C#多线程编程实战(三):使用线程池
3.1 简介:
3.2 在线程池中调用委托
using System; using System.Threading; using static System.Console; using static System.Threading.Thread; namespace Chapter3.Recipe1 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { int threadId = 0; RunOnThreadPool poolDelegate = Test; var t = new Thread(() => Test(out threadId)); t.Start(); t.Join(); WriteLine($"Main->Thread id: {threadId}"); IAsyncResult r = poolDelegate.BeginInvoke(out threadId, Callback, "委托异步调用"); r.AsyncWaitHandle.WaitOne(); string result = poolDelegate.EndInvoke(out threadId, r); WriteLine($"Main->Thread pool worker thread id: {threadId}"); WriteLine(result); Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); Console.ReadKey(); } private delegate string RunOnThreadPool(out int threadId); private static void Callback(IAsyncResult ar) { WriteLine("Callback->Starting a callback..."); WriteLine($"Callback->State passed to a callbak: {ar.AsyncState}"); WriteLine($"Callback->Is thread pool thread: {CurrentThread.IsThreadPoolThread}"); WriteLine($"Callback->Thread pool worker thread id: {CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId}"); } private static string Test(out int threadId) { WriteLine("Test->Starting..."); WriteLine($"Test->Is thread pool thread: {CurrentThread.IsThreadPoolThread}"); Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); threadId = CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId; return $"Test->Thread pool worker thread id was: {threadId}"; } } }
结果:
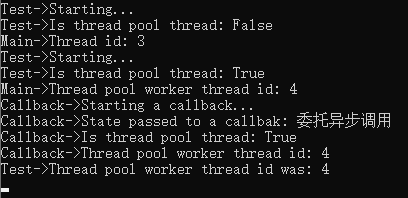
3.3 向线程池中放入异步操作
using System; using System.Threading; using static System.Console; using static System.Threading.Thread; namespace Chapter3.Recipe2 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { const int x = 1; const int y = 2; const string lambdaState = "lambda state 2"; ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(AsyncOperation); Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(1)); ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(AsyncOperation, "async state"); Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(1)); ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(state => { WriteLine($"state->Operation state: {state}"); WriteLine($"state->Worker thread id: {CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId}"); Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); }, "lambda state"); ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(_ => { WriteLine($"->Operation state: {x + y}, {lambdaState}"); WriteLine($"->Worker thread id: {CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId}"); Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); }, "lambda state"); Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); Console.ReadKey(); } private static void AsyncOperation(object state) { WriteLine($"AsyncOperation->Operation state: {state ?? "(null)"}"); WriteLine($"AsyncOperation->Worker thread id: {CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId}"); Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); } } }
结果:
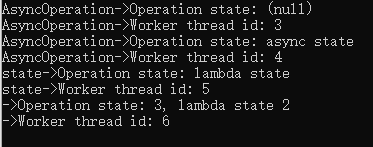
3.4 线程池与并行度
using System; using System.Diagnostics; using System.Threading; using static System.Console; using static System.Threading.Thread; namespace Chapter3.Recipe3 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { const int numberOfOperations = 500; var sw = new Stopwatch(); sw.Start(); UseThreads(numberOfOperations); sw.Stop(); WriteLine($"Main->Execution time using threads: {sw.ElapsedMilliseconds}"); sw.Reset(); sw.Start(); UseThreadPool(numberOfOperations); sw.Stop(); WriteLine($"Main->Execution time using the thread pool: {sw.ElapsedMilliseconds}"); ReadKey(); } static void UseThreads(int numberOfOperations) { using (var countdown = new CountdownEvent(numberOfOperations)) { WriteLine("UseThreads->Scheduling work by creating threads"); for (int i = 0; i < numberOfOperations; i++) { var thread = new Thread(() => { Write($"UseThreads->{CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId},"); Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(0.1)); countdown.Signal(); }); thread.Start(); } countdown.Wait(); WriteLine(); } } static void UseThreadPool(int numberOfOperations) { using (var countdown = new CountdownEvent(numberOfOperations)) { WriteLine("UseThreadPool->Starting work on a threadpool"); for (int i = 0; i < numberOfOperations; i++) { ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(_ => { Write($"UseThreadPool->{CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId},"); Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(0.1)); countdown.Signal(); }); } countdown.Wait(); WriteLine(); } } } }
结果:

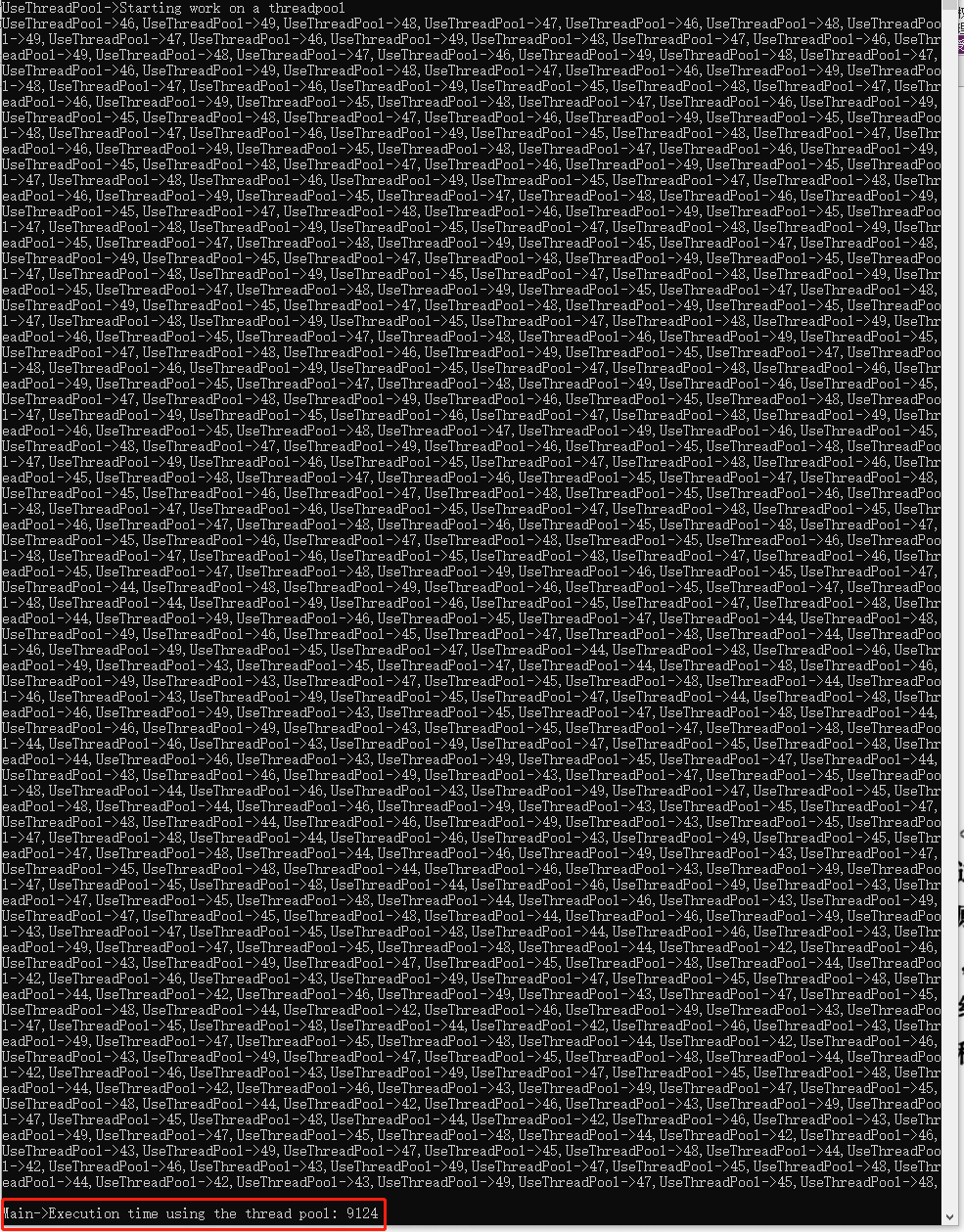
注释:
当主程序启动时,创建了很多不同的线程,每个线程都运行一个操作。该操作打印出线程并阻塞线程100毫秒。结果我们创建了500个线程,全部并行运行这些操作。虽然在我的机器上的总耗时是300毫秒,但是所有线程消耗了大量的操作系统资源;然后我们使用了执行同样的任务,只不过不为每个操作创建一个线程,而将它们放入到线程池中。然后线程池开始执行这些操作。线程池在快结束时创建更多的线程,但是仍然花费了更多的时间,在我机器上是12秒。我们为操作系统节省了内存和线程数,但是为此付出了更长的执行时间。
3.5 实现一个取消项
using System; using System.Threading; using static System.Console; using static System.Threading.Thread; namespace Chapter3.Recipe4 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { using (var cts = new CancellationTokenSource()) { CancellationToken token = cts.Token; ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(_ => AsyncOperation1(token)); Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); cts.Cancel(); } using (var cts = new CancellationTokenSource()) { CancellationToken token = cts.Token; ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(_ => AsyncOperation2(token)); Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); // cts.Cancel(); } using (var cts = new CancellationTokenSource()) { CancellationToken token = cts.Token; ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(_ => AsyncOperation3(token)); Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); cts.Cancel(); } Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); ReadKey(); } static void AsyncOperation1(CancellationToken token) { WriteLine("AsyncOperation1->Starting the first task"); for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { WriteLine($"AsyncOperation1->{i}"); //第一个是轮询来检查 Cancellation Token.IsCancellation Requested属性。如果该属性为true,则说明操作需要被取消,我们必须放弃该操作。 if (token.IsCancellationRequested) { WriteLine("AsyncOperation1->The first task has been canceled."); return; } Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(1)); } WriteLine("AsyncOperation1->The first task has completed succesfully"); } static void AsyncOperation2(CancellationToken token) { try { WriteLine("AsyncOperation2->Starting the second task"); //抛出一个 Operation Cancelled Exception异常。这允许在操作之外控制取消过程,即需要取消操作时,通过操作之外的代码来处理。 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { WriteLine($"AsyncOperation2->{i}"); token.ThrowIfCancellationRequested(); Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(1)); } WriteLine("AsyncOperation2->The second task has completed succesfully"); } catch (OperationCanceledException) { WriteLine("AsyncOperation2->The second task has been canceled."); } } static void AsyncOperation3(CancellationToken token) { bool cancellationFlag = false; //注册一个回调函数。当操作被取消时,在线程池将调用该回调函数。这允许链式传递一个取消逻辑到另一个异步操作中。 token.Register(() => cancellationFlag = true); WriteLine("AsyncOperation3->Starting the third task"); for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { WriteLine($"AsyncOperation3->{i}"); if (cancellationFlag) { WriteLine("AsyncOperation3->The third task has been canceled."); return; } Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(1)); } WriteLine("AsyncOperation3->The third task has completed succesfully"); } } }
结果:

3.6 在线程池中使用等待事件处理器及超时
using System; using System.Threading; using static System.Console; using static System.Threading.Thread; namespace Chapter3.Recipe5 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { RunOperations(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(5)); RunOperations(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(7)); ReadKey(); } static void RunOperations(TimeSpan workerOperationTimeout) { using (var evt = new ManualResetEvent(false)) using (var cts = new CancellationTokenSource()) { WriteLine("RunOperations->Registering timeout operation..."); var worker = ThreadPool.RegisterWaitForSingleObject(evt , (state, isTimedOut) => WorkerOperationWait(cts, isTimedOut) , null , workerOperationTimeout , true); WriteLine("RunOperations->Starting long running operation..."); ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(_ => WorkerOperation(cts.Token, evt)); Sleep(workerOperationTimeout.Add(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2))); worker.Unregister(evt); } } static void WorkerOperation(CancellationToken token, ManualResetEvent evt) { for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) { if (token.IsCancellationRequested) { return; } Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(1)); } evt.Set(); } static void WorkerOperationWait(CancellationTokenSource cts, bool isTimedOut) { if (isTimedOut) { cts.Cancel(); WriteLine("WorkerOperationWait->Worker operation timed out and was canceled."); } else { WriteLine("WorkerOperationWait->Worker operation succeded."); } } } }
结果:
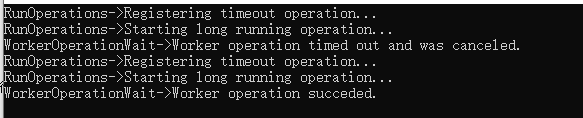
注释:
线程池还有一个有用的方法: ThreadPool Register WaitForSingleObject该方法允许我们将回调函数放入线程池中的队列中。当提供的等待事件处理器收到信号或发生超时时,该回调函数将被调用。这允许我们为线程池中的操作实现超时功能。
首先按顺序向线程池中放入一个耗时长的操作。它运行6秒钟然后一旦成功完成,会设置一个 ManualResetEvent信号类。其他的情况下,比如需要取消操作,则该操作会被丢弃。
然后我们注册了第二个异步操作。当从 ManualReset Event对象接受到一个信号后,该异步操作会被调用。如果第一个操作顺利完成,会设置该信号量。另一种情况是第一个操作还未完成就已经超时。如果发生了该情况,我们会使用 Cancellation Token来取消第一个操作。
最后,为操作提供5秒的超时时间是不够的。这是因为操作会花费6秒来完成,只能取消该操作。所以如果提供7秒的超时时间是可行的,该操作会顺利完成。
当有大量的线程必须处于阻塞状态中等待一些多线程事件发信号时,以上方式非常有用。借助于线程池的基础设施,我们无需阻塞所有这样的线程。可以释放这些线程直到信号事件被设置。在服务器端应用程序中这是个非常重要的应用场景,因为服务器端应用程序要求高伸缩性及高性能。
3.7 使用计时器
using System; using System.Threading; using static System.Console; using static System.Threading.Thread; namespace Chapter3.Recipe6 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { WriteLine("Press 'Enter' to stop the timer..."); DateTime start = DateTime.Now; _timer = new Timer(_ => TimerOperation(start), null, TimeSpan.FromSeconds(1),TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); try { Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(6)); _timer.Change(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(1), TimeSpan.FromSeconds(4)); ReadLine(); } finally { _timer.Dispose(); } } static Timer _timer; static void TimerOperation(DateTime start) { TimeSpan elapsed = DateTime.Now - start; WriteLine($"TimerOperation->{elapsed.Seconds} seconds from {start}. " + $"TimerOperation->Timer thread pool thread id: {CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId}"); } } }
结果:
注释:
计时器还可以更复杂!可以以更复杂的方式使用计时器。比如,可以通过 Timeout, Infinet值提供给计时器个间隔参数来只允许计时器操作一次。然后在计时器异步操作内,能够设置下一次计时器操作将被执行的时间。具体时间取决于自定义业务逻辑。
3.8 使用 BackgroundWorker组件
using System; using System.ComponentModel; using static System.Console; using static System.Threading.Thread; namespace Chapter3.Recipe7 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { var bw = new BackgroundWorker(); bw.WorkerReportsProgress = true; bw.WorkerSupportsCancellation = true; bw.DoWork += Worker_DoWork; bw.ProgressChanged += Worker_ProgressChanged; bw.RunWorkerCompleted += Worker_Completed; bw.RunWorkerAsync(); WriteLine("Main->Press C to cancel work"); do { if (ReadKey(true).KeyChar == 'C') { bw.CancelAsync(); } } while(bw.IsBusy); } static void Worker_DoWork(object sender, DoWorkEventArgs e) { WriteLine($"Worker_DoWork->DoWork thread pool thread id: {CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId}"); var bw = (BackgroundWorker) sender; for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) { if (bw.CancellationPending) { e.Cancel = true; return; } if (i%10 == 0) { bw.ReportProgress(i); } Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(0.1)); } e.Result = 42; } static void Worker_ProgressChanged(object sender, ProgressChangedEventArgs e) { WriteLine($"Worker_ProgressChanged->{e.ProgressPercentage}% completed. " + $"Progress thread pool thread id: {CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId}"); } static void Worker_Completed(object sender, RunWorkerCompletedEventArgs e) { WriteLine($"Worker_Completed->Completed thread pool thread id: {CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId}"); if (e.Error != null) { WriteLine($"Exception {e.Error.Message} has occured."); } else if (e.Cancelled) { WriteLine($"Worker_Completed->Operation has been canceled."); } else { WriteLine($"Worker_Completed->The answer is: {e.Result}"); } } } }
结果:







 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号