1].location.type = cudaMemLocationTypeDevice;
// access being requested for device 0 & 2. Device 1 access requirement left
implicit.
accessDescs[0].location.id = 0;
accessDescs[1].location.id = 2;
// access request array has 2 entries.
params.accessDescCount = 2;
params.accessDescs = accessDescs;
// allocate an allocation resident on device 1 accessible from devices 0, 1 and 2.
(0 & 2 from the descriptors, 1 from it being the resident device).
cudaGraphAddMemAllocNode(&allocNode, graph, NULL, 0, ¶ms);
G.7.2 流捕获模式下的多GPU访问
在流捕获过程中,分配节点会记录捕获时刻内存池的跨设备访问权限。即便在捕获cudaMallocFromPoolAsync调用后修改内存池的跨设备访问权限,也不会影响该分配在图执行时实际建立的映射关系。
// boilerplate for the access descs (only ReadWrite and Device access supported by
the add node api)
accessDesc.flags = cudaMemAccessFlagsProtReadWrite;
accessDesc.location.type = cudaMemLocationTypeDevice;
accessDesc.location.id = 1;
// let memPool be resident and accessible on device 0
cudaStreamBeginCapture(stream);
cudaMallocAsync(&dptr1, size, memPool, stream);
cudaStreamEndCapture(stream, &graph1);
cudaMemPoolSetAccess(memPool, &accessDesc, 1);
cudaStreamBeginCapture(stream);
cudaMallocAsync(&dptr2, size, memPool, stream);
cudaStreamEndCapture(stream, &graph2);
//The graph node allocating dptr1 would only have the device 0 accessibility even
though memPool now has device 1 accessibility.
//The graph node allocating dptr2 will have device 0 and device 1 accessibility,
since that was the pool accessibility at the time of the cudaMallocAsync call.



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号