Java基础篇——常用类
-
Objec类
Test t1 = new Test(); Test t2 = new Test(); //toString方法,对某个对象的字符串输出 //getClass方法,返回该对象的Class类型 Class c = t1.getClass(); //hashCode方法,返回某个对象地址的哈希码(int 型) //equals方法,比较该对象和形参对象的地址值 eg:t1.equals(t2)==false; //finalize方法,jvm会自动调用该方法回收垃圾对象,程序员也可以主动提示jvm回收"System.gc()" -
Integer整数缓冲区
Integer integer1 = new Integer(100); Integer integer2 = new Integer(100); System.out.println(integer1==integer2); //自动装箱,实际调用Integer.valueOf() Integer integer3 = 100; Integer integer4 = 100; System.out.println(integer3=integer4); Integer integer5 = 500; Integer integer6 = 500; System.out.println(integer5==integer6);输出为:
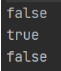
第一个false是因为integer1和integer2虽然都为100,但是确指向了堆中的两个不同的包装类对象,虽然内容一样,但是实际堆中地址不同。
第二个true和第三个false就涉及到了缓冲区
java预先在堆里创建了256个缓冲区,存放了数值为-128~127的整数包装类对象,称为IntegerCatchpublic static Integer valueOf(int i) {//valueOf方法实现细节 if (i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high) return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)]; return new Integer(i); }//IntegerCache即为缓冲区,low为-128,high为127,合起来为256个数 // cache = new Integer[(high - low) + 1]; 因为-128≥100≤127所以integer3和integer4实际指向的是整数包装类缓冲区中的100对象,所以返回为true 但是500≥127,所以返回的是new Integer(500);,即3和4实际上和integer1、integer2是等价的 -
String类
字符串是常量,存储在方法区中的字符串池中(便与共享),创建后不可改变(指存储在字符串池中的对象不可改变)
String name="zhangsan"; name="lisi";//重新创建lisi对象用name指向,原zhangsan对象依然存在,不过变为垃圾对象常用方法:
//length属性,存储字符串长度 //charAt(int )方法,下标读取,类似于数组下标 //contains(String )方法,判断该字符串中有没有包含参数字符串 //toCharArray方法,将字符串转为数组返回 //indexOf(String )方法,返回参数字符串在该字符串中第一次出现的位置下标 //trim方法,去掉字符串前后的空格(不包括中间) //toUpperCase/toLowerCase方法,大小写转换 //startsWith(String )/endsWith()方法,是否以参数字符串开头或结尾 //replace(String old,String new)方法,以new去替换该字符串中的old //split(String )以参数字符串分割该字符串 String name="java is the best languge,do you agree?"; String[] array=name.split(" ") //同时用","和" "分割 name.split("[ ,]");可变长String类
StringBuffer:效率慢,线程安全
//append(String)方法,向该字符串后追加参数字符串 //insert(int , String)方法,向位置int插入参数字符串 //replace(int start,int end,String)用参数字符串替换start-end位置的字符串(左闭右开区间) //delete(int start,int end)方法,删除位置start-end的字符串StringBuilder:效率快,线程不安全,适用于单线程
方法和StringBuffer相同
-
BigDecimal类
为浮点数计算而生
//subtract(Bigdecimal )减法 原-参 //add(Bigdecimal) 加法 //multiply(Bigdecimal) 乘法 //divide (BigDecimal ) 除法 原/参 //除法中可以指定保留小数和进位方式 //divide(BigDecimal,2,BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP)用四舍五入法保留两位小数


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号